Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Research Paper With Abstract (Kirti)
Transféré par
piyushji125Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Research Paper With Abstract (Kirti)
Transféré par
piyushji125Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Abstract:
In an ad hoc network, the transmission range of nodes are limited; hence nodes mutually cooperate with its neighboring nodes in order to extend the overall communication. However, along with the combination of nodes, there may be some reluctant nodes like selfish nodes and malicious nodes present in the network. Such nodes degrade the performance of the network. This paper, gives a solution using reputation based mechanism and credit based mechanism. These include different strategies by which non cooperative nodes are detected, isolated and/or prevented, their advantages and limitations. Also, a global reputation based scheme is proposed in this paper for the detection and isolation of selfish node. A cluster head is used which is responsible for reputation management of each node in the network. Detection of selfish nodes is accomplished which are created due to nodes conserving their energy using NS2. After their detection, performance analysis of network with selfish node and the network after isolation of selfish node is carried out. Keyword: Manet,ns2,RIP,tcp,wireless,aodv.
simulation results. In the last Section V concludes and direction for future work.
Literature survey:
1. Isolating selfish nodes by Reputation based mechanism M. Refaei [1] introduces a reputation mechanism for building trust among nodes. Here, a distributed Tamer reputation evaluation scheme is implemented by neighboring nodes based on completion of the requested services. For each successful delivery of packets, node increases the reputation index of its next neighbor that forwarded the packet and packet delivery failures result in penalty applied to such node by decreasing their reputation index. There is no need of exchanging of reputation information among nodes, Thus involves less overhead. 2. CORE Pietro Michiardi and Refik Molva et al [2] schematized a Collaborative Reputation mechanism which is use to calculate reputation value of node to make decision about isolated and cooperative nodes. Core uses a watchdog component for monitoring nodes reputation with the help of past behavior. It awarded nodes for their good behavior and punish for their bad behavior. 3. Reputation based system for encouraging the cooperation of nodes. Tiranuch Anantvalee and Jie Wu[3] proposed a new category of a node known as Suspicious node beside between cooperative and selfish node. In this paper, they describe a state model for deciding what to do with node in each state and state is controlled by timing period. 4. Reputation based dynamic source routing protocol
Introduction: A Mobile ad-hoc network is a set
of self-directed nodes that communicate with each other in dynamic topology environment. There is no centralized management for the nodes. In order for a node to communicate to other node that is out of its radio range, then the cooperation of intermediate nodes is most important in the network. This type of communication is called multi hop communication. MANET provides anytime and anywhere services to user for collaboration among nodes. The main concentration is on packet forwarding because some nodes only cooperate for their own communication, such nodes known as selfish nodes. A selfish node damage or interrupt the network. Our goal is to construct a victorious atmosphere. The next section entails a discussion of some related efforts which is followed by RIP system design in section III. Section IV describes protocol and
Sangheetaa Sukumran[4] present a reputation mechanism using watchdog monitoring for construction of trustable network. In this packet route determine by reputation value. Nodes can maintain high reputation value only by successful packet delivery. If a node reputation is lower than threshold value than nodes are put in the gray list and if a node reputation is decrease continuously than node puts into black list and denote as a selfish node. But this protocol does not deal with selfish nodes.
The Proposed Approach: Description: Operation: Design Consideration (Parameter) End to End Delay Throughput Packet Delivery Ratio: This Paper proposes a new solution that is an enhancement of the basic AODV routing protocol, which will be able to avoid black holes. To reduce the probability it is proposed to wait and check the replies from all the neighboring nodes to find a safe route. According to this proposed solution the requesting node without sending the DATA packets to the reply node at once, it has to wait till other replies with next hop details from the other neighboring nodes. After receiving the first request it sets timer in the Timer Expired Table, for collecting the further requests from different nodes that having hop count equals to 2. It will store the sequence number, and the time at which the packet arrives, from those nodes to check which node is replying. The time for which every node will wait is proportional to its distance from the source. It calculates the timeout value based on arriving time of the first route request. According to Trust Based AODV the requesting node transmit request to the node having hop count 2, then calculate the ratio of their total reply and time taken by all reply and generate trust value between 0 to 10, for those the neighboring nodes who reply for the request will
have trust value greater than 5, the neighboring node that are reply for some of the request will have reply ratio less than those neighbor who are good to reply, and these neighbor have trust value less than 5, based on these trust values we find neighbors who have trust value minimum and remove its entry from the routing table, and based on trust values a safe route to the destination to reduce the probability of Black Hole Attack is generated. After the trust value calculation, it first checks in Routing Table whether there is any entry for the node and its trust value for hop node. If any entry to next hop node is present in the reply paths it assumes the paths are correct or the chance of malicious paths is limited.
