Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Mass Transfer
Transféré par
balajigandhirajanDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Mass Transfer
Transféré par
balajigandhirajanDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Part A : 1. Examples of Diffusion mass transfer 2. Ficks law of diffusion. 3. Two examples of convective mass transfer. 4.
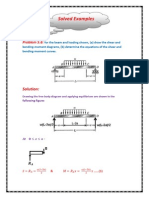
Define i) Mass concentration ii) Mole fraction 5. Define Sherwood number & Schmidt number for mass transfer. Part B 1. (a) A mixture of O2 and N2 with their partial pressures in the ratio 0.21 to 0.79 is in a container at 25C. Calculate the molar concentration, the mass density, the mole fraction and the mass fraction of each species for a total pressure of 1 bar. ( b) Write short note Equimolar counter diffusion. (6) 2. (a) Estimate the diffusion rate of water from the bottom of the test tube 10 mm diameter and 15 cm long in to dry atmospheric air at 25C. Diffusion coefficient -4 2 of water in air is 0.255 x 10 m /s. (8) (b) An open pan, 20 cm diameter and 8 cm deep contains water at 25C and is exposed to dry atmospheric air. Estimate the diffusion coefficient of water in air, -4 if the rate of diffusion of water is 8.54 x 10 kg/h. (8) 3. (a) Dry air at 20C ( = 1.2 kg/m , v = 15 x l0 m /s, Dab = 4.2 x l0 m /s) flows over a flat plate of length 50 cm which is covered with a thin layer of water at a velocity of 1 m/s. Estimate the average mass transfer coefficient. (8) (b) Air at 20C and atmospheric pressure, containing small quantities of iodine flows with a velocity of 4 m/s inside a 4 cm inner diameter tube. Determine the -5 2 mass transfer coefficient. Assume Dab = 0.75 x l0 m /s. (8) Part A : 1. Examples of Diffusion mass transfer 2. Ficks law of diffusion. 3. Two examples of convective mass transfer. 4. Define i) Mass concentration ii) Mole fraction 5. Define Sherwood number & Schmidt number for mass transfer. Part B 1. (a) A mixture of O2 and N2 with their partial pressures in the ratio 0.21 to 0.79 is in a container at 25C. Calculate the molar concentration, the mass density, the mole fraction and the mass fraction of each species for a total pressure of 1 bar. ( b) Write short note Equimolar counter diffusion. (6) 2. (a) Estimate the diffusion rate of water from the bottom of the test tube 10 mm diameter and 15 cm long in to dry atmospheric air at 25C. Diffusion coefficient -4 2 of water in air is 0.255 x 10 m /s. (8) (b) An open pan, 20 cm diameter and 8 cm deep contains water at 25C and is exposed to dry atmospheric air. Estimate the diffusion coefficient of water in air, -4 if the rate of diffusion of water is 8.54 x 10 kg/h. (8) 3. (a) Dry air at 20C ( = 1.2 kg/m , v = 15 x l0 m /s, Dab = 4.2 x l0 m /s) flows over a flat plate of length 50 cm which is covered with a thin layer of water at a velocity of 1 m/s. Estimate the average mass transfer coefficient. (8) (b) Air at 20C and atmospheric pressure, containing small quantities of iodine flows with a velocity of 4 m/s inside a 4 cm inner diameter tube. Determine the -5 2 mass transfer coefficient. Assume Dab = 0.75 x l0 m /s. (8)
3 -6 2 -5 2 3 -6 2 -5 2
