Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Viscosity and Consistency Properties of Foods
Transféré par
Anabelle SabanganTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Viscosity and Consistency Properties of Foods
Transféré par
Anabelle SabanganDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Introduction Viscosity and consistency are rheological properties of food.
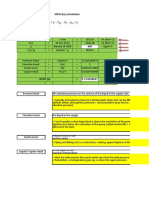
This property of food is very significant for the food analysis of foods in liquid or gas state. Viscosity is the measure of liquids resistance to flow. It describes the internal friction of a moving fluid. A fluid with large viscosity resists motion because its molecular make up gives it a lot of internal friction [1]. A fluid with low viscosity flows easily because its molecular make up results in very little friction when it is in motion. With these two definitions, Newtonian and Non-Newtonian fluid takes place. Non-Newtonian fluid is a fluid whose flow properties differ in any way from those of Newtonian fluids. Most commonly the viscosity of non-Newtonian fluids is not independent of shear rate or shear rate history. However, there are some non-Newtonian fluids with shear-independent viscosity, which nonetheless exhibit normal stress-differences or other non-Newtonian behavior [2]. Example of Non-Newtonian fluid is catsup, gravy, custard, condensed milk, concentrated juice and many others. On the other hand, Newtonian fluid is fluid that exhibits a viscosity that remains constant regardless of any external stress that is place upon it [3]. Example of a Newtonian liquid is water, since it flows the same way regardless of whether it is left alone or agitated vigorously. Consistency in the other hand, is the relative mobility or ability of freshly mixed concrete or mortar to flow; the usual measurements are slump for concrete, flow for mortar or grout, and penetration resistance for neat cement paste [4]. Flow rate is the term used to describe how quickly fluids move. Flow rate measures the volume of liquid moving past a certain point in a given amount of time [5]. Flow rate depends on several factors: the type of liquid that is flowing (thin fluids flow faster than thick ones); the force pushing on the fluid (stronger forces produce faster flow rates); the size of the pipe or opening the fluid is flowing through (larger openings allow for faster flow); the type of surface over which the fluid is flowing (smooth surfaces allow for faster flow). In this experiment, flow test, line spread test and pipette flow test were conducted to differentiate Non-Newtonian liquids from Newtonian liquids and also to measure flow rate and spread ability of various liquid foods. The line spread test of viscosity is a
quick, inexpensive, and reliable test for comparing the relative viscosities of various comparable products or comparing the effect of a particular ingredient on the viscosity of a given product [6]. In all, the viscosity of a fluid food is very important to know especially in food industry. It will help us identify in which category our product belongs and with it we would be able to know if that fluid food meets the product quality that it is intended to do so. References: [1]http://www.princeton.edu/~gasdyn/Research/TC_Research_Folder/Viscosity_def.htm l [2] http://www.princeton.edu/~achaney/tmve/wiki100k/docs/Non-Newtonian_fluid.html [3] http://www.wisegeek.org/what-is-a-newtonian-fluid.htm [4] http://ciks.cbt.nist.gov/~garbocz/SP946/node16.htm [5] http://hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca/walkerk/7.3%20Flow%20Rate%20and%20Viscosity.pdf [6] http://cbs-he.blogspot.com/2005/07/linespread-test.html
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Viscosity of Newtonian and non-Newtonian Fluids: Understanding Flow BehaviorDocument5 pagesViscosity of Newtonian and non-Newtonian Fluids: Understanding Flow Behaviormarifa16Pas encore d'évaluation
