Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
SpecialDiscrete Distributions Workbook
Transféré par
Anthea ClarkeCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
SpecialDiscrete Distributions Workbook
Transféré par
Anthea ClarkeDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
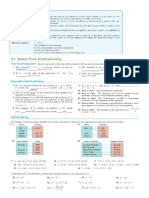
SPECIAL DISCRETE PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS THE BINOMIAL PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTION One of the most widely known of all discrete
probability distributions is the binomial distribution. Several characteristics underlie the use of the binomial distribution. Characteristics of the Binomial Distribution 1. The experiment consists of n identical trials. 2. Each trial has only one of the two possible mutually exclusive outcomes, success (p) or a failure (q). 3. The probability of each outcome does not change from trial to trial, and 4. The trials are independent, thus we must sample with replacement. Notation: Formula: Combinations
10
x ~ Bin (n, p) , n = number of trials, p = probability of success and q = 1 p
P( x) n C x p x q n x
n
Cx
10
gives the number of ways of choosing x things from n things
10
C0
C1
C2
10
C10
1. Use the Formula to find probabilities where x ~ Bin (10, 0.4) (a) P(x = 0) = (b) P(x = 1) = (c) P(x=2 ) = (d) P (x 2) = (e) P (x > 2 ) = (f) P (x 2 ) =
2. Use the Binomial Tables to find the above binomial probabilities.
Mean and Standard deviation Mean:
np
Standard deviation npq
Shape of the distribution Symmetrical if p = 0.5 Skewed to the right if p < 0.5 Skewed to the left if p > 0.5
POISSON PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTION The Poisson distribution is used for circumstances like the following: The number of airline crashes next year The number of people arriving at a drive-through window in the next hour The number of lightbulbs removed from inventory today The number of people arriving at your store in the next hour The number of typographical errors in our textbook on a given page Characteristics of the Poisson Distribution 1. There are a number of a certain occurences in a certain interval of time (or space). 2. The occurences are random and independent. 3. The occurences may be infinite. Notation: x ~ Po () , Formula: = mean number of occurrences in specific time period,
P( x)
x e
x!
1. Use the Formula to find probabilities where x ~ Po (9.5) (a) P(x = 0) =
(b) P(x = 1) =
(c) P(x=2 )= (d) P (x 2) =
(e) P (x > 2 ) = (f) P (x 2 ) =
2. Use the Poisson Tables to find the above probabilities.
Mean and Standard deviation Mean:
Standard deviation
Chapter 5 - Review Part B Discussion Questions 1. What is the difference between a binomial random variable and a Poisson random variable? 2. When can you use = np and = npq? 3. What is meant by the probability of at most one? 4. Describe a binomial experiment. 5. What are the conditions of a Poisson experiment?
Multiple choice 1. The factorial of 8 is: a. 36 b. 40,320 c. 5040 d. 35
2. The number of combinations for selecting 7 elements from 10 distinct elements is: a. 70 b. 120 c. 3 d. 100 3. The factorial of (9 9) is: a. zero
b. 362,880
c. 1
d. 81
4. The factorial of (4 0) is: a. 24 b. 1
c. zero
d. 10
5. The number of combinations for selecting zero elements from 7 distinct elements is: a. 1 b. 5040 c. 7 d. zero 6. The number of combinations for selecting 9 elements from 9 distinct elements is: a. zero b. 1 c. 81 d. 362,880 7. A court randomly selects a jury of five persons from a group of 15 persons. The total number of combinations is: a. 3,628,800 b. 5005 c. 3003 d.120 8. An investor randomly selects six stocks from 18 stocks for an investment portfolio. The total number of combinations is: a. 18,564 b. 479,001,600 c. 720 d. 8,568
9. In binomial experiments, the outcome called a success is an outcome: a. that is always beneficial b. that is linked to success c. to which the question refers d. that is favorable 10. Which of the following is not a condition of the binomial experiment? a. There are only two trials. b. Each trial has two and only two outcomes. c. p is the probability of success, q is the probability of failure, and p + q = 1. d. The trials are independent.
11. The parameters of the binomial probability distribution are: a. n, p, and q b. n, p, q, and x c. n, p, and x d. n and p 12. The binomial probability distribution is symmetric if: a. p is equal to .25 b. p is equal to .50 c. p is less than .50
d. p is greater than .50
13. The binomial probability distribution is skewed to the right if: a. p is equal to .25 b. p is equal to .50 c. p is less than .50 14. The binomial probability distribution is left skewed if: a. p is equal to .25 b. p is equal to .50 c. p is less than .50 15. The mean of a binomial distribution is: a. npq b. np c. square of npqd.
d. p is greater than .50
d. p is greater than .50
d. square root of npq
16. The standard deviation of a binomial distribution is: a. npq b. np c. square of npqd. d. square root of npq
17. Which of the following is an example of a binomial experiment? a. Rolling a die 10 times and observing for a number b. Selecting five persons and observing whether they are in favor of an issue, against it, or have no opinion c. Tossing a coin 20 times and observing for a head or a tail d. Drawing three marbles from a box that contains red, blue, and yellow marbles 18. Which of the following is not a condition to apply the Poisson probability distribution? a. x is a discrete random variable. c. The occurrences are random. b. There are n identical occurrences. d. The occurrences are independent.