In the above figure 3, S wants to transmit to D. So it first transmits the route request to all the neighboring nodes. Here node 1, node M and node 2 receive this request. The malicious node M has no intention to transmit the DATA packets to the destination node D but it wants to intercept/collect the DATA from the source node S. So it immediately replies to the request as (M 4). Instead of transmitting the DATA packets immediately through M, S has to wait for the
reply from the other nodes. After some time it will receive the reply from node 1 as (1 3), and node 2 as (2 3). According to this proposed solution it first checks the path in the routing table that contains trust value acceptable for next hop node to the destination. If there is a path node having trust than select that path and transmits the data through that path. The routing table from S to D is given in table 1.
Evaluation: 1. Existing Model
2. 3.
Existing model with Attack Improvement in existing model with attack
S.NO. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 7
Parameter No of Simulating Nodes Area size of topography x(m) Area size of topography y(m) Simulating routing protocol Simulating time Traffic Type Data Type Packet Size Node Placement
Value 30 800 600 AODV 100 second CBR/FT P TCP/U DP 1500 Byte Dynam ic 250 m
Wireless range
Speed
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Active RF Id Reader DescriptionDocument2 pagesActive RF Id Reader Descriptionpiyushji125Pas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Supply of Electronic Components As Per List Annexure IDocument10 pages1 Supply of Electronic Components As Per List Annexure Ipiyushji125Pas encore d'évaluation
- Small Print ComponentDocument4 pagesSmall Print Componentpiyushji125Pas encore d'évaluation
- Energy Efficient Approach For Converss: Routing Protocol For Wireless NetworksDocument4 pagesEnergy Efficient Approach For Converss: Routing Protocol For Wireless Networkspiyushji125Pas encore d'évaluation
- Voice Recorder IcDocument43 pagesVoice Recorder Icpiyushji125Pas encore d'évaluation
- XbeeDocument33 pagesXbeepiyushji125Pas encore d'évaluation
- SMS Based Enotice Board For CollegeDocument21 pagesSMS Based Enotice Board For Collegepiyushji125Pas encore d'évaluation
- Uc AT89s52: LCD Display KeypadDocument2 pagesUc AT89s52: LCD Display Keypadpiyushji125Pas encore d'évaluation
- Diploma B.E./B.Tech M.E./M.TechDocument1 pageDiploma B.E./B.Tech M.E./M.Techpiyushji125Pas encore d'évaluation
- Building Sensors and Motors For The Handy Board: Connector Wiring TechniqueDocument8 pagesBuilding Sensors and Motors For The Handy Board: Connector Wiring Techniquepiyushji125Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ravi Yadav: Central India Institute of TechnologyDocument4 pagesRavi Yadav: Central India Institute of Technologypiyushji125Pas encore d'évaluation
- Synopsis Point M.tech III SemDocument7 pagesSynopsis Point M.tech III Sempiyushji125Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ijser: GUI Based Device Controller Using MATLABDocument4 pagesIjser: GUI Based Device Controller Using MATLABpiyushji125Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5795)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Train TicketDocument2 pagesTrain TicketGautam KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Ge Washing Machine ManualDocument52 pagesGe Washing Machine Manuallillith1723Pas encore d'évaluation
- Media DRIVEON Vol25 No2Document21 pagesMedia DRIVEON Vol25 No2Nagenthara PoobathyPas encore d'évaluation
- Tugas Moneter CH 4 - Dewi Lucky Aryanti Sinaga F1119025Document4 pagesTugas Moneter CH 4 - Dewi Lucky Aryanti Sinaga F1119025Scream InungPas encore d'évaluation
