Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
V12 RX Clinical Data - 0562
Transféré par
biomedical_com_brDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
V12 RX Clinical Data - 0562
Transféré par
biomedical_com_brDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Renal Clinical Data
Limitations of Prior Renal Randomized Controlled Trials
Prior renal focused trials such as the ASTRAL, STAR and DRASTIC, failed to show a clear benefit of renal artery stenting compared to medical therapy alone. Numerous critiques on the methodology and design of these trials have been published. The limitations of these studies and how they have impacted the outcomes of the trials are briefly outlined below.
Limitations of Prior Renal Trials
Implications on Trial Outcomes
Physicians had to be undecided on whether the patient should undergo revascularization or medical management alone which led to excluding patients who would have benefited from revascularization.4 Asymptomatic or minimally symptomatic patients were enrolled and unlikely to benefit from revascularization.1
Selection bias
1,4
Underpowered % of participants were not eligible/did 2,3,4 not receive treatment/crossed over
Underpowered studies can lack evidence or be misleading.
Low numbers of enrollment per year with high rates of adverse 4 events observed
Not consistent with historically low adverse event rates for renal stenting. This may have contributed to the neutral outcomes. The degree of stenosis was likely overestimated by visual inspection and was not validated.4 Patients were enrolled at physician's discretion.
No core laboratory or Objective enrollment criteria
2,3,4
1. 2. 3. 4.
White J. Kiss My Astral: One Seriously Flawed Study of Renal Artery Stenting After Another. Catheterization and Cardiovascular Interventions 2010; Volume 75: 305-307. Bax L, et al. Stent Placement In Patients with Atherosclerotic Renal Artery Stenosis and Impaired Renal Function: a Randomized Trial. Annals of Internal Medicine 2009; Volume 150, Issue 12: 840-848. Jaarsveld B, Et Al. The Eect of Balloon Angioplasty on Hypertension in Atherosclerotic Renal-Artery Stenosis. New England Journal of Medicine 2000; Volume 342:1007-1014. Wheatley K, et al. J. Revascularization Versus Medical Therapy for Renal-Artery Stenosis. New England Journal of Medicine 2009; 361:19531962.
Unsurpassed Deliverability
Is Renal Artery Stenting the Right Choice for Your Patient?
ASTRAL and STAR demonstrated that careful patient selection is critical for successful endovascular treatment of renal artery disease. The following conditions can help you determine if renal artery stenting is the right choice for your patient.
Patients that Do NOT Benet from Renal Artery Stenting
Patients with renal function that has remained stable over the past 6 to 12 months and hypertension that can be controlled medically9 Patients with preserved or even decreased but stable renal function9 Hemodynamically non-significant stenosis with arterial hypertension or renal function impairment from other etiologies10 Patients with high intrarenal resistive index > 0.81 Patients with a stenosed renal artery supplying a small atrophic kidney1,2
Patients that Do Benet from Renal Artery Stenting
Hemodynamically significant renal artery stenosis (RAS) 70%5 Resistant hypertension despite the use of >3 antihypertensive agents of different classes, including a diuretic9 Unilateral RAS of a single kidney and bilateral RAS1 Patients with bilateral stenosis with flash pulmonary edema1,9 Progressive decline in GFR during treatment of hypertension with ACE inhibitors or ARBs11 Intrarenal resistive index < 0.89 Translesional pressure gradient > 20mm Hg4,8 Normal kidney size of > 8.0cm1 Patients with CKD stages 4/56 (The above criteria may show benet alone or in combination)
1. Adamczak M, Wiecek A. The Management of Atherosclerotic Renovascular Disease. Kidney and Blood Pressure Research 2011; 34 (4):277-83. 2. Chrysochou C, et al. Proteinuria As A Predictor of Renal Functional outcome After Revascularizationin Atherosclerotic Renovascular Disease (ARVD). QJM 2009; 102:283-288. 3. Cheung C, Chrysochou C, Kalra P. The Management of Renovascular Disease: ASTRAL and Beyond. Current Opinion in Nephrology and Hypertension 2011; 20: 89-94. 4. De Bruyne, et al. Assessment of Renal Artery Stenosis Severity by Pressure Gradient Measurements. J Am Coll Cardiology 2006; 48(9):1851-1855. 5. Hirsch, et al.. ACC/AHA Practice Guidelines for The Management of Patients With Peripheral Arterial Disease. Journal of Vascular Interv. Radiology 2006;17:1383-1398. 6. Kalra P, et al.. The Benet of Renal Artery Stenting in Patients With Atheromatous Renovascular Disease and Advanced Chronic Kidney Disease. Catheterization and Cardiovascular Interventions 2010; 75:1-10. 7. Mangiacapra F, et al. Translesional Pressure Gradients to Predict Blood Pressure Response After Renal Artery Stenting in Patients With Renovascular Hypertension. Circ. Cardiovas. Interv. 2010; Dec, 3(6):537-542. 8. Silva J, et al. Elevated Brain Natriuretic Peptide Predicts Blood Pressure Response After Stent Revascularization in Patients with Renal Artery Stenosis. Circulation 2005; 111:328-333. 9. Simon J. Stenting Atherosclerotic Renal Arteries: Time to be Less Aggressive. Cleveland Clinic J Med. 2010, Mar; 77(3):178-189. 10. Sapoval M, et al. One Year Clinical Outcomes of Renal Artery Stenting: The Results of ODORI Registry. Cardiovascular Interventional Radiology 2010, June; 33(3): 475-483. Epub 2009 Nov 12. 11. Textor S, et al. Timing and Selection for Renal Revascularization in an Era Of Negative Trials: What to Do? Progressive Cardiovascular Disease 2009, Nov-Dec;52(3):220-228.
