Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Vocab
Transféré par
Czar ParrenoCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Vocab
Transféré par
Czar ParrenoDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
K
Absorb Adaptation
I
To take up and store energy without reflecting or transmitting that energy. A characteristic of an organism that increases its chances of survival in its environment.
M
Plants absorb energy from the sun. Adaptation helps animals survive.
Analyze
To examine methodically by separating into parts and studying their interrelatedness.
Scientists analyze data.
Asteroid
A rocky or metallic object that orbits the Sun and is much smaller than a planet.
Asteroids orbit the sun.
Attraction
A term used to describe the electric or magnetic force exerted by oppositely charged objects or to describe the gravitational force that pulls objects toward each other.
The opposite sides of magnets attract.
Balanced forces
Forces that is equal in size but opposite in direction. See also force and unbalanced forces.
Balanced forces have the same size.
Behavior
A plant or animal action, reaction, or activity that occurs in response to stimuli (e.g., gravity, light, temperature).
Prey behaves carefully unlike predators.
Carnivore
An animal that obtains nutrients from eating other animals.
Carnivores get energy from other organisms.
Characteristic
A feature, quality, property, or trait of an object or organism.
Characteristics describe a feature of an organism.
Chemical change
Process by which substances are changed into different substances with different properties.
Chemical changes cant be undone.
Classify
To arrange in a specific order or group by categories based on similarities.
Scientist classify new animals by their characteristics.
Cleavage
A property used to describe how a mineral breaks apart along smooth surfaces.
The minerals cleavage was high.
Climate
The average pattern of weather that occurs in a certain location over many years.
The north has a cold climate
Community
Populations of different species of organisms Zebras and lions live in living together in the same geographic area. the same community.
Complete metamorphosis
Type of insect development characterized by Complete the presence of a larval stage with different metamorphosis has a feeding habits. larval stage.
Conclusion
A statement that tells what an investigation showed, based on observations and data.
After studying data scientists may lead to a conclusion.
Condensation .
The process by which water is changed from In condensation water a gas (water vapor) to a liquid; a stage of goes from a gas to a the water cycle liquid.
Conduct
To transmit heat, sound, or electricity through a medium.
Metals are good heat conductors.
Consumer
An organism in a food chain that obtains nutrients from producers or other consumers; consumers may be herbivores or carnivores. A group in a scientific experiment that serves as a reference for comparison to the experimental group; a group that is untreated by the factor being tested. Measurements or observations collected and recorded in an experiment or investigation.
Carnivores are consumers.
Control group
Controlled groups dont receive the independent variable.
Data
Data is collected from experiments.
Ecosystem
All the living and nonliving things that interact with each other in an environment.
Ecosystems include nonliving things.
Endangered species
A species whose population is so small that it is in danger of extinction.
Many animals are endangered species because of hunters.
Environment
An area that includes all living organisms and the surrounding physical features such as air, water, soil, weather, and landforms.
Desert animals live in a desert environment.
Erosion
The process by which rock, soil, and other weathered earth materials are moved from one place to another.
Erosion cause weathering.
Evaporation
The process by which water is changed from In evaporation water a liquid to a gas (water vapor); a stage of goes from liquid to gas. the water cycle.
Experiment
A scientific test or procedure that is carried out under controlled conditions to answer a scientific question.
In an experiment the hypothesis is tested.
Extinct species
A species that no longer exists.
Extinct species have no population.
Fertilization
The process by which the female reproductive cell (egg) is united with the male reproductive cell (sperm).
Fertilization is when an egg unites with a sperm.
Food chain
A diagram representing the transfer of energy from the Sun through producers and a series of consumers.
the first object in a food chain is the sun.
Force
A push or a pull that one object exerts on another object with or without direct contact (e.g., friction, gravity). See also balanced forces and unbalanced forces. A force that opposes motion through direct contact.
A force can be a pull or push.
Friction
During friction the things have to touch.
