Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Financial Environment
Transféré par
Umair AzizTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Financial Environment
Transféré par
Umair AzizDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Financial Environment
Financial environment is the outcome of a range of functions of the economy on all financial outcomes of an area or a country. It includes forex markets, bond markets, stock markets and commodity markets. Financial information is used to measure performance and help make decisions about how an organisation should operate. Despite its importance, many managers do not fully understand the financial information they use or how it fits into a wider business context.
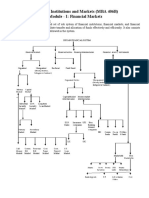
'Financial Market'
A market is a place where two parties are involved in transaction of goods and services in exchange of money. The two parties involved are:
Buyer Seller
In a market the buyer and seller comes on a common platform, where buyer purchases goods and services from the seller in exchange of money.
What is a Financial Market ?
A place where individuals are involved in any kind of financial transaction refers to financial market . Financial market is a platform where buyers and sellers are involved in sale and purchase of financial products like shares, mutual funds, bonds and so on. Let us go through the various types of financial market:
Capital Market
A market where individuals invest for a longer duration i.e. more than a year is called as capital market. In a capital market various financial institutions raise money from individuals and invest it for a longer period. Capital Market is further divided into: i. Primary Market: Primary Market is a form of capital market where various companies issue new stock, shares and bonds to investors in the form of IPOs (Initial Public Offering). Primary Market is a form of market where stocks and securities are issued for the first time by organizations. Secondary Market: Secondary market is a form of capital market where stocks and securities which have been previously issued are bought and sold.
ii.
Types of Capital Market
1. 2. 3. Stock Markets: Stock Market is a type of Capital market which deals with the issuance and trading of shares and stocks at a certain price. Bond Markets: Bond Market is a form of capital market where buyers and sellers are involved in the trading of bonds. Commodity Market: A market which facilitates the sale and purchase of raw goods is called a commodity market. Commodity market like any other market includes a buyer and a seller. In such a market buyer purchases raw products like rice, wheat, grain, cattle and so on from the seller at a mutually agreed rate.
4.
Money Market: As the name suggests, money market involves individuals who deal with the lending and borrowing of money for a short time frame. 5. Derivatives Market: The market which deals with the trading of contracts which are derived from any other asset is called as derivative market. 6. Future Market: Future market is a type of financial market which deals with the trading of financial instruments at a specific rate where in the delivery takes place in future. 7. Insurance Market: Insurance market deals with the trading of insurance products. Insurance companies pay a certain amount to the immediate family members of owner of the policy in case of his untimely death. 8. Foreign Exchange Market: Foreign exchange market is a globally operating market dealing in the sale and purchase of foreign currencies. 9. Private Market: Private market is a form of market where transaction of financial products takes place between two parties directly. 10. Mortgage Market: A type of market where various financial organizations are involved in providing loans to individuals on various residential and commercial properties for a specific duration is called a mortgage market. The payment is made to the individual concerned on submitting certain necessary documents and fulfilling certain basic criteria.
Financial instruments in Pakistan
In Pakistan there are a number of financial instruments which are traded in the capital market. Before the discussion is extended to the topic a brief description is necessary about the financial market. These are of two types: (1) Primary Market, is one in which new financial claims are issued, (2) Secondary Market, is one in which previously issued financial claims are traded; this is a conceptual definition but there are many cases in which it becomes blurred in practice. Broadly speaking financial instruments can be classified as under:Common Stock, Bonds, Commercial Papers, Options, Forward Foreign Exchange Contracts, Deposits, Insurance Policy, Mutual Fund etc. Shares Some of the securities will be discussed in detail, common stock or ordinary shares are issued by public limited companies for securing fund from the public against the issue of shares. Prices of the shares are determined by the rule of demand and supply, shares of the companies. With good performance and higher pay-out are in demand and their market prices are higher. Bonds Different types of bonds are issued by the Government of Pakistan. Most common are the prize bonds of different denominations. They are issued by State Bank of Pakistan to general public. Periodical balloting is held for the distribution of cash prizes they carry. WAPDA Bonds They are of two types: registered & Bearer Bonds. Return on these bonds is 19 per cent per annum and is payable every sixth month, the period for maturity is 10 years. These bonds are acceptable as security in lieu of bid bonds, earnest money, bank guarantee, performance bond by WAPDA etc. The bonds are available in the denominations of 10,000/-, 50,000/100,000/- and 500,000/- each. Recently the government has issued sixth subscription of WAPDA Bonds. Euro Bonds These bonds are floated in European Market in order to generate funds in international currencies. They are issued in US dollars, Swiss franc, Japanese yen & German mark (DM), 56 per cent of the total floatation are in US dollars. Euro Bonds issue would require a company to have a credit rating from one of the rating agencies and a market, a capitalisation of US$ 1 billion. Dewan Salman Fabric is the first Pakistani company to go for such an issue.