19. The parameter(s) of the Poisson probability distribution is(are): a. n, x, and b. n and c. d.
and x
20. Which of the following is an example of a Poisson experiment? a. Tossing a coin 20 times and observing for a head or a tail b. Rolling a die 10 times and observing for a number c. Drawing without replacement three yellow marbles from a box that contains 7 blue, and 11 yellow marbles. d. Finding the probability that a salesperson who sells 2.5 mobile phones per day sells 5 today
Structured Questions BINOMIAL 1. For the binomial distribution with n = 10 and p = 0.3, find the probability of (a) Five or more successes. (b) At most two successes. (c) At least one success. 2. A university found that 20% of its students withdraw without completing the introductory statistics course. Assume that 20 students have registered for the course this term. a)What is the probability that exactly four will withdraw? [2] b) What is the probability that 2 or fewer will withdraw? [3] 3. In a recent survey, 70% of human resource directors thought that it was very important for business students to take a course in business ethics. For a random sample of 5 human resource directors, what is the probability that at least two of them does not think it very important for business students to take a business ethics course? [4] 4. A manufacturing process produces small bolts. 5 % of all bolts produced in this process are defective. What is the probability than in a sample of 40 randomly selected bolts, (i) exactly 5 will be defective? [4] (ii) at least 2 will be defective? [7] 5. When an assembly machine is properly calibrated approximately 5% of the finished products are defective. Periodically the quality control engineer randomly selects 20 products at random, and tests them. He will halt the production line to check (and reconfigure, if necessary) the calibration if any of the tested products are defective. Assuming that the machine is properly calibrated, what is the probability that production must be halted? POISSON 1. An average of 6 students arrives randomly and independently at COSTAATT between 7:00 am and 7:15 am every morning. What is the probability that, i. there are 2 arrivals in the 15-minute period? [2] ii. at most 2 arrivals arrive in the 15-minute period? [2] 2. TWA receives an average of 9.5 complaints per day from its passengers. (a) Find the probability that on a certain day TWA will receive exactly 6 complaints. (b) Find the probability that on a certain day TWA will receive at least 2 complaints.
[2] [6]
3. On average, the bank manager at Quest Bank Inc found that there are 12 customers entering the bank during the period 12:00 pm to 1:00pm. What is the probability that there are exactly 2 customers entering the bank between 12:00 pm and 12:30pm? 4. A Statistics lecturer claims that there is an average of 10 interruptions during his 3-hour lecture sessions. What is the probability that in the next such session there will be? (i) more than 3 interruptions [4] (ii) either 12 or 13 interruptions [4]
5. On average, 5 hurricanes hit the Caribbean region in a given hurricane season. Assume that these occurrences are independent of each another. Find the probability that in the next hurricane season exactly 4 hurricanes will hit the Caribbean region. (5)
MIXED 1. (a) Cyber Electronics, a company that makes DVD players, rates customer satisfaction as a top priority. They guarantee a refund or a replacement for any DVD player that malfunctions within two years from the date of purchase. It is known from past data that 5% of the DVD players malfunction within a two year period. The company mails a package of 20 randomly selected DVD players to their retail outlet. In that package of 20 DVD players, find the probability that (i) exactly 8 will need to be replaced within two years. [3] (ii) 8 or more will need to be replaced within two years. [5] (b) Customers arrive randomly at the retail outlet of Cyber Electronics at an average of 3.4 per minute. Calculate the probability that (i) no customers arrive in any particular minute, [2] (ii) exactly one customer arrives in any particular minute [2] (iii)two or more customers arrive in any particular minute [3]
2. . It is known that 80% of the walk in customers at a large post office are satisfied with the products and services. If a random sample of 20 customers is questioned about their walk in experience, what is the probability that (i) exactly 19 of them are satisfied customers. [5] (ii) fewer than 19 of them are satisfied customers. [4] (b) It has been found that the mean number of customer arrivals at a certain TTPOST line is 3.2 per hour. Find the probability that in any given hour there are fewer than 2 arrivals. [6]
