Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Sathyabama University: (Established Under Section 3 of UGC Act, 1956)
Transféré par
Mahendranath RamakrishnanTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Sathyabama University: (Established Under Section 3 of UGC Act, 1956)
Transféré par
Mahendranath RamakrishnanDroits d'auteur :
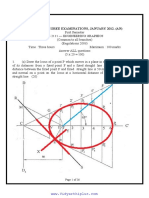
Formats disponibles
Register Number
SATHYABAMA UNIVERSITY
(Established under section 3 of UGC Act,1956)
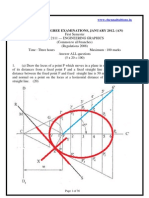
Course & Branch :B.E - AERO Title of the Paper :Engineering Graphics II Sub. Code :5ET215(2005) Date :31/05/2012 PART - A Answer ALL the Questions What is meant by orthographic projection?
Max. Marks:80 Time : 3 Hours Session :FN (10 x 2 = 20)
______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9.
State the top and front views of a vertical cylinder of diameter 50 mm and height 70 mm resting on HP with one of its bases. What are the various methods of development? State any two applications of intersection of surfaces. Mention any two advantages of isometric projection. Name any two methods of drawing the isometric projection of a circle. Define ground plane. Define centre of vision in perspective projection. What is the R.C.C. mix used for lintel and ground floor concrete?
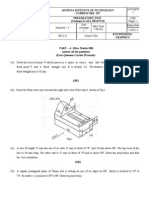
10. What is weathering course? Give the details of it used for house building. PART B (5 x 12 = 60) Answer All the Questions 11. Draw top, front and side view of the object given below. Indicate major dimensions.
(or) 12. (a) Describe the method of obtaining the orthographic projections of an object with example. (b) State the conventions to be followed while drawing dotted lines. 13. A hexagonal prism of base side 20 mm and height 45 mm is resting on one of its ends on the HP with two of its lateral faces parallel to the VP. It is cut by a plane perpendicular to the VP and inclined at 30 to the HP. The plane meets the axis at a distance of 20 mm above the base. Draw the development of the lateral surfaces of the lower portion of the prism. (or) 14. A cylinder of diameter 40 mm and axis length 100 mm penetrates fully in to a vertical cylinder of diameter 60 mm and axis length
80 mm. The axes of the cylinder bisect each other at right angles. The axis of the horizontal cylinder is parallel to the VP. Draw the development of the lateral surfaces of the two intersecting cylinders. 15. A hemi spherical vessel of diameter 90 mm is placed centrally over a cylinder of diameter 60 mm and height 75 mm which, in turn, is kept centrally over a square prism of base side 80 mm and height 20 mm. Draw the isometric projection of the disposition of the solids. (or) 16. A cone of base diameter 50 mm and height 55 mm is resting on its base on the HP. It is cut by a plane perpendicular to the VP and inclined at 30 to the HP. The plane meets the axis at a distance of 25mm from the apex. Draw the isometric view of the truncated cone. 17. Draw the perspective view of a square prism of base side 20 mm and height 35 mm resting on an end on the ground with a rectangular face parallel to the picture plane. The axis of the prism is 25 mm behind the PP and 25 mm to the right of the eye. The eye is 50 mm in front of the PP and 50 mm above the ground. (or) 18. A cube of 35 mm edge lies with a face on the ground and an edge on the picture plane. All the vertical faces are equally inclined to the PP. The station point is 80 mm in front of the PP and 60 mm from the ground. The edge of the cube in contact with the picture plane is situated 10 mm to the right of the station point. Draw the perspective of the cube. 19. The line diagram of a village library building is shown below. Draw the top view of the building taking section at window sill level. Also draw the front view of the building. Partition walls are
of 100 thick and main walls are of 200 thick. Assume suitable data wherever necessary.
