Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Electric Drive 2
Transféré par
Gthulasi78Description originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Electric Drive 2
Transféré par
Gthulasi78Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Modern Electrical Drive Systems
About 50% of electrical energy used for drives Can be either used for fixed speed or variable speed
75% - constant speed, 25% variable speed (expanding)
Variable speed drives typically used PEC to supply the motors
DC motors (brushed) SRM BLDC
AC motors - IM - PMSM
Modern Electrical Drive Systems
Classic Electrical Drive for Variable Speed Application :
Bulky Inefficient inflexible
Modern Electrical Drive Systems
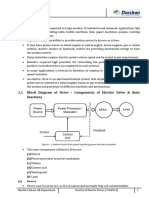
Typical Modern Electric Drive Systems Power Electronic Converters
Electric Energy - Unregulated Electric Energy - Regulated Electric Energy
Electric Motor
Mechanical Energy
POWER IN
Power Electronic Converters
feedback
Moto r
Load
Reference
Controller
Modern Electrical Drive Systems
Example on VSD application
Constant speed
valve Supply motor pump
Variable Speed Drives
Power out Power In
Power loss
Mainly in valve
Modern Electrical Drive Systems
Example on VSD application
Constant speed
valve Supply motor pump Supply PEC motor pump
Variable Speed Drives
Power out Power In Power In
Power out
Power loss
Mainly in valve
Power loss
Modern Electrical Drive Systems
Example on VSD application
Constant speed
valve Supply motor pump Supply PEC motor pump
Variable Speed Drives
Power out Power In Power In
Power out
Power loss
Mainly in valve
Power loss
Modern Electrical Drive Systems
Example on VSD application Electric motor consumes more than half of electrical energy in the US
Fixed speed
Variable speed
Improvements in energy utilization in electric motors give large impact to the overall energy consumption HOW ? Replacing fixed speed drives with variable speed drives Using the high efficiency motors Improves the existing power converterbased drive systems
Modern Electrical Drive Systems
Overview of AC and DC drives
DC drives: Electrical drives that use DC motors as the prime mover Regular maintenance, heavy, expensive, speed limit Easy control, decouple control of torque and flux AC drives: Electrical drives that use AC motors as the prime mover Less maintenance, light, less expensive, high speed Coupling between torque and flux variable spatial angle between rotor and stator flux
Modern Electrical Drive Systems
Overview of AC and DC drives Before semiconductor devices were introduced (<1950) AC motors for fixed speed applications DC motors for variable speed applications After semiconductor devices were introduced (1960s) Variable frequency sources available AC motors in variable speed applications Coupling between flux and torque control Application limited to medium performance applications fans, blowers, compressors scalar control High performance applications dominated by DC motors tractions, elevators, servos, etc
Modern Electrical Drive Systems
Overview of AC and DC drives After vector control drives were introduced (1980s) AC motors used in high performance applications elevators, tractions, servos AC motors favorable than DC motors however control is complex hence expensive Cost of microprocessor/semiconductors decreasing predicted 30 years ago AC motors would take over DC motors
Modern Electrical Drive Systems
Overview of AC and DC drives
Extracted from Boldea & Nasar
Power Electronic Converters in ED Systems
Converters for Motor Drives (some possible configurations)
DC Drives
AC Drives
AC Source
DC Source
AC Source