Part A : 1. Examples of Diffusion mass transfer 2. Ficks law of diffusion. 3. Two examples of convective mass transfer. 4. Define i) Mass concentration ii) Mole fraction 5. Define Sherwood number & Schmidt number for mass transfer. Part B 1. (a) A mixture of O2 and N2 with their partial pressures in the ratio 0.21 to 0.79 is in a container at 25C. Calculate the molar concentration, the mass density, the mole fraction and the mass fraction of each species for a total pressure of 1 bar. ( b) Write short note Equimolar counter diffusion. (6) 2. (a) Estimate the diffusion rate of water from the bottom of the test tube 10 mm diameter and 15 cm long in to dry atmospheric air at 25C. Diffusion coefficient -4 2 of water in air is 0.255 x 10 m /s. (8) (b) An open pan, 20 cm diameter and 8 cm deep contains water at 25C and is exposed to dry atmospheric air. Estimate the diffusion coefficient of water in air, -4 if the rate of diffusion of water is 8.54 x 10 kg/h. (8) 3. (a) Dry air at 20C ( = 1.2 kg/m , v = 15 x l0 m /s, Dab = 4.2 x l0 m /s) flows over a flat plate of length 50 cm which is covered with a thin layer of water at a velocity of 1 m/s. Estimate the average mass transfer coefficient. (8) (b) Air at 20C and atmospheric pressure, containing small quantities of iodine flows with a velocity of 4 m/s inside a 4 cm inner diameter tube. Determine the -5 2 mass transfer coefficient. Assume Dab = 0.75 x l0 m /s. (8) Part A : 1. Examples of Diffusion mass transfer 2. Ficks law of diffusion. 3. Two examples of convective mass transfer. 4. Define i) Mass concentration ii) Mole fraction 5. Define Sherwood number & Schmidt number for mass transfer. Part B 1. (a) A mixture of O2 and N2 with their partial pressures in the ratio 0.21 to 0.79 is in a container at 25C. Calculate the molar concentration, the mass density, the mole fraction and the mass fraction of each species for a total pressure of 1 bar. ( b) Write short note Equimolar counter diffusion. (6) 2. (a) Estimate the diffusion rate of water from the bottom of the test tube 10 mm diameter and 15 cm long in to dry atmospheric air at 25C. Diffusion coefficient -4 2 of water in air is 0.255 x 10 m /s. (8) (b) An open pan, 20 cm diameter and 8 cm deep contains water at 25C and is exposed to dry atmospheric air. Estimate the diffusion coefficient of water in air, -4 if the rate of diffusion of water is 8.54 x 10 kg/h. (8) 3. (a) Dry air at 20C ( = 1.2 kg/m , v = 15 x l0 m /s, Dab = 4.2 x l0 m /s) flows over a flat plate of length 50 cm which is covered with a thin layer of water at a velocity of 1 m/s. Estimate the average mass transfer coefficient. (8) (b) Air at 20C and atmospheric pressure, containing small quantities of iodine flows with a velocity of 4 m/s inside a 4 cm inner diameter tube. Determine the -5 2 mass transfer coefficient. Assume Dab = 0.75 x l0 m /s. (8)
3 -6 2 -5 2 3 -6 2 -5 2
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- HMT 113401 Anna UnivDocument3 pagesHMT 113401 Anna Univsathiya_ramPas encore d'évaluation
- HMT Model-II 15.05.13Document2 pagesHMT Model-II 15.05.13tagoreboopathyPas encore d'évaluation
- SP 1 Assignment 30 March 2022Document2 pagesSP 1 Assignment 30 March 2022ONKAR ARORA0% (1)
- Short Answer QuestionsDocument7 pagesShort Answer Questionsvenky437Pas encore d'évaluation
- Diffusion Mass Transfer Solved ProblemsDocument22 pagesDiffusion Mass Transfer Solved ProblemsSteph Kier PonterasPas encore d'évaluation
- Ch8551 Mass Transfer-I Unit I - (Diffusion) C303.1: Department of Chemical Engineering, VSBECDocument12 pagesCh8551 Mass Transfer-I Unit I - (Diffusion) C303.1: Department of Chemical Engineering, VSBECSaravanan SundaramPas encore d'évaluation
