Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Introduction To Markets
Transféré par
Hari BalasubramaniamTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Introduction To Markets
Transféré par
Hari BalasubramaniamDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Beta Series on Finance
Introduction to Markets
Building blocks
22/08/10 Beta Series on Finance 2
Global Capital Markets
Equity Capital Markets
Fixed Income, Currency and
Commodities
FX
Fixed Income
Securities
Rates Credit
Commodity
Capital Market
A capital market is a market for securities
where enterprises raise long term funds
Equity Market
Debt Market
22/08/10 Beta Series on Finance
Risk and Return
What is risk? What is uncertainty? Are they
the same?
Is risk always bad?
An investor will always take a position with
lower risk for the same level of return
22/08/10 Beta Series on Finance
Types of Risk
Systematic Risk
Risk associated with aggregate market returns
Unsystematic Risk
Risk associated with a particular security that is
being held by an investor
Diversification
The process of mitigating unsystematic risk
through investing in different instruments
22/08/10 Beta Series on Finance
Diversification example
22/08/10 Beta Series on Finance
Capital Asset Pricing Model
r
A
= r
f
+ *(r
m
- r
f
)
Any asset can be replicated as a combination of a
risk-free asset and market portfolio
The market rewards only systematic risk and there
is no compensation for holding undiversified
portfolio
CAPM is used extensively to estimate expected
returns Ex. in valuation of companies
Single period model
Mean variance optimized
22/08/10 Beta Series on Finance
Assumptions of CAPM
Investors are rational and risk averse
They aim to maximize economic utility
They are price takers
Investors can lend and borrow unlimited
amounts at the risk-free rate of interest
Absence of transaction costs and taxation
All information is available to everyone
22/08/10 Beta Series on Finance
Equities
What is a stock? What is a share? Is there a
difference?
Types of stocks
Common stock
Preferred stock
Convertible stock
22/08/10 Beta Series on Finance
Fixed Income Securities
Fixed income security refers to any type of
instrument that yields regular (fixed
schedule) of cash flows
Ex. A bank loan yields EMI for the bank a part of
which is used to repay the interest and a part is
used to amortize the principal
Does an FIS guarantee fixed return?
22/08/10 Beta Series on Finance
Bonds
22/08/10 Beta Series on Finance
Bond Holder
Bond Issuer
Pays the price of this INSTRUMENT
Periodic payments as defined by FIXED conditions
Can you visualize this as debt and repayment !!!
Now what is the difference between a normal Bank Loan and this ???
Bonds Building Blocks
Face Value
How much is the debt amount* !!!
Coupon Rate
How much shall you be paid !!!
Maturity
How long shall you receive the
payments !!!
22/08/10 Beta Series on Finance
Bond Holder
Bond Issuer
INR 100*
6% p.a for 10 Years
* Assuming you buy the bond directly from
the issuer at Face Value
Example of bonds
4.4% 5 year Treasury Note
Coupon paid semi-annually (2.2% every 6
months)
Note matures in 5 years
Issued by US Treasury
3 month LIBOR + 20 basis points, 5 Year
Floating Rate Note (FRN)
Bond pays 3 month LIBOR + 20 basis points
22/08/10 Beta Series on Finance
Price of a bond
Known cash flows
Coupon Rate * Face Value
Known schedules
So price = PV(Coupons) + PV (Face Value)
22/08/10 Beta Series on Finance
N
N
N N
N
N
n
n
r
P
r r
C
r
P
r
C
B
) 1 ( ) 1 (
1
1
) 1 ( ) 1 (
1
0
+
+
(
+
=
+
+
+
=
=
Annuity
Discount Rate ???
Accrued Interest
22/08/10 Beta Series on Finance
Dirty Price = Clean Price + Accrued Interest
Bonds are quoted in the markets in terms of
their clean price
However, the actual trade is done at the
dirty price
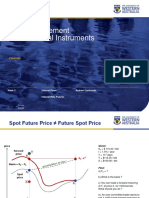
Bond Price Yield to Maturity
Remember Bonds are traded instruments, so
there is a market view of the risks
Remember Risk and Return ???