- Rheolog Y OF Fluids: BY: Vidhi DoshiDocument14 pagesRheolog Y OF Fluids: BY: Vidhi DoshiAmlan PalPas encore d'évaluation
- Newtonian and Non-Newtonian FluidsDocument21 pagesNewtonian and Non-Newtonian FluidsyokaPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment Viscosity AhmadDocument3 pagesExperiment Viscosity AhmadAhmad AbdulsattarPas encore d'évaluation
- Viscosity of Fluids-Newtonian and Non Newtonian Analysis As Applied To PlasticsDocument20 pagesViscosity of Fluids-Newtonian and Non Newtonian Analysis As Applied To PlasticsSushmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Measurement of Viscosity in Foods Using Brookfield ViscometerDocument9 pagesMeasurement of Viscosity in Foods Using Brookfield ViscometerainsyuhadaazizPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 2 RheologyDocument25 pagesUnit 2 RheologyMutale InongePas encore d'évaluation
- Bawah Abdul-Rashid 3645009 Chemical Engineering Kwame Nkrumah University of Science and Technology SEPTEMBER 14, 2010Document5 pagesBawah Abdul-Rashid 3645009 Chemical Engineering Kwame Nkrumah University of Science and Technology SEPTEMBER 14, 2010Ing Rashid BawahPas encore d'évaluation
- Dynamic and Kinamatic ViscosityDocument4 pagesDynamic and Kinamatic ViscosityMartin Flex-b EyangoPas encore d'évaluation
- Viscosity Report of Chemical Engineering DepartmentDocument10 pagesViscosity Report of Chemical Engineering Departmentمنار علي محسن 72 صباحيPas encore d'évaluation
- Measure Viscosity of LiquidsDocument2 pagesMeasure Viscosity of LiquidsAseel KhaledPas encore d'évaluation
- Dynamic Vs Kinematic ViscosityDocument7 pagesDynamic Vs Kinematic ViscosityHASSAN ARSHADPas encore d'évaluation
- Terms for Quality TestsDocument5 pagesTerms for Quality TestsEmmanuelPas encore d'évaluation
- Non-Newtonian Fluid PDFDocument6 pagesNon-Newtonian Fluid PDFJaime BallesterosPas encore d'évaluation
- Nonnewtonian Fluid ReportDocument2 pagesNonnewtonian Fluid ReportNone NamedPas encore d'évaluation
- Rheology: Roselyn Aperocho-Naranjo Faculty, College of Pharmacy UspfDocument20 pagesRheology: Roselyn Aperocho-Naranjo Faculty, College of Pharmacy Uspfasit_mPas encore d'évaluation
- Laboratory Report Experiment 4 - Group 7Document23 pagesLaboratory Report Experiment 4 - Group 7Jeremy Kyle Edson AustriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Project FluidDocument12 pagesProject FluidisyraffitriPas encore d'évaluation
- BFBM Unit - 2Document27 pagesBFBM Unit - 2Kripa NPas encore d'évaluation
- What Are The Differences Between Newtonian and Non NewtonianDocument1 pageWhat Are The Differences Between Newtonian and Non NewtonianAb SiPas encore d'évaluation
- Physical pharmacy viscosity rheologyDocument4 pagesPhysical pharmacy viscosity rheologyاسامه المكابريPas encore d'évaluation
- 4827baa5 1613967939866Document39 pages4827baa5 1613967939866Dayana PereraPas encore d'évaluation
- Table of Contents: Viscosity and ViscometersDocument10 pagesTable of Contents: Viscosity and ViscometersAdanPas encore d'évaluation
- Viscosity - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument21 pagesViscosity - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaJohnPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Properties AND Pressure Measurement: Unit IDocument76 pagesFluid Properties AND Pressure Measurement: Unit Ihari7037Pas encore d'évaluation
- Rheologgy of FoosDocument13 pagesRheologgy of FoosSakshiPas encore d'évaluation
- Rheologgy of FoosDocument13 pagesRheologgy of FoosSakshiPas encore d'évaluation
- Dr. Babasaheb Ambedkar Technological University, LonereDocument19 pagesDr. Babasaheb Ambedkar Technological University, LonereAmey RajePas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Mechanics IntroductionDocument4 pagesFluid Mechanics IntroductionAvinash GarikapatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Rhe OlogyDocument3 pagesRhe OlogyAldiDamoraPas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding The Properties of Fluid and Rheology of Fluid FoodDocument11 pagesUnderstanding The Properties of Fluid and Rheology of Fluid FoodTanvir BhagatPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry Lab Report 3Document6 pagesChemistry Lab Report 3Jinyoung KimPas encore d'évaluation
