Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Embryology
Transféré par
Sper BacenaDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Embryology
Transféré par
Sper BacenaDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
General Zoology Laboratory EXERCISE V EMBRYOLOGY Frog egg mesolecithal
1st Semester 201 2012 2013 2013
yolk is more or less concentrated in the Vegetal pole (lightly pigmented hemisphere) cytoplasm & nucleus are found in the Animal Pole (darkly pigmented hemisphere) Gray crescent formed on the side of the egg opposite that which the spermatozoon entered Note: before fertilization the egg has radial symmetry & after fertilization the egg has bilateral symmetry
CLEAVAGE STAGE: (Segmentation) Zygote undergoes a series of mitotic divisions or segmentations called CLEAVAGE The groove marks the 1st cleavage plane dividing the egg into 2 equal cells (vertically) 2nd Cleavage plane: vertical & perpendicular to the 1st 3rd Cleavage plane: horizontally (a little above the equator of the egg but at right angles to the first two planes 4th Cleavage plane: 2 vertical 5th Cleavage plane: 2 horizontal Note: presence of yolk in the vegetal pole retards cell division thus, cleavage occurs faster in the animal poles Morula Stage contains 16 to 32 cells (late cleavage = 64 cells) Blastomeres / cells (Micromeres animal pole; Macromeres vegetal pole)
General Zoology Laboratory BLASTULA STAGE:
1st Semester 201 2012 2013 2013
Formation of a segmentation cavity near the animal pole due to continuous cell divisions Segmentation Cavity Blastocoel Layer of cells around the cavity forms the blastoderm composed of embryonic cells called blastomeres One-cell layer thick: Monodermic
GASTRULA STAGE Marked by the morphogenetic movements to form the primitive germ layers of the embryo: Ectoderm, Endoderm, & Mesoderm Movements: 1. Involution inward rolling 2. Evagination outward 3. Invagination sinking in 4. Epiboly spreading then enveloping formed structures As growth continues, blastopore (opening) lips draw closer together over the vegetal cells until only a small mass of vegetal cells is left showing the yolk plug As gastrulation progresses, the inward rolling (INVOLUTION) of cells results in an expanding fold enclosing the ARCHENTERON / GASTOCOEL The roof is composed of the involuted layer forming the endoderm & mesoderm & an outer layer the ectoderm; Floor is composed of the endoderm Cavity formed below the notch marks the beginning of the Gastrocoel or Archenteron Blastocoel is displaced during the formation of the gastrocoel (Gastrocoel is attached to the dorsal lip)
General Zoology Laboratory NEURULA: Formation of the neural tube
1st Semester 201 2012 2013 2013
Neural Plate: Elongation of embryo Development of thick epidermal cells neural plate
Neural Groove: Plate invaginates to a depression bounded by two lateral folds (Neural Folds)
Neural Tube: Folds fuse at midline has a head and tail region has a dorsal surface and a ventral surface has a primitive central nervous system (the neural tube) has a skeletal support rod (notochord located ventral to the neural tube) has a primitive gut (archenteron) Brain: o Prosencephalon with optic vesicles o Mesencephalon o Rhombencephalon Spinal cord
General Zoology Laboratory Organogenesis: started by Neurula Stage ECTODERM SKIN & CNS Brain Spinal cord Other neurons Sense receptors
1st Semester 201 2012 2013 2013
MESODERM Notochord Muscles Blood Bone Sex organs
ENDODERM Internal organs related to digestion Lining of gut, lungs, bladder Liver pancreas
Later Stages of Development: A. Nervous System simple neural tube divisions 1. Prosencephalon anterior, with thick lateral walls & dorsoventrally elongated cavity called PROSOCOEL 2. Mesemcephalon midbrain with cavity called MESOCOEL 3. Rhombencephalon or Hindbrain with cavity called RHOMBOCOEL 4. Spinal Cord small round vesicle found posterior to rhombencephalon B. Other Structures 1. Epiphysis 2. Optic vesicles 3. External flares / olfactory pits 4. Ear vesicles / otic vesicles 5. External gills 6. Pharyngeal pouches 7. Adhesive glands 8. Tail pins 9. Limb buds 10. Resorbed tails
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (120)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- Experimental Nucleonics PDFDocument1 pageExperimental Nucleonics PDFEricPas encore d'évaluation
- Neurovascular Holding PointsDocument8 pagesNeurovascular Holding PointsAlexandru Baciu100% (1)
- AvocadoDocument8 pagesAvocadoSper BacenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4 Significance of The Events IndustryDocument12 pagesChapter 4 Significance of The Events IndustrySper BacenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cursive Practice A ZDocument26 pagesCursive Practice A Zavabhyankar9393Pas encore d'évaluation
