Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Lecture 20
Transféré par
Shawn WaltzCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Lecture 20
Transféré par
Shawn WaltzDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Effect of Distribution of Molecular Weight
A - Mw/Mn=1.09 B - Mw/Mn= 2.0 C - branched
Figure 6.14, p. 179 Berry and Fox; PVA solns in DEP Faith A. Morrison, Michigan Tech U.
Types of polymer architecture
short-chain branching
long-chain branching
hyperbranching
star
dendrimer
Faith A. Morrison, Michigan Tech U.
Motion of Branched Polymers
Entangled linear polymer
chains move principally along their contour
Entangled branched polymer
branch points retard motion
once disentangled (high shear rate), branched polymers flow more freely
Faith A. Morrison, Michigan Tech U.
Effect of Branching on
= low
= 20s 1
linear 3-arm star 4-arm star
linear 3-arm star 4-arm star
Figures 6.17, 6.18, pp. 181,3 Kraus & Gruver; PB
Faith A. Morrison, Michigan Tech U.
Steady shear rheology of PAMAM dendrimers
1.E+09
1.E+08
1.E+07
viscosity, poise
Gen 0 Gen 1 Gen 2 Gen 3 Gen 4 Gen 5 Gen 6
1.E+06
1.E+05
1.E+04
1.E+03
1.E+02 1.E-06
1.E-05
1.E-04
1.E-03
1.E-02
1.E-01
1.E+00
1.E+01
1.E+02
aT
Figure 6.20 p. 183; from Uppuluri
aT * shear rate, 1/s
Faith A. Morrison, Michigan Tech U.
Mixtures of Polymers with other materials - Filler Effect
(specific chemical interactions)
(no specific interactions)
Figure 6.22, p. 184 Chapman and Lee; PP and filled PP
For more on filled systems, see Larson, The Structure and Rheology of Complex Fluids, Oxford, 1999. Faith A. Morrison, Michigan Tech U.
Steady shear viscosity - shear thickening
10
( Pa s )
0.1
vol % TiO2
0.01
47 42 38 27.2 12
0.001 1
Figure 6.27, p. 188 Metzner and Whitlock; TiO2/water suspensions
10
100
, s
1000
10000
Faith A. Morrison, Michigan Tech U.
Steady shear viscosity - temperature dependence
10
, Poise
1
viscosity (Poise) 300 K viscosity (Poise) 339 K viscosity (Poise) 380 K viscosity (Poise) 425 K
0.1
0.01 0.1 1
Figure 6.28, p. 189 Gruver and Kraus; PB melt
, s 1
10
100
Faith A. Morrison, Michigan Tech U.
Steady shear viscosity - pressure dependence
100,000
apparent viscosity, Pa s
10,000
PS, T=196C PE, T=149C
1,000
100
10 0 50 100 150 200
Figure 6.29, p. 189 Maxwell and Jung; PS and PE
hydrostatic pressure, MPa
Faith A. Morrison, Michigan Tech U.
Steady shear flow - Summary
Linear Polymers - complex rheology Limits on measurability - instabilities Material effects - MW, MWD, branching, mixtures, copolymers - strongly affect rheology Temperature and pressure - T strongly affects rheology; P
less of an effect, but can be important Next:
Unsteady shear flow (SAOS, step strain) Steady elongation Unsteady elongation
Faith A. Morrison, Michigan Tech U.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- Finite Element Analysis in The Design of Reinforced Concrete BuildingsDocument55 pagesFinite Element Analysis in The Design of Reinforced Concrete Buildingstien2506online100% (3)
- Slotted Link MechanismDocument6 pagesSlotted Link MechanismShawn Waltz50% (2)
- QFog CCT 1100 Operating ManualDocument65 pagesQFog CCT 1100 Operating ManualEmerson CalixPas encore d'évaluation
- Bolt 1Document10 pagesBolt 1Shawn WaltzPas encore d'évaluation
- RULA Employee Assessment Worksheet: A. Arm and Wrist Analysis B. Neck, Trunk and Leg Analysis ScoresDocument1 pageRULA Employee Assessment Worksheet: A. Arm and Wrist Analysis B. Neck, Trunk and Leg Analysis ScoresAlvinWijayaPas encore d'évaluation
- An Adaptive Thresholding-Based Process Variability MonitoringDocument16 pagesAn Adaptive Thresholding-Based Process Variability MonitoringShawn WaltzPas encore d'évaluation
