Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 1 Introduction To Science
Transféré par
Nor Amidah Md AminDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Chapter 1 Introduction To Science
Transféré par
Nor Amidah Md AminDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Form 1 Science Chapter 1
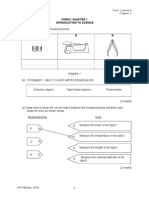
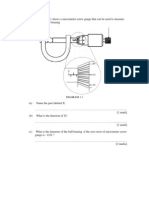
FORM 1 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION TO SCIENCE 1. Diagram 1 shows some measuring tools. P Q R
Diagram 1 (a) On Diagram 1, label P, Q and R with the following words.
External calipers
Triple Beam balance
Thermometer
[3 marks] (b) Draw lines to show the correct match between the measuring tools and their uses. Draw the lines as shown below. Measuring tools Uses Measure the mass of an object P Measure the temperature of an object Q Measure the weight of an object R
Measure the external diameter of an object [2 marks]
JPN Pahang 2009
Form 1 Science Chapter 1
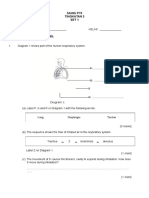
2. Diagram 2.1 shows some measuring tools commonly used in the science laboratory. P Q R
..
..
Diagram 2.1 (a) Label P, Q and R on Diagram 2.1 with the words given below.
Pipette
Burette
Measuring cylinder
[3 marks] (b) A student wants to measure a fixed volume of liquid, which measuring tool should he use? [1 mark] (c) A student carried out an activity to find the volume of a cork as shown in Diagram 2.2.
JPN Pahang 2009
Form 1 Science Chapter 1
m 100 90
m 100 90
m 100 90
80 70
80 70
80 70
60 50 40 30
60 50
60 50
Cork
40 30 40 30
20
20
20
10
10
Stone
10
Diagram 2.2 (i) Name the method that is used to find the volume of the cork. [1 mark] (ii) What is the volume of the cork?
[2 marks]
JPN Pahang 2009
Form 1 Science Chapter 1
3. A pupil carried out an experiment to determine the time taken for one complete swing of a pendulum as shown in Diagram 3. The time taken for 10 complete swings is recorded and the experiment is repeated using strings of different lengths. Wood pieces
string Length of pendulum
Pendulum bob One complete swing Diagram 3 (a) State a hypothesis for this experiment. .. . 1 mark] (b) State the variables involved in this experiment. .. ..
Manipulated variable:
Responding variable:
Fixed variable:
[3 marks]
JPN Pahang 2009
Form 1 Science Chapter 1
(c)(i) The time taken for 10 complete swings is shown below. Record the time taken for 10 complete swings in the space provided.
Length of pendulum = 10 cm
Second
Time taken = 10 s
Length of pendulum = 20 cm
Second
Time taken = .. s
Second
Length of pendulum = 30 cm Time taken = .. s
Length of pendulum = 40 cm
Second
Time taken = .. s
JPN Pahang 2009
Form 1 Science Chapter 1
Second
The length of pendulum = 50 cm Time taken = .. s
[2 marks] (ii) Complete the table below by recording the time taken for the various length of pendulum. Calculate the time taken for one complete swing.
Length of pendulum (cm)
10
20
30
40
50
Time taken for 10 complete swings (s)
10
Time taken for 1 complete swing (s)
1.0
[2 marks] (d) Using the table, plot a graph of time taken for 1 complete swing against the length of pendulum.
Time taken for one complete swing (s)
3.0 5
2.0
1.0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
[2 marks]
Length of pendulum (cm)
JPN Pahang 2009
Form 1 Science Chapter 1
(e) State the relationship between the length of the pendulum and the time taken for one complete swing. .. .. [1 mark] (f) Based on the graph in 8(d), predict the time taken for 1 complete swing when the length of the pendulum is 60 cm. [1 mark]
JPN Pahang 2009
Form 1 Science Chapter 1
4. Diagram 4.1 shows a method of measuring length.
0
cm 6
Diagram 4.1 (a) What is the length of the pencil shown in Diagram 4.1? [1 mark] (b) Mark X in the box provided on Diagram 4.1 to show the correct position of the eye in taking the reading. [1 mark]
(c) Diagram 4.2 shows a curved line.