with Ultra Low Profile
Advantages of Atriums Balloon Expandable Covered Stents
Bare Metal Renal Artery Stenting has Demonstrated High Restenosis Rates
Bare Metal Restenosis Rates
1
Study Renaissance Trial Lederman, et al
2
Follow-up Period 9 months 16 months
21.3% 21.0%
Challenges Associated with Bare Metal Stents
Intimal Hyperplasia: Excessive neointimal growth is exhibited with bare metal stents due to vessel wall damage from isolated bare metal stent struts leading to inflammation and smooth muscle disruption.
Rogers and Edelman proved V12 reduced neointimal growth 3 by 80%
Neointimal growth of a bare metal stent at 28 days Neointimal growth of V12 at 28 days
Distal Embolization: Bare metal stents have the ability to disrupt or "cheese grate" plaque and thrombus through the open bare metal struts causing distal embolization. Whereas, V12s simultaneous dog-bone balloon inflation, along with the proprietary PTFE covering, has the ability to trap embolic debris against the vessel wall minimizing embolization.
Bare Metal Stent
V12
V12
Plaque and thrombus dislodged during bare metal stent deployment
Embolic debris trapped against vessel wall during V12 dog-bone ination
V12 deployed with reduced risk of distal embolization
1. Rocha-Singh K, Ja M, Kelley E. Renal Artery Stenting with Noninvasive Duplex Ultrasound Follow-up: 3 Year Results from the RENAISSANCE Renal Stent Trial. Catheterization and Cardiovascular Interventions 2008; 72: 853-862. 2. Lederman R, Mendelsohn F, Santos R, et al. Primary Renal Artery Stenting: Characteristics and Outcomes After 363 Procedures. American Heart Journal 1999; 142(2): 314-323 3. Rogers C, Tseng DY, Gingras PH, Karwoski T, Martakos P, Edelman ER. Expanded Polytetrauoroethylene Stent Graft Encapsulation ReducesIntimal Thickening Regardless of Stent Design. Journal of the American College of Cardiology 1998, Abstract:1163-80.
Confidence Instilled from
Atriums Proven Renal Clinical Data
Treating Renal In-Stent Restenosis with Atriums Covered Stent
Study Ruggiero, II, et al. 2010 Lookstein, 2011 Bray, 2009 3
2 1
Primary Patency 100% 100% 100%
Clinical Follow Up 1 year 13 months 2 years
Ruggiero, II, et al. 20101 - A review of Atriums covered stent for the treatment of renal artery in-stent restenosis. 100% technical success and 100% primary patency at 1 year.
Lookstein, 20112 - Atriums covered stent demonstrated 100% patency in patients that were treated for bare metal in-stent restenosis at 13 months.
Bray, 20093 - Studied the eect of utilizing V12 in renal arteries to treat bare metal in-stent restenosis. Bray reported 100% technical success and 100% patency at 2 years.
Renal Fenestration Study
Number of Stents BX Covered Stent BMS
* statistical signicance p < 0.05
Renal Occlusion Rate (2 yrs) 2.2%* 4.5%
Renal Restenosis Rate (2 yrs) 2.5%* 10%
231 287
Review comparing outcomes of BX covered vs. bare metal stents (BMS) when used in conjunction with fenestrated AAA devices during endovascular repair of abdominal aneurysms4.
1. 2. 3 4.