These vouchers will act as a first step in the privatisation of Pakistan Telecommunication Corporation. In total 1 million vouchers were offered for sale at @ Re.30 per voucher. Each voucher will be represented by one certificate of PTCL which will be exchangeable by 100 shares of PTCL, within a period of two years. These vouchers are backed by the buy bank guarantee of government of Pakistan at the rate of Rs.38.40/- voucher if, for any reason, the company was not quoted by August 17, 1996. In addition to these Financial Instruments there are various types of instruments issued by NDFC, NIT, IDBP, ICP & National savings etc. These vary in return depending upon the period of maturity for which they are issued.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Minute Paper - Philippine Financial MarketDocument1 pageMinute Paper - Philippine Financial MarketIan Paul CONSTANTINOPas encore d'évaluation
- Financial markets and institutions lectureDocument93 pagesFinancial markets and institutions lecturejain_ashish_19888651Pas encore d'évaluation
- Compilation of Reports From Group 1 6Document104 pagesCompilation of Reports From Group 1 6Kearn CercadoPas encore d'évaluation
- FMDocument7 pagesFMA.K.S.PPas encore d'évaluation
- Stock and Commodity Markets OverviewDocument53 pagesStock and Commodity Markets OverviewRAJATPas encore d'évaluation
- Investment NotesDocument30 pagesInvestment Notesshantanu100% (2)
- Business EconomicsDocument9 pagesBusiness EconomicsSachin MethreePas encore d'évaluation
- Financial Markets and Their Role in EconomyDocument6 pagesFinancial Markets and Their Role in EconomyMuzammil ShahzadPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Financial MarketDocument30 pagesIntroduction To Financial Marketmaria evangelistaPas encore d'évaluation
- Capital MarketDocument8 pagesCapital Marketkomal_studentPas encore d'évaluation
- (NR) Financial Markets and InstitutionDocument8 pages(NR) Financial Markets and InstitutionMichael MendozaPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 04 Financial Markets and InstrumentsDocument13 pagesModule 04 Financial Markets and InstrumentsGovindPas encore d'évaluation
- Portfolio InvestmentDocument129 pagesPortfolio Investmentanchal1987Pas encore d'évaluation
- Classification of Financial MarketsDocument12 pagesClassification of Financial Marketsvijaybhaskarreddymee67% (6)
- GR12 Business Finance Module 3-4Document8 pagesGR12 Business Finance Module 3-4Jean Diane JoveloPas encore d'évaluation
- 1-Bond MarketDocument85 pages1-Bond Marketdharmtamanna80% (5)
- Bangladesh Financial System StructureDocument18 pagesBangladesh Financial System StructureTarequr RahmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Capital Market InstrumentsDocument4 pagesCapital Market InstrumentsJanhavi SrivastavaPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic 2Document5 pagesTopic 2Jeffrey RiveraPas encore d'évaluation
- A Comprehensive Study on the Money MarketDocument42 pagesA Comprehensive Study on the Money MarketpavithrajiPas encore d'évaluation
- FM3A Financial Market FunctionsDocument5 pagesFM3A Financial Market FunctionsRoxanne Jhoy Calangi VillaPas encore d'évaluation
- Financial Institutions and Markets: Prof. Manisha SanghviDocument85 pagesFinancial Institutions and Markets: Prof. Manisha SanghviinderpretationPas encore d'évaluation
- Nepal's Economy & Financial MarketsDocument87 pagesNepal's Economy & Financial MarketsnirajPas encore d'évaluation
- Differentiate Financial MarketsDocument10 pagesDifferentiate Financial MarketsJohn Stephen PendonPas encore d'évaluation
- FMI All ModulesDocument81 pagesFMI All ModulesSandeepMishraPas encore d'évaluation
