Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Malignant Salivary Gland Tumors (Mucoepidermoid, Aca, Acc)
Transféré par
Eastma MeiliDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Malignant Salivary Gland Tumors (Mucoepidermoid, Aca, Acc)
Transféré par
Eastma MeiliDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
MALIGNANT SALIVARY GLAND TUMORS
Mucoepidermoid carcinoma VS Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma VS Acinic Cell Adenocarcinoma
MALIGNANT SALIVARY GLAND TUMORS Definition
Mucoepidermoid carcinoma
Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma (ACC)
Acinic Cell Adenocarcinoma (ACA) A neoplastic growth of epithelial cells showing serous acinar differentiation All acinic cell tumors have some amount of malignant potential.
A malignant epithelial neoplasm of ductal (lumial) and myoepithelial (abluminal) cells growing in cribriform, tubular, solid and cystic patterns
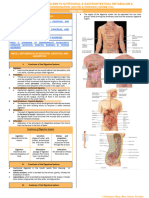
Most common malignancy
salivary
gland
5-9% of salivary neoplasms Characteristics Parotid 45-70% of cases Palate 18% 3rd-8th decades, peak in 5th decade F>M Caucasian > African American Most common salivary gland tumor of children
Mucoepidermoid carcinoma
Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma (ACC) Overall 2nd most common malignancy
Acinic Cell Adenocarcinoma (ACA) Occurs most commonly in parotid gland Occurs unilaterally. May occur bilaterally. Occurs more frequently in women than men (3:2) Occurs in young and old individuals Slowly growing, mobile or fixed mass of various durations Asymptomatic Pain or tenderness
Clinical features
Presentation Low-grade: slow growing, painless mass High-grade: rapidly enlarging, +/- pain **Minor salivary glands: may be mistaken for benign or inflammatory process Hemangioma Papilloma Tori
Most common in palatae,submandibular, and minor salivary glands F> M 5th decade Presentation Asymptomatic enlarging mass or associated Pain, paresthesia, facial weakness/paralysis ACC has a marked tendency to spread through perineural spaces
Facial muscle weakness Well-circumscribed to partially encapsulated to unencapsulated Solid tumor with cystic spaces Gross pathology infiltrative Resemble P.A Well-circumscribed Solid, rarely with cystic spaces Well-demarcated Most often homogeneous
Mucoepidermoid carcinoma 3 types of cells (a)Mucous secreting cells -various shapes -abundant -pale foamy cytoplasm -stains +ve for mucin stains. (b)Epidermoid cells -polygonal -squamoid feature -intercellular bridges -rarely keratinization (c)Intermediate cells -resembles basaloid cells -LARGER than BASAL CELLS -smaller than sq. cells
Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma 1.Cribriform pattern Most common Basaloid epithelial cell nests forming multiple cylindrical cyst like patterns swiss cheese appearance
Acinic Cell Adenocarcinoma (ACA) 1.Different Patterns Sheets (Solid) Cysts, some with papillary growth Microcystic Follicles (similar to thyroid)
Histology
2.Tubular pattern Layered cells forming duct-like structures Basophilic mucinous substance
2.Acinar epithelium 3.Large polygonal 4.Lightly basophilic cytoplasm 5.Uniform to variable eccentric nuclei (blue dot tumors) 6.Cytoplasmic granules mucicarmine positive) (PAS positive;
7.Central lumen of various size
Mucoepidermoid carcinoma
Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma
Acinic Cell Adenocarcinoma (ACA)
3.Solid pattern Solid nests of cells without cystic or tubular spaces
Influenced by site, stage, grade Treatment & Prognosis Stage I & II Wide local excision Stage III & IV Radical excision +/- neck dissection +/- postoperative radiation therapy
Treatment Complete local excision Tendency for perineural invasion: facial nerve sacrifice Postoperative XRT Prognosis Local recurrence: 42% Distant metastasis: lung Indolent course: 5-year survival 75%, 20-year survival 13%
Treatment Complete local excision +/- postoperative XRT Prognosis 5-year survival: 82% 10-year survival: 68% 25-year survival: 50%
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5795)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- Prosthodontics by Prof. Sajid NaeemDocument211 pagesProsthodontics by Prof. Sajid NaeemFA Khan50% (2)
- Radioprotectors: Afifah BT Johari 101323044 Nur Ismawani BT Ishak 101323045Document32 pagesRadioprotectors: Afifah BT Johari 101323044 Nur Ismawani BT Ishak 101323045Eastma MeiliPas encore d'évaluation
- Core of Medical Physiology 2 Ed3 PDFDocument442 pagesCore of Medical Physiology 2 Ed3 PDFHamid Hussain Hamid94% (17)
