Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Sintesis III Periodo
Transféré par
NiJoha SJDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Sintesis III Periodo
Transféré par
NiJoha SJDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
The members of family are:
Grandfather (or granddad), grandmother (or grandma), father, mother, brother, sister (son and girl - children), aunt, uncle, cousin, nephew (man), niece (woman), grandson (granddaughter), brother and sister-in-law and so on. Days of the Week The history of the days of the week is closely intertwined with the advancement of mankind through the centuries. The Week came to have seven days mainly because it was a relatively easy way to break up the month into four manageable segments. There was also the fact that the Hebrews believed that God created the Earth and heavens in seven days. This notion of a holy sanction for the seven day week was passed on to other peoples and religions, including Christians and Moslems. Sunday is the Lord's day for Christians, yet it is named for the sun. Like many other days of the week it was actually named by the Norsemen who invaded England in the centuries preceding the Norman Conquest. It is a Norse change of the Roman designation of the day. If the sun has its own day why not the moon on Monday? Astronomic bodies played a prominent place in the beliefs of early peoples. The moon and its phaseswas especially fascinating. Tuesday is not named for the number. It is named for the Norse god of War. WasWednesday named for weddings? Not even close. (Close only counts inhorseshoes and hand grenades.) Another in the line of days named for Norse gods. This one was for Woden (or Odin), the chief of the pantheon. When you hear thunder on Thursday you will remember how this day got its name. It was named for the Scandanavian god of thunder, Thor. Friday is the only day of the week named for a woman. Her name was Frigga and she was the consort of Odin. If Friday falls on the 13th, it is considered by some to be unlucky. The last day of the week is Saturday. It is the only day of the week in the English language that retained its Roman character. It takes its name from the Roman god of time and the harvest.
Click on the links in the navbar above to find the history of a particular day, or read through the entire site by clicking on the "next page" links at the bottom of each page.
A CALENDAR There are 12 months in a year. The first month of the year is January. The last month of the year is December. Some months have 30 days and some have 31. January, March, May, July, August, October and December have 31 days. April, June September and November have 30 days. February has 28 days and sometimes 29. We use the months of the year to write the important dates about us, for example our birthday, our familiar dates and special dates of our country as the independence Day and more of them.
The months of the year are:
What are senses? Sight
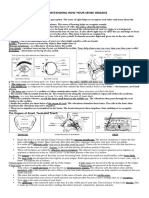
In this painting by Pietro Paolini, each individual represents one of the five senses. [3] The Walters Art Museum. Sight or vision is the capability of the eye(s) to focus and detect images of visible light on photoreceptors in the retina of each eye that generates electrical nerve impulses for varying colors, hues, and brightness. There are two types of photoreceptors: rods and cones. Rods are very sensitive to light, but do not distinguish colors. Cones distinguish colors, but are less sensitive to dim light. There is some disagreement as to whether this constitutes one, two or three senses. Neuroanatomists generally regard it as two senses, given that different receptors are responsible for the perception of color and brightness. Some argue[citation needed] that stereopsis, the perception of depth using both eyes, also constitutes a sense, but it is generally regarded as a cognitive (that is, post-sensory) function of the visual cortex of the brain where patterns and objects in images are recognized and interpreted based on previously learned information. This is called visual memory. The inability to see is called blindness. Blindness may result from damage to the eyeball, especially to the retina, damage to the optic nerve that connects each eye to the brain, and/or from stroke (infarcts in the brain). Temporary or permanent blindness can be caused by poisons or medications. Hearing Hearing or audition is the sense of sound perception. Hearing is all about vibration. Mechanoreceptors turn motion into electrical nerve pulses, which are located in the inner ear. Since sound is vibrations propagating through a medium such as air, the detection of these vibrations, that is the sense of the hearing, is a mechanical sense because these vibrations are mechanically conducted from the eardrum through a series of tiny bones to hair-like fibers in the inner ear, which detect mechanical motion of the fibers within a range of about 20 to 20,000 hertz,[4] with substantial variation between individuals. Hearing at high frequencies declines with an increase in age. Inability to hear is called deafness or hearing impairment. Sound can also be detected as vibrations conducted through the body by tactition. Lower frequencies than can be heard are detected this way.