Yield to Maturity
The discount rate at which the PV of Cash flows
= Market Price
So given Price, when you solve for r , you get
the YTM
Market perception of Risk involved and return
required
22/08/10 Beta Series on Finance
So if YTM > Coupon, bond
price is greater or lesser
than par ???
Bonds outlining the risks
TANSTAAFL !
Interest Rate Risk ( remember the r ? )
Default Risk ( Would you like to lend to just anybody !)
Reinvestment Risk
Liquidity Risk
We shall primarily discuss Interest Rate Risk
Dealing with bonds is primarily dealing with rates
Shall rising rates increase or decrease bond prices ?
22/08/10 Beta Series on Finance
N
N
N N
N
N
n
n
r
P
r r
C
r
P
r
C
B
) 1 ( ) 1 (
1
1
) 1 ( ) 1 (
1
0
+
+
(
+
=
+
+
+
=
=
Price-Yield Relationship
Generated using Excel price( )
22/08/10 Beta Series on Finance
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
140
160
0% 5% 10% 15% 20% 25% 30% 35%
P
r
i
c
e
Yield
Measuring Interest Rate Risk
Duration
Interest Rate sensitivity of price
Percent change of price/unit change in yield
Whats the unit ?
Macaulay Duration (formula)
So what does Macaulay duration of 5 year signify ?
Interest rate sensitivity of the given bond is equivalent to that of a 5
year zero coupon bond !
DV01 (Dollar value of 1 basis point) measures the change in price of
bond for 1 basis point change in yield to maturity
22/08/10 Beta Series on Finance
Price-Yield Relationship
Generated using Excel price( )
22/08/10 Beta Series on Finance
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
140
160
0% 5% 10% 15% 20% 25% 30% 35%
P
r
i
c
e
Yield
-DP/Dr
Non Linear curve !!!
Does the tangent capture the risk fully ???
Convexity
Convexity
Why convexity exists?
Remember the price equation ?
Convexity is your friend . Always ?
Price drop due to rise in yield < Price rise due to drop in
yield
22/08/10 Beta Series on Finance
Risks and moving on to
derivatives
By holding which category of risks do you earn your return
Systematic risk or non-diversifiable risk
So how about an instrument which specifically allows you
to manage risks !
Enter Derivatives
Derives its value from an underlying
The underlying can be anything, a stock, an interest rate or even an
event !
22/08/10 Beta Series on Finance
Common types of derivatives
Forwards
Fix the price at which you
would transact at a future
date
Futures
Similar to forwards but
standardized and exchange
traded
22/08/10 Beta Series on Finance
-60
-40
-20
0
20
40
60
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
P
a
y
o
f
f
Spot Rate
Payoff to long forward position
Strike Price
Common types of derivatives
Options
Right but not the obligation to
transact at a future date
Call Option : Right to buy
Put Option : Right to sell
Swaps
Exchanging one stream of cash
flow for another
22/08/10 Beta Series on Finance
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
P
a
y
o
f
f
Spot Rate
Call option Payoff
Strike Price
A B
Fixed cash flow
Floating cash flow
Why derivatives* ?
Hedging Vs Speculation
22/08/10 Beta Series on Finance
Impact on Rambhais business ?
Rambhai can hedge his risks
through a rainfall derivative which
pays
X if it rains
None if it does not
Remember Rambhai stands to
lose from his standalone business
when it rains
Say its likely to rain next Monday
Impact on me ??? As of
now, nothing !!!
But I too can bet that it
wont rain and buy a
derivative such that I get
0 when it rains
X when it doesnt
I am just speculating here,
and have no other loss/gain
from either outcome !