- Anna University:: Chennai - 600 025 Model Question PaperDocument3 pagesAnna University:: Chennai - 600 025 Model Question PaperMD SHAHJADPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment MT1-2015-4Document7 pagesAssignment MT1-2015-4Ashwin HatwarPas encore d'évaluation
- BE ChemDocument53 pagesBE ChemMuddasar ShaikhPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 1Document3 pagesUnit 1sreenivasMtechdisPas encore d'évaluation
- Slu - Sea - Che 520 L - Separations Technology Diffusion, EvaporationDocument2 pagesSlu - Sea - Che 520 L - Separations Technology Diffusion, EvaporationAileen MayaPas encore d'évaluation
- 2428Document8 pages2428kiranin10Pas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial-Sums DiffusionDocument11 pagesTutorial-Sums DiffusionHridyaAshokanPas encore d'évaluation
- MTO Question BankDocument2 pagesMTO Question Bankmishrajitesh2004Pas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment Sheet IDocument2 pagesAssignment Sheet IUtkarsh TripathiPas encore d'évaluation
- Mass Transfer Operations Model QuestionsDocument8 pagesMass Transfer Operations Model QuestionsIastraPas encore d'évaluation
- Screenshot 2023-10-09 at 3.54.38 AMDocument5 pagesScreenshot 2023-10-09 at 3.54.38 AMhnsm9bwtqrPas encore d'évaluation
- Sathyabama University: Register NumberDocument4 pagesSathyabama University: Register NumberRAVIPas encore d'évaluation
- Faculty of Engineering Mass Transfer Cairo M5zncomnewuploads20131003pdfm5znDocument4 pagesFaculty of Engineering Mass Transfer Cairo M5zncomnewuploads20131003pdfm5znMm ShdedPas encore d'évaluation
- Answer All QuestionDocument2 pagesAnswer All QuestionSamuelEmebuPas encore d'évaluation
- Orca Share Media1541752718539 PDFDocument15 pagesOrca Share Media1541752718539 PDFJuneNeilBalacuitPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment 2Document3 pagesAssignment 2Robert JacksonPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial4 6Document4 pagesTutorial4 6Chinmay JoshiPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment 4 5Document4 pagesAssignment 4 5maluPas encore d'évaluation
- Diffusion Coefficient Full Report TiqaDocument19 pagesDiffusion Coefficient Full Report TiqaprmzPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial PackedBedDocument2 pagesTutorial PackedBedtejkiranPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial Mass TransferDocument5 pagesTutorial Mass TransferAimy YasminPas encore d'évaluation
- Numerical Unit1Document3 pagesNumerical Unit1Ayush DubeyPas encore d'évaluation
- R5102306 Process Engineering PrinciplesDocument1 pageR5102306 Process Engineering PrinciplessivabharathamurthyPas encore d'évaluation
- AIRCONDITIONING ProblemsDocument28 pagesAIRCONDITIONING Problemsعبدالرحمن منصورPas encore d'évaluation
- 2020 Dec. MET203-ADocument3 pages2020 Dec. MET203-Ared18ggmuPas encore d'évaluation
- Institute Open Elective Course Fluid Mechanics (CHO 102) Assignment IIIDocument2 pagesInstitute Open Elective Course Fluid Mechanics (CHO 102) Assignment IIIarunPas encore d'évaluation
- Evaporation in Porous Media With Small Evaporation RatesDocument18 pagesEvaporation in Porous Media With Small Evaporation RatesmanigandanPas encore d'évaluation
- Absorption: A, For The Absorption of SODocument3 pagesAbsorption: A, For The Absorption of SOErvz Mission0% (1)
