Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Investment Banking Firms (Handouts)
Transféré par
Joyce Ann SosaTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Investment Banking Firms (Handouts)
Transféré par
Joyce Ann SosaDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
INVESTMENT BANKING FIRMS GOING PUBLIC Right offering- new shares are sold to existing stockholder.
. Private placement- the firm sells new securities directly to an investor or a group of investors. Public offering- in which it offers its shares for the sale to the general public. Initial Public Offering (IPO) The first public sale of a firms stock. Prospectus a portfolio of a security registration statement that describes the key aspects of the issuer, and its managements and financial position. Red herring a preliminary prospectus made available to prospective investors during the waiting period between the registration statements filling with the SEC and its approval. Investment Banker Financial intermediary that specializes in selling new security issues and advising firms with regard to major financial transactions. Underwriting The role of the investment banker in bearing the risk of reselling, at a profit, the securities purchased from an issuing corporation at an agreedon price. Underwriting syndicate A group formed by an investment banker to share the financial risk associated with underwriting new securities. Selling group A large number of brokerage firms that join the originating investment banker(s); each accepts responsibility for selling a certain portion of a new security issue on a commission basis. Trading 1. Position Trading- involves purchases of large blocks of securities on the expectation of a favorable price move. 2. Pure Arbitrage- entails buying an asset in one price and selling it immediately in another market at a higher price. 3. Risk Arbitrage- involves buying securities in anticipation of some information release- such as a merger or takeover announcement on a Federal Reserve interest rate announcement. 4. Program Trading- a type of pure arbitrage trading in that it is often associated with seeking to profit from differences between the
cash market price and the futures market price of a particular instrument. 5. Stock Brokerage- involves the trading of securities on behalf of individuals who want to transact in the money or capital markets. 6. Electronic Brokerage- offered by major brokers, involves direct access, via the Internet, to the trading floor therefore bypassing traditional brokers. Private placement A securities issue placed with one or a few large institutional investors. Cash Management Accounts Money market mutual fund sold by investment banks that offer check-writing privileges. Venture capital A professionally managed pool of money used to finance to finance new and often high-risk firms. Institutional Venture Capital Firms Business entities whose sole purpose is to find and fund the most promising new firms. Angel Venture Capitalist (angel) Wealthy individuals who make equity investments. Mergers and acquisition Merger the combination of two or more firms, in which the resulting firm maintains the identity of one of the firms, usually the larger. Consolidation the combination of two or more firms to form a completely new corporation. Holding Company- A corporation that has voting control of one or more other corporations. Subsidiaries the companies controlled by a holding company. Acquiring company the firm in a merger transaction THAT attempts to acquire another firm. Target company the firm in a merger transaction that the acquiring company is pursuing. Friendly Merger Vs Hostile Merger Friendly Merger a merger transaction endorsed by the target firms management approved by its stockholders, and easily consummated. Hostile Merger a merger transaction that the target firms management does not support, the acquiring company to
try to gain control of the firm buying shares in the marketplace. Strategic merger vs financial merger Strategic merger a merger transaction undertaken to achieve economist of scale Financial merger a merger transaction undertaken with the goal of restructuring the acquired company to improve its cash flow and unlock its hidden value.
Type of merger Horizontal merger- a merger of two firms in the same line of business. Vertical merger- a merger in which a firm acquires a supplier or a customers. Congeneric merger- a merger in which one of the firm acquires another firm that is in the same general industry but neither in the same line of business nor a supplier or customer. Conglomerate merger- a merger combining firms in unrelated businesses.
