Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Training
Transféré par
Shashikant BhandariDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Training
Transféré par
Shashikant BhandariDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Quality and Employee Training
Training
Training is an organized, systematic series of activities designed to enhance an individual's work-related knowledge, skills and understanding and /or motivatio n
LEARNING A relatively permanent change in behavior due to knowledge and experience
Changes in immediate or potential behavior Change must be relatively permanent C hange must be due to knowledge and/or experience
Need for training Quality of the existing labor pool Global competition ogy transfer problems Changing demographic Rapid and continual change technol
Benefits of Training
Fewer production Errors Increased productivity Improved quality Decreased turnov er rate Lower staffing costs Improved safety and health Fewer accidents Minimize d insurance costs Increased flexibility of employees better response to change I mproved communication Better teamwork Better interpersonal relationship
CONDITIONS OF THE LEARNING ENVIORNMENT Learner readiness Previous Knowledge Whole versus part learning massed versus sp ace practice Reward motivates over learning Knowledge of result (feedback) atten tion Retention
People learn best when they are ready to learn
Previous Knowledge
People learn more easily when what they are learn can be related to something th ey already know
WHOLE VERSUS PART LEARNING Complex task is to be broken down into its parts and the learner should learn ea ch part separately. The process starts with the simplest task and going on the m ost difficult.
Massed versus spaced practice Practicing the new behavior and taking rest periods in between is more effective than practing the new behavior without break
Success in learning tends to stimulate additional learning
Overlearning Overlearning is desirable when the task to be learned in program is not likely t o be immediately practiced in the work situation and when performance must be ma intained during periods of emergency and stress.
Knowledge of Results For trainee to improve training performance , they need to receive timely and sp ecific feedback or knowledge of results
Attention Trainers should try to design training programs and materials to ensure that tra inees devote attention to them.
Retention Trainer should make the content meaningful to them and they should have an easie r time understanding and remembering it Trainer can make training meaningful by
Overview of what is to be learned Using examples and terms familiar to the train ee Organizing material from simple to complex Rehearsal
Training methods selected should be Motivate the trainee to learn the new skill Illustrate the desired skills to be learned Be consistent with the content Allow for active participation by trainees to fit with adult learning model Provide o pportunities for practice and over learning Provide feedback on performance duri ng training Encourage positive transfer from the training to the job Be cost eff ective Training Methods
General Tips Don't be too quick to select course delivery mode. Don't jump to the decision on course delivery medium until you have complete and accurate definitions of thre e things: (Performance objectives - obtained during task analysis). What the learner must be able to do at the conclusion of the training What the learner already knows a nd can already do before the training begins
Tip 2: Document the Audience Analysis and make it a part of the training design documentation. Concentrate on the characteristics of the new-hire forming the job. Workers who are currently per
Tip 3: Make sure the Task Analysis is complete and accurate. . An accurate and complete task analysis is the key to effective and efficient tra ining. Weaknesses in the task analysis can result in wasted time, wasted money, and poor worker performance.
Tip 4: Be specific when defining prerequisite skills and knowledge. In many programs, prerequisite skills and knowledge are defined in such ambiguou s terms or at such a high level that the prerequisite training developed (or pur chased) is far more than is needed or prudent.
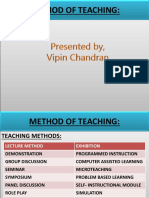
Choosing the methods for the Training program TRAINING METHODS METHODS TRANSMITTING INFORMATION TO THE LEARNER METHODS EXPERIINTIAL IN NATURE
INFORMATIONAL TRAINING METHODS
LECTURES AUDIOVISUALS INDEPENDENT STUDY PROGRAMMED INSTRUCTION
EXPERIENTAIL METHODS ON JOB TRAINING (OJT) COMPUTER BASED TRAING (CBT) COMPUTER ASSISTED TRAINING (CA I) EQUIPMENT SIMULATIONS GAMES AND OTHER SIMULATIONS CASE ANALYSIS ROLE PLAYING BEHAVIOR MODELING
INFORATMIONAL TRAINNING METHODS USERS LECTURE Gaining new knowledge To present introductory material Equally as good as PI an Low Cost. Reaches a large audience at one time. Audience is often comfortable wi th it. Learners are passive Poor transfer. Depends on the lecturer's ability. Is not tailored to individual trainees. BENEFITS LIMITATION AUDIOVISUALS Gaining new knowledge Gaining attention Can reach a large audience at one time Allows for replays. Versatility Is not tailored to individual trainees. Must be updated. Passive Learners.