- Rr310804 Mass Transfer Operations IDocument8 pagesRr310804 Mass Transfer Operations ISrinivasa Rao GPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Chapter 9 Fluid Dynamics Worksheet 1Document2 pagesPhysics Chapter 9 Fluid Dynamics Worksheet 1Khairunnisa FahrinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Taller MasaDocument2 pagesTaller Masa__Caro26__Pas encore d'évaluation
- Assignmnet 2 - Mass Transfer IDocument2 pagesAssignmnet 2 - Mass Transfer IManas Akash100% (1)
- 26 (Surface Tension, Viscosity)Document3 pages26 (Surface Tension, Viscosity)Kaveesh KulkarniPas encore d'évaluation
- TPDocument3 pagesTPDolly PriyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Mechanics QPDocument8 pagesFluid Mechanics QPCrucifiedBishwarupPas encore d'évaluation
- Answer All Questions. Each Question Carries 2 Marks.: Sixth Semester B.Tech Degree ExaminationDocument3 pagesAnswer All Questions. Each Question Carries 2 Marks.: Sixth Semester B.Tech Degree ExaminationKrishna YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit Operations Tutorial 2015-2016Document13 pagesUnit Operations Tutorial 2015-2016hazimraad0% (1)
- Assignment 1Document2 pagesAssignment 1Aini LeePas encore d'évaluation
- Example From JB SlidesDocument14 pagesExample From JB SlidesSangetha Chelladorai0% (3)
- Falling Head Permeability TestDocument9 pagesFalling Head Permeability TestFaeez Zain83% (6)
- Momentum TransferDocument2 pagesMomentum TransferrahulPas encore d'évaluation
- Mass Transfer Fundamentals Ch.E-304: Muhammad Rashed JavedDocument6 pagesMass Transfer Fundamentals Ch.E-304: Muhammad Rashed JavedTalha ImtiazPas encore d'évaluation
- Prueba Fisica 11 3 Er PeriodoDocument3 pagesPrueba Fisica 11 3 Er PeriodoJulio Cèsar GarcìaPas encore d'évaluation
- November 2016 Board Exam Quastions PDFDocument11 pagesNovember 2016 Board Exam Quastions PDFBethel Grace TalhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Heat and Moisture Transfer between Human Body and EnvironmentD'EverandHeat and Moisture Transfer between Human Body and EnvironmentPas encore d'évaluation
- NR-310804 - Mass Transfer Operations - IDocument8 pagesNR-310804 - Mass Transfer Operations - ISrinivasa Rao G100% (1)
- Gojan School of Business and Technology: Department of Aeronautical EngineeringDocument7 pagesGojan School of Business and Technology: Department of Aeronautical EngineeringRameez FaroukPas encore d'évaluation
- Falling Head Permeability Test Lab ReportDocument8 pagesFalling Head Permeability Test Lab Reportmr_sam91100% (1)
- 25 0 ChE MOCK BOARD 4 4may2016 ANS KEY and SolnDocument6 pages25 0 ChE MOCK BOARD 4 4may2016 ANS KEY and SolnFran LeePas encore d'évaluation
- Geo TechnicalDocument105 pagesGeo TechnicalSigue Ramel HinayasPas encore d'évaluation
- Gaseous Diffusion CoefficientDocument3 pagesGaseous Diffusion CoefficientChun LimPas encore d'évaluation
- CH - 2 & 3 Worked ExamplesDocument16 pagesCH - 2 & 3 Worked ExamplesAsegid Bezabih100% (2)
- HW4 6130Document4 pagesHW4 6130Jorn DoePas encore d'évaluation
- Dictionary of Water and Waste ManagementD'EverandDictionary of Water and Waste ManagementÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (3)
- Em Unit 5 PDFDocument17 pagesEm Unit 5 PDFLindsay RandallPas encore d'évaluation
- 6 Fluid MechanicsDocument14 pages6 Fluid MechanicsbalajigandhirajanPas encore d'évaluation
- IIT Kharagpur LecturesDocument616 pagesIIT Kharagpur LecturesBhavanarayana Chakka67% (3)
