Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Caustic Injury To The Esophagus
Transféré par
Louis FortunatoDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Caustic Injury To The Esophagus
Transféré par
Louis FortunatoDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
CAUSTIC INJURY TO THE ESOPHAGUS
ESOPHAGEAL REPLACEMENT AND ITS COMPLICATIONS caustic ingestions remain major source of toxic exposure in children and suicide attempt in adults Severity and site of UGI injury depends on type of substance ingested, duration of contact Alkali agents cause liquefaction necrosis (Drano, laundry detergents, hair relaxers, batteries) Acid agents cause coagulation necrosis, limiting deep penetration and perforation Liquid agents travel more distal than powder agents Bleach has neutral pH, causing less long term issues for patients Caustic injuries develop over time - burn wound. healing, scar, stricture o Early (minutes) - erythema, inflammation, edema o 2-4 days - liquefaction necrosis, sloughing, blood vessel formation o 7 days - granulation tissue, greatest risk of perforation o 4-8 weeks - scar tissue formation
Initial management: See diagram on last page Dilations: o 60-80% success rate o Full thickness burns, long strictures, multiple strictures - unlikely to respond to dilation o Esophageal replacement procedures: Colonic interposition based on middle or left colic artery most common Retrosternal intrathoracic Gastric pull-up Jejunal interposition with microvascular anastomosis Experience with colonic interposition Esophageal Replacement Using the Colon: Is it a Good Choice? Ahmad et al., J Pediatric Surgery, 1996,31(8): 1026-1031 o 31 year experience o 38 colonic interpositions between 1962-1993 for atresia (24), lye (8), reflux (5), radiation injury (1 ) o Average age at surgery - 52 months o Median follow-up 12 months, and available in 20 patients o Right colon - 61%, transverse colon 39%, retrosternal 63%, left thoracic 37% o Early complications: Cervical leak 11 (29%) - 9/11 resolved spontaneously; 10/11 were substernal (significant); 4 developed stricture after leak Pulmonary complications 9 o Late complications 5 proximal and 5 distal strictures 4/5 cervical strictures had leak 36
4/5 distal strictures transthoracic 4 obstructions of graft 4 with redundancy requiring replacement(3) or segmental resection (1) 7 graft failures requiring resection - redundancy, tracheocolonic fistula, ulceration and bleeding, perforation o 14/38 required no further surgery (37%) Caustic Esophageal Stricture in Children: 30 Year's Experience Hamza et a1., J Pediatric Surgery, 2003; 38(6): 828-833 High incidence of caustic injury to esophagus in children Repeated dilations have 60-80% success rate but can be psychologically detrimental to child 850 cases of esophageal replacement o 75 gastric pull-up o 550 retrosternal colonic replacement o 225 transhiatal esophagectomy with posterior mediastinal colon replacement o 475 cases done for caustic esophageal injury 317 retrosternal colonic replacement 158 transhiatal approach 468 left colic, 3 middle colic, 5 antiperistaltic right colon on ileocolic 47 cervical esophagocolic leaks 25 colo-esophageal stricture (3 required revision surgically) 17 redundancy 15/17 retrosternal 4/17 required revision
Ulka Sachdev, M.D. December 9, 2004
37
38
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5795)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1091)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Portfolio COM3702Document42 pagesPortfolio COM3702yog devi67% (9)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- 07 PETImagingDocument61 pages07 PETImagingLouis FortunatoPas encore d'évaluation
- Latent TBDocument24 pagesLatent TBLouis FortunatoPas encore d'évaluation
- Biological Effects of Ionizing RadiationDocument18 pagesBiological Effects of Ionizing RadiationLouis FortunatoPas encore d'évaluation
- Retroperitoneal SarcomaDocument2 pagesRetroperitoneal SarcomaLouis FortunatoPas encore d'évaluation
- 10 - HIDA ScanDocument19 pages10 - HIDA ScanLouis FortunatoPas encore d'évaluation
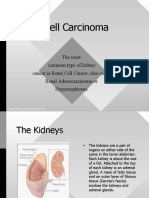
- Renal Cell CarcinomaDocument9 pagesRenal Cell CarcinomaboianlinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Hernias, Mesh Repairs and InfectionDocument2 pagesHernias, Mesh Repairs and InfectionLouis FortunatoPas encore d'évaluation
- Brain Cancer: by Cara KlingamanDocument16 pagesBrain Cancer: by Cara KlingamanLouis FortunatoPas encore d'évaluation
- Lower GI Bleeding - 1Document6 pagesLower GI Bleeding - 1Louis FortunatoPas encore d'évaluation
- Multiple Myeloma PresentationDocument15 pagesMultiple Myeloma PresentationLouis FortunatoPas encore d'évaluation