3. (a) Suppose one in every four new clients approached by an insurance salesman purchases an insurance policy. If the salesman randomly approaches ten new clients: I. Find the probability that exactly two will buy a policy. II. Find the probability that at most two will buy a policy. [3] [4]
(b) On an average, six people per hour enter a furniture shop. Find the probability that in a half hour period: I. One person will enter the store [3] II. More than three people will enter the shop. [5]
4. (a) Consider that there is a 20% chance that a patient is allergic to aspirin. Assuming that the drug is administered to five patients, i) Find the probability that all five patients are allergic to the drug (4) ii) Find the probability that at least one of them is not allergic to the drug. (4) (b) A store manager has found that, on average, 8 customers enter a particular store in the hour before closing time. Find the probability that in the next hour before closing time no more than 2 customers enter the store. (5)
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (894)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- Understanding Randomised Controlled TrialsDocument5 pagesUnderstanding Randomised Controlled TrialsWafiy AkmalPas encore d'évaluation
- Linear Equations Cheat SheetDocument1 pageLinear Equations Cheat SheetAnthea ClarkePas encore d'évaluation
- Curriculum Evaluation Final3Document41 pagesCurriculum Evaluation Final3Mrz DordasPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 Neo-Classical and Modern Management TheoriesDocument39 pages2 Neo-Classical and Modern Management TheoriesYASH SANJAY.INGLEPas encore d'évaluation
- Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument34 pagesMultiple Choice QuestionsAnthea ClarkePas encore d'évaluation
- Patient Identification PolicyDocument26 pagesPatient Identification PolicyrenalgoodPas encore d'évaluation
- Standardizing Completion and Workover Riser AssessmentsDocument26 pagesStandardizing Completion and Workover Riser Assessmentsvictor gerardoPas encore d'évaluation
- Alg 1 EOC Mock ExamDocument26 pagesAlg 1 EOC Mock ExamSomari MontanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Pre Calculus Finals (July 2012)Document5 pagesPre Calculus Finals (July 2012)Anthea ClarkePas encore d'évaluation
- College of Science, Technology and Applied Arts of Trinidad and TobagoDocument1 pageCollege of Science, Technology and Applied Arts of Trinidad and TobagoAnthea ClarkePas encore d'évaluation
- My Conceptual FrameworkDocument1 pageMy Conceptual FrameworkAnthea ClarkePas encore d'évaluation
- Descriptive Statistics - Histograms and other plotsDocument10 pagesDescriptive Statistics - Histograms and other plotsAnthea ClarkePas encore d'évaluation
- Systems of InequalitiesDocument6 pagesSystems of InequalitiesAnthony Musengezi 'TudechiPas encore d'évaluation
- Circle ExerciseDocument1 pageCircle ExerciseAnthea ClarkePas encore d'évaluation
- Do Dec CalendarDocument1 pageDo Dec CalendarAnthea ClarkePas encore d'évaluation
- 1 ReferencesDocument2 pages1 ReferencesAnthea ClarkePas encore d'évaluation
- Emoticon Keyboard ShortcutsDocument2 pagesEmoticon Keyboard ShortcutsAnthea ClarkePas encore d'évaluation
- Storyboard For GeometryDocument8 pagesStoryboard For GeometryAnthea ClarkePas encore d'évaluation
- Group Presentation RubricDocument2 pagesGroup Presentation RubricAnthea ClarkePas encore d'évaluation
- Linear Inequalities and Linear Programming: Section R ReviewDocument5 pagesLinear Inequalities and Linear Programming: Section R ReviewAnthea ClarkePas encore d'évaluation
- The Lesson Study ApproachDocument7 pagesThe Lesson Study ApproachAnthea ClarkePas encore d'évaluation
- Math Study Skills For Adult StudentsDocument2 pagesMath Study Skills For Adult StudentsAnthea ClarkePas encore d'évaluation
- Types of QuadrilateralsDocument3 pagesTypes of QuadrilateralsAnthea ClarkePas encore d'évaluation
- Precalculus ExamDocument4 pagesPrecalculus ExamAnthea ClarkePas encore d'évaluation
- Applications of Quadratic FunctionsDocument6 pagesApplications of Quadratic Functionsrich50% (2)
- Discrete Distributions (Binomial)Document11 pagesDiscrete Distributions (Binomial)Anthea ClarkePas encore d'évaluation