- Heat and Mass Transfer (NPTEL) PDFDocument569 pagesHeat and Mass Transfer (NPTEL) PDFArnab Midya83% (12)
- Mba-Ii-Enterpreneurial Development (14mba26) - Notes PDFDocument68 pagesMba-Ii-Enterpreneurial Development (14mba26) - Notes PDFbalajigandhirajan59% (17)
- Ch5problems 110523050326 Phpapp02Document15 pagesCh5problems 110523050326 Phpapp02balajigandhirajanPas encore d'évaluation
- Inderscience List of JournalsDocument29 pagesInderscience List of Journalsbalajimeie100% (1)
- 2MARKSDocument85 pages2MARKSNithyanandmPas encore d'évaluation
- All Unit UnitwiseDocument17 pagesAll Unit UnitwisebalajigandhirajanPas encore d'évaluation
- International Journal of Computational Intelligence SystemsDocument15 pagesInternational Journal of Computational Intelligence SystemsbalajigandhirajanPas encore d'évaluation
- Condensation HMTDocument22 pagesCondensation HMTbalakalees100% (1)
- Banking E BookDocument378 pagesBanking E Book✬ SHANZA MALIK ✬Pas encore d'évaluation
- Psna College of Engineering and Technology Department of Mechanical Engineering Machine ShopDocument1 pagePsna College of Engineering and Technology Department of Mechanical Engineering Machine ShopbalakaleesPas encore d'évaluation
- 10122MEE51 Lessonplan orDocument3 pages10122MEE51 Lessonplan orbalajigandhirajanPas encore d'évaluation
- Working of Steam Turbines and Its AuxillariesDocument48 pagesWorking of Steam Turbines and Its AuxillariesbalajigandhirajanPas encore d'évaluation
- GC Circular - 2012 To 2013Document11 pagesGC Circular - 2012 To 2013balajigandhirajanPas encore d'évaluation
- GC Circular - 2012 To 2013Document11 pagesGC Circular - 2012 To 2013balajigandhirajanPas encore d'évaluation
- Centroids Moments of InertiaDocument62 pagesCentroids Moments of InertiabalajigandhirajanPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.ansys Fluid Dynamics r14Document8 pages2.ansys Fluid Dynamics r14Saumya SinhaPas encore d'évaluation
- JR of Cleaner ProductionDocument2 pagesJR of Cleaner ProductionbalajimeiePas encore d'évaluation
- International Journal of Production ResearchDocument10 pagesInternational Journal of Production ResearchbalakaleesPas encore d'évaluation
- Taguchi Based Six SigmaDocument10 pagesTaguchi Based Six SigmabalakaleesPas encore d'évaluation
- GBM Mech PartialDocument21 pagesGBM Mech PartialbalajigandhirajanPas encore d'évaluation
- Au ResultsDocument9 pagesAu ResultsbalajimeiePas encore d'évaluation
- Supply Chain Taylor and FrancisDocument55 pagesSupply Chain Taylor and FrancisbalajigandhirajanPas encore d'évaluation
- Part 3 03Document16 pagesPart 3 03balajigandhirajanPas encore d'évaluation
- Electro Magnetic Forming A Russis Based Book LandscapeDocument272 pagesElectro Magnetic Forming A Russis Based Book LandscapebalajigandhirajanPas encore d'évaluation
- Part 4 03Document13 pagesPart 4 03balajigandhirajanPas encore d'évaluation
- Aii Bbrc4103Document15 pagesAii Bbrc4103Holy Tan100% (1)
- Basic Anova PDFDocument6 pagesBasic Anova PDFEmmanuel Jimenez-Bacud, CSE-Professional,BA-MA Pol SciPas encore d'évaluation
- CIEM AssignmentDocument3 pagesCIEM Assignmenthklois0% (1)
- MSM Specification: Discrete TimeDocument5 pagesMSM Specification: Discrete TimeNicolas MarionPas encore d'évaluation
- Wind Actions and Responses of Steel ChimneysDocument9 pagesWind Actions and Responses of Steel ChimneyszmtdialogPas encore d'évaluation
- Handbook of Sugar A 00 BrowneDocument990 pagesHandbook of Sugar A 00 BrowneHugo Tototzintle75% (4)