Ruggiero N, Garasic J, Ja M, et al. The Utilization of PTFE Covered Stents for the Treatment of Renal Artery In-Stent Restenosis. Journal of American College of Cardiology 2010; 55(10A). Lookstein, Robert. The Use of Balloon Expandable Covered Stents for the Treatment of Renal Artery In-Stent Restenosis. VEITH. NYC. 2011. Bray, Alan. Patency of a Covered Stent for Renal Artery In-Stent Restenosis and After Fenestration. Vascular Meeting. Sydney, Australia. 2009. Mohabbat W, Greenberg R, Mastracci T, et al. Revised Duplex Criteria and Outcomes for Renal Stents and Stent Grafts Following Endovascular Repair of Juxtarenal and Thoracoabdominal Aneurysms. Journal of Vascular Surgery 2009; 49: 827-837.
Proven Clinical Outcomes
Clinical Experiences
Renal Stenosis > Optimal treatment strategy for renal artery stenosis. PTFE stent encapsulation minimizes neointimal in-growth and renal restenosis.
Left renal artery stenosis
6 X 24mm V12 RX deployed in renal artery
Renal Aneurysm > Life-saving endovascular solution
Renal artery aneurysm measuring 2.5 cm
5 X 24mm V12 RX stent successfully deployed excluding aneurysm
Renal Fenestration > Covered renal stents are associated with a lower incidence of in-stent stenosis and are thus recommended over bare metal stents...1
Bilateral renal fenestrations with V12 covered stents
Over 150,000 Patients Successfully Treated
1. Revised Duplex Criteria and Outcomes for Renal Stents and Stent Grafts Following Endovascular Repair of Juxtarenal and Thoracoabdominal Aneurysms. Greenberg et al. JVS, April 2009.
V12 RX Covered Stent - Get where you need to go
Product Features
Enhanced deliverability and trackability .014 rapid exchange platform Ultra low profile - 5Fr & 6Fr introducer sheath compatible - 6Fr & 7Fr guide catheter compatible Available in diameters of 5, 6 and 7 mm and lengths of 16, 21 and 24 mm Additional lengths and diameters pending CE approval One-step precision deployment Controls embolic debris
Atriums Superior Covering Technology
Thermo-conformable PTFE covering expands uniformly at body temperature One piece PTFE construction completely encapsulates stent struts Customize to fit vessel anatomy - flare and post-dilate (up to 8mm*) Designed to minimize intimal hyperplasia while still allowing tissue attachment for an optimal fit and healing response
*6 and 7 mm diameters are capable of post-dilation to 8mm V12 RX is CE marked for restoring the patency of iliac and renal arteries V12 RX is TGA registered for restoring the patency of renal arteries. V12 is not available in the U.S.
V12 RX Covered Stent
The World Leader in Balloon Expandable Covered Stents
Over 150,000 patients treated worldwide Over 145 clinical publications and presentations
Ordering Information:
Able to be post-dilated up to 8mm*
Code # 140 cm Catheter Length
85278 85279 85280 85285 85286 85287 85292 85293 85294
.014'' guidewire
Introducer Compatibility Guide Catheter Compatibility+
6 FR 6 FR 6 FR 6 FR 6 FR 6 FR 7 FR 7 FR 7 FR
Stent Diameter/ Length
5 x 16 mm 5 x 21 mm 5 x 24 mm 6 x 16 mm 6 x 21 mm 6 x 24 mm 7 x 16 mm 7 x 21 mm 7 x 24 mm
*6 & 7mm diameters can be post-dilated to 8mm + Most common size guide catheters were tested
5 FR 5 FR 5 FR 5 FR 5 FR 5 FR 6 FR 6 FR 6 FR
To learn more about V12 product offerings, visit us online at: www.atriummed.com
ATRIUM MEDICAL CORPORATION
ATRIUM EUROPE B.V.
ATRIUM AUSTRALIA-PACIFIC RIM PTY. LTD.
5 Wentworth Drive Hudson, New Hampshire 03051 U.S.A. 1-603-880-1433 1- 603-880-6718
Rendementsweg 20 B 3641 SL Mijdrecht, The Netherlands +31 297 230 420 +31 297 282 653
Level 6, 579 Harris Street Ultimo NSW 2007 Australia +61 2 8272 3100 +61 2 8272 3199
Atrium Medical Corporation 2012. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. 8/12 Part #0562. Atrium and V12 are trademarks of Atrium Medical Corporation, a MAQUET GETINGE GROUP company.