* Other uses may include leverage,
trading on untraded underlyings etc
References for further reading
Options, Futures and Other Derivatives, Hull
& Basu, Seventh Edition
Chapters 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9, 10
Principles of Corporate Finance, Brealey-
Myers-Allen, Ninth Edition
Chapters 8, 9
22/08/10 Beta Series on Finance
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- BOND VALUATION With SolutionsDocument30 pagesBOND VALUATION With Solutionschiaraferragni75% (8)
- Embedded Systems DesignDocument576 pagesEmbedded Systems Designnad_chadi8816100% (4)
- Abdul Qadir Khan (Fixed Income Assignement No.4)Document8 pagesAbdul Qadir Khan (Fixed Income Assignement No.4)muhammadvaqasPas encore d'évaluation
- Bond ValuationDocument57 pagesBond ValuationRajib BurmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 8: ACCG3001 Organisational Planning and Control Tutorial In-Class Exercise - Student HandoutDocument3 pagesWeek 8: ACCG3001 Organisational Planning and Control Tutorial In-Class Exercise - Student Handoutdwkwhdq dwdPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 Financial Markets and InstrumentsDocument31 pages2 Financial Markets and InstrumentsMd parvezsharifPas encore d'évaluation
- EFB344 Lecture06, Forwards and Futures 2Document36 pagesEFB344 Lecture06, Forwards and Futures 2Tibet LovePas encore d'évaluation
- Investment Basics I: ObjectivesDocument14 pagesInvestment Basics I: Objectivesno namePas encore d'évaluation
- Bond ValuationDocument46 pagesBond ValuationNor Shakirah ShariffuddinPas encore d'évaluation
- Bond Valuation 1Document33 pagesBond Valuation 1bhaskkarPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 7 BondsDocument47 pagesLecture 7 BondsHuế HoàngPas encore d'évaluation
- BondsDocument55 pagesBondsfecaxeyivuPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 11 Bond Prices and YieldsDocument36 pagesChapter 11 Bond Prices and Yieldssharktale2828Pas encore d'évaluation
- How To Value Bonds?: Application of Time Value of MoneyDocument36 pagesHow To Value Bonds?: Application of Time Value of Moneyabhishek dharPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic 1 - Intro To Financial Markets: Create Base On The Revision Slide On Black BoardDocument15 pagesTopic 1 - Intro To Financial Markets: Create Base On The Revision Slide On Black BoardChip choiPas encore d'évaluation
- FINA5520 WK3 IntRatesAndIntRateFuturesDocument46 pagesFINA5520 WK3 IntRatesAndIntRateFuturesthelittlebirdyPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 9.pptx - WatermarkDocument99 pagesWeek 9.pptx - Watermarkkhushi jaiswalPas encore d'évaluation
- Booth Cleary 2nd Edition Chapter 6 - Bond Valuation and Interest RatesDocument93 pagesBooth Cleary 2nd Edition Chapter 6 - Bond Valuation and Interest RatesQurat.ul.ain MumtazPas encore d'évaluation
- Sesi 5 Valuasi ObligasiDocument17 pagesSesi 5 Valuasi ObligasigalihPas encore d'évaluation
- TFS 2015 Lecture 12 Open Revision SessionV2Document29 pagesTFS 2015 Lecture 12 Open Revision SessionV2ThorPas encore d'évaluation
- Bond Market 2019Document57 pagesBond Market 2019GBMS gorakhnagarPas encore d'évaluation
- Fixed Income SecuritiesDocument28 pagesFixed Income SecuritiesanuragPas encore d'évaluation
- The Valuation of Long-Term Securities: Syed Ahsan AmanDocument64 pagesThe Valuation of Long-Term Securities: Syed Ahsan AmanAndrew AndersonPas encore d'évaluation
- Bank Debt vs. Bond and The European Syndicated Loan MarketDocument23 pagesBank Debt vs. Bond and The European Syndicated Loan MarketzoomyadavPas encore d'évaluation
- Yield Curve Analysis and Fixed-Income ArbitrageDocument33 pagesYield Curve Analysis and Fixed-Income Arbitrageandrewfu1988Pas encore d'évaluation
- 17 Dec Capital Structure TheoriesDocument39 pages17 Dec Capital Structure TheoriesKritika BhattPas encore d'évaluation