Germination
The process by which plants begin to grow from a seed or a spore.
During germination, a plant grows from a seed or spore.
Hardness
A property of a mineral that describes how easily it can be scratched.
If a substance has low hardness it can be scratched easily.
Hemisphere
Half of Earth (i.e., Northern, Southern, Eastern, Western).
Hemisphere is half the earth.
Herbivore
An animal that obtains nutrients only from plants.
Herbivores eat plants.
Humidity
A measure of the amount of water vapor in the air.
When it rains the air is humid.
Igneous rock
A type of rock that forms from cooled magma or lava.
Igneous rock comes from magma or lava.
Incomplete metamorphosis
Type of insect development characterized by the similar appearance of pre-adults and adults. An explanation based on evidence that is not directly observed.
The insect is going through incomplete metamorphosis.
Inference
Books are used for inference.
Inherited trait
A trait or characteristic that is passed from parent to offspring.
Children inherit traits from their parents.
Insulator
A material used to reduce or prevent the transfer of electricity, heat, or sound.
Non-metals are good insulators.
Invertebrate
An animal that lacks a backbone.
The spine is the invertebrate.
Investigation
An organized scientific study of the natural world that may include making systematic observations, asking questions, gathering information, analyzing data, summarizing results, drawing conclusions, and/or communicating results.
Scientist investigate the natural world.
Larva
An early stage in the life cycle of an organism that will undergo complete metamorphosis.
The caterpillar was in a larva.
Life cycle
The stages of an organisms growth and development.
The life cycle of insects is short.
Luster
A property of a mineral that describes how it appears when it reflects light.
Gold has high luster.
Mass
The amount of matter a substance or object has.
Solids have more matter in them than gases.
Matter
Anything that takes up space and has mass.
Everything but energy has matter.
Mechanical energy
A type of energy an object has due to its motion or position.
The moving car has high mechanical energy.
Metamorphic rock
A type of rock that is formed over time from existing rock due to extreme pressure and/or heat.
The metamorphic rock came from underground.
Mineral
A naturally occurring inorganic solid with a distinct chemical composition and crystalline structure.
The minerals are rare.
Moon
A natural object that orbits a planet.
The moon orbits the earth.
Nutrient
A substance that an organism needs to survive and grow.
Animals get nutrients from other organisms.
Nymph
A pre-adult insect undergoing incomplete metamorphosis.
Nymphs undergo incomplete metamorphosis.
Observation
Information about the natural world gathered through the senses and/or scientific instruments.
Data is gathered from observation.
Omnivore
An organism that obtains nutrients from both plants and animals.
Omnivores eat both plants and animals.
Organism
A living thing.
Any living thing is an organism.
Ovary
The female reproductive organ that produces and contains egg cells.
Ovaries contain eggs.
Physical change
A change of a substance from one form to another without a change in its chemical properties.
Physicals changes can be undone.
Pistil
The female reproductive structure of a flowering plant.
The pistil is the female reproductive structure of a flowering plant. Younger people have higher pitched voices.
Pitch
The relative frequency (high or low) of a sound as perceived by a listener.
Planet
A large body in space that orbits a star and does not produce its own light.
Earth is a planet.
Polar zone
A climate zone characterized by very little precipitation and extremely cold temperatures.
Antarctica is a polar zone.
Pollen
The fine dustlike powder that contains the male reproductive cells of seed-bearing plants.
Bees carry pollen
Pollinate
To transfer the pollen from the male reproductive structure to the female reproductive structure to fertilize flowering plants. All members of the same species living together at the same time in the same area.
Bess pollinate flowers.
Population
China has a high population.
Precipitation
A form of water (e.g., hail, rain, sleet, snow) that condenses in the atmosphere and falls to Earths surface.
Precipitation forms in clouds.
Predator
An organism that kills and eats other organisms (prey).
Wolves are predators.
