Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Copd Cad Pathophysiology (Revised)
Transféré par
Israel Soria EsperoDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Copd Cad Pathophysiology (Revised)
Transféré par
Israel Soria EsperoDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
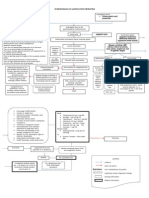
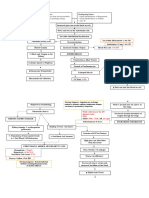
PATHOPHYSIOLGY
Predisposing Factors: 83 y/o History of DM & HPN Obesity Faulty Diet Asian Race Insulin Resistance Hyperglycemia Precipitating Factors: Heart disease Prolonged Tobacco used systemic O2 demand Exposure to air pollution Recurrent respiratory infection
blood osmolality Fluid shift to extracellular Space (edema) DHN (unicellular) Thirst sensation Polydipsia
blood sugar excess renal threshold Glycosuria osmotic dieresis urine output polyuria
Cellular starvation sensation of hunger Polyphagia
Gluconeogenesis CHON breakdown muscle wasting & poor wound healing
Lyposlysis Accumulation of by product
Fatty acid
Atherosclerosis
Ketones Metabolic acidosis
Narrowing of blood Vessels oxygenation HR, CO
Micropathy
Ketonuria Diabetic Ketoacidosis
neuropathy nephropathy weakness ESRD Activity Intolerance
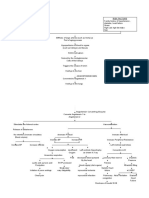
Elasticity of blood vessels and formation of plaques Narrowing of the blood vessels Necrosis and scarring of the vascular endothelium Impecliment of blood flow Workload of the heart Dilation of ventricles and increase in preload Stretching of myocardial muscle Oxygen demand of cardiac muscles, thus, there are is a contraction of the heart Cardiac output and systemic perfusion Stimulation of neurohormonal to circulating blood vessels Cardiac remodelling Stroke volume and Wall tension and pulmonary pressure Impaired left ventricular relaxation Diastolic pressure exceeding osmotic pressure in the pulmonary capillaries Capillary pressure in the lungs Fluid shift Pulmonary congestion Bilateral crackles Lung expansion Dyspnea Orthopnea output blood filling CAD
Inadequate perfusion Pallor Blood flow to the kidneys RAAS Na and water retention Periorbital edema, ascites Conversion of aerobic metabolism to anaerobic, thus, decrease in adenosine Lactic acid production Chest pain Cardiac contractility Bradycardia Pulmonary pressure Fatigue and weakness Perfusion in the coronary arteries ( supply of nutrients) Ischemia
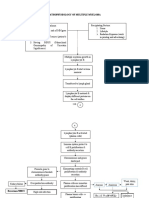
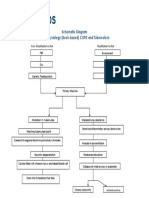
Chronic irritation to the airflows in the lungs
Irritation of lymphocytes, macrophages, and polymorpnonuclear lymphocytes in the mucosal area Vasodilation and congestion, edema of bronchial mucosa Thickening due to excessive mucous plug formation and rigidity of bronchi Narrowing of nasal passages Chronic Bronchitis
Destruction of elastin and fiber network of the alveoli Enlargement of wall of alveoli Consistent destruction of alveoli and alveolar walls Enlargement of acini Reduction of the alveolar diffusing space and some tissue changes Pulmonary Emphysema COPD
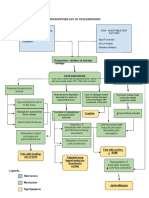
Malformation of RAAS
Hypertension vascular resistance O2 renal perfusion GFR Na retention, K excretion Water retention
160/100
Edema Heart Failure Hypertension
prodn of erythropoietin Anemia (RBC= 2.93) (HGB=110)
Periorbital edema
Ineffective tissue perfusion
Edema
Ineffective peripheral tissue perfusion
Pulmonary congestion
Oliguria
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Non-Modifiable Risk Factors: Modifiable Risk FactorsDocument9 pagesNon-Modifiable Risk Factors: Modifiable Risk FactorsKimberly Bomediano100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Chronic Renal Failure: By: Jonnel Montoya Musngi BSN 4-BDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Chronic Renal Failure: By: Jonnel Montoya Musngi BSN 4-BKenrick Randell IbanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology of HyperthyroidismDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of HyperthyroidismKitty YuffiePas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology of MI, COPD and BPHDocument10 pagesPathophysiology of MI, COPD and BPHSarah Lim100% (1)