DC Source
DC-AC-DC AC-DC AC-DC-DC
DC-DC AC-DC-AC AC-AC DC-AC DC-DC-AC
Const. DC
Variable DC
NCC
FCC
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Electrical Motors EPDI2013Document51 pagesElectrical Motors EPDI2013neocentricgeniusPas encore d'évaluation
- Elevator DrivesDocument41 pagesElevator DrivesMohammad Gulam AhamadPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Electrical Drives PDFDocument52 pagesIntroduction To Electrical Drives PDFanand94% (16)
- Electric Drives System - PGDocument252 pagesElectric Drives System - PGKrishna SahooPas encore d'évaluation
- Electric Motor Control: DC, AC, and BLDC MotorsD'EverandElectric Motor Control: DC, AC, and BLDC MotorsÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (19)
- Introduction To Industrial DrivesDocument70 pagesIntroduction To Industrial Drivesvnyshreyas100% (4)
- Industrial Drives and ControlDocument10 pagesIndustrial Drives and ControlMohit SanandiyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Electrical DrivesDocument18 pagesIntroduction To Electrical DrivesSidali Chaib50% (2)
- Design 5 A.C. GeneratorDocument7 pagesDesign 5 A.C. GeneratorNoykols GRncPas encore d'évaluation
- MmuDocument113 pagesMmuSunny SanPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical DC Motor Drives PDFDocument126 pagesElectrical DC Motor Drives PDFMaitriyaditya BaruaPas encore d'évaluation
- EPD Introduction ModuleDocument20 pagesEPD Introduction Modulesubhasish nayakPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Electric DrivesDocument75 pagesIntroduction To Electric DrivesVikas PooniaPas encore d'évaluation
- Aed Unit3Document68 pagesAed Unit3Anser Pasha100% (1)
- Drives Acdc - CNCDocument42 pagesDrives Acdc - CNCShami KunalPas encore d'évaluation
- المحاضرة الثانيةDocument56 pagesالمحاضرة الثانيةسيمون عزتPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 3Document52 pagesUnit 3kishorghatage89Pas encore d'évaluation
- Electric Machine ApplicationsDocument24 pagesElectric Machine ApplicationsAriesFranandaPanjaitanPas encore d'évaluation
- DC DrivesDocument20 pagesDC Drivesvinay345Pas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Electrical Drives: Figure 1 Conventional Variable Speed Electrical Drive SystemDocument19 pagesIntroduction To Electrical Drives: Figure 1 Conventional Variable Speed Electrical Drive SystemChakradhara TheppavariPas encore d'évaluation
- PECED IntroductionDocument44 pagesPECED IntroductionBishnuPas encore d'évaluation
- Cha 1Document14 pagesCha 1yaredPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.1 IntroductionDocument15 pages1.1 IntroductionAlphaBravoPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical Ac & DC Drives: S.Sumalatha G.Lakshmi PrasannaDocument20 pagesElectrical Ac & DC Drives: S.Sumalatha G.Lakshmi PrasannageniunetPas encore d'évaluation
- Industrial Drives and ApplicationDocument10 pagesIndustrial Drives and ApplicationkicchasandeepPas encore d'évaluation
- 8 AktuatorDocument45 pages8 Aktuatormur tazaPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical Drives IntroDocument6 pagesElectrical Drives IntroAnoop MathewPas encore d'évaluation
- Motor Speed ControlDocument11 pagesMotor Speed ControlCharle CandelarioPas encore d'évaluation
- Electric Drives: Dr. Sasidharan SreedharanDocument27 pagesElectric Drives: Dr. Sasidharan SreedharanaswardiPas encore d'évaluation
- V S DDocument17 pagesV S DveguruprasadPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter - 1 DET5063 Combine pdf-1Document30 pagesChapter - 1 DET5063 Combine pdf-1Muhd FaizPas encore d'évaluation