- 2018 Dataset Rare Event Classification in Multivariate Time SeriesDocument7 pages2018 Dataset Rare Event Classification in Multivariate Time SeriesMacLeodPas encore d'évaluation
- Wind Turbine Fault Diagnosis and Predictive Maintenance Through Statistical Process Control and Machine LearningDocument13 pagesWind Turbine Fault Diagnosis and Predictive Maintenance Through Statistical Process Control and Machine LearningShawn WaltzPas encore d'évaluation
- Facility Design - An Introduction (Compatibility Mode)Document46 pagesFacility Design - An Introduction (Compatibility Mode)Vikas KatiyarPas encore d'évaluation
- Application of Statistical Process Control Theory in Coal and Gas Outburst PreventionDocument9 pagesApplication of Statistical Process Control Theory in Coal and Gas Outburst PreventionShawn WaltzPas encore d'évaluation
- Statistical Process ControlDocument7 pagesStatistical Process Controlชนพัทธ์ คงพ่วงPas encore d'évaluation
- Case 1Document10 pagesCase 1Shawn WaltzPas encore d'évaluation
- Pneumatics SymbolsDocument2 pagesPneumatics SymbolsShawn WaltzPas encore d'évaluation
- Hydraulic Symbols: Lines Miscellaneous Units Hydraulic PumpsDocument2 pagesHydraulic Symbols: Lines Miscellaneous Units Hydraulic PumpsShawn WaltzPas encore d'évaluation
- Facilities Planning and Design - Lecture NotesDocument162 pagesFacilities Planning and Design - Lecture NotesVitor Moreira100% (4)
- Engineering Physics Text BookDocument314 pagesEngineering Physics Text BookShawn Waltz33% (3)
- Assessing Risk of A Serious Failure Mode Based On Limited Field DataDocument12 pagesAssessing Risk of A Serious Failure Mode Based On Limited Field DataShawn WaltzPas encore d'évaluation
- Functional Gage DesignDocument32 pagesFunctional Gage DesignShawn Waltz100% (1)
- Lecture 2Document52 pagesLecture 2Shawn WaltzPas encore d'évaluation
- Formula Sheet FourierDocument3 pagesFormula Sheet FourierShawn WaltzPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4 Second Order DEsDocument59 pagesChapter 4 Second Order DEsShawn WaltzPas encore d'évaluation
- 62 Design Specification For Gauges EnglishDocument17 pages62 Design Specification For Gauges EnglishShawn WaltzPas encore d'évaluation
- Me 3560 Presentation CH ViiDocument16 pagesMe 3560 Presentation CH ViiShawn WaltzPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial Cylinder Simple MeshDocument9 pagesTutorial Cylinder Simple MeshShawn WaltzPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial Cylinder Refined MeshDocument9 pagesTutorial Cylinder Refined MeshShawn WaltzPas encore d'évaluation
- Me 3560 Presentation CH ViiDocument16 pagesMe 3560 Presentation CH ViiShawn WaltzPas encore d'évaluation
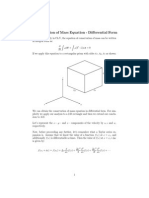
- Conservation of Mass Equation - Di Erential FormDocument4 pagesConservation of Mass Equation - Di Erential FormShawn WaltzPas encore d'évaluation
- Conservation of Mass Equation - Di Erential FormDocument4 pagesConservation of Mass Equation - Di Erential FormShawn WaltzPas encore d'évaluation
- Me 3560 Schedule Summer 2014Document16 pagesMe 3560 Schedule Summer 2014Shawn WaltzPas encore d'évaluation
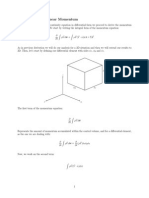
- Conservation of Linear MomentumDocument7 pagesConservation of Linear MomentumShawn WaltzPas encore d'évaluation
- Me 3560 Presentation ChiDocument55 pagesMe 3560 Presentation ChiShawn WaltzPas encore d'évaluation
- ME3560. Fluid Mechanics - TEST No. 2Document5 pagesME3560. Fluid Mechanics - TEST No. 2Shawn WaltzPas encore d'évaluation