(or) 20. The line diagram of a residential building is shown below. Draw to a suitable scale, front view, top view and sectional view taken along AA. Make suitable assumptions. The following standard dimensions for doors and windows may be taken: D Panelled door 900 x 1950 D1 Door 800 x 1950 D2 Door 800 x 1800 W Window 1200 x 1000 V Ventilator 800 x 600
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Register Number Projections and ViewsDocument3 pagesRegister Number Projections and ViewsMahendranath RamakrishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- Manual of Engineering Drawing: British and International StandardsD'EverandManual of Engineering Drawing: British and International StandardsÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (4)
- EG QuestionsDocument36 pagesEG QuestionsRajueswarPas encore d'évaluation
- Autodesk 3ds Max 2015 Essentials: Autodesk Official PressD'EverandAutodesk 3ds Max 2015 Essentials: Autodesk Official PressÉvaluation : 1 sur 5 étoiles1/5 (1)
- Graphic QP Model 2Document2 pagesGraphic QP Model 2VIMAL APas encore d'évaluation
- Tribhuvan University Engineering Drawing Tutorial SheetsDocument29 pagesTribhuvan University Engineering Drawing Tutorial SheetsManoj Paudel67% (6)
- 09A10491 Engg DrawingDocument8 pages09A10491 Engg DrawingSaquib SalahiPas encore d'évaluation
- Prompting Science and Engineering Students in Practical TrigonometryD'EverandPrompting Science and Engineering Students in Practical TrigonometryPas encore d'évaluation
- SET-1 R09: Code No: 09A10291Document8 pagesSET-1 R09: Code No: 09A10291Joel WallerPas encore d'évaluation
- A Guide to Making a Leather Wallet - A Collection of Historical Articles on Designs and Methods for Making Wallets and BillfoldsD'EverandA Guide to Making a Leather Wallet - A Collection of Historical Articles on Designs and Methods for Making Wallets and BillfoldsPas encore d'évaluation
- 9a03101d Engineering DrawingDocument4 pages9a03101d Engineering DrawingsivabharathamurthyPas encore d'évaluation
- SSM Institute of Engineering and TechnologyDocument4 pagesSSM Institute of Engineering and TechnologyDhileepan KumarasamyPas encore d'évaluation
- 9a03101c Engineering DrawingDocument7 pages9a03101c Engineering DrawingsivabharathamurthyPas encore d'évaluation
- R5100107 Engineering GraphicsDocument2 pagesR5100107 Engineering GraphicssivabharathamurthyPas encore d'évaluation
- 1260R05010107 Engineering Graphics PDFDocument8 pages1260R05010107 Engineering Graphics PDFSridhar Atla100% (1)
- CAED Dec 2010 NewDocument1 pageCAED Dec 2010 NewPrasad C MPas encore d'évaluation
- r05010107 Engineering GraphicsDocument8 pagesr05010107 Engineering GraphicsSRINIVASA RAO GANTAPas encore d'évaluation
- ADITHYA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY COIMBATORE -107 PREPARATORY TESTDocument3 pagesADITHYA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY COIMBATORE -107 PREPARATORY TESTAnya CooperPas encore d'évaluation
- BMSCE Mechanical Engineering Dept CAMD TestDocument3 pagesBMSCE Mechanical Engineering Dept CAMD TestAll_regPas encore d'évaluation
- set-8Document1 pageset-8sivashanmugamPas encore d'évaluation
- Sheeet 12....Document3 pagesSheeet 12....sikandarPas encore d'évaluation
- CMS COLLEGE ENGINEERING INTERNAL TEST-III ECE-A/MECH-BDocument1 pageCMS COLLEGE ENGINEERING INTERNAL TEST-III ECE-A/MECH-Bsamy_175Pas encore d'évaluation
- 131AF012020 (1)Document2 pages131AF012020 (1)M S SHARATHPas encore d'évaluation
- 07a10191 Engineering GraphicsDocument11 pages07a10191 Engineering GraphicsSRINIVASA RAO GANTA100% (1)
- Medha Institute of Science&TechnologyDocument10 pagesMedha Institute of Science&TechnologyRama PrasadPas encore d'évaluation
- 9a03101c Engineering DrawingDocument1 page9a03101c Engineering DrawingsivabharathamurthyPas encore d'évaluation
- Anna University3Document2 pagesAnna University3madhes14Pas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering DrawingDocument5 pagesEngineering Drawingrsinha.0604Pas encore d'évaluation
- 9a03101e Engineering DrawingDocument4 pages9a03101e Engineering DrawingsivabharathamurthyPas encore d'évaluation
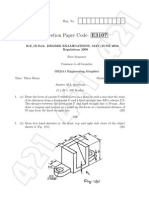
- Question Paper Code: E3107Document2 pagesQuestion Paper Code: E3107Jayakrishna KandasamyPas encore d'évaluation
- QP EG Model NIT R2023Document2 pagesQP EG Model NIT R2023ajayprakash4141Pas encore d'évaluation
- CVR College Engineering Graphics ExamDocument4 pagesCVR College Engineering Graphics ExamvenkateshPas encore d'évaluation
- Isometric and Perspective ViewsDocument15 pagesIsometric and Perspective ViewsVenkatesh MohanPas encore d'évaluation
- 9a03101b Engineering DrawingDocument5 pages9a03101b Engineering DrawingsivabharathamurthyPas encore d'évaluation
- 08 March 20 Assignment 4Document1 page08 March 20 Assignment 4pochireddy revathiPas encore d'évaluation