- Cricothyroidotomy 1Document42 pagesCricothyroidotomy 1Louis FortunatoPas encore d'évaluation
- Oral Cancer PresentationDocument14 pagesOral Cancer PresentationLouis FortunatoPas encore d'évaluation
- Laparoscopic vs. Open Colectomy For Colon CancerDocument4 pagesLaparoscopic vs. Open Colectomy For Colon CancerLouis FortunatoPas encore d'évaluation
- Liver BiopsyDocument4 pagesLiver BiopsyLouis FortunatoPas encore d'évaluation
- Medical Malpractice: Vithal Vernenkar, D.O St. Barnabas Hospital Department of SurgeryDocument15 pagesMedical Malpractice: Vithal Vernenkar, D.O St. Barnabas Hospital Department of SurgeryLouis FortunatoPas encore d'évaluation
- Laparoscopic Vs Open Ventral Hernia RepairDocument4 pagesLaparoscopic Vs Open Ventral Hernia RepairLouis FortunatoPas encore d'évaluation
- GIST of The StomachDocument3 pagesGIST of The StomachLouis FortunatoPas encore d'évaluation
- Aurobindo Pharma LimitedDocument1 pageAurobindo Pharma LimitedDeepthi Siri0% (1)
- GRE FlashcardDocument304 pagesGRE FlashcardAjayPas encore d'évaluation
- ISO TS 13136 - 2012 - Shiga Toxins (FR)Document30 pagesISO TS 13136 - 2012 - Shiga Toxins (FR)cramosPas encore d'évaluation
- 5cf4cc5d7e37f1559546973-Therapeutic Index Final CTP File 2019 MayDocument120 pages5cf4cc5d7e37f1559546973-Therapeutic Index Final CTP File 2019 MaycyruswillmottPas encore d'évaluation
- Finals Examination Biochemistry Lecture RNA Translation and MutationDocument7 pagesFinals Examination Biochemistry Lecture RNA Translation and MutationAlbertPas encore d'évaluation
- ELC Persuasive OutlineDocument3 pagesELC Persuasive OutlineNURUL ANIS SURAYA MOHD SUKRIPas encore d'évaluation
- Strategic Group Minutes October 7th 2021 DraftDocument10 pagesStrategic Group Minutes October 7th 2021 Draftapi-349611130Pas encore d'évaluation
- Viro Final 6Document10 pagesViro Final 6Muhammad Arslan UsmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Study Session 1 Introduction To Sanitation and Waste Management PrintableDocument20 pagesStudy Session 1 Introduction To Sanitation and Waste Management PrintableSreerag SPas encore d'évaluation
- Greek and Latin Root Words MasterDocument7 pagesGreek and Latin Root Words Masterdoug_hewinsPas encore d'évaluation
- Controlo Optimo Aplicado ADocument21 pagesControlo Optimo Aplicado AVivaldo BilaPas encore d'évaluation
- Path-Fit 1-Module-1-3Document19 pagesPath-Fit 1-Module-1-3Rubina Sadernas MalicdemPas encore d'évaluation
- Other Health Impairment (OHI) : Teacher Tips/Learning StrategiesDocument1 pageOther Health Impairment (OHI) : Teacher Tips/Learning Strategiesapi-236207623Pas encore d'évaluation
- Study Plan for Doctoral Degree Program: 研究课题名称/ Research titleDocument5 pagesStudy Plan for Doctoral Degree Program: 研究课题名称/ Research titleAbou NdikumanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Etika Hub DR - PasienDocument27 pagesEtika Hub DR - PasienJamali GagahPas encore d'évaluation
- Dwnload Full Nutrition Exercise and Behavior An Integrated Approach To Weight Management 3rd Edition Summerfield Solutions Manual PDFDocument36 pagesDwnload Full Nutrition Exercise and Behavior An Integrated Approach To Weight Management 3rd Edition Summerfield Solutions Manual PDFbokcardera100% (12)
- Anal and Perianal ConditionsDocument58 pagesAnal and Perianal ConditionsYonas YemidiralemPas encore d'évaluation
- 11 - Manoj Kumar MinjDocument8 pages11 - Manoj Kumar MinjIndah SarihandayaniPas encore d'évaluation
- MRCP Part 1 (1)Document23 pagesMRCP Part 1 (1)ChloePas encore d'évaluation
- BASCO, Aila O. - Assignment 2 - OAMT 40033 MEDICAL TRANSCRIPTIONDocument3 pagesBASCO, Aila O. - Assignment 2 - OAMT 40033 MEDICAL TRANSCRIPTIONAila BascoPas encore d'évaluation
- Guardian Health & Life Insurance FormDocument2 pagesGuardian Health & Life Insurance Formsmbdy tbhhhPas encore d'évaluation
- Bariatric Surgery PresentationDocument25 pagesBariatric Surgery PresentationAHMEDPas encore d'évaluation
- Albumina Spinreact AutomáticoDocument4 pagesAlbumina Spinreact AutomáticojhonatanPas encore d'évaluation
- Active Management of 3RD Stage of LaborDocument7 pagesActive Management of 3RD Stage of LaborFarheen khanPas encore d'évaluation
- 382 FullDocument23 pages382 FullRahma WirdaPas encore d'évaluation
- Hari IniDocument2 pagesHari IniTrihariPas encore d'évaluation
- Tinea Corporis An Updated ReviewDocument12 pagesTinea Corporis An Updated ReviewM Ilham FadillahPas encore d'évaluation
- Eucalyptol Safety and Pharmacological ProfileDocument8 pagesEucalyptol Safety and Pharmacological ProfileTim ThomasPas encore d'évaluation
- Dgca Module 09 Part 01Document11 pagesDgca Module 09 Part 01RAVI SHUKLAPas encore d'évaluation