V12 RX is CE marked for restoring the patency of iliac and renal arteries. V12 RX is TGA registered for restoring the patency of renal arteries. V12 is not available in the U.S.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- CVC Pressure Injectable Poster PDFDocument2 pagesCVC Pressure Injectable Poster PDFbiomedical_com_brPas encore d'évaluation
- Pressure Injectable CVC Ifu PDFDocument20 pagesPressure Injectable CVC Ifu PDFbiomedical_com_brPas encore d'évaluation
- Merit Finale Brochure PDFDocument2 pagesMerit Finale Brochure PDFbiomedical_com_brPas encore d'évaluation
- IFU Oasis EN PDFDocument3 pagesIFU Oasis EN PDFbiomedical_com_brPas encore d'évaluation
- F PDFDocument30 pagesF PDFbiomedical_com_brPas encore d'évaluation
- Folder - Ocean PDFDocument2 pagesFolder - Ocean PDFbiomedical_com_brPas encore d'évaluation
- A PDFDocument1 pageA PDFbiomedical_com_brPas encore d'évaluation
- A PDFDocument2 pagesA PDFbiomedical_com_brPas encore d'évaluation
- 006 PDFDocument40 pages006 PDFbiomedical_com_brPas encore d'évaluation
- A PDFDocument12 pagesA PDFbiomedical_com_brPas encore d'évaluation
- Folder - Express PDFDocument2 pagesFolder - Express PDFbiomedical_com_brPas encore d'évaluation
- Express II 005558 EN PDFDocument3 pagesExpress II 005558 EN PDFbiomedical_com_brPas encore d'évaluation
- IFU Ocean EN PDFDocument3 pagesIFU Ocean EN PDFbiomedical_com_brPas encore d'évaluation
- Folder - OasisDocument2 pagesFolder - Oasisbiomedical_com_brPas encore d'évaluation
- DDocument12 pagesDbiomedical_com_brPas encore d'évaluation
- When Seconds Count: Aspiration Catheter and KitDocument4 pagesWhen Seconds Count: Aspiration Catheter and Kitbiomedical_com_brPas encore d'évaluation
- ADocument4 pagesAbiomedical_com_brPas encore d'évaluation
- Folder Drenos PDFDocument6 pagesFolder Drenos PDFbiomedical_com_brPas encore d'évaluation
- EN Snare Endovascular SystemDocument4 pagesEN Snare Endovascular SystemradeonunPas encore d'évaluation
- BDocument16 pagesBbiomedical_com_brPas encore d'évaluation
- 1flixene - IFG - Implantation - Brochure 0341C PDFDocument1 page1flixene - IFG - Implantation - Brochure 0341C PDFbiomedical_com_brPas encore d'évaluation
- EN Snare Endovascular SystemDocument4 pagesEN Snare Endovascular SystemradeonunPas encore d'évaluation
- BDocument10 pagesBbiomedical_com_brPas encore d'évaluation
- A Master in The Art of Multipurpose MicrocathetersDocument4 pagesA Master in The Art of Multipurpose Microcathetersbiomedical_com_brPas encore d'évaluation
- Instructions For Use: © 2010 Atrium and Flixene Are Trademarks of Atrium Medical Corporation Rev. 2010/04Document5 pagesInstructions For Use: © 2010 Atrium and Flixene Are Trademarks of Atrium Medical Corporation Rev. 2010/04biomedical_com_brPas encore d'évaluation
- DDocument2 pagesDbiomedical_com_brPas encore d'évaluation
- Flixene - IFG - Implantation - Brochure 0341C PDFDocument6 pagesFlixene - IFG - Implantation - Brochure 0341C PDFbiomedical_com_brPas encore d'évaluation
- Merit Hemostasis Valves and Angioplasty AccessoriesDocument4 pagesMerit Hemostasis Valves and Angioplasty AccessoriesradeonunPas encore d'évaluation
- Insufladores Basix Compak Monarch MeritDocument6 pagesInsufladores Basix Compak Monarch Meritbiomedical_com_brPas encore d'évaluation
- Angiographic Catheters Sondes Angiographiques Cateteri Angiografici Angiographiekatheter Catéteres AngiográficosDocument2 pagesAngiographic Catheters Sondes Angiographiques Cateteri Angiografici Angiographiekatheter Catéteres Angiográficosbiomedical_com_brPas encore d'évaluation
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- STG-General Hospital PDFDocument704 pagesSTG-General Hospital PDFBirhane100% (1)
- Miss Evers Boys Draft 4Document2 pagesMiss Evers Boys Draft 4api-291172102Pas encore d'évaluation