INFORATMIONAL TRAINNING METHODS USERS Independent Study Gaining new knowledge Completing degree requirements Continuous education Allows trainees to go at their own pace. Minimizes trainers time. Expensive to develop a library of materials. Materials must be designed to adjust to varying reading levels. Performance depends on trainees motivation. Is not applicable to all jobs BENEFITS LIMITATION Minimizes costs of development Programmed Instruction Gaining new knowledge preparation to ensure that all trainees have similar backg rounds. Allows trainees to go at their own pace. Can guarantee mastery at a spec ified level. Encourages active trainee involvement. Provides immediate feedback to trainees. Expensive to develop Is not applicable to all tasks (e.g., cognitiv e tasks). Does not lead to higher performance than lectures
EXPERIENTIAL TRAINNING METHODS USERS BENEFITS Good transfer. LIMITATION Depends on the trainers skills and willingness. OJT Learning job skills Apprenticeship training Job rotation Limited trainer costs. High trainee motivation since training is relevant. May be costly due to lost production and mistakes. May have frequent interruptions due to job demands. Often is haphazardly done. T rainees may learn bad habits CBT Gaining new knowledge Drill and practice Individualized training Self-paced. Sta ndardization of training over time. Feedback given. Good retention Costly. Train ees may fear using computers. Limited opportunities for trainee interaction. Les s useful for training interpersonal skills.
EXPERIENTIAL TRAINNING METHODS USERS Equipment Simulators To reproduce real-world conditions For physical and cognitive skills For team tr aining BENEFITS Effective for learning and transfer. LIMITATION Costly to develop. Can practice most of the job skills Sickness can occur Requires good fidelity. Games and Simulations Decision-making skills Management training Interpersonal skills Resembles the job tasks. Highly competitive. Provides feedback. Presents realistic challenges Time-consuming May stifle creativity
EXPERIENTIAL TRAINNING METHODS USERS Case Study or Analysis Decision making skills Analytical skills Real-world training materials. Criticiz ed as being unable to teach general management skills. Trainers often dominate d iscussions BENEFITS Decision-making practice. LIMITATION Must be updated Communication skills To illustrate diversity of solutions Active learning Good for developing problemsolving skills Role Play For changing attitudes To practice skills Gain experience of other roles. Active learning. Initial resistance of trainees. Trainees do not take it seriously To analyze interpersonal problems Close to reality
EXPERIENTIAL TRAINNING METHODS USERS Behavior Modeling To teach interpersonal skills To teach cognitive skills Provides feedback. Reten tion is improved. Can improve self-concept. May be costly to develop BENEFITS Allows practice. LIMITATION Time-consuming Sensitivity Training To enhance selfawareness To allow trainees to see how others see them To improve insights into differences May be threatening. Can reduce prejudice. May have limited generalizability to job situations Can change interpersonal behaviors
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Recycling Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesRecycling Lesson Planapi-315487341100% (3)
- Variation in Inter Language (Tarone 1988)Document4 pagesVariation in Inter Language (Tarone 1988)mrouhaneePas encore d'évaluation