Taste Taste (or, the more formal term, gustation; adjectival form: "gustatory") is one of the traditional five senses. It refers to the capability to detect the taste of substances such as food, certain minerals, and poisons, etc. The sense of taste is often confused with the "sense" of flavor, which is a combination of taste and smell perception. Flavor depends on odor, texture, and temperature as well as on taste. Humans receive tastes through sensory organs called taste buds, or gustatory calyculi, concentrated on the upper surface of the tongue. The sensation of taste can be categorized by five primary taste qualities: sweetness, bitterness, sourness, saltiness and umami (pronounced OO-MAH-MEE), which means "meaty" or "savory" in Japanese. Other tastes such as calcium [5] and free fatty acids [6] may be other basic tastes but have yet to receive widespread acceptance. The recognition and awareness of umami is a relatively recent development in Western cuisine.[7] MSG produces a strong umami taste so much so that it is said to taste soapy by itself.[8] Smell Smell or olfaction is the other "chemical" sense. Unlike taste, there are hundreds of olfactory receptors (388 according to one source[9]), each binding to a particular molecular feature. Odor molecules possess a variety of features and, thus, excite specific receptors more or less strongly. This combination of excitatory signals from different receptors makes up what we perceive as the molecule's smell. In the brain, olfaction is processed by the olfactory system. Olfactory receptor neurons in the nose differ from most other neurons in that they die and regenerate on a regular basis. The inability to smell is called anosmia. Some neurons in the nose are specialized to detect pheromones.[10] Touch Touch or somatosensory, also called tactition or mechanoreception, is a perception resulting from activation of neural receptors, generally in the skin including hair follicles, but also in the tongue, throat, and mucosa. A variety of pressure receptors respond to variations in pressure (firm, brushing, sustained, etc.). The touch sense of itching caused by insect bites or allergies involves special itch-specific neurons in the skin and spinal cord.[11] The loss or impairment of the ability to feel anything touched is called tactile anesthesia. Paresthesia is a sensation of tingling, pricking, or numbness of the skin that may result from nerve damage and may be permanent or temporary.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Skeletal SystemDocument29 pagesSkeletal SystemCrii XiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Keely Presentation3Document93 pagesKeely Presentation3KIRILL100% (6)
- KHC 6 Advanced Fingering SessionsDocument20 pagesKHC 6 Advanced Fingering SessionsjustnewaroundPas encore d'évaluation
- Sensory Deprivation NewDocument19 pagesSensory Deprivation NewSREEDEVI T SURESHPas encore d'évaluation
- Sensing and PerceivingDocument38 pagesSensing and Perceivingsaba naheedPas encore d'évaluation
- Bladder Outlet Obstruction in Children PDFDocument64 pagesBladder Outlet Obstruction in Children PDFalaaPas encore d'évaluation
- Sensation and PerceptionDocument13 pagesSensation and PerceptionRiza Roncales100% (1)
- The Nature and Fundamental of The Learner Sensation: Abigail Salazar BPE III-3Document5 pagesThe Nature and Fundamental of The Learner Sensation: Abigail Salazar BPE III-3Ernielle Clark DionisioPas encore d'évaluation
- Guidelines For Fcps-I (Medicine)Document3 pagesGuidelines For Fcps-I (Medicine)Israr Ul HaqPas encore d'évaluation
- Sensory and Motor SystemDocument12 pagesSensory and Motor SystemrobertoPas encore d'évaluation
- Sense Organ PDFDocument5 pagesSense Organ PDFPerry Sin75% (4)
- Five SensesDocument41 pagesFive SensesJobel Sibal CapunfuerzaPas encore d'évaluation
- Menstrual CycleDocument10 pagesMenstrual CycleintanPas encore d'évaluation
- Sense of Hearing: How You HearDocument8 pagesSense of Hearing: How You HearZuLianaPas encore d'évaluation