THE SELLING PROCESS FOR A LARGE SECURITIES ISSUE
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Common StockDocument20 pagesCommon StockAfifa AkterPas encore d'évaluation
- Issue ManagementDocument8 pagesIssue ManagementarvinPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 1: Understanding Equity: Public Equity Versus Private EquityDocument3 pagesUnit 1: Understanding Equity: Public Equity Versus Private Equityaashu0123Pas encore d'évaluation
- Private Equity NotesDocument5 pagesPrivate Equity NotesSaad KundiPas encore d'évaluation
- Finals Fnm103Document40 pagesFinals Fnm103Novelyn DuyoganPas encore d'évaluation
- IM Module 2Document57 pagesIM Module 2vanitha gkPas encore d'évaluation
- GovernanceDocument21 pagesGovernancemicaPas encore d'évaluation
- Investment Banking Course GlossaryDocument6 pagesInvestment Banking Course GlossaryYahya AçafPas encore d'évaluation
- Iapm - Unit-2 & 3 (Mba-3)Document38 pagesIapm - Unit-2 & 3 (Mba-3)Kelvin SavaliyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter Four Financial Market in The Financial SystemsDocument136 pagesChapter Four Financial Market in The Financial SystemsNatnael Asfaw100% (1)
- Mastering the Markets: Advanced Trading Strategies for Success and Ethical Trading PracticesD'EverandMastering the Markets: Advanced Trading Strategies for Success and Ethical Trading PracticesPas encore d'évaluation
- Venture Capital FinanceDocument7 pagesVenture Capital FinanceSachi LunechiyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4 FIDocument7 pagesChapter 4 FISeid KassawPas encore d'évaluation
- Stock Market: Over-The-Counter (OTC) or Off-Exchange Trading Is Done Directly Between TwoDocument4 pagesStock Market: Over-The-Counter (OTC) or Off-Exchange Trading Is Done Directly Between TwoAli JumaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 2Document6 pagesUnit 2Om PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- Mastering the Market: A Comprehensive Guide to Successful Stock InvestingD'EverandMastering the Market: A Comprehensive Guide to Successful Stock InvestingPas encore d'évaluation
- Case 4Document3 pagesCase 4Melana MuliPas encore d'évaluation
- Wall Street Jargon Cheat Sheet 1711318755Document4 pagesWall Street Jargon Cheat Sheet 1711318755Saul VillarrealPas encore d'évaluation
- Corporate LawDocument15 pagesCorporate LawLaxmi WankhedePas encore d'évaluation
- Interview QuestionsDocument7 pagesInterview QuestionsGaurav TripathiPas encore d'évaluation
- Conceptual QuestionsDocument5 pagesConceptual QuestionsSarwanti PurwandariPas encore d'évaluation
- Glosssry IVCADocument10 pagesGlosssry IVCAapi-3865133Pas encore d'évaluation
- Unit - Iv - NVP-1Document47 pagesUnit - Iv - NVP-1Pruthvi RajPas encore d'évaluation
- Stock Market I. What Are Stocks?Document9 pagesStock Market I. What Are Stocks?JehannahBaratPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 16 - Securities Firms and Investment BanksDocument2 pagesChapter 16 - Securities Firms and Investment Banksmvlg26Pas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced Chapter-4Document35 pagesAdvanced Chapter-4Yeber MelkemiyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Financial Institutions and MarketsDocument10 pagesFinancial Institutions and MarketsVikkuPas encore d'évaluation
- 210fin-Ch15 4Document33 pages210fin-Ch15 4Mazen SalahPas encore d'évaluation
- Primary Market &: The Underwriting of SecurityDocument32 pagesPrimary Market &: The Underwriting of SecuritySumon100% (1)
- FNM 106 M-TERM lECTURE 3,4Document10 pagesFNM 106 M-TERM lECTURE 3,4haron franciscoPas encore d'évaluation
- Concept of Venture CapitalDocument18 pagesConcept of Venture CapitalRishika GoyalPas encore d'évaluation
- MF - Unit IiiDocument15 pagesMF - Unit IiiIndrani DasguptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Investment Banking Firms Lesson 4Document8 pagesInvestment Banking Firms Lesson 4Febie Gayap FelixPas encore d'évaluation
- Primary MarketDocument15 pagesPrimary MarketKapil KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Finance Impt Topics For PlacementDocument3 pagesFinance Impt Topics For PlacementMRIDUL GOELPas encore d'évaluation