- 12 - Chapter 5 PDFDocument49 pages12 - Chapter 5 PDFShipra Chaudhary100% (1)
- Financial Markets in India ClassificationDocument49 pagesFinancial Markets in India ClassificationNew OldPas encore d'évaluation
- Financial MarketDocument68 pagesFinancial MarketAikanshi JadaunPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Finacial Markets Final With Refence To CDSLDocument40 pagesIntroduction To Finacial Markets Final With Refence To CDSLShoumi Mahapatra100% (1)
- INDIAN FINANCIAL MARKETSDocument52 pagesINDIAN FINANCIAL MARKETSDhruv MishraPas encore d'évaluation
- Financial Market TopicDocument31 pagesFinancial Market TopicGautam MahtoPas encore d'évaluation
- International Financial MarketDocument36 pagesInternational Financial MarketSmitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 5 - Understanding The Role of Financial Markets and InstitutionsDocument7 pagesModule 5 - Understanding The Role of Financial Markets and InstitutionsMarjon Dimafilis100% (1)
- Financial MarketDocument13 pagesFinancial MarketRajeswari KuttimaluPas encore d'évaluation
- Deranatung Government College Itanagar Arumachal Pradesh Departnment of CommerceDocument16 pagesDeranatung Government College Itanagar Arumachal Pradesh Departnment of CommerceAbhinandan soniPas encore d'évaluation
- Financial System and MarketsDocument32 pagesFinancial System and Marketsmohamedsafwan0480Pas encore d'évaluation
- Nism Sorm Notes Nov 2012 2.1 PDFDocument23 pagesNism Sorm Notes Nov 2012 2.1 PDFpankajmadhavPas encore d'évaluation
- Capital MarketDocument34 pagesCapital MarketVaibhavRanjankarPas encore d'évaluation
- Financial Market FinalDocument58 pagesFinancial Market FinalMUEKSH MANWANIPas encore d'évaluation
- Financial System of BangladeshDocument14 pagesFinancial System of BangladeshMosharraf SauravPas encore d'évaluation
- AssignmentDocument30 pagesAssignmentKavita BagewadiPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter-2-Indian Capital MarketDocument70 pagesChapter-2-Indian Capital MarketGowtham SrinivasPas encore d'évaluation
- Financial Institution and Marketing Cha 4Document23 pagesFinancial Institution and Marketing Cha 4Gadisa TarikuPas encore d'évaluation
- Financial Institutions and MarketsDocument84 pagesFinancial Institutions and MarketsShreekumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Financial MarketsDocument2 pagesFinancial MarketsSaira Ishfaq 84-FMS/PHDFIN/F16Pas encore d'évaluation
- Role of Financial Markets and Institutions ChapterDocument25 pagesRole of Financial Markets and Institutions ChapterMomenul Islam Mridha Murad100% (2)
- Financial Markets Overview (MBA 406BDocument62 pagesFinancial Markets Overview (MBA 406BamitPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is A Financial MarketDocument1 pageWhat Is A Financial Marketamitrao1983Pas encore d'évaluation
- Financial Markets and Institutionschap 2Document8 pagesFinancial Markets and Institutionschap 2Ini IchiiiPas encore d'évaluation
- Financial Markets Meaning, Types and WorkingDocument15 pagesFinancial Markets Meaning, Types and WorkingRainman577100% (1)
- Topic 2Document6 pagesTopic 2Regine TorrelizaPas encore d'évaluation
- Financial Markets Notes for ExamsDocument10 pagesFinancial Markets Notes for ExamsAadeesh JainPas encore d'évaluation
- Meaning and Concept of Capital MarketDocument12 pagesMeaning and Concept of Capital MarketDrTanushree GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- NUML Islamabad Assignment on Financial MarketsDocument12 pagesNUML Islamabad Assignment on Financial MarketsYousif RazaPas encore d'évaluation