- Role of Hormones in Reproductive PDFDocument46 pagesRole of Hormones in Reproductive PDFJenica Angeles100% (1)
- Sensory OrganDocument20 pagesSensory OrganJanePas encore d'évaluation
- The Five Human SensesDocument17 pagesThe Five Human SensesAntonio Gonzalez100% (1)
- Lecture & Review Guide in HEMATOLOGY 1 & 2 (COMPLETE)Document58 pagesLecture & Review Guide in HEMATOLOGY 1 & 2 (COMPLETE)Kirt Anonuevo100% (3)
- The Urinary System: Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical CollegeDocument91 pagesThe Urinary System: Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical CollegeNicole NipasPas encore d'évaluation
- Ashley MontaguDocument404 pagesAshley Montagumanuelmcorrea100% (2)
- Curs 11.3 ADKDocument33 pagesCurs 11.3 ADKBrînzǎ Maria-CristinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Smelling to Survive: The Amazing World of Our Sense of SmellD'EverandSmelling to Survive: The Amazing World of Our Sense of SmellÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Test Science 6º Unit 1Document2 pagesTest Science 6º Unit 1Cristina Araque Díaz de los BernardosPas encore d'évaluation
- Sense: Pietro PaoliniDocument34 pagesSense: Pietro PaolinisameshPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit Three Sensation and Perception: Learning ObjectivesDocument65 pagesUnit Three Sensation and Perception: Learning ObjectivesAnonymous Y2J3QRfdPas encore d'évaluation
- General Psychology AssignmentDocument4 pagesGeneral Psychology AssignmentSaaB PanaraagPas encore d'évaluation
- Sensory ReceptionDocument4 pagesSensory ReceptionFIZA MALIKPas encore d'évaluation
- READINGDocument7 pagesREADING102221019 RAFIFAH TRIANANDA SUHARDIPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy and Structure of Human Sense OrgansDocument6 pagesAnatomy and Structure of Human Sense OrgansBonjovi VerdejoPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy and Structure of Human Sense OrgansDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Structure of Human Sense OrgansMelanie GialogoPas encore d'évaluation
- Audition: Hearing, The Ear, and Sound LocalizationDocument5 pagesAudition: Hearing, The Ear, and Sound LocalizationTanishqa RawlaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy and Structure of Human Sense OrgansDocument10 pagesAnatomy and Structure of Human Sense OrgansPaula QuinteroPas encore d'évaluation
- Sensing The World Around UsDocument3 pagesSensing The World Around UsSyed Muzafar AliPas encore d'évaluation
- Laporan SenseDocument16 pagesLaporan SenseladylomoPas encore d'évaluation
- The World Through Our Senses: Form Two Science, Chapter OneDocument10 pagesThe World Through Our Senses: Form Two Science, Chapter Onegan tong hock a.k.a ganosPas encore d'évaluation
- Sensation: Studying The Gateways of Experience: Topic 4Document36 pagesSensation: Studying The Gateways of Experience: Topic 4marium aslamPas encore d'évaluation
- JasonRoss Smell 0Document5 pagesJasonRoss Smell 0Victor_Brujan_2831Pas encore d'évaluation
- Is Your Skin, Nose, Tongue, Ears, and Eyes Right? I. ObjectivesDocument11 pagesIs Your Skin, Nose, Tongue, Ears, and Eyes Right? I. ObjectivesHafizah Ghany HayudinnaPas encore d'évaluation
- Evs 1 BrianDocument3 pagesEvs 1 Briangeorge baruahPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 6 Laboratory AssignmentDocument2 pagesWeek 6 Laboratory Assignmentraine tiroPas encore d'évaluation
- Q2 L4 HandoutDocument4 pagesQ2 L4 HandoutmiatamayoqtPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment-3: Sensation: Sensation in Psychology Is Any Concrete, Conscious ExperienceDocument13 pagesAssignment-3: Sensation: Sensation in Psychology Is Any Concrete, Conscious ExperienceHimanshi ShokeenPas encore d'évaluation
- 5 SensesDocument1 page5 SensespsathishthevanPas encore d'évaluation
- Sensation and Perception (Contd.) The Other Senses Depth Perception Perception MovementDocument14 pagesSensation and Perception (Contd.) The Other Senses Depth Perception Perception MovementNael Nasir ChiraghPas encore d'évaluation
- Stimuli For Different SensesDocument8 pagesStimuli For Different SenseskeshatPas encore d'évaluation