- MB II Unit Final StudentsDocument70 pagesMB II Unit Final StudentsHema vijay sPas encore d'évaluation
- Equity MarketDocument13 pagesEquity MarketBrandon LumibaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Stock Valuation Written ReportDocument14 pagesStock Valuation Written ReportJesse John A. CorpuzPas encore d'évaluation
- Investing Made Easy: Finding the Right Opportunities for YouD'EverandInvesting Made Easy: Finding the Right Opportunities for YouPas encore d'évaluation
- Equity GlossaryDocument11 pagesEquity GlossaryAnurag DhawanPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter - 4: Business of Combination 4.1 Business of Combination: An Overview 4.1.1 Definition of Business CombinationDocument32 pagesChapter - 4: Business of Combination 4.1 Business of Combination: An Overview 4.1.1 Definition of Business CombinationYeber MelkemiyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Key Factors in Attracting Venture CapitalDocument4 pagesKey Factors in Attracting Venture CapitalPadmavathi HanmanthraoPas encore d'évaluation
- Investment Key TermsDocument32 pagesInvestment Key TermsAnikaPas encore d'évaluation
- Methods of IP1Document9 pagesMethods of IP1MESRETPas encore d'évaluation
- Untitled DocumentDocument5 pagesUntitled DocumentMarjorie Salvador VallePas encore d'évaluation
- Venture CapitalDocument4 pagesVenture CapitalVinayPas encore d'évaluation
- Brian Ghilliotti-Money and Banking-Ch 10 SummaryDocument7 pagesBrian Ghilliotti-Money and Banking-Ch 10 SummaryBrian GhilliottiPas encore d'évaluation
- Role of Primary MarketDocument24 pagesRole of Primary Marketprashantgorule100% (4)
- Equity Market: Equity Market Is One of The Key Sectors of Financial Markets Where Long-Term FinancialDocument10 pagesEquity Market: Equity Market Is One of The Key Sectors of Financial Markets Where Long-Term Financialfrancis dungcaPas encore d'évaluation
- Definition: The Corporate Restructuring Is The Process ofDocument8 pagesDefinition: The Corporate Restructuring Is The Process ofHARSHITA SOANPas encore d'évaluation
- UntitledDocument2 pagesUntitledUmi AnggraeniPas encore d'évaluation
- Venture CapitalDocument17 pagesVenture CapitalNor Azlan RamliPas encore d'évaluation
- Sources of FinanceDocument39 pagesSources of Financenomanameer324Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2 Financial Intermediaries and Other ParticipantsDocument45 pagesChapter 2 Financial Intermediaries and Other ParticipantsWill De OcampoPas encore d'évaluation
- Top Private Equity Analyst Interview Questions and Answers Helpful For The BelowDocument7 pagesTop Private Equity Analyst Interview Questions and Answers Helpful For The BelowTushar NegiPas encore d'évaluation
- Neha Siddique 02-111201-222 BBA-4B Fundamentals of Finance: Integrated Case StudyDocument8 pagesNeha Siddique 02-111201-222 BBA-4B Fundamentals of Finance: Integrated Case StudyArishfa khanPas encore d'évaluation
- A Project Report On NSEDocument64 pagesA Project Report On NSEMukesh ChhotalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Group No. 3Document13 pagesGroup No. 3kiran rokadePas encore d'évaluation
- Presentation On: Private EquityDocument45 pagesPresentation On: Private EquityKetan BhatiaPas encore d'évaluation
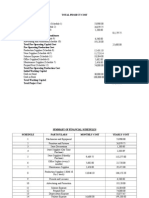
- Financial SchedulesDocument10 pagesFinancial SchedulesJoyce Ann SosaPas encore d'évaluation
- Open High Low Close AverageDocument13 pagesOpen High Low Close AverageJoyce Ann SosaPas encore d'évaluation
- Metrobank Reports First Half Income of P18Document11 pagesMetrobank Reports First Half Income of P18Joyce Ann SosaPas encore d'évaluation
- Metrobank 2012 AnalysisDocument11 pagesMetrobank 2012 AnalysisJoyce Ann Sosa100% (1)
- NarcoticsDocument3 pagesNarcoticsJoyce Ann SosaPas encore d'évaluation
- Equilibrium and Disequilibrium in Bop (Handouts)Document2 pagesEquilibrium and Disequilibrium in Bop (Handouts)Joyce Ann Sosa67% (3)
- Humanities 1 Art AppreciationDocument3 pagesHumanities 1 Art AppreciationJoyce Ann SosaPas encore d'évaluation
- Fin 8 INVESTMENT BANKING FIRMSDocument23 pagesFin 8 INVESTMENT BANKING FIRMSJoyce Ann SosaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Case of The Returned CollateralDocument18 pagesThe Case of The Returned CollateralJoyce Ann Sosa60% (5)