- Fixed IncomeDocument36 pagesFixed IncomeAnkit ShahPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 5Document29 pagesWeek 5jc cPas encore d'évaluation
- BFC5926 Seminar 5 - Long-Term Debt MarketsDocument58 pagesBFC5926 Seminar 5 - Long-Term Debt MarketsMengdi ZhangPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 08Document59 pagesCH 08T L K LyPas encore d'évaluation
- Principles of Business Finance: Lecture 6: Interest Rates and Bond ValuationDocument28 pagesPrinciples of Business Finance: Lecture 6: Interest Rates and Bond ValuationAmandaPas encore d'évaluation
- INVS & Port Lec-03Document36 pagesINVS & Port Lec-03johnymascularPas encore d'évaluation
- THREEBond and Stock Valuation - BondDocument22 pagesTHREEBond and Stock Valuation - BondRaasu KuttyPas encore d'évaluation
- Interest Rates and Bond Valuation: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinDocument28 pagesInterest Rates and Bond Valuation: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinCharbel HatemPas encore d'évaluation
- Govt SecuritiesDocument81 pagesGovt SecuritiesJeenal KaraniPas encore d'évaluation
- Valuation of Bonds and DebenturesDocument48 pagesValuation of Bonds and DebenturesRadhakrishna MishraPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 4 - Fixed Income SecurityDocument49 pagesCH 4 - Fixed Income SecurityALEMU TADESSEPas encore d'évaluation
- Debt MarketDocument25 pagesDebt MarketSuraj DasPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 Bond and StockDocument32 pages4 Bond and Stockmahwish111Pas encore d'évaluation
- Valuation of Financial AssetsDocument47 pagesValuation of Financial AssetsprashantkumbhaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic 6Document82 pagesTopic 6Narcisse ChanPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Financial Concepts - FinalDocument34 pagesBasic Financial Concepts - FinalDu Baladad Andrew MichaelPas encore d'évaluation
- Sem in Finance-Notes To Final Exam Readings Part 2Document82 pagesSem in Finance-Notes To Final Exam Readings Part 2hantrankha75Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fm1 MergedDocument168 pagesFm1 MergedrishPas encore d'évaluation
- Relative ValuationDocument29 pagesRelative ValuationCheTanBonDardePas encore d'évaluation
- Bond Pricing and Bond Yield SRPM2012Document57 pagesBond Pricing and Bond Yield SRPM2012ashishbansal85Pas encore d'évaluation
- Bond Pricing and Bond Yield New - 1Document66 pagesBond Pricing and Bond Yield New - 1Sarang Gupta100% (1)
- Chapter 2: How Interest Rates Are DeterminedDocument62 pagesChapter 2: How Interest Rates Are DeterminedAykaPas encore d'évaluation
- Strategic Financial Planning Lec 2Document62 pagesStrategic Financial Planning Lec 2MALIK WASEEM JANPas encore d'évaluation
- BUSINESS FINANCE .. Anthony & BrainDocument264 pagesBUSINESS FINANCE .. Anthony & BrainAnita SmithPas encore d'évaluation
- Relative ValuationDocument29 pagesRelative ValuationOnal RautPas encore d'évaluation
- Determination of Forward & Future Prices: R. SrinivasanDocument18 pagesDetermination of Forward & Future Prices: R. SrinivasanorazikmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Techniques of Asset/liability Management: Futures, Options, and SwapsDocument19 pagesTechniques of Asset/liability Management: Futures, Options, and SwapsNishant Verma100% (1)
- Stock InvestmentDocument61 pagesStock InvestmentKurt Geeno Du VencerPas encore d'évaluation
- Bond FundamentalsDocument19 pagesBond FundamentalsInstiRevenPas encore d'évaluation
- Chap 5 Money Bond MarketsDocument37 pagesChap 5 Money Bond MarketsGayatheri PerumalPas encore d'évaluation
- Cost of CapitalDocument37 pagesCost of Capitalrajthakre81Pas encore d'évaluation
- Revision MidtermDocument12 pagesRevision MidtermKim NgânPas encore d'évaluation