Diagram 4.2 (i) How would you measure the length of the curved line? . [1 mark] A student carried out an activity to measure the length of the curve shown in Diagram 4.2. The results are shown in Table 4.3. Reading Length of curved line (cm) 1 8.6 Table 4.3 2 8.8 3 8.7
JPN Pahang 2009
Form 1 Science Chapter 1
(ii) Why did the student take three readings? .... [1 mark] (iii) Based on Table 4.3, what is the length of the curved line? . [1 mark] (d) What is the SI unit for length? .. [1 mark]
JPN Pahang 2009
Form 1 Science Chapter 1
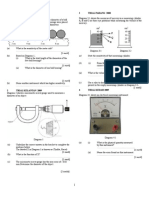
5. Diagram 5 shows measuring apparatus P and Q.
P: . Diagram 5 (a) Label P and Q in Diagram 5.
Q: .
[2 marks] (b) What is the physical quantity that is measured by P: Q: [2 marks] (c) (i) If an astronaut has a mass of 70 kg on Earth. What will be his mass in space? [1 mark] (ii) Explain your answer in (c)(i). [1 mark] (d) State one difference between mass and weight. [1 mark]
JPN Pahang 2009
10
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Chapter 1 Introduction To ScienceDocument10 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To ScienceHaslina Abdul MananPas encore d'évaluation
- Sains Form 1Document10 pagesSains Form 1aymynetPas encore d'évaluation
- Science Form 1Document7 pagesScience Form 1Anonymous fXgylsW4wrPas encore d'évaluation
- Answer All Questions.: Sains Pt3 Tingkatan 3 Set 1Document9 pagesAnswer All Questions.: Sains Pt3 Tingkatan 3 Set 1Wan NazrinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Kertas 2 Sains SPMDocument19 pagesKertas 2 Sains SPMNormawarni HasanPas encore d'évaluation
- Set 6 Paper 2 PDFDocument15 pagesSet 6 Paper 2 PDFChan Wai KeiPas encore d'évaluation
- Sains Bahagia A UpsrDocument5 pagesSains Bahagia A UpsrCharlsvia SilasPas encore d'évaluation
- Mid Year Form 4 2014 (P2)Document18 pagesMid Year Form 4 2014 (P2)Shakirah NorsaidPas encore d'évaluation
- Section ADocument51 pagesSection AGuru Damai JayaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ulangkaji SPMDocument46 pagesUlangkaji SPMkushahPas encore d'évaluation
- Science Form 4 SET 5 PAPER 2Document17 pagesScience Form 4 SET 5 PAPER 2Angie Kong Su MeiPas encore d'évaluation
- Jawab Semua Soalan.: Answer All QuestionsDocument18 pagesJawab Semua Soalan.: Answer All QuestionsArrow BlackPas encore d'évaluation
- Form 3 Chapter 7Document15 pagesForm 3 Chapter 7lccjane8504Pas encore d'évaluation
- Soalan Science Tingkatan 1Document9 pagesSoalan Science Tingkatan 1Sabri AwangPas encore d'évaluation
- Upp1 2019 Form 4 2Document6 pagesUpp1 2019 Form 4 2nurulafiqah1713Pas encore d'évaluation
- July Test THN 5 09Document6 pagesJuly Test THN 5 09Farahahmad FarahPas encore d'évaluation
- Bengkel Dan Teknik Menjawab SPM 2011: 1511/2 Science Paper 2 2 HoursDocument15 pagesBengkel Dan Teknik Menjawab SPM 2011: 1511/2 Science Paper 2 2 HoursHairolhamzi Bin BahroddinPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1 Introduction To ScienceDocument10 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To Scienceduit_sekupangPas encore d'évaluation
- INSTRUMENTSDocument3 pagesINSTRUMENTSjesunathan44@yahoo.comPas encore d'évaluation
- Exercise Form 1 Chapter 5 Air Around UsDocument9 pagesExercise Form 1 Chapter 5 Air Around UsAimi Nadia Yusof100% (1)
- QP2 CH 1&2 ADocument23 pagesQP2 CH 1&2 ASelvarani NasaratnamPas encore d'évaluation
- Science PP1 K2 2011 T2Document12 pagesScience PP1 K2 2011 T2Syafiqah ZulkifliPas encore d'évaluation