Predict
To state what one thinks will happen under certain conditions based on data or observation.
Fortune tellers predict the future.
Prey
An organism that is killed and/or eaten by another organism (predator).
Prey gets eaten by predators.
Producer
An organism that produces its own food.
Producers produce their own food.
Pupa
A stage in the life cycle of an insect that occurs between larva and adult.
Pupas occur between larva and adult.
Reflect
To bounce light, sound, or heat off of a surface.
Mirrors reflect light.
Repel
To force away or apart.
Bugs repellents repel bugs.
Reproduction
The process of making more organisms of the same kind.
Reproduction makes more of the same organisms.
Revolution
The motion of one object around another object.
The moon revolves around the earth.
Rotation
The turning of an object on its axis.
The earth rotates on its axis.
Sedimentary rock
A type of rock formed from layers of sediment.
Sedimentary rock forms from layers.
Soil
The loose top layer of Earths surface made of weathered rock and organic matter.
The soil is filled with nutrients for plants.
Solar system
A system of planets and other bodies that orbits a star.
A solar system only has one star.
Species
A group of the same kind of organisms that can mate and produce offspring that can reproduce.
Cats and dogs arent in the same species.
Speed
The distance traveled by an object in a given amount of time.
The cars speed is fast.
Spore
A seedlike structure that produces a new plant (e.g., ferns or mosses).
Spores produce a new plant.
Stamen
The male reproductive structure of a flowering plant.
The stamen is the male reproductive structure of a plant.
Star
A large object in space that is made of gas and produces its own light.
The sun is a star.
State of matter
The form matter can take (e.g., solid, liquid, gas).
Water is a liquid.
Streak
The color of the powder of a mineral when it is rubbed on a streak plate.
The mineral has a yellow streak.
Technology
The use of scientific knowledge and processes to solve practical problems.
Anything manmade is technology.
Temperate zone
A climate zone located between the tropics and the polar circles generally characterized by moderate temperatures rather than extremely hot or cold temperatures. A term used to describe a question that can be answered through an experiment or observation.
Polar bears live in cold temperature zones.
Testable (scientifically testable)
Questions about time travel are not testable.
Texture
A physical property of a solid used to describe its surface.
The rock had a rough texture.
Trials
Multiple sets of measurements or observations in a scientific investigation.
In an experiment you have to do at least 3 trials.
Tropical zone
A climate zone near the equator characterized by warm temperatures.
Tropical zone are near the equator.
Unbalanced forces
Forces that are unequal in size and may or may not be opposite in direction. See also balanced forces and force. A term used to describe the certainty of data or results of an investigation or experiment.
Unbalanced forces are not equal.
Valid
Is? Is not a valid question.
Variable
An event, condition, or factor that can be changed or controlled in order to study or test a hypothesis in a scientific experiment.
There are 3 types of variables.
Vertebrate
An animal that has a backbone.
Humans are vertebrates.
Volume
Theamount of space an object or substance occupies.
The boxes volume was 3ft squared.
Water cycle
The continuous movement of water through the environment by evaporation, condensation, precipitation, and runoff.
Water undergoes the water cycle.
Water vapor
The gas state of water.
The air is filled with water vapor.
Weather
The condition of the atmosphere at a given time and place.
How the weather today?
Weathering
The process by which rocks and other surfaces are broken down.
During weathering rocks break down.
Weight
A measure of the force of gravity on an object.