- 50 To 50000Document23 pages50 To 50000Slavko Svagelj80% (5)
- BA Sample Paper Questions2Document17 pagesBA Sample Paper Questions2kr1zhna0% (1)
- GREEN Belt Statistics Cheat SheetDocument13 pagesGREEN Belt Statistics Cheat SheetjgkjPas encore d'évaluation
- Design of Melka-Gobera Irrigation Project ESSAYDocument61 pagesDesign of Melka-Gobera Irrigation Project ESSAYyared100% (1)
- Multiple+Choice+Questions ForecastingDocument3 pagesMultiple+Choice+Questions Forecastingjackywen102486% (7)
- Engineering and Chemical Thermodynamics 2e: Chapter 1 SolutionsDocument41 pagesEngineering and Chemical Thermodynamics 2e: Chapter 1 SolutionsLalo RubioPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 4 Introduction To KrigingDocument55 pagesLecture 4 Introduction To KrigingsattammashanPas encore d'évaluation
- QT Quiz FinalDocument223 pagesQT Quiz Finalparikh_prateek063784Pas encore d'évaluation
- AspirinDocument8 pagesAspirinchristelPas encore d'évaluation
- Roc Curve MeaningDocument8 pagesRoc Curve MeaningAnonymous rfn4FLKD8Pas encore d'évaluation
- Makesens - Temperatuur2 (Mann Kendall Test)Document14 pagesMakesens - Temperatuur2 (Mann Kendall Test)Vinay ChandwaniPas encore d'évaluation
- STD 12 Maths 2 Board Question Paper Maharashtra BoardDocument6 pagesSTD 12 Maths 2 Board Question Paper Maharashtra BoardYash ChaudhauryPas encore d'évaluation
- Wheat Crop Yield Prediction Using Deep LSTM ModelDocument8 pagesWheat Crop Yield Prediction Using Deep LSTM ModelEndalew SimiePas encore d'évaluation
- Standard Maxwell-Boltzmann Distribution - Definition and PropertiesDocument16 pagesStandard Maxwell-Boltzmann Distribution - Definition and PropertiesHugo HernandezPas encore d'évaluation
- 1999 Xu and GoswamiDocument12 pages1999 Xu and GoswamiimeqingenieriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Guidelines of The Swedish Weight Sounding Test (SWST) in The Philippine SettingDocument9 pagesGuidelines of The Swedish Weight Sounding Test (SWST) in The Philippine Settingmark_zarcoPas encore d'évaluation
- Entec ReportDocument199 pagesEntec ReportTudose Adrian-IonuțPas encore d'évaluation
- 3 5SMPRGuidelinev12 1 PDFDocument27 pages3 5SMPRGuidelinev12 1 PDFMelisa PurnamasariPas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematical Assessment Synthetic Hydrology: Vol. $, No. 4 Water Resources Research Fourth Quarter 1967Document9 pagesMathematical Assessment Synthetic Hydrology: Vol. $, No. 4 Water Resources Research Fourth Quarter 1967LeandroPérezPas encore d'évaluation
- Forecast Model Using Regression AnalysisDocument5 pagesForecast Model Using Regression AnalysisAbir AnsariPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Wind Speed Map Under High Emission Extreme Scenario and Probable Structural Loading PDFDocument128 pagesBasic Wind Speed Map Under High Emission Extreme Scenario and Probable Structural Loading PDFdxzaberPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 2 Time Series ForecastingDocument49 pagesLecture 2 Time Series Forecastingرضا قاجهPas encore d'évaluation
- Communication Lab Matlab-ZeytinogluDocument114 pagesCommunication Lab Matlab-ZeytinogluHoàng NamPas encore d'évaluation
- Blast Vibration Study To Analyse The Response of A Wind Tower Close To An Open Pit MineDocument8 pagesBlast Vibration Study To Analyse The Response of A Wind Tower Close To An Open Pit MinehectorPas encore d'évaluation