- Myasthenia GravisDocument7 pagesMyasthenia Gravisエド パジャロン100% (1)
- PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesPathophysiologyKarla Karina Dela CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- Concept Map (Aplastic Anemia) b1Document6 pagesConcept Map (Aplastic Anemia) b1Ran PioloPas encore d'évaluation
- Bachelor of Nursing Science With HonoursDocument17 pagesBachelor of Nursing Science With HonoursMaryam HasanahPas encore d'évaluation
- Copd Pathophysiology DiagramDocument2 pagesCopd Pathophysiology DiagramVHyneh Basher100% (1)
- Lacunar Stroke Guide - Causes, Symptoms and Treatment OptionsDocument6 pagesLacunar Stroke Guide - Causes, Symptoms and Treatment OptionsRismanto TorsioPas encore d'évaluation
- ACS PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesACS PathophysiologyFerliza OblenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology ErDocument3 pagesPathophysiology ErAlexa A. AldayPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study GuideDocument2 pagesDrug Study GuideAubrey Sunga100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DisorderDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DisorderBlessyl Mae EstenzoPas encore d'évaluation
- (Patho) PTB COPDDocument1 page(Patho) PTB COPDKyle HannahPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology of Brain Abscess Secondary To Chronic Otitis MediaDocument5 pagesPathophysiology of Brain Abscess Secondary To Chronic Otitis Mediafufulabrador100% (1)
- Pathophysiology Copd-ChfDocument2 pagesPathophysiology Copd-ChfZaira Batalo100% (2)
- Concept MapDocument4 pagesConcept Mapdejosep_informaticsPas encore d'évaluation
- Qtsoi Concept MapDocument5 pagesQtsoi Concept MapGenella BabantoPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology of COPD - The BasicsDocument11 pagesPathophysiology of COPD - The BasicstiaranindyPas encore d'évaluation
- HELLP Concept Map RevisedDocument1 pageHELLP Concept Map RevisedwandaPas encore d'évaluation
- COPD PathoDocument1 pageCOPD PathoLeah May AnchetaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology of GooDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of GooTania Noviza100% (1)
- Pathophysiology Sickle Cell Anemia PDFDocument1 pagePathophysiology Sickle Cell Anemia PDFTine GuibaoPas encore d'évaluation
- PathophysiologyDocument1 pagePathophysiologyHazel PalomaresPas encore d'évaluation
- Final patho-HCVDDocument2 pagesFinal patho-HCVDAlvin RamirezPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology of Multiple Myeloma OkDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Multiple Myeloma OkRifa'atul MahmudahPas encore d'évaluation
- Copd PathoDocument2 pagesCopd PathoAlvin RamirezPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysio Chronic GlomerulonephritisDocument1 pagePathophysio Chronic GlomerulonephritisRan Ma100% (1)
- Hypertensive Cardiovascular DiseaseDocument5 pagesHypertensive Cardiovascular DiseaseAna Katrina OcanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology of Heart FailureDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Heart FailureabbeeyyPas encore d'évaluation
- COPD PathophysioDocument1 pageCOPD Pathophysionanette flores dela cruzPas encore d'évaluation
- Angina Pectoris PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesAngina Pectoris PathophysiologyALIANA KIMBERLY MALQUESTOPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute Lymphocytic LeukemiaDocument12 pagesAcute Lymphocytic Leukemiajustin_sanePas encore d'évaluation