- Bond Prices and Yields: Figuring Out The Assured ReturnsDocument36 pagesBond Prices and Yields: Figuring Out The Assured ReturnsvaibhavPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 08Document60 pagesCH 08Duc Tai NguyenPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic 2 - Bond Valuation-A132Document58 pagesTopic 2 - Bond Valuation-A132Baby KhorPas encore d'évaluation
- Fixed Income Securities: A Beginner's Guide to Understand, Invest and Evaluate Fixed Income Securities: Investment series, #2D'EverandFixed Income Securities: A Beginner's Guide to Understand, Invest and Evaluate Fixed Income Securities: Investment series, #2Pas encore d'évaluation
- 1934 PARIS AIRSHOW REPORT - Part1 PDFDocument11 pages1934 PARIS AIRSHOW REPORT - Part1 PDFstarsalingsoul8000Pas encore d'évaluation
- PeopleSoft Application Engine Program PDFDocument17 pagesPeopleSoft Application Engine Program PDFSaurabh MehtaPas encore d'évaluation
- Level 3 Repair: 8-1. Block DiagramDocument30 pagesLevel 3 Repair: 8-1. Block DiagramPaulo HenriquePas encore d'évaluation
- Appendix - 5 (Under The Bye-Law No. 19 (B) )Document3 pagesAppendix - 5 (Under The Bye-Law No. 19 (B) )jytj1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Richards Laura - The Golden WindowsDocument147 pagesRichards Laura - The Golden Windowsmars3942Pas encore d'évaluation
- LMU-2100™ Gprs/Cdmahspa Series: Insurance Tracking Unit With Leading TechnologiesDocument2 pagesLMU-2100™ Gprs/Cdmahspa Series: Insurance Tracking Unit With Leading TechnologiesRobert MateoPas encore d'évaluation
- Ingles Avanzado 1 Trabajo FinalDocument4 pagesIngles Avanzado 1 Trabajo FinalFrancis GarciaPas encore d'évaluation
- Shubham Tonk - ResumeDocument2 pagesShubham Tonk - ResumerajivPas encore d'évaluation
- Channel Tables1Document17 pagesChannel Tables1erajayagrawalPas encore d'évaluation
- CIR Vs PAL - ConstructionDocument8 pagesCIR Vs PAL - ConstructionEvan NervezaPas encore d'évaluation
- SILABO 29-MT247-Sensors-and-Signal-ConditioningDocument2 pagesSILABO 29-MT247-Sensors-and-Signal-ConditioningDiego CastilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Oracle Exadata Database Machine X4-2: Features and FactsDocument17 pagesOracle Exadata Database Machine X4-2: Features and FactsGanesh JPas encore d'évaluation
- 18PGHR11 - MDI - Aditya JainDocument4 pages18PGHR11 - MDI - Aditya JainSamanway BhowmikPas encore d'évaluation
- TAS5431-Q1EVM User's GuideDocument23 pagesTAS5431-Q1EVM User's GuideAlissonPas encore d'évaluation
- RENCANA KERJA Serious Inspeksi#3 Maret-April 2019Document2 pagesRENCANA KERJA Serious Inspeksi#3 Maret-April 2019Nur Ali SaidPas encore d'évaluation
- Rating SheetDocument3 pagesRating SheetShirwin OliverioPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 PBDocument14 pages1 PBSaepul HayatPas encore d'évaluation
- Portrait of An INTJDocument2 pagesPortrait of An INTJDelia VlasceanuPas encore d'évaluation
- Properties of Moist AirDocument11 pagesProperties of Moist AirKarthik HarithPas encore d'évaluation
- L1 L2 Highway and Railroad EngineeringDocument7 pagesL1 L2 Highway and Railroad Engineeringeutikol69Pas encore d'évaluation
- 48 Volt Battery ChargerDocument5 pages48 Volt Battery ChargerpradeeepgargPas encore d'évaluation
- Amerisolar AS 7M144 HC Module Specification - CompressedDocument2 pagesAmerisolar AS 7M144 HC Module Specification - CompressedMarcus AlbaniPas encore d'évaluation
- 199437-Unit 4Document36 pages199437-Unit 4Yeswanth rajaPas encore d'évaluation
- Tivoli Performance ViewerDocument4 pagesTivoli Performance ViewernaveedshakurPas encore d'évaluation
- Droplet Precautions PatientsDocument1 pageDroplet Precautions PatientsMaga42Pas encore d'évaluation
- Form16 2018 2019Document10 pagesForm16 2018 2019LogeshwaranPas encore d'évaluation
- Familiarization With Apparatus and Equipment Used in Testing of MaterialsDocument5 pagesFamiliarization With Apparatus and Equipment Used in Testing of MaterialsEmanoAce33% (6)
- Tinplate CompanyDocument32 pagesTinplate CompanysnbtccaPas encore d'évaluation