- The Five SensesDocument11 pagesThe Five SensesNichole HattonPas encore d'évaluation
- Psychodynamic Perspective:: How Strong A Stimulus To Be Detected?Document5 pagesPsychodynamic Perspective:: How Strong A Stimulus To Be Detected?Lyanna MormontPas encore d'évaluation
- Design Features of LanguageDocument28 pagesDesign Features of LanguageMUHAMMAD SHAHZAD QAISARPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 10Document23 pagesLesson 10Naka LimutPas encore d'évaluation
- III. Sensation and PerceptionDocument60 pagesIII. Sensation and PerceptionLabida SirenPas encore d'évaluation
- Sound Healing ManualDocument57 pagesSound Healing ManualMike LPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is Sensory Processes: 1.absolute ThresholdsDocument4 pagesWhat Is Sensory Processes: 1.absolute ThresholdslucasPas encore d'évaluation
- Cognitive PaperDocument5 pagesCognitive Paperapi-351181611Pas encore d'évaluation
- Special SensesDocument6 pagesSpecial Sensesvivian.obadePas encore d'évaluation
- The SensesDocument41 pagesThe Sensesfemfen1225Pas encore d'évaluation
- Soc AssignmentDocument3 pagesSoc AssignmentIsraq AhmmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 8 Sensory Motor MechanismDocument4 pagesLesson 8 Sensory Motor Mechanismcabahugmarlon2.5Pas encore d'évaluation
- Organ SensorikDocument62 pagesOrgan SensorikPutri Dwi lestariPas encore d'évaluation
- Science Form 2Document9 pagesScience Form 2yvonne vonne vonnePas encore d'évaluation
- Sensory Organs: What Are The Sense Organs?Document3 pagesSensory Organs: What Are The Sense Organs?ajay kalangiPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy of Human EarDocument2 pagesAnatomy of Human EarAbdullah Ahsan AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Let's Remember: Understanding How Your Sense OrgansDocument1 pageLet's Remember: Understanding How Your Sense OrgansJohn LimPas encore d'évaluation
- Self Knowledge PreviewDocument10 pagesSelf Knowledge PreviewEmburyPas encore d'évaluation
- Form 2 Science Chapter 1Document26 pagesForm 2 Science Chapter 1EeJun LeePas encore d'évaluation
- App P2Document26 pagesApp P2Khamron BridgewaterPas encore d'évaluation
- About The Nervous SystemDocument4 pagesAbout The Nervous SystemKrishaa ShahPas encore d'évaluation
- Sintesis Iv 3°Document13 pagesSintesis Iv 3°NiJoha SJPas encore d'évaluation
- Synthesis IV TermDocument9 pagesSynthesis IV TermNiJoha SJPas encore d'évaluation
- Assigments September From 23 To 27Document1 pageAssigments September From 23 To 27NiJoha SJPas encore d'évaluation
- Synthesis IV TermDocument9 pagesSynthesis IV TermNiJoha SJPas encore d'évaluation
- Synthesis IV Term 2°Document16 pagesSynthesis IV Term 2°NiJoha SJPas encore d'évaluation
- First Grade Second Grade Third Grade Fourth Grade Fifth GradeDocument1 pageFirst Grade Second Grade Third Grade Fourth Grade Fifth GradeNiJoha SJPas encore d'évaluation
- Assigments September From 23 To 27Document1 pageAssigments September From 23 To 27NiJoha SJPas encore d'évaluation
- Assigments September From 23 To 27Document1 pageAssigments September From 23 To 27NiJoha SJPas encore d'évaluation
- Logros Cuarto PeriodoDocument4 pagesLogros Cuarto PeriodoNiJoha SJPas encore d'évaluation
- Sintesis Periodo Iii Periodo 4° GradoDocument19 pagesSintesis Periodo Iii Periodo 4° GradoNiJoha SJPas encore d'évaluation
- Assigments September From 23 To 27Document1 pageAssigments September From 23 To 27NiJoha SJPas encore d'évaluation
- This Week You Have: September From 2 To 4: Monday: Social Test Tuesday: English Test Wednesday: Science TestDocument1 pageThis Week You Have: September From 2 To 4: Monday: Social Test Tuesday: English Test Wednesday: Science TestNiJoha SJPas encore d'évaluation
- Assigments From 16 To 20 SeptemberDocument1 pageAssigments From 16 To 20 SeptemberNiJoha SJPas encore d'évaluation
- Sintesis de Periodo Segundo III PeriodoDocument18 pagesSintesis de Periodo Segundo III PeriodoNiJoha SJPas encore d'évaluation
- Jueves de Prueba Tercer PeriodoDocument10 pagesJueves de Prueba Tercer PeriodoNiJoha SJPas encore d'évaluation