- Investment Vs Speculation Vs GamblingDocument11 pagesInvestment Vs Speculation Vs GamblingAshutosh SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Indian Financial SystemDocument34 pagesIndian Financial SystemVivek SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Equity Investment for CFA level 1: CFA level 1, #2D'EverandEquity Investment for CFA level 1: CFA level 1, #2Évaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Bull's Eye- A stock market investment guide for beginnersD'EverandBull's Eye- A stock market investment guide for beginnersPas encore d'évaluation
- World Pneumonia Day - RYKDocument15 pagesWorld Pneumonia Day - RYKUmair AzizPas encore d'évaluation
- FINAL Closing Report of VTP - RC-RYK - RohiDocument10 pagesFINAL Closing Report of VTP - RC-RYK - RohiUmair AzizPas encore d'évaluation
- World Pneumonia Day - RYKDocument15 pagesWorld Pneumonia Day - RYKUmair AzizPas encore d'évaluation
- Concept of Development PDFDocument33 pagesConcept of Development PDFGerard Espinoza EspinozaPas encore d'évaluation
- Punjab Public Information Officers For PT and RTI Act, 2013Document37 pagesPunjab Public Information Officers For PT and RTI Act, 2013Naeem-IqbalPas encore d'évaluation
- Rotary Club of Rahim Yar Khan ROHI: Highlight's of Activity During The Last MeetingsDocument2 pagesRotary Club of Rahim Yar Khan ROHI: Highlight's of Activity During The Last MeetingsUmair AzizPas encore d'évaluation
- End Polio Now Cycling RaceDocument1 pageEnd Polio Now Cycling RaceUmair AzizPas encore d'évaluation
- Sociological TheoriessDocument22 pagesSociological TheoriessUmair AzizPas encore d'évaluation
- Principlesofislamicjurisprudence 130105092908 Phpapp02Document263 pagesPrinciplesofislamicjurisprudence 130105092908 Phpapp02Ahamed HilmyPas encore d'évaluation
- Social Studies LobeDocument37 pagesSocial Studies LobeUmair AzizPas encore d'évaluation
- MUSLIM SCIENTISTSDocument34 pagesMUSLIM SCIENTISTSinfiniti786Pas encore d'évaluation
- Principles of Islamic Jurisprudence ExplainedDocument147 pagesPrinciples of Islamic Jurisprudence ExplainedUmair AzizPas encore d'évaluation
- State of PakistanDocument36 pagesState of PakistanSana UllahPas encore d'évaluation
- Tib e Nabvi PBUH in Urdu PDFDocument499 pagesTib e Nabvi PBUH in Urdu PDFumer shafiquePas encore d'évaluation
- A Level Accounting 21 June2011Document12 pagesA Level Accounting 21 June2011Umair AzizPas encore d'évaluation
- Reasons For and Impact of Low Literacy Levels in AdultsDocument1 pageReasons For and Impact of Low Literacy Levels in AdultsUmair AzizPas encore d'évaluation
- Journalism Subject Paper-2014 PDFDocument1 pageJournalism Subject Paper-2014 PDFfahad iqbal khanPas encore d'évaluation
- Judicial Structure of PakistanDocument31 pagesJudicial Structure of PakistanUmair AzizPas encore d'évaluation
- Money Market Instruments in Pakistan ExplainedDocument48 pagesMoney Market Instruments in Pakistan ExplainedUmair AzizPas encore d'évaluation
- The Court SystemDocument25 pagesThe Court SystemUmair Aziz100% (1)
- Characteristics of A Successful StudentDocument12 pagesCharacteristics of A Successful StudentUmair Aziz100% (2)
- Umair Aziz: Career ObjectiveDocument3 pagesUmair Aziz: Career ObjectiveUmair AzizPas encore d'évaluation
- Umair Aziz CVDocument3 pagesUmair Aziz CVUmair AzizPas encore d'évaluation
- Islamic JurisprudenceDocument26 pagesIslamic JurisprudenceUmair Aziz67% (3)
- BOP Download Application Form Apna Rozgar SchemeDocument4 pagesBOP Download Application Form Apna Rozgar SchemeShawn ParkerPas encore d'évaluation
- Paper PatternDocument3 pagesPaper PatternHaseeb HassanPas encore d'évaluation
- Money Market Instruments in Pakistan Term PaperDocument16 pagesMoney Market Instruments in Pakistan Term PaperUmair AzizPas encore d'évaluation