- Willyoustillloveme PDFDocument2 pagesWillyoustillloveme PDFSper BacenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Masao Takahashi and Family. Mastering Judo PDFDocument225 pagesMasao Takahashi and Family. Mastering Judo PDFMario Bertoluci100% (3)
- Pointers For Prelims Mt13110Document1 pagePointers For Prelims Mt13110Sper BacenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chap 4 BioDocument2 pagesChap 4 BioSper BacenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Locomotor and NonlocomotorDocument1 pageLocomotor and NonlocomotorSper BacenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Locomotor and NonlocomotorDocument1 pageLocomotor and NonlocomotorSper BacenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1: Invitation To BiologyDocument1 pageChapter 1: Invitation To BiologySper BacenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Test Bank For Essentials of Human Development A Life Span View 2nd Edition by KailDocument24 pagesTest Bank For Essentials of Human Development A Life Span View 2nd Edition by Kailmichaelwatson05082003xns100% (47)
- Yangkam WordlistDocument19 pagesYangkam Wordlistxdboy2006Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2020-08-17 WITS - MECN 5005A - Systems MGMT - Lecture 2 of 8 - SharedDocument73 pages2020-08-17 WITS - MECN 5005A - Systems MGMT - Lecture 2 of 8 - SharedUnarine MutshinyaloPas encore d'évaluation
- Anya Detonnancourt - Student Filmmaker ReflectionsDocument2 pagesAnya Detonnancourt - Student Filmmaker Reflectionsapi-550252062Pas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction and Assessment of The Renal - Urological SystemDocument182 pagesIntroduction and Assessment of The Renal - Urological SystemValerie Suge-Michieka100% (1)
- Orthogonal Curvilinear CoordinatesDocument16 pagesOrthogonal Curvilinear CoordinatesstriaukasPas encore d'évaluation
- Estoryang BinisayaDocument27 pagesEstoryang BinisayaAngel GellaPas encore d'évaluation
- Internetworking Concepts Overview: © 1999, Cisco Systems, IncDocument50 pagesInternetworking Concepts Overview: © 1999, Cisco Systems, IncShashi Kant RaviPas encore d'évaluation
- River: A Boon or A BaneDocument3 pagesRiver: A Boon or A BaneIJELS Research JournalPas encore d'évaluation
- Music TherapyDocument13 pagesMusic TherapyXavier KiranPas encore d'évaluation
- Effective Leadership Case Study AssignmentDocument5 pagesEffective Leadership Case Study AssignmentAboubakr Soultan67% (3)
- The Oldest Man - Made Structures On EarthDocument5 pagesThe Oldest Man - Made Structures On EarthDoug Hoseck100% (1)
- TNR Evaluation RD 2Document7 pagesTNR Evaluation RD 2api-302840901Pas encore d'évaluation
- Torts and Damages Midterm ReviewerDocument25 pagesTorts and Damages Midterm ReviewerErika-Anne TheresePas encore d'évaluation
- Naija Docs Magazine Issue 6Document46 pagesNaija Docs Magazine Issue 6Olumide ElebutePas encore d'évaluation
- HRA Strategic PlanDocument40 pagesHRA Strategic PlanjughomPas encore d'évaluation
- Arup Kumar Mandal (New Format)Document2 pagesArup Kumar Mandal (New Format)sharafat_321Pas encore d'évaluation
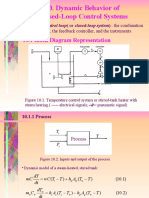
- Dynamic Behavior of Closed-Loop Control Systems: 10.1 Block Diagram RepresentationDocument26 pagesDynamic Behavior of Closed-Loop Control Systems: 10.1 Block Diagram Representationratan_nitPas encore d'évaluation
- Catherine The Great: Catherine II, Empress of RussiaDocument7 pagesCatherine The Great: Catherine II, Empress of RussiaLawrence James ParbaPas encore d'évaluation
- 13 19 PBDocument183 pages13 19 PBmaxim reinerPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To SAP Business OneDocument29 pagesIntroduction To SAP Business OneMoussa0% (1)
- SkripsiDocument101 pagesSkripsiNurul Maharani PutriPas encore d'évaluation
- The Hollow ManDocument13 pagesThe Hollow ManAya ArmandoPas encore d'évaluation
- Why Is "Being Religious Interreligiously" Imperative For Us Today?Document1 pageWhy Is "Being Religious Interreligiously" Imperative For Us Today?Lex HenonPas encore d'évaluation
- Hemzo M. Marketing Luxury Services. Concepts, Strategy and Practice 2023Document219 pagesHemzo M. Marketing Luxury Services. Concepts, Strategy and Practice 2023ichigosonix66Pas encore d'évaluation
- Types of Communicative StrategyDocument46 pagesTypes of Communicative StrategyMyra Bolinas100% (1)
- The Tamil Nadu Commercial Taxes ServiceDocument9 pagesThe Tamil Nadu Commercial Taxes ServiceKumar AvelPas encore d'évaluation
- 3 - QMT425-T3 Linear Programming (29-74)Document46 pages3 - QMT425-T3 Linear Programming (29-74)Ashraf RadzaliPas encore d'évaluation