- SCI115 - BSE I-2 - Module1-Activity 1 - Kizha Mae V MarianoDocument4 pagesSCI115 - BSE I-2 - Module1-Activity 1 - Kizha Mae V MarianoKM MarianoPas encore d'évaluation
- Mud Rheology Test ResultsDocument14 pagesMud Rheology Test ResultsAbdullwahid AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Food Analysis-6Document25 pagesFood Analysis-6MD. Humayun KobirPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 4Document10 pagesUnit 423/CH/002 AADITYAVASHISHTPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid MechanichDocument5 pagesFluid Mechanichasishraj2003Pas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding The Properties of Fluid and Rheology of Fluid FoodDocument19 pagesUnderstanding The Properties of Fluid and Rheology of Fluid FoodTanvir BhagatPas encore d'évaluation
- fluid lec 1Document5 pagesfluid lec 1ZHSUST ChEPas encore d'évaluation
- Rheological Testing of FRoodsDocument8 pagesRheological Testing of FRoodslickaa200Pas encore d'évaluation
- Newtonian Fluid Vs Non - Newtonian FluidDocument1 pageNewtonian Fluid Vs Non - Newtonian FluidAnik AichPas encore d'évaluation
- Factors Affecting Viscosity of A Liquid: Presented byDocument9 pagesFactors Affecting Viscosity of A Liquid: Presented byJay WhitePas encore d'évaluation
- Measuring Viscosity TechniquesDocument6 pagesMeasuring Viscosity Techniquesmorry123Pas encore d'évaluation
- ViscosityDocument5 pagesViscositydwarika2006Pas encore d'évaluation
- ACT 1.4-LopezMedinaDocument15 pagesACT 1.4-LopezMedinaELVIS URIEL LOPEZ MEDINAPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 2 Rheology and Classification of FluidsDocument19 pagesLecture 2 Rheology and Classification of FluidsmpdmlnsPas encore d'évaluation
- Qtheory VuitDocument8 pagesQtheory VuitCHANDRASEKAR RPas encore d'évaluation
- Laju's Viscosity ReportDocument6 pagesLaju's Viscosity ReportLaju AjagbawaPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is ViscosityDocument8 pagesWhat Is ViscosityNandaKishorePatraPas encore d'évaluation
- Non Newtonian Fluids and Their Effect On BearingDocument25 pagesNon Newtonian Fluids and Their Effect On BearingShivaprasad.PPas encore d'évaluation
- Covenant GEC 223 Lecture Note 1 Week 2-MoodleDocument53 pagesCovenant GEC 223 Lecture Note 1 Week 2-MoodleAdeolu-Idowu AbiolaPas encore d'évaluation
- RheologyDocument5 pagesRheology207581Pas encore d'évaluation
- Measuring Viscosity: by Richard Crowley Contributing EditorDocument3 pagesMeasuring Viscosity: by Richard Crowley Contributing Editortrangthuan010187Pas encore d'évaluation
- Rheology: Dairy Processing Handbook/chapter 3Document8 pagesRheology: Dairy Processing Handbook/chapter 3Margo SmithPas encore d'évaluation
- Polymer Rheology and Morphology Part 2Document35 pagesPolymer Rheology and Morphology Part 2AmyPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 3 RheologyDocument32 pagesLecture 3 Rheologybattal eduPas encore d'évaluation
- Met. Rheological Characterization PDFDocument7 pagesMet. Rheological Characterization PDFDiana Zulima Paez RojasPas encore d'évaluation
- FLUICMECHDocument4 pagesFLUICMECHROBYLYN C. GAVINPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluids and Electrolytes: An Easy and Intuitive Way to Understand and Memorize Fluids, Electrolytes, and Acidic-Base BalanceD'EverandFluids and Electrolytes: An Easy and Intuitive Way to Understand and Memorize Fluids, Electrolytes, and Acidic-Base BalanceÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (2)