- Umair CVDocument1 pageUmair CVUmair AzizPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 12Document7 pagesChapter 12Ednel GubacPas encore d'évaluation
- Course ListDocument4 pagesCourse ListhiyyearPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 7: Replacement Analysis (Chap 9)Document35 pagesModule 7: Replacement Analysis (Chap 9)우마이라UmairahPas encore d'évaluation
- Grants Interest Rate ObserverDocument28 pagesGrants Interest Rate ObserverZerohedgePas encore d'évaluation
- Investment Analysis and Portfolio Management: Frank K. Reilly & Keith C. BrownDocument48 pagesInvestment Analysis and Portfolio Management: Frank K. Reilly & Keith C. BrownUsman KWLPas encore d'évaluation
- TinsDocument3 pagesTinsIman Nurakhmad FajarPas encore d'évaluation
- Ethiopia Investment GuideDocument20 pagesEthiopia Investment GuideAbhishek Yadav100% (1)
- Baupost Group outlines value-focused thrift stock analysisDocument11 pagesBaupost Group outlines value-focused thrift stock analysisDavid Collon100% (1)
- SAM SEIDEN ARTICLES CLASSICAL PATTERNS AND SUPPLY DEMANDDocument8 pagesSAM SEIDEN ARTICLES CLASSICAL PATTERNS AND SUPPLY DEMANDAbhinav KeshariPas encore d'évaluation
- CFA Level II Quicksheet 2022 - SchweserDocument7 pagesCFA Level II Quicksheet 2022 - SchweserslaranPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 12 - Multinational Capital Structure and Cost of CapitalDocument7 pagesLecture 12 - Multinational Capital Structure and Cost of CapitalTrương Ngọc Minh ĐăngPas encore d'évaluation
- Mcncies 7 S Consortium-Securities-LtdDocument42 pagesMcncies 7 S Consortium-Securities-LtdAkhil Raj VPas encore d'évaluation
- Analysis of Deposit Schemes at CBLDocument51 pagesAnalysis of Deposit Schemes at CBLsadiyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Maybank - Aviation Report On CaamDocument7 pagesMaybank - Aviation Report On CaamNinerMike MysPas encore d'évaluation
- Microfinance Risk ManagementDocument241 pagesMicrofinance Risk ManagementSabelo100% (1)
- Earnings-At-Risk ("Ear") : Tiaa: Sandeep@1Document5 pagesEarnings-At-Risk ("Ear") : Tiaa: Sandeep@1Praddy BrookPas encore d'évaluation
- GTDT M and A 2017Document11 pagesGTDT M and A 2017Franz AndreanPas encore d'évaluation
- Vetted Prospectus Robi 2020 PDFDocument386 pagesVetted Prospectus Robi 2020 PDFmd nuruddinPas encore d'évaluation
- SFM Chapter 1 To 6Document124 pagesSFM Chapter 1 To 6spam mailPas encore d'évaluation
- Capital Budgeting DetailDocument64 pagesCapital Budgeting DetailDEV BHADANAPas encore d'évaluation
- Buscom ReviewerDocument23 pagesBuscom ReviewerSarah GPas encore d'évaluation
- ECM106 Muhammednur 1Document6 pagesECM106 Muhammednur 1muhammednur100% (1)
- MBA Project Report On Financial AnalysisDocument73 pagesMBA Project Report On Financial AnalysisShainaDhiman79% (24)
- Stoxx IndexguideDocument118 pagesStoxx IndexguideCharles MañePas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4 Commercial BanksDocument33 pagesChapter 4 Commercial BanksChichay KarenJoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Acct-111e - Quiz CompDocument18 pagesAcct-111e - Quiz CompJap Keren LirazanPas encore d'évaluation
- Accounting ratios and formulas explainedDocument2 pagesAccounting ratios and formulas explainedDeky Oktary PratamaPas encore d'évaluation
- Solutions Worksheets - Chapt 3Document35 pagesSolutions Worksheets - Chapt 3Nam PhươngPas encore d'évaluation
- Margin of Safety Summary: Risk Averse Value Investing Strategies For The Thoughtful InvestorDocument8 pagesMargin of Safety Summary: Risk Averse Value Investing Strategies For The Thoughtful InvestorscottymcconPas encore d'évaluation
- IAS 23 - SemDocument3 pagesIAS 23 - SemMeo MeoPas encore d'évaluation