- Energy Efficiency in Electric Motor SystemsDocument13 pagesEnergy Efficiency in Electric Motor SystemsAnkit AvishekPas encore d'évaluation
- Presentation 1Document22 pagesPresentation 1Alif GhozaliPas encore d'évaluation
- Design of Fluid Power Systems: - Stuart J. WilliamsDocument37 pagesDesign of Fluid Power Systems: - Stuart J. WilliamsAnonymous Ms8nYcbxY2Pas encore d'évaluation
- N.B.K.R. Institute of Science & Technology (Autonomous) Affiliated To JNTUA, AnantapuramuDocument42 pagesN.B.K.R. Institute of Science & Technology (Autonomous) Affiliated To JNTUA, AnantapuramuMunvar AliPas encore d'évaluation
- Electric Drive: IntroductionDocument5 pagesElectric Drive: IntroductionThomas RussellPas encore d'évaluation
- Variable Frequency DrivesDocument23 pagesVariable Frequency DrivesMadanKarkiPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit Ii Robot Drive Systems AND End Effectors: Prepared by B.Balasubramanian Ap/Mech CcetDocument89 pagesUnit Ii Robot Drive Systems AND End Effectors: Prepared by B.Balasubramanian Ap/Mech CcetBala mechPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1 Det50063 - IntroductionDocument12 pagesChapter 1 Det50063 - IntroductionFara FaraPas encore d'évaluation
- CompressorDocument178 pagesCompressor332-65 Nitin ShindePas encore d'évaluation
- Mechatronics ActuatorDocument22 pagesMechatronics ActuatorSuresh Kumar GPas encore d'évaluation
- E DriveDocument11 pagesE DrivetinashechiveroPas encore d'évaluation
- @6 - Power Electronics - Thyristors - Part II - v2 - ReducedDocument354 pages@6 - Power Electronics - Thyristors - Part II - v2 - ReducedLộc Phạm vănPas encore d'évaluation
- Final PDF EditedDocument6 pagesFinal PDF EditedFirdous NaazPas encore d'évaluation
- TOPIK1 - 27.9.2021 Versi 2 BARUDocument45 pagesTOPIK1 - 27.9.2021 Versi 2 BARUtiagoPas encore d'évaluation
- Electric Drives Part 2Document18 pagesElectric Drives Part 2Srujana TallaPas encore d'évaluation
- Robot Actuators & Feed Back ComponentsDocument25 pagesRobot Actuators & Feed Back ComponentsANONYMOUS PDFSPas encore d'évaluation
- Electric Traction SystemDocument23 pagesElectric Traction SystemAniket LikharPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Electric Drives: by Dr. P.K Biswas Asst. Professor Department of Electrical Engineering NIT MizoramDocument21 pagesIntroduction To Electric Drives: by Dr. P.K Biswas Asst. Professor Department of Electrical Engineering NIT MizoramtoshaliPas encore d'évaluation
- SUMMARYDocument11 pagesSUMMARYCyber-Mohd Salah ShotyPas encore d'évaluation
- DC and AC Motor ControlDocument6 pagesDC and AC Motor Controldes tosPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.1 Latest ImprovementsDocument1 page1.1 Latest ImprovementsMukul DasPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.1 Latest ImprovementsDocument1 page1.1 Latest ImprovementsMukul DasPas encore d'évaluation
- Principal of Electric DrivesDocument52 pagesPrincipal of Electric DrivesMallickarjuna A.SPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical Drives NotesDocument6 pagesElectrical Drives Noteskaushik9595Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1 - Electric DriveDocument76 pagesChapter 1 - Electric DriveNajihah YusofPas encore d'évaluation
- Electric Motors: - Classification / TypesDocument24 pagesElectric Motors: - Classification / TypesBholendra ShakarPas encore d'évaluation
- CED CH 1 Introduction v1 03042018 095851AMDocument7 pagesCED CH 1 Introduction v1 03042018 095851AMRizwan AhemadPas encore d'évaluation
- Eee-Vii-Industrial Drives and Applications (10ee74) - NotesDocument90 pagesEee-Vii-Industrial Drives and Applications (10ee74) - NotesMohammed AlhakeemiPas encore d'évaluation