- Sps Module Science SPM (Paper 2)Document88 pagesSps Module Science SPM (Paper 2)nursyidhassanPas encore d'évaluation
- Science Form 1 Chapter-5 - The Air-Around-UsDocument16 pagesScience Form 1 Chapter-5 - The Air-Around-UsLouis Lim0% (1)
- Ats Phy 09 F4 P2Document60 pagesAts Phy 09 F4 P2nik mohamad solehinPas encore d'évaluation
- Form 3 Chapter 1 Respiratory SystemDocument5 pagesForm 3 Chapter 1 Respiratory SystemZacky Zack AsfanuddinPas encore d'évaluation
- Form 3 Chapter 1Document6 pagesForm 3 Chapter 1naza977590% (29)
- 1 LATIHAN PhysicDocument10 pages1 LATIHAN PhysicRushdi RosniPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio P3 Trials 2010 SMKCCDocument8 pagesBio P3 Trials 2010 SMKCCmith777Pas encore d'évaluation
- Paper 3 ChemDocument7 pagesPaper 3 ChemMaxwell RipinPas encore d'évaluation
- Bahan Latih Tubi SPM Fizik 2010Document85 pagesBahan Latih Tubi SPM Fizik 2010sensei85100% (1)
- Soalan PPT Sains f5Document16 pagesSoalan PPT Sains f5AimiAmiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Soalan Pecutan Akhir Fizik SPM 2010 Kertas 2 Set 3 PDFDocument18 pagesSoalan Pecutan Akhir Fizik SPM 2010 Kertas 2 Set 3 PDFAnna Latifah CammryPas encore d'évaluation
- End Yr Physics F4 2009 Paper 3Document6 pagesEnd Yr Physics F4 2009 Paper 3Vyvian LeowPas encore d'évaluation
- Soalan SN T1 2016Document21 pagesSoalan SN T1 2016Nia IrahasaPas encore d'évaluation
- Form 2 Chapter 1 The World Around UsDocument6 pagesForm 2 Chapter 1 The World Around UsAnonymous o7B02XWOJpPas encore d'évaluation
- Form 3 Chapter 3Document7 pagesForm 3 Chapter 3naza977582% (11)
- Chapter 2 Force and Motion FORM 4 2022Document16 pagesChapter 2 Force and Motion FORM 4 2022APas encore d'évaluation
- Do Not Open This Question Paper Unless ToldDocument15 pagesDo Not Open This Question Paper Unless Told242111Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mock Examinations February/ March 2021 Name: Section:: InstructionDocument10 pagesMock Examinations February/ March 2021 Name: Section:: InstructionJiana LakdawalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Kelas Tambahan SPSDocument7 pagesKelas Tambahan SPSNorazura ZuraPas encore d'évaluation
- Bengkel Teknik Menjawab Fizik 2013Document8 pagesBengkel Teknik Menjawab Fizik 2013leelee1127Pas encore d'évaluation
- Part 4 Cakna Set BDocument17 pagesPart 4 Cakna Set BazharsarahPas encore d'évaluation
- SSU Science P2Document14 pagesSSU Science P2Zainurain Zainal AbidinPas encore d'évaluation
- Madhrasathul Ahmadhiyya, Male' Scond Term Test 2003Document5 pagesMadhrasathul Ahmadhiyya, Male' Scond Term Test 2003afoo1234Pas encore d'évaluation
- 018/2 Sains April 2009: Sulit 018 1Document8 pages018/2 Sains April 2009: Sulit 018 1Misnadie MnPas encore d'évaluation
- This Question Paper Consists of 10 Questions. Answer All Questions in This Question PaperDocument6 pagesThis Question Paper Consists of 10 Questions. Answer All Questions in This Question PaperMaestra SorayaPas encore d'évaluation
- Paper 2 f2Document10 pagesPaper 2 f2Saffieyya Abd RahimPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 10 / 04: Madhrasathul Ahmadhiyya First Term Test - 2008Document9 pagesGrade 10 / 04: Madhrasathul Ahmadhiyya First Term Test - 2008afoo1234Pas encore d'évaluation
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 3D'EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 3Évaluation : 3 sur 5 étoiles3/5 (1)