- Fossil Fuel: Non-Renewable Energy Renewable Energy Biomass Hydropower Wind PowerDocument33 pagesFossil Fuel: Non-Renewable Energy Renewable Energy Biomass Hydropower Wind PowerJoyce Ann SosaPas encore d'évaluation
- Braintrain: Summer Camp WorksheetDocument9 pagesBraintrain: Summer Camp WorksheetPadhmennPas encore d'évaluation
- Fundamentals of Accounting I Accounting For Manufacturing BusinessDocument14 pagesFundamentals of Accounting I Accounting For Manufacturing BusinessBenedict rivera100% (2)
- 2016 VTN Issue 026Document24 pages2016 VTN Issue 026Bounna PhoumalavongPas encore d'évaluation
- Police Information Part 8Document8 pagesPolice Information Part 8Mariemel EsparagozaPas encore d'évaluation
- Problem 1246 Dan 1247Document2 pagesProblem 1246 Dan 1247Gilang Anwar HakimPas encore d'évaluation
- Claremont COURIER 1-30-15Document28 pagesClaremont COURIER 1-30-15Claremont CourierPas encore d'évaluation
- RanbaxyDocument2 pagesRanbaxyAmit BorsePas encore d'évaluation
- As Built - X-Section - 160+700 To 1660+825Document5 pagesAs Built - X-Section - 160+700 To 1660+825Md Mukul MiahPas encore d'évaluation
- StudioArabiyaTimes Magazine Spring 2022Document58 pagesStudioArabiyaTimes Magazine Spring 2022Ali IshaanPas encore d'évaluation
- Letter of Appeal Pacheck Kay Tita ConnieDocument2 pagesLetter of Appeal Pacheck Kay Tita ConnieNikko Avila IgdalinoPas encore d'évaluation
- Front Cover NME Music MagazineDocument5 pagesFront Cover NME Music Magazineasmediae12Pas encore d'évaluation
- Hymns by John Henry NewmanDocument286 pagesHymns by John Henry Newmanthepillquill100% (1)
- Essay On FamilyDocument2 pagesEssay On Familyapi-277963081Pas encore d'évaluation
- Schonsee Square Brochure - July 11, 2017Document4 pagesSchonsee Square Brochure - July 11, 2017Scott MydanPas encore d'évaluation
- CT-e: Legal Change: Configuration GuideDocument14 pagesCT-e: Legal Change: Configuration GuidecamillagouveaPas encore d'évaluation
- Resume 2Document2 pagesResume 2Ryan AlyasPas encore d'évaluation
- IIM Kashipur Master of Business Administration (MBA) Microeconomics, Term I, Academic Year 2021-2022 Syllabus I. Instructor DetailDocument20 pagesIIM Kashipur Master of Business Administration (MBA) Microeconomics, Term I, Academic Year 2021-2022 Syllabus I. Instructor DetailSai Teja MekalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Puyat vs. Arco Amusement Co (Gaspar)Document2 pagesPuyat vs. Arco Amusement Co (Gaspar)Maria Angela GasparPas encore d'évaluation
- Toms River Fair Share Housing AgreementDocument120 pagesToms River Fair Share Housing AgreementRise Up Ocean CountyPas encore d'évaluation
- Seryu Cargo Coret CoreDocument30 pagesSeryu Cargo Coret CoreMusicer EditingPas encore d'évaluation
- Analysis of Chapter 8 of Positive Psychology By::-Alan CarrDocument3 pagesAnalysis of Chapter 8 of Positive Psychology By::-Alan CarrLaiba HaroonPas encore d'évaluation
- People vs. Patulot - Case DigestDocument5 pagesPeople vs. Patulot - Case DigestGendale Am-isPas encore d'évaluation
- Intermarket AnaDocument7 pagesIntermarket Anamanjunathaug3Pas encore d'évaluation
- LAZ PAPER Ethics Ethical Conduct Challenges and Opportunities in Modern PracticeDocument15 pagesLAZ PAPER Ethics Ethical Conduct Challenges and Opportunities in Modern PracticenkwetoPas encore d'évaluation
- Mubashir Malik: Administrative Technical AssistantDocument1 pageMubashir Malik: Administrative Technical AssistantMUBASHIR MALIKPas encore d'évaluation
- Indicator - Individual Dietary Diversity ScoreDocument3 pagesIndicator - Individual Dietary Diversity Scorehisbullah smithPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 2 - BasicDocument7 pagesLesson 2 - BasicMichael MccormickPas encore d'évaluation
- Manual On Cargo Clearance Process (E2m Customs Import Assessment System)Document43 pagesManual On Cargo Clearance Process (E2m Customs Import Assessment System)Musa Batugan Jr.100% (1)
- Verbal Reasoning 8Document64 pagesVerbal Reasoning 8cyoung360% (1)
- SAHANA Disaster Management System and Tracking Disaster VictimsDocument30 pagesSAHANA Disaster Management System and Tracking Disaster VictimsAmalkrishnaPas encore d'évaluation