- White Paper - Data Communication in Substation Automation System SAS - Part 1 Original 23353Document5 pagesWhite Paper - Data Communication in Substation Automation System SAS - Part 1 Original 23353sabrahimaPas encore d'évaluation
- Eligibility To Become IAS Officer: Career As A IAS Officer About IAS OfficerDocument4 pagesEligibility To Become IAS Officer: Career As A IAS Officer About IAS Officersamiie30Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sub Clause 1.15 Limitation of Liability PDFDocument4 pagesSub Clause 1.15 Limitation of Liability PDFBogdanPas encore d'évaluation
- Fernbetätigte Armaturen: Remote Controlled Valve SystemsDocument14 pagesFernbetätigte Armaturen: Remote Controlled Valve SystemslequangPas encore d'évaluation
- Namma Kalvi 12th Maths Chapter 4 Study Material em 213434Document17 pagesNamma Kalvi 12th Maths Chapter 4 Study Material em 213434TSG gaming 12Pas encore d'évaluation
- Read Me - CADWorx Plant 2019 SP2 HF1Document4 pagesRead Me - CADWorx Plant 2019 SP2 HF1Himanshu Patel (Himan)Pas encore d'évaluation
- BS en 12285-1-2003 (2006)Document162 pagesBS en 12285-1-2003 (2006)dahzahPas encore d'évaluation
- Design of Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion Cages With Various Infill Pattern For 3D Printing ApplicationDocument7 pagesDesign of Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion Cages With Various Infill Pattern For 3D Printing ApplicationdhazliPas encore d'évaluation
- Tapspp0101 PDFDocument119 pagesTapspp0101 PDFAldriel GabayanPas encore d'évaluation
- Precision Probability Index (Elf)Document20 pagesPrecision Probability Index (Elf)EdsonnSPBrPas encore d'évaluation
- BioEdit Version 7.0.0 PDFDocument192 pagesBioEdit Version 7.0.0 PDFJovanderson JacksonPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermo King CG 2000Document155 pagesThermo King CG 2000Connie TaibaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ap Human Geography Unit 5Document4 pagesAp Human Geography Unit 5api-287341145Pas encore d'évaluation
- Metric MIL-STD-1504C (USAF) 01 March 2007 Supersedes MIL-STD-1504B 8 June 1989Document11 pagesMetric MIL-STD-1504C (USAF) 01 March 2007 Supersedes MIL-STD-1504B 8 June 1989HenryPas encore d'évaluation
- Unclaimed Abandoned Vehicles Feb 2022Document66 pagesUnclaimed Abandoned Vehicles Feb 2022kumar himanshuPas encore d'évaluation
- 02 - STD - Bimetal Overload Relay - (2.07 - 2.08)Document2 pages02 - STD - Bimetal Overload Relay - (2.07 - 2.08)ThilinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Mid Semester Question Paper Programming in CDocument8 pagesMid Semester Question Paper Programming in CbakaPas encore d'évaluation
- Sample Rubrics MakingDocument4 pagesSample Rubrics MakingKerstmis “Scale” NataliaPas encore d'évaluation
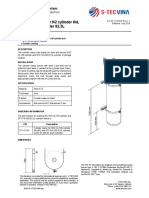
- Cylinder Clamp For N2 Cylinder 84L and FM-200 Cylinder 82.5LDocument1 pageCylinder Clamp For N2 Cylinder 84L and FM-200 Cylinder 82.5LNguyễn Minh ThiệuPas encore d'évaluation
- Ebook Principles of Corporate Finance PDF Full Chapter PDFDocument67 pagesEbook Principles of Corporate Finance PDF Full Chapter PDFmichelle.haas303100% (28)
- Guide To Manually Importing/Transferring Your Livery For FH4/FM7/FH3 PCDocument12 pagesGuide To Manually Importing/Transferring Your Livery For FH4/FM7/FH3 PCLennike SantosPas encore d'évaluation
- (L) Examples of Machine Shop Practice (1910)Document54 pages(L) Examples of Machine Shop Practice (1910)Ismael 8877100% (1)
- Corality ModelOff Sample Answer Hard TimesDocument81 pagesCorality ModelOff Sample Answer Hard TimesserpepePas encore d'évaluation
- Tween 80 CoADocument1 pageTween 80 CoATấn Huy HồPas encore d'évaluation
- User's Guide: Smartpack2 Master ControllerDocument32 pagesUser's Guide: Smartpack2 Master Controllermelouahhh100% (1)
- Lesson Worksheet: 6.1A MeanDocument7 pagesLesson Worksheet: 6.1A Meanwaiman fuPas encore d'évaluation