- Electromagnetic Flow MeterDocument4 pagesElectromagnetic Flow MeterDavi RebouçasPas encore d'évaluation
- AP Chemistry Unit 10 Packet 1 AnswersDocument26 pagesAP Chemistry Unit 10 Packet 1 AnswersBrandon BaxterPas encore d'évaluation
- Construction Materials and Testing Apparatus & Equipment: Essential QuestionsDocument9 pagesConstruction Materials and Testing Apparatus & Equipment: Essential QuestionsDiane de OcampoPas encore d'évaluation
- Optical Fiber Communication 10ec72 SolutionDocument73 pagesOptical Fiber Communication 10ec72 Solutionshashank gupta100% (1)
- Monsoon in India Upsc Notes 58Document3 pagesMonsoon in India Upsc Notes 58nikitasharma1431234Pas encore d'évaluation
- TsunamiDocument13 pagesTsunamiVageesha Shantha Veerabhadra SwamyPas encore d'évaluation
- Kpa C Kpa C Kpa C: Fig. 9 Comparison Between Bearing Capacity Values DeterminedDocument5 pagesKpa C Kpa C Kpa C: Fig. 9 Comparison Between Bearing Capacity Values DeterminedfacedonePas encore d'évaluation
- tHREAD 2 MATERI OL 2 (PG Gerak)Document4 pagestHREAD 2 MATERI OL 2 (PG Gerak)festus wikannandaPas encore d'évaluation
- FIITJEE - Phase Test (JEE-Advanced) : Physics, Chemistry & MathematicsDocument12 pagesFIITJEE - Phase Test (JEE-Advanced) : Physics, Chemistry & MathematicsXYZPas encore d'évaluation
- FRN Seminar Notes PDFDocument183 pagesFRN Seminar Notes PDFnamdaeyoung100% (3)
- MPAPS A-37 - Stainless-Heat Resistant Steels and Finish RequirementsDocument18 pagesMPAPS A-37 - Stainless-Heat Resistant Steels and Finish RequirementsPANKAJ CHAUHANPas encore d'évaluation
- A Method of Creep Rupture Data Extrapolation Based On Physical ProcessesDocument10 pagesA Method of Creep Rupture Data Extrapolation Based On Physical ProcessesAndrea CalderaPas encore d'évaluation
- Aquatic Adaptations - Poonam SinghDocument46 pagesAquatic Adaptations - Poonam Singhaksahu01234Pas encore d'évaluation
- Price Summary: Date: 22/5/2019Document72 pagesPrice Summary: Date: 22/5/2019Reda ChattahyPas encore d'évaluation
- r059211401 Thermal ScienceDocument8 pagesr059211401 Thermal ScienceSrinivasa Rao GPas encore d'évaluation
- Formula+data Sheet For Edexcel Ial MathDocument4 pagesFormula+data Sheet For Edexcel Ial Mathlinda heatherPas encore d'évaluation
- Heat Losses From Bare and Lagged Pipe: Ii. MaterialsDocument6 pagesHeat Losses From Bare and Lagged Pipe: Ii. MaterialsRyan VasquezPas encore d'évaluation
- Self-Healing Concrete With Crystalline AdmixtureDocument8 pagesSelf-Healing Concrete With Crystalline AdmixtureAlexander HierroPas encore d'évaluation
- T2 Skript CH 4Document26 pagesT2 Skript CH 4Muhammad SaleemPas encore d'évaluation
- Automobile Skills, Communication, Interpersonal SkillsDocument14 pagesAutomobile Skills, Communication, Interpersonal SkillsvigneshPas encore d'évaluation
- Rheflat Plus PDB EngDocument2 pagesRheflat Plus PDB EngJose AlejandroBlanco100% (1)
- Part I Planet Earth NotesDocument14 pagesPart I Planet Earth NotesHon KwanPas encore d'évaluation
- Valve Clarkson KgaDocument6 pagesValve Clarkson KgaFlores CesarPas encore d'évaluation
- Steel Plate Shear Wall Design Michel BruneauDocument25 pagesSteel Plate Shear Wall Design Michel BruneauAMAN FREDY100% (1)
- Slab Manual DesignDocument1 pageSlab Manual DesignAtul ShrivastavaPas encore d'évaluation
- Steel Structure ConnectionsDocument34 pagesSteel Structure ConnectionsSreedhar Patnaik.MPas encore d'évaluation
- ResumeDocument2 pagesResumeNu'eng KritsakornPas encore d'évaluation
- James Deane Resume 2022Document3 pagesJames Deane Resume 2022api-623113366Pas encore d'évaluation