- Division of Liberal Arts and Human Services Mathematics DepartmentDocument5 pagesDivision of Liberal Arts and Human Services Mathematics DepartmentAnthea ClarkePas encore d'évaluation
- Functions and Graphs Ex 2.1Document2 pagesFunctions and Graphs Ex 2.1Anthea ClarkePas encore d'évaluation
- Normal Distribution Notes and WorkbookDocument6 pagesNormal Distribution Notes and WorkbookAnthea ClarkePas encore d'évaluation
- Integration and Applications of IntegrationDocument2 pagesIntegration and Applications of IntegrationAnthea ClarkePas encore d'évaluation
- 4 1 Sull Precalc MiniDocument2 pages4 1 Sull Precalc MiniAnthea ClarkePas encore d'évaluation
- Lcture Topic 3 - NotesDocument2 pagesLcture Topic 3 - NotesAnthea ClarkePas encore d'évaluation
- Graph PaperDocument2 pagesGraph PaperAnthea ClarkePas encore d'évaluation
- Absolute Value NotesDocument1 pageAbsolute Value NotesAnthea ClarkePas encore d'évaluation
- Grading Rubric for Geometry Project PresentationsDocument2 pagesGrading Rubric for Geometry Project PresentationsAnthea ClarkePas encore d'évaluation
- EAPP LECTURE 2 Danica Espinosa 11 CharityDocument10 pagesEAPP LECTURE 2 Danica Espinosa 11 CharityNicki EspinosaPas encore d'évaluation
- p3 PiliavinDocument2 pagesp3 PiliavinSwimmyCj xoxoPas encore d'évaluation
- Syllabus: Maharashtra University of Health Sciences, NashikDocument5 pagesSyllabus: Maharashtra University of Health Sciences, NashikRuchi HumanePas encore d'évaluation
- MonographDocument8 pagesMonographtaha shabanPas encore d'évaluation
- Dissertation Statistics HelpDocument7 pagesDissertation Statistics HelpBuyCheapPaperOnlineScottsdale100% (1)
- (John Tulloch) Watching Television Audiences CultDocument271 pages(John Tulloch) Watching Television Audiences CultMelina MeimaridisPas encore d'évaluation
- Research on the correlation between IRI and PSI in VietnamDocument6 pagesResearch on the correlation between IRI and PSI in VietnamOrlando RojasPas encore d'évaluation
- Pump Performance Lab ReportDocument8 pagesPump Performance Lab ReportEdgar Dizal0% (1)
- UNICEF WASH Officer Job ProfileDocument5 pagesUNICEF WASH Officer Job ProfileazizrbgPas encore d'évaluation
- Climate Change Strategies' Model in Teaching Science 7Document10 pagesClimate Change Strategies' Model in Teaching Science 7Psychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalPas encore d'évaluation
- Breadth RequirementsDocument2 pagesBreadth RequirementsJulian ChoPas encore d'évaluation
- 5-The Dual and Mix ProblemsDocument23 pages5-The Dual and Mix Problemsthe_cool48Pas encore d'évaluation
- Tools For Analysis of Accelerated Life and ADT DATA 2016Document7 pagesTools For Analysis of Accelerated Life and ADT DATA 2016sadeqPas encore d'évaluation
- Autobiography of Apj Abdul KalamDocument5 pagesAutobiography of Apj Abdul KalamNavpreet Singh100% (1)
- Customer Retention Practices of Microfinance BanksDocument7 pagesCustomer Retention Practices of Microfinance BanksIkechukwu AchaPas encore d'évaluation
- Impact of Digital Marketing On Online Purchase Intention: Mediation Effect of Customer Relationship ManagementDocument17 pagesImpact of Digital Marketing On Online Purchase Intention: Mediation Effect of Customer Relationship Managementayou yooobPas encore d'évaluation
- Automatic Dismissal Alarm for Time AwarenessDocument54 pagesAutomatic Dismissal Alarm for Time AwarenessArnie John P. MendozaPas encore d'évaluation
- Tylers Curriculum ModelDocument15 pagesTylers Curriculum ModelchaPas encore d'évaluation
- Activity Guide and Evaluation Rubric - Unit 1 - Task 2 - Writing ProductionDocument10 pagesActivity Guide and Evaluation Rubric - Unit 1 - Task 2 - Writing Productionfernando MuñozPas encore d'évaluation
- E-Commerce in The Distribution Management: Shu-Hung HsuDocument8 pagesE-Commerce in The Distribution Management: Shu-Hung HsuAinul mardziahPas encore d'évaluation
- GFDGFDGDocument32 pagesGFDGFDGKelli Moura Kimarrison SouzaPas encore d'évaluation
- Investors Preference in Commodities MarketDocument7 pagesInvestors Preference in Commodities MarketMuthu9751Pas encore d'évaluation
- Untitled 2Document75 pagesUntitled 2Kumari Ujwala SinhaPas encore d'évaluation
- 2015 Global-Manufacturing-Outlook-KPMG PDFDocument36 pages2015 Global-Manufacturing-Outlook-KPMG PDFivan jessicaPas encore d'évaluation
- English For Bussiness: Mirwan Surya Perdhana, SE, MM, Ph.D. Class C GroupDocument2 pagesEnglish For Bussiness: Mirwan Surya Perdhana, SE, MM, Ph.D. Class C GroupZidny IrvanPas encore d'évaluation