- Sintesis de Periodo Iii Periodo 5°Document13 pagesSintesis de Periodo Iii Periodo 5°NiJoha SJPas encore d'évaluation
- Sintesis de Periodo 1Document29 pagesSintesis de Periodo 1NiJoha SJPas encore d'évaluation
- Sintesis de III Periodo Grado 3Document19 pagesSintesis de III Periodo Grado 3NiJoha SJPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignments Week 22 To 26Document1 pageAssignments Week 22 To 26NiJoha SJPas encore d'évaluation
- Sintesis de Periodo IIIDocument17 pagesSintesis de Periodo IIINiJoha SJPas encore d'évaluation
- Sintesis de Periodo IIIDocument17 pagesSintesis de Periodo IIINiJoha SJPas encore d'évaluation
- Jueves de Prueba Tercer PeriodoDocument11 pagesJueves de Prueba Tercer PeriodoNiJoha SJPas encore d'évaluation
- Assigments From 20 To 23Document1 pageAssigments From 20 To 23NiJoha SJPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignments Week From July 29 To August 2Document1 pageAssignments Week From July 29 To August 2NiJoha SJPas encore d'évaluation
- Ingles Tercer Periodo - LogrosDocument4 pagesIngles Tercer Periodo - LogrosNiJoha SJPas encore d'évaluation
- Acompañamiento RecuperacionesDocument2 pagesAcompañamiento RecuperacionesNiJoha SJPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignments Week 16 To 19Document1 pageAssignments Week 16 To 19NiJoha SJPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignments Week 22 To 26Document1 pageAssignments Week 22 To 26NiJoha SJPas encore d'évaluation
- Acompañamiento Segundo MathDocument1 pageAcompañamiento Segundo MathNiJoha SJPas encore d'évaluation
- Addison+conn+cush+feo+adr IncidentalomaDocument65 pagesAddison+conn+cush+feo+adr IncidentalomaMjn BausatPas encore d'évaluation
- Phylum Arthropoda-2 Subphylum Crustacea: Ana Huamantinco Araujo 2018Document34 pagesPhylum Arthropoda-2 Subphylum Crustacea: Ana Huamantinco Araujo 2018Joselyn CarmenPas encore d'évaluation
- Segmental Neuromyotherapy - Basic Concepts and Practical ApplicationsDocument4 pagesSegmental Neuromyotherapy - Basic Concepts and Practical Applicationsweb3351Pas encore d'évaluation
- Bio 11 Lab Exam 3 ReviewerDocument5 pagesBio 11 Lab Exam 3 Revieweririsiri28Pas encore d'évaluation
- Non Skilled OSPE - EndocrineDocument8 pagesNon Skilled OSPE - EndocrineUltra Gamer promaxPas encore d'évaluation
- JeromeDocument2 pagesJeromeNads DecapiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Gen Bio 2 Q4 LAS 4 Module 14Document5 pagesGen Bio 2 Q4 LAS 4 Module 14KatsumiJ Aki100% (1)
- Assessment of Patients With Renal Disorders Management of Urinary Tract DisordersDocument16 pagesAssessment of Patients With Renal Disorders Management of Urinary Tract DisordersJhosita Flora LarocoPas encore d'évaluation
- 9 Abdominopelvic Regions of The BodyDocument25 pages9 Abdominopelvic Regions of The BodyTherese Mae DedoroyPas encore d'évaluation
- Blood Supply of The BrainDocument55 pagesBlood Supply of The BrainueumanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Sheehan SyndromeDocument6 pagesSheehan SyndromeArvie TagnongPas encore d'évaluation
- Kriya Sharir Paper 2Document11 pagesKriya Sharir Paper 2Amit PandyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Late Lower Arch CrowdingDocument4 pagesLate Lower Arch CrowdingchaitreePas encore d'évaluation
- Hemodynamics and Factors Affecting Blood FlowDocument13 pagesHemodynamics and Factors Affecting Blood Flowalfianhasbi2Pas encore d'évaluation
- KL MCQ 2Document2 pagesKL MCQ 2majaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pig DissectionDocument8 pagesPig DissectiondvinalPas encore d'évaluation
- Neurological Examination of The NewbornDocument21 pagesNeurological Examination of The Newborncristieristiie100% (1)
- Science Form 2 - Chapter 1Document46 pagesScience Form 2 - Chapter 1Mohamad TarmiziPas encore d'évaluation
- Hematopoiesis ErythropoiesisDocument8 pagesHematopoiesis ErythropoiesisASHLEY ALEXIS GUEVARRAPas encore d'évaluation
- Past Papers Section2Document13 pagesPast Papers Section2Jerilee SoCute Watts50% (2)