- Acute Kidney Injury Concept MapDocument1 pageAcute Kidney Injury Concept MapKEn PilapilPas encore d'évaluation
- Myonal, LevoprontDocument1 pageMyonal, LevoprontMarieCrisPas encore d'évaluation
- Non-Modifiable Risk Factors: Modifiable Risk FactorsDocument6 pagesNon-Modifiable Risk Factors: Modifiable Risk FactorsNeil Andro Marcelo100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of COPDDocument42 pagesPathophysiology of COPDRegineCuasSulib100% (3)
- Anal Canal: Fissure in Ano HaemorrhoidsDocument37 pagesAnal Canal: Fissure in Ano Haemorrhoidsyash shrivastavaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ischemic StrokeDocument49 pagesIschemic StrokeMirna Ayu Permata SariPas encore d'évaluation
- Buerger's DiseaseDocument5 pagesBuerger's Diseaseglie_e52164100% (5)
- Pathophysiology of OsteoarthritisDocument1 pagePathophysiology of OsteoarthritisGLADYS GARCIAPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug 101Document12 pagesDrug 101Alyzza DagoyPas encore d'évaluation
- PATHOPHYDocument3 pagesPATHOPHYArlly Faena AbadPas encore d'évaluation
- General Pathophysiology: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsDocument2 pagesGeneral Pathophysiology: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsIrish Nicole DCPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology of Status EpilepticusDocument6 pagesPathophysiology of Status EpilepticusKysha Ruth SevillaPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute Myocardial InfarctionDocument2 pagesAcute Myocardial InfarctionhailleyannPas encore d'évaluation
- Human Diseases Case Study 18 ADocument4 pagesHuman Diseases Case Study 18 Aairickann100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of VSDDocument1 pagePathophysiology of VSDMarlon CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- Schematic Diagram Pathophysiology (Book-Based) COPD and TuberculosisDocument1 pageSchematic Diagram Pathophysiology (Book-Based) COPD and Tuberculosispragna novaPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy Myocardial InfarctionDocument5 pagesAnatomy Myocardial InfarctionLyka Milo AvilaPas encore d'évaluation
- DB13 - Pathophysiology of AtherosclerosisDocument2 pagesDB13 - Pathophysiology of Atherosclerosisi_vhie03Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pathway CKDDocument2 pagesPathway CKDRizki August Cullen67% (3)
- Congestive Heart Failure Pathophysiology Schematic DiagramDocument3 pagesCongestive Heart Failure Pathophysiology Schematic DiagramJacinthaVanathayahPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid and Hemo Dynamic Imbalances W 2Document49 pagesFluid and Hemo Dynamic Imbalances W 2erwilli5Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology HypertensionDocument1 pagePathophysiology HypertensionAlinor Abubacar100% (3)
- Pathophysiology CHFDocument3 pagesPathophysiology CHFKim Franzel M. Rabe100% (1)
- Pato PDocument2 pagesPato PAnj GaliPas encore d'évaluation
- Concept Map of Subarachnoid Hemmorhage by Rhealyn NograDocument3 pagesConcept Map of Subarachnoid Hemmorhage by Rhealyn NograRhealyn NograPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathway CKDDocument1 pagePathway CKDocsitaocsitulPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology of Peptic Ulcer Disease DefinitionDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Peptic Ulcer Disease DefinitionIsrael Soria EsperoPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP Sleep DisturbanceDocument1 pageNCP Sleep DisturbanceIsrael Soria EsperoPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP Acute PainDocument3 pagesNCP Acute PainIsrael Soria EsperoPas encore d'évaluation
- Impaired Skin IntegrityDocument7 pagesImpaired Skin Integrityprickybiik100% (8)
- Nursing Responsibilities For METRONIDAZOLEDocument1 pageNursing Responsibilities For METRONIDAZOLEIsrael Soria Espero63% (8)