- Electric Traction PDFDocument54 pagesElectric Traction PDFLalit ChaudharyPas encore d'évaluation
- Manual Transmission - 2Document6 pagesManual Transmission - 2Gthulasi78Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Steady State Magnetic FieldDocument28 pagesThe Steady State Magnetic FieldRashmi HarishPas encore d'évaluation
- Manual Transmission - 1Document6 pagesManual Transmission - 1Gthulasi78Pas encore d'évaluation
- Engine Dynamic Properties-2Document5 pagesEngine Dynamic Properties-2Gthulasi78Pas encore d'évaluation
- Weibull Tutorial 1Document5 pagesWeibull Tutorial 1Gthulasi78Pas encore d'évaluation
- BLDC 5Document7 pagesBLDC 5Gthulasi78Pas encore d'évaluation
- Engine Dynamic Properties-1Document5 pagesEngine Dynamic Properties-1Gthulasi78Pas encore d'évaluation
- Weibull Tutorial 2Document6 pagesWeibull Tutorial 2Gthulasi78Pas encore d'évaluation
- BLDC 2Document4 pagesBLDC 2Gthulasi78Pas encore d'évaluation
- BLDC 3Document4 pagesBLDC 3Gthulasi78Pas encore d'évaluation
- BLDC 4Document5 pagesBLDC 4Gthulasi78Pas encore d'évaluation
- BLDC 3Document4 pagesBLDC 3Gthulasi78Pas encore d'évaluation
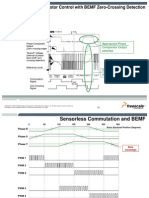
- Sensorless BLDC Motor Control With BEMF Zero-Crossing DetectionDocument6 pagesSensorless BLDC Motor Control With BEMF Zero-Crossing DetectionGthulasi78Pas encore d'évaluation
- Brushless DC Motors Are A Type of Synchronous MotorDocument5 pagesBrushless DC Motors Are A Type of Synchronous MotorGthulasi78Pas encore d'évaluation
- BLDC 3Document4 pagesBLDC 3Gthulasi78Pas encore d'évaluation
- BLDC 2Document4 pagesBLDC 2Gthulasi78Pas encore d'évaluation
- SensorlessBLDCControl 2Document7 pagesSensorlessBLDCControl 2Gthulasi78Pas encore d'évaluation
- Synchronous PM Motors: Stator Field Needs To Be Close To Orthogonal (90°) To Rotor Field To GetDocument4 pagesSynchronous PM Motors: Stator Field Needs To Be Close To Orthogonal (90°) To Rotor Field To GetGthulasi78Pas encore d'évaluation
- SensorlessBLDCControl 2Document7 pagesSensorlessBLDCControl 2Gthulasi78Pas encore d'évaluation
- 3-Phase Sensorless BLDC Motor Control Using MC9S08MP16: PresentationDocument7 pages3-Phase Sensorless BLDC Motor Control Using MC9S08MP16: PresentationGthulasi78Pas encore d'évaluation
- Reliability Prediction 1Document6 pagesReliability Prediction 1Gthulasi78Pas encore d'évaluation
- Brushless DC Motors Are A Type of Synchronous MotorDocument5 pagesBrushless DC Motors Are A Type of Synchronous MotorGthulasi78Pas encore d'évaluation
- BLDC - 2 Of3Document5 pagesBLDC - 2 Of3Gthulasi78Pas encore d'évaluation
- Engine Dynamic Properties - 7Document3 pagesEngine Dynamic Properties - 7Gthulasi78Pas encore d'évaluation
- Engine Dynamic Properties - 4Document5 pagesEngine Dynamic Properties - 4Gthulasi78Pas encore d'évaluation
- Brushless DC Motors Are A Type of Synchronous MotorDocument5 pagesBrushless DC Motors Are A Type of Synchronous MotorGthulasi78Pas encore d'évaluation
- Engine Dynamic Properties - 5Document5 pagesEngine Dynamic Properties - 5Gthulasi78Pas encore d'évaluation
- Engine Dynamic Properties - 6Document5 pagesEngine Dynamic Properties - 6Gthulasi78Pas encore d'évaluation
- Engine Dynamic Properties - 3Document5 pagesEngine Dynamic Properties - 3Gthulasi78Pas encore d'évaluation
- Engine Dynamic Properties - 2Document5 pagesEngine Dynamic Properties - 2Gthulasi78Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 3C - Steady State Operation of Synchronous MotorDocument26 pagesLesson 3C - Steady State Operation of Synchronous MotorJay LopezPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical Machineghvhvs2tuts2013!14!1Document8 pagesElectrical Machineghvhvs2tuts2013!14!1Utkarsh Verma100% (1)