- Comparative Summary of 5 Learning TheoriesDocument2 pagesComparative Summary of 5 Learning TheoriesMonique Gabrielle Nacianceno AalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Brainstorming - by Alex Osborn of USA in 1950Document9 pagesBrainstorming - by Alex Osborn of USA in 1950Sreenath NavaneethanPas encore d'évaluation
- ArgumentDocument36 pagesArgumentAhmad Fahrurrozi ZSPas encore d'évaluation
- Assessment 5 Guidelines - Reflective Learning (FINAL)Document3 pagesAssessment 5 Guidelines - Reflective Learning (FINAL)amanittaPas encore d'évaluation
- Method of TeachingDocument79 pagesMethod of TeachingSubhada GosaviPas encore d'évaluation
- ThelenDocument18 pagesThelenAvadani Diana100% (1)
- Week 2 Language Acquisition Theories and Teaching Methodologies PDFDocument3 pagesWeek 2 Language Acquisition Theories and Teaching Methodologies PDFMeryem AfayaPas encore d'évaluation
- Stanford-Binet Test Scoring Explained - Stanford-Binet IQ TestDocument3 pagesStanford-Binet Test Scoring Explained - Stanford-Binet IQ TestLM R50% (2)
- Cheatham-Clark Kozma DebateDocument8 pagesCheatham-Clark Kozma Debateapi-377835688Pas encore d'évaluation
- Presentation On PSYCHOLOGY : Historical PerspectiveDocument22 pagesPresentation On PSYCHOLOGY : Historical PerspectiveKaveri ChauhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Air Balloon Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesAir Balloon Lesson Planapi-311863648Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sir Ahmad Assignmnt 1Document5 pagesSir Ahmad Assignmnt 1Saba HanifPas encore d'évaluation
- Philosophy of ManDocument22 pagesPhilosophy of ManHNicdaoPas encore d'évaluation
- The Allegory of The Cave: They Used Applied To The Things They See Passing Before ThemDocument1 pageThe Allegory of The Cave: They Used Applied To The Things They See Passing Before ThemJhane AbaricoPas encore d'évaluation
- Descartes S Conception of Mind Through TDocument26 pagesDescartes S Conception of Mind Through TAnonymous pZ2FXUycPas encore d'évaluation
- BDI AgentDocument26 pagesBDI AgentAnkurGuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- American Psychologist Volume 34 Issue 10 1979 (Doi 10.1037 - 0003-066x.34.10.906) Flavell, John H.Document6 pagesAmerican Psychologist Volume 34 Issue 10 1979 (Doi 10.1037 - 0003-066x.34.10.906) Flavell, John H.Shoffan ShoffaPas encore d'évaluation
- Three Domains of LearningDocument1 pageThree Domains of Learningapi-418085936Pas encore d'évaluation
- Document 2Document13 pagesDocument 2sobia sajjadPas encore d'évaluation
- UNDERSTANDING THE SELF - Revised Chapter 1Document15 pagesUNDERSTANDING THE SELF - Revised Chapter 1Lady Jane MadridPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 6 Consumer Perception: Consumer Behavior, 10e (Schiffman/Kanuk)Document32 pagesChapter 6 Consumer Perception: Consumer Behavior, 10e (Schiffman/Kanuk)sidhanthaPas encore d'évaluation
- Artificial Intelligence Vs Human IntelligenceDocument11 pagesArtificial Intelligence Vs Human IntelligenceSusirani50% (2)
- AS OF: Lesson 2: Authentic AssessmentDocument2 pagesAS OF: Lesson 2: Authentic AssessmentRc Consultado Cecogo100% (2)
- Id490 How Students Learn and StudyDocument4 pagesId490 How Students Learn and StudyB.y. NgPas encore d'évaluation
- x3B Marzano - New - Taxonomy - Chart - With - Verbs - 3.16.121 PDFDocument1 pagex3B Marzano - New - Taxonomy - Chart - With - Verbs - 3.16.121 PDFSistemas EdutecPas encore d'évaluation
- My QuestionsDocument31 pagesMy QuestionsfenixicaPas encore d'évaluation
- Make It Stick The Science of Successful Learning by Peter CDocument5 pagesMake It Stick The Science of Successful Learning by Peter Capi-502145517Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pedagogy QuizDocument8 pagesPedagogy QuizUsman MariPas encore d'évaluation