- Flow charts of pharmaceutical quality control tests for different dosage formsD'EverandFlow charts of pharmaceutical quality control tests for different dosage formsPas encore d'évaluation
- PVT Concepts Reservoir ConceptDocument23 pagesPVT Concepts Reservoir ConceptherikugisPas encore d'évaluation
- Conventional SeparatorsDocument27 pagesConventional SeparatorsMax Singh100% (1)
- STU02 Boundry Layer TheoryDocument135 pagesSTU02 Boundry Layer TheoryCornelius RheedersPas encore d'évaluation
- Short Intro To EFDCDocument22 pagesShort Intro To EFDCMohd. YunusPas encore d'évaluation
- Trane CVHFDocument49 pagesTrane CVHFJFBD Builders100% (1)
- Finepac Structures PVT - LTD: GAS Liquid (15000BPD) (Oil/Water)Document2 pagesFinepac Structures PVT - LTD: GAS Liquid (15000BPD) (Oil/Water)Dhanraj VasanthPas encore d'évaluation
- NPSH CalculationDocument8 pagesNPSH Calculationagung sudarsonoPas encore d'évaluation
- Measure Flow Rates with 7 DevicesDocument12 pagesMeasure Flow Rates with 7 DevicesAdellPas encore d'évaluation
- Correl Mock Hydraulics Set ADocument15 pagesCorrel Mock Hydraulics Set AMariah Kathleen LacsinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Power and Industrial Plant Engineering TerminologiesDocument10 pagesPower and Industrial Plant Engineering TerminologiesFrei MagsinoPas encore d'évaluation
- Hydraulic Fracturing Design Procedure Using PKN ModelDocument3 pagesHydraulic Fracturing Design Procedure Using PKN ModelJatin RamboPas encore d'évaluation
- Chevron Y Texaco TablaDocument40 pagesChevron Y Texaco TablasofelsbabaPas encore d'évaluation
- NozzlesDocument5 pagesNozzlessreelu100% (1)
- Military Fuel Codes and SpecDocument3 pagesMilitary Fuel Codes and SpecPAUL HEALDPas encore d'évaluation
- 3-Turbulent Flow PDFDocument16 pages3-Turbulent Flow PDFAbhinav AbhiPas encore d'évaluation
- A Class of Exact Solutions To Navier-Stokes Equations For The Given VorticityDocument9 pagesA Class of Exact Solutions To Navier-Stokes Equations For The Given VorticityMarco Picchi ScardaoniPas encore d'évaluation
- Specific Gravity Determination Using U-Tube ManometerDocument9 pagesSpecific Gravity Determination Using U-Tube ManometerEly ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Sanitary Survey of Drinking WaterDocument19 pagesSanitary Survey of Drinking Waterahmad shodiqPas encore d'évaluation
- Pre-Inspection Checklist For Low Pressure Steam Boilers: Chapter 296-104 WAC Chapter 70.79 RCWDocument4 pagesPre-Inspection Checklist For Low Pressure Steam Boilers: Chapter 296-104 WAC Chapter 70.79 RCWMohammedPas encore d'évaluation
- Reservoir Engineering by DR Anil KumarDocument70 pagesReservoir Engineering by DR Anil KumarJassiePas encore d'évaluation
- FUCHS RENOLIN B SeriesDocument1 pageFUCHS RENOLIN B SeriesAnonymous srwHCpAPas encore d'évaluation
- WWEDocument4 pagesWWEMasnun RahmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Cold Cranking Simulator Viscosity StandardsDocument1 pageCold Cranking Simulator Viscosity StandardsJaison JacobPas encore d'évaluation
- GTU CIVIL ENGINEERING WATER & WASTE WATER ENGINEERINGDocument4 pagesGTU CIVIL ENGINEERING WATER & WASTE WATER ENGINEERINGDevang ShahPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 s2.0 S0142727X17310354 MainDocument21 pages1 s2.0 S0142727X17310354 MainYash Sanjay ShewalePas encore d'évaluation
- NBR Piston Cup Seal: General Cylinders Pneumatic CylindersDocument10 pagesNBR Piston Cup Seal: General Cylinders Pneumatic CylindersSHANEPas encore d'évaluation
- Rain Water Harvesting: The PotentialDocument25 pagesRain Water Harvesting: The PotentialMohamed NaveenPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 6Document19 pagesLab 6IzzatiHazwaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Control Valve Anti Cavitation DetailsDocument14 pagesControl Valve Anti Cavitation DetailsAnupam A. GandhewarPas encore d'évaluation
- Glycol Recovery Plant PFD - Hamriya UnitDocument1 pageGlycol Recovery Plant PFD - Hamriya Unitpriyanka barikPas encore d'évaluation