Weight differs due to gravity.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Design With Nature by Ian McHargDocument9 pagesDesign With Nature by Ian McHarganamontana23100% (3)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- TKT CLIL - CLIL Lesson On CellsDocument5 pagesTKT CLIL - CLIL Lesson On CellsMaksym BuchekPas encore d'évaluation
- Business Proposal FinalDocument17 pagesBusiness Proposal FinalAnne AsuncionPas encore d'évaluation
- Ecology Notes!!Document10 pagesEcology Notes!!Raudha Athif100% (3)
- Lesson 2 Leaves - The Food Factory of PlantsDocument4 pagesLesson 2 Leaves - The Food Factory of PlantsRama Nathan0% (2)
- Growing Crops by Electricity 1916 Dudgeon PDFDocument48 pagesGrowing Crops by Electricity 1916 Dudgeon PDFMarkAban100% (5)
- Cornstarch As A Thickening AgentDocument2 pagesCornstarch As A Thickening AgentCreciabullecerPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Structure FunctionDocument26 pagesCell Structure FunctionRonnelPas encore d'évaluation
- Effects of Exposing Green Plants To Green LightDocument3 pagesEffects of Exposing Green Plants To Green LightffPas encore d'évaluation
- Saving The PlanetDocument2 pagesSaving The Planetjhudy roaPas encore d'évaluation
- From Seed To Plant Kindergarten Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesFrom Seed To Plant Kindergarten Lesson Planapi-396744514100% (1)
- Biology Reviewer Biological DiversityDocument23 pagesBiology Reviewer Biological DiversityAndrea Grace Bayot AdanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit Lesson PlanDocument23 pagesUnit Lesson PlanDena SiegelPas encore d'évaluation
- Nutrition Foundation: Healthy Soils For A Healthy LifeDocument1 pageNutrition Foundation: Healthy Soils For A Healthy Liferon9123Pas encore d'évaluation
- AQA GCSE Combined B1 Test 1 Beginner QPDocument20 pagesAQA GCSE Combined B1 Test 1 Beginner QPMax CollinsPas encore d'évaluation
- Parts and Functions of PlantsDocument21 pagesParts and Functions of PlantsRaz QuipedPas encore d'évaluation
- Class 8 Science NCERT +Document5 pagesClass 8 Science NCERT +Titan MusicPas encore d'évaluation
- Xenoscape Quickstart EngDocument90 pagesXenoscape Quickstart Engyb6j7g9h7rPas encore d'évaluation
- Aging of PlantDocument30 pagesAging of PlantMujahid HussainPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic 8: Transport in PlantsDocument18 pagesTopic 8: Transport in PlantsCOXMIC FNPas encore d'évaluation
- Worksheet 1.1A: Plant Cell Structure and FunctionDocument38 pagesWorksheet 1.1A: Plant Cell Structure and FunctionLyaz Antony100% (5)
- WWW Luxurydefinedcom April 2018pdfDocument2 pagesWWW Luxurydefinedcom April 2018pdfnudchaPas encore d'évaluation
- Performance of Fig (Ficus Carica L.) Under Different Planting DensitiesDocument9 pagesPerformance of Fig (Ficus Carica L.) Under Different Planting DensitiesPiragas Naìdu KumaravellPas encore d'évaluation
- Flower Seeds - Biology and TechnologyDocument383 pagesFlower Seeds - Biology and TechnologyLuis F. García100% (5)
- Morrison 1988Document18 pagesMorrison 1988Kristem KertzeifPas encore d'évaluation
- Practice Tests - For TuesdayDocument92 pagesPractice Tests - For Tuesday2004 2810Pas encore d'évaluation
- Class X Bioworksheet-1Document5 pagesClass X Bioworksheet-1krithikPas encore d'évaluation
- Exotic Plants As A Key Resource For Frugivorous Birds in Anthropized EnvironmentsDocument2 pagesExotic Plants As A Key Resource For Frugivorous Birds in Anthropized EnvironmentsdarlellyPas encore d'évaluation
- 5th Liquid Filter GreenhouseDocument47 pages5th Liquid Filter GreenhouseChristopher SojournerPas encore d'évaluation
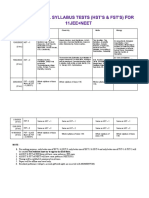
- 11hst & FST Final ScheduleDocument2 pages11hst & FST Final SchedulePawowPas encore d'évaluation