- Anderson2008 Levofloxasin A ReviewDocument31 pagesAnderson2008 Levofloxasin A ReviewFazdrah AssyuaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Hypertension: Rojina Bhurtel Lecturer MmihsDocument36 pagesHypertension: Rojina Bhurtel Lecturer MmihsRojina Bhurtel100% (2)
- Bowel Preparation Colon ResectionDocument28 pagesBowel Preparation Colon ResectioncristiangallardovPas encore d'évaluation
- MidazolamDocument18 pagesMidazolamHarnugrahanto AankPas encore d'évaluation
- Growth PredictionDocument101 pagesGrowth PredictionKristty Magallanes100% (1)
- Ateneo de Zamboanga University Nursing Skills Output (NSO) Week BiopsyDocument4 pagesAteneo de Zamboanga University Nursing Skills Output (NSO) Week BiopsyHaifi HunPas encore d'évaluation
- Yorkville Advisors Completes $7.5M Equity Facility With EntreMed, Inc.Document2 pagesYorkville Advisors Completes $7.5M Equity Facility With EntreMed, Inc.YorkvilleAdvisorsPas encore d'évaluation
- Birtcher 774 ESU - User and Service Manual PDFDocument39 pagesBirtcher 774 ESU - User and Service Manual PDFLuis Fernando Garcia SPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study DengueDocument3 pagesDrug Study DengueiamELHIZAPas encore d'évaluation
- Ramadan NutritionDocument27 pagesRamadan NutritionselcankhatunPas encore d'évaluation
- Types of Hyperlipoproteinemia and Lipid AbnormalitiesDocument22 pagesTypes of Hyperlipoproteinemia and Lipid Abnormalitiescollege3Pas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument17 pagesDrug StudyJoan RabePas encore d'évaluation
- Chester V Afshar (2005) 1 A.C. 134Document33 pagesChester V Afshar (2005) 1 A.C. 134V100% (1)
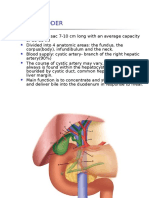
- Gallbladder and Bile Duct Anatomy, Function and DiseasesDocument16 pagesGallbladder and Bile Duct Anatomy, Function and DiseasesKadenceFreya-Charisse G PosadasBulintao100% (2)
- Obat SpesialisDocument16 pagesObat SpesialisLAILATUL AFIYAHPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 - General Indications and Contraindications - 2019 - Lumbar Interbody FusionsDocument12 pages1 - General Indications and Contraindications - 2019 - Lumbar Interbody FusionsSergiu MalinPas encore d'évaluation
- Arthritis astrology signs and planetsDocument5 pagesArthritis astrology signs and planetsJatinder SandhuPas encore d'évaluation
- HEALTHY JUICES AND THEIR BENEFITSDocument7 pagesHEALTHY JUICES AND THEIR BENEFITSdeepaliPas encore d'évaluation
- Quantitative analysis of iron (III) in Ferimax and Ferrum Lek syrupsDocument5 pagesQuantitative analysis of iron (III) in Ferimax and Ferrum Lek syrupsLipsi MerchánPas encore d'évaluation
- Rhubarb April 2017Document17 pagesRhubarb April 2017ISADD LietuvaPas encore d'évaluation
- Mnemonics For PharmacologyDocument46 pagesMnemonics For PharmacologysnehaPas encore d'évaluation
- 3M Slide - CHG Dressing For CRBSI (Juli 2022)Document20 pages3M Slide - CHG Dressing For CRBSI (Juli 2022)SilviyhaPas encore d'évaluation
- DLP in MAPEH - Grade 9 Myths and Misconceptions About DrugsDocument4 pagesDLP in MAPEH - Grade 9 Myths and Misconceptions About DrugsMa. Reina Gail T. Lizaso100% (5)
- Daftar Pustaka KolelitiasisDocument2 pagesDaftar Pustaka KolelitiasisReni IstiarPas encore d'évaluation
- History Taking in JaundiceDocument2 pagesHistory Taking in Jaundiceshanyiar100% (5)
- Fatal Airway Obstruction Due To Ludwig'sDocument6 pagesFatal Airway Obstruction Due To Ludwig'sRegina MugopalPas encore d'évaluation
- Supine Cervical Traction After Anterior Cervical Diskectomy and FusionDocument4 pagesSupine Cervical Traction After Anterior Cervical Diskectomy and FusionOscar NgPas encore d'évaluation
- The Role of Personality in Sport and Physical ActivityDocument7 pagesThe Role of Personality in Sport and Physical ActivityWanRezawanaWanDaudPas encore d'évaluation