- Drug Study - Paracetamol Ambroxol, Ascorbic Acid, CefuroximeDocument4 pagesDrug Study - Paracetamol Ambroxol, Ascorbic Acid, Cefuroximeapi-3701489100% (12)
- Neuroblastoma PDFDocument5 pagesNeuroblastoma PDFHanna G. FauziaPas encore d'évaluation
- 10 1016@j Jconrel 2017 08 033 PDFDocument63 pages10 1016@j Jconrel 2017 08 033 PDFRinaldi SatriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Crimes of The Century: Occupation & Contaminating Iraq With Depleted UraniumDocument28 pagesCrimes of The Century: Occupation & Contaminating Iraq With Depleted Uraniumpaola pisiPas encore d'évaluation
- Rectal ExaminationDocument21 pagesRectal ExaminationAlexandra HornariuPas encore d'évaluation
- Thyroglossal Duct Cyst in The Suprasternal RegionDocument3 pagesThyroglossal Duct Cyst in The Suprasternal RegionKhairuman anandaPas encore d'évaluation
- BIOL 2210 Chapter 6, Integument System-1Document15 pagesBIOL 2210 Chapter 6, Integument System-1KellyPatrick SpencerPas encore d'évaluation
- Breast Cancer TCM 2Document5 pagesBreast Cancer TCM 2Ivonne Flores FernándezPas encore d'évaluation
- ResourcesDocument166 pagesResourcesaeryll1305Pas encore d'évaluation
- Leukocoria 2016Document35 pagesLeukocoria 2016DiskaAstarini100% (1)
- BIRADS Poster 36x24in FDocument1 pageBIRADS Poster 36x24in FBk Del Riego100% (1)
- Pathophysiology Nf1.Nms OrthoDocument4 pagesPathophysiology Nf1.Nms OrthoSienaPas encore d'évaluation
- Central Giant Cell Granuloma A Case ReportDocument5 pagesCentral Giant Cell Granuloma A Case ReportYara Arafat NueratPas encore d'évaluation
- Assessment and Management of Patients With Breast Disorders Assessment and Management of Patients With Breast DisordersDocument36 pagesAssessment and Management of Patients With Breast Disorders Assessment and Management of Patients With Breast DisordersMozart OlarioPas encore d'évaluation
- Common Diseases in ChildrenDocument263 pagesCommon Diseases in ChildrenSuneethaVangala100% (1)
- Care of The Clients With Eye and Ear DisorderDocument35 pagesCare of The Clients With Eye and Ear DisorderKristine Joy RevañoPas encore d'évaluation
- 2007 SaeDocument20 pages2007 Saelila1284Pas encore d'évaluation
- Eyelid Cancer by Skin Cancer FoundationDocument5 pagesEyelid Cancer by Skin Cancer Foundationamrita90031Pas encore d'évaluation
- Conective Issue Massage PDFDocument3 pagesConective Issue Massage PDFSergio Andres ZeitgeistPas encore d'évaluation
- Curriculum Vitae Name: Dr. J.P. Jose MerlinDocument7 pagesCurriculum Vitae Name: Dr. J.P. Jose MerlinramPas encore d'évaluation
- Meaning Different Disease PDFDocument7 pagesMeaning Different Disease PDFrashmiPas encore d'évaluation
- General Pathology 4.03 Endocrine System Super SummaryDocument15 pagesGeneral Pathology 4.03 Endocrine System Super SummaryJade MonrealPas encore d'évaluation
- Cancer Is DEAD Cancer Cures From A To ZDocument169 pagesCancer Is DEAD Cancer Cures From A To Zcamjob80% (5)
- Alcohol & Drug Abuse PolicyDocument15 pagesAlcohol & Drug Abuse PolicyAnonymous xnuIuLLaFLPas encore d'évaluation
- CBE - Platelet AbnormalitiesDocument3 pagesCBE - Platelet AbnormalitiesRuxandra MesarosPas encore d'évaluation
- Ulcerative Colitis in ChildrenDocument5 pagesUlcerative Colitis in ChildrentheservantPas encore d'évaluation
- Ultima AzbDocument6 pagesUltima AzbsoetaciekPas encore d'évaluation
- Cat 2009 para JumbledDocument2 pagesCat 2009 para JumbledmymentorpalasiaPas encore d'évaluation
- @@assessment of Medical Documentation As Per Joint Commission InternationDocument6 pages@@assessment of Medical Documentation As Per Joint Commission InternationNahari ArifinPas encore d'évaluation
- Profile of GlaxoSmithKlineDocument22 pagesProfile of GlaxoSmithKlineNilufar Sharmin JessyPas encore d'évaluation
- DelphiDocument28 pagesDelphiMEANMYFATHERAREONE100% (1)