- Neural Mechanisms of Salivary Gland SecretionDocument247 pagesNeural Mechanisms of Salivary Gland SecretionMassimo Baudo100% (1)
- Biology of Tooth MovementDocument40 pagesBiology of Tooth MovementEastma MeiliPas encore d'évaluation
- MatricesDocument46 pagesMatricesEastma MeiliPas encore d'évaluation
- Contacts and ContoursDocument45 pagesContacts and ContoursEastma Meili100% (4)
- Brighter Futures - Orthodontics and Dental TraumaDocument2 pagesBrighter Futures - Orthodontics and Dental TraumaEastma MeiliPas encore d'évaluation
- E FracturesDocument11 pagesE FracturesEastma MeiliPas encore d'évaluation
- Cranial CavityDocument49 pagesCranial CavityEastma MeiliPas encore d'évaluation
- Children Make You Want To Start Life Over They Are 1/3 of Our Population and All of Our FutureDocument16 pagesChildren Make You Want To Start Life Over They Are 1/3 of Our Population and All of Our FutureEastma MeiliPas encore d'évaluation
- Icd X Dan Icd 9 CM Who Dentistry: International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health ProblemsDocument25 pagesIcd X Dan Icd 9 CM Who Dentistry: International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health ProblemsElon LiliPas encore d'évaluation
- 10 1016@j Archoralbio 2019 104593 PDFDocument3 pages10 1016@j Archoralbio 2019 104593 PDFSaeful RamadonPas encore d'évaluation
- Prosthetic Management of Edentulous Mandibulectomy Patients JCDocument21 pagesProsthetic Management of Edentulous Mandibulectomy Patients JCVaishnavi KarthikeyanPas encore d'évaluation
- Jhfdsxavier University Ateneo de Cagayan: Salivary Digestion (Laboratory Report No. 11)Document11 pagesJhfdsxavier University Ateneo de Cagayan: Salivary Digestion (Laboratory Report No. 11)Elyka AbellaPas encore d'évaluation
- Mouth and Nose HaDocument56 pagesMouth and Nose HaSheen CatayongPas encore d'évaluation
- Reviewer Digestive SystemDocument12 pagesReviewer Digestive SystemLorenzo Gabriel RSPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 14 - Digestive SystemsDocument103 pagesChapter 14 - Digestive Systemsnokate konkoorPas encore d'évaluation
- Chem Lab Final Exam Notes 2Document7 pagesChem Lab Final Exam Notes 2Jaira Emmarina100% (1)
- Question Bank First YearDocument12 pagesQuestion Bank First YearBalakrishna ReddyPas encore d'évaluation
- JISPPD Supplement 19 PDFDocument71 pagesJISPPD Supplement 19 PDFHARSH KUMARPas encore d'évaluation
- Scientific Thought and Clinical Practice - Edit. Dejan MarkovicDocument251 pagesScientific Thought and Clinical Practice - Edit. Dejan MarkovicskychiPas encore d'évaluation
- Action of Salivary Amylase On StarchDocument4 pagesAction of Salivary Amylase On StarchJoseph Albert HernandezPas encore d'évaluation
- Milk - Experiment 11Document16 pagesMilk - Experiment 11Joshuel MontecilloPas encore d'évaluation
- A Review On Oral Mucosal Drug Delivery SystemDocument8 pagesA Review On Oral Mucosal Drug Delivery SystemPharmacognosy JournalPas encore d'évaluation
- Pemicu 1 Blok GIT: Theffany 405120198 Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas TarumanagaraDocument99 pagesPemicu 1 Blok GIT: Theffany 405120198 Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas TarumanagaraTheffany KasiranPas encore d'évaluation
- Head and Neck QuestionsDocument2 pagesHead and Neck QuestionsPulkitPas encore d'évaluation
- Diseases of Salivary Glands: Prepared By: Dr. Ahlam A. AlesayiDocument96 pagesDiseases of Salivary Glands: Prepared By: Dr. Ahlam A. AlesayiWaqas Iqbal100% (1)
- BADBREATHDocument23 pagesBADBREATHBilly TrầnPas encore d'évaluation
- Tongue Lesions and HomoeopathyDocument12 pagesTongue Lesions and HomoeopathyDr. Rajneesh Kumar Sharma MD Hom100% (2)
- NCMB 316Document46 pagesNCMB 316andreatrojilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Digestive System Anatomy and Physiology - NurseslabsDocument33 pagesDigestive System Anatomy and Physiology - NurseslabsMari FePas encore d'évaluation
- MNJJDocument12 pagesMNJJFadhli AzhimiPas encore d'évaluation
- Review On SalivaDocument8 pagesReview On SalivastartabrezPas encore d'évaluation
- Parotid TumorDocument37 pagesParotid TumorRiyan SaputraPas encore d'évaluation
- The Colleges of Medicine of South AfricaDocument2 pagesThe Colleges of Medicine of South AfricadujdjsPas encore d'évaluation
- Gerodontology BaruDocument53 pagesGerodontology BaruHappy Septianto S100% (1)
- Saliva - A Diagnostic ToolDocument30 pagesSaliva - A Diagnostic ToolPrathusha UmakhanthPas encore d'évaluation