- HET 225 HEt 228 Tutorial 3 Solution S2 2014Document4 pagesHET 225 HEt 228 Tutorial 3 Solution S2 2014Ibrahim Hussain0% (1)
- AC Commutator Motors Repulsion Series Motor UniversalDocument3 pagesAC Commutator Motors Repulsion Series Motor UniversalwhrferPas encore d'évaluation
- University of Sharjah Electrical and Electronics Engineering Electromechanical Systems PROJECT (Fall Semester 2010-2011)Document13 pagesUniversity of Sharjah Electrical and Electronics Engineering Electromechanical Systems PROJECT (Fall Semester 2010-2011)sara_shedid100% (1)
- 332b Notes PT 2Document70 pages332b Notes PT 2Uditha MuthumalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical Machine Tutorial 1Document3 pagesElectrical Machine Tutorial 1afiqPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical Machine 7-26-2016Document94 pagesElectrical Machine 7-26-2016Engr. Raheel khanPas encore d'évaluation
- Single Phase I.M. Understanding LevelDocument3 pagesSingle Phase I.M. Understanding LevelK S Ravi Kumar (MVGR EEE)Pas encore d'évaluation
- Elevator Brushes, Springs, Holders & Coils: Product CatalogDocument27 pagesElevator Brushes, Springs, Holders & Coils: Product Catalogzied ben hassinePas encore d'évaluation
- Industrial AC Machines DOL StarterDocument20 pagesIndustrial AC Machines DOL Starterhrishikesh barvePas encore d'évaluation
- Subject Code: ELC 221 Diagramming of DC Motors and GeneratorsDocument19 pagesSubject Code: ELC 221 Diagramming of DC Motors and GeneratorsHaruu ChanPas encore d'évaluation
- Based On Drive SystemDocument21 pagesBased On Drive SystemAjay MedikondaPas encore d'évaluation
- Paginas 4,46,47 TP-6395 10 - 20REOZD KOHLER Parts CatalogDocument3 pagesPaginas 4,46,47 TP-6395 10 - 20REOZD KOHLER Parts CatalogGalindez JoséPas encore d'évaluation
- Resolver Functional PrincipleDocument8 pagesResolver Functional PrincipleNick RivieraPas encore d'évaluation
- Wa0010.Document6 pagesWa0010.Zaid Hasan KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Intelligent Pantry Waste Collection and Segregation in Indian Railway CoachDocument11 pagesIntelligent Pantry Waste Collection and Segregation in Indian Railway CoachSharanu S KadakalPas encore d'évaluation
- Relays N SolenoidsDocument2 pagesRelays N SolenoidsDavison ThomasPas encore d'évaluation
- Effect EsDocument2 pagesEffect EsSK VISHNUPas encore d'évaluation
- A Direct Torque Controller For Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor DrivesDocument6 pagesA Direct Torque Controller For Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor DrivesGo GoPas encore d'évaluation
- Technics EPS 270CDocument1 pageTechnics EPS 270Ccaf_desknote0% (1)
- Hawkins Electrical Guide v. 02 of 10Document232 pagesHawkins Electrical Guide v. 02 of 10Kachi AbidiPas encore d'évaluation
- Brushless DC Electric MotorDocument8 pagesBrushless DC Electric MotorankitPas encore d'évaluation
- AE55et PDFDocument3 pagesAE55et PDFLahari Ratnanjali ModuguPas encore d'évaluation
- TR 06 Test Reports-1Document13 pagesTR 06 Test Reports-1Siva SankarPas encore d'évaluation
- 10 11 EMEC DCmachinesDocument38 pages10 11 EMEC DCmachinesOruc MusayevPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Single-Phase Motor 2020Document22 pages1 Single-Phase Motor 2020SerajPas encore d'évaluation
- EMF Assignment1Document5 pagesEMF Assignment1Ahtasham ArshadPas encore d'évaluation
- Working Principle of A DC Motor - Circuit GlobeDocument6 pagesWorking Principle of A DC Motor - Circuit GlobeHumair AhmedPas encore d'évaluation