- GEETHANJALI ENGINEERING DRAWING DEVELOPMENT QUESTIONSDocument2 pagesGEETHANJALI ENGINEERING DRAWING DEVELOPMENT QUESTIONSramu vasaPas encore d'évaluation
- Rr10107 Engineering GraphicsDocument8 pagesRr10107 Engineering GraphicsSRINIVASA RAO GANTAPas encore d'évaluation
- 131AF052019Document2 pages131AF052019M S SHARATHPas encore d'évaluation
- Au Coe QP: Question Paper CodeDocument2 pagesAu Coe QP: Question Paper CodeSAISANDEEP K M UEC19340Pas encore d'évaluation
- Edrg 101Document1 pageEdrg 101Ramesh AdhikariPas encore d'évaluation
- Anna University GE2111 Engineering Graphics Dec 2011 Question PaperDocument4 pagesAnna University GE2111 Engineering Graphics Dec 2011 Question PaperPrem KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- 9a03101a Engineering DrawingDocument4 pages9a03101a Engineering DrawingsivabharathamurthyPas encore d'évaluation
- RazizDocument48 pagesRazizChandramohan GPas encore d'évaluation
- Computer Aided Engineering DrawingDocument11 pagesComputer Aided Engineering DrawingSyedZameerPas encore d'évaluation
- BE OU FirstYear EnggGraph May June 12Document12 pagesBE OU FirstYear EnggGraph May June 12Sri DPas encore d'évaluation
- Section of SolidsDocument4 pagesSection of Solidsanandandmeena100% (1)
- 266 - GE8152 Engineering Graphics - Jan 2018Document3 pages266 - GE8152 Engineering Graphics - Jan 2018Shahbaz KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Qus PaperDocument6 pagesQus PaperBalamurugan KarnanPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Drawing II Tutorial PDFDocument38 pagesEngineering Drawing II Tutorial PDFskumaranspPas encore d'évaluation
- Draw An INVOLUTE of Square With Side Length of 35mm Using AUTOCADDocument8 pagesDraw An INVOLUTE of Square With Side Length of 35mm Using AUTOCADDhileepan KumarasamyPas encore d'évaluation
- Jan-2011 Engineering Graphics Anna UniversityDocument2 pagesJan-2011 Engineering Graphics Anna UniversityChennaiSuperkingsPas encore d'évaluation
- Eg 2 TutorialDocument10 pagesEg 2 TutorialGanni GowthamPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Graphics Exam Drawing ProblemsDocument2 pagesEngineering Graphics Exam Drawing ProblemsSalim Saifudeen SaifudeenPas encore d'évaluation
- Projection of SolidsDocument8 pagesProjection of SolidsDrkumar SwamyPas encore d'évaluation
- ENGINEERING GRAPHICS UNIVERSITY QUESTION PAPERS With AnswersDocument36 pagesENGINEERING GRAPHICS UNIVERSITY QUESTION PAPERS With Answersculverts100% (4)
- BT I/d 20Document3 pagesBT I/d 20Aditya BhukkarPas encore d'évaluation
- e G in-III Int ExamDocument1 pagee G in-III Int Examsamy_175Pas encore d'évaluation
- Altenwörth 0 CH - 100: Greifenstein 40Document3 pagesAltenwörth 0 CH - 100: Greifenstein 40Mahendranath RamakrishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- Power FlowDocument31 pagesPower FlowumamaheshwarraoPas encore d'évaluation
- University Practical Schedule March - May 2014Document1 pageUniversity Practical Schedule March - May 2014Mahendranath RamakrishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- 30 2 CarsonDocument14 pages30 2 Carsonrussell_mahmoodPas encore d'évaluation
- A Year in LoveDocument2 pagesA Year in LoveMahendranath RamakrishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- 009 Holmes Layout-1aDocument14 pages009 Holmes Layout-1aMahendranath RamakrishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- TorrentsDocument3 pagesTorrentsMahendranath RamakrishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- Power FlowDocument31 pagesPower FlowumamaheshwarraoPas encore d'évaluation
- Power FlowDocument31 pagesPower FlowumamaheshwarraoPas encore d'évaluation
- Epic ObituaryDocument62 pagesEpic ObituaryMahendranath RamakrishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- C++ Notes: LIX, Ecole PolytechniqueDocument35 pagesC++ Notes: LIX, Ecole PolytechniqueMahendranath RamakrishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- JWDocument2 pagesJWNavarshi VishnubhotlaPas encore d'évaluation
- Allot - Jan 2014Document10 pagesAllot - Jan 2014Mahendranath RamakrishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- Theory VenturiDocument7 pagesTheory VenturiMahendranath RamakrishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- SBU UNit 2Document5 pagesSBU UNit 2Mahendranath RamakrishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- Solid Works Lab ManualDocument3 pagesSolid Works Lab ManualMahendranath RamakrishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- Sampling Theory and Hypothesis TestingDocument21 pagesSampling Theory and Hypothesis TestingMahendranath RamakrishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- Twelve ArticlesDocument107 pagesTwelve ArticlesMahendranath RamakrishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- 6C0075 (2006-07-08-09)Document4 pages6C0075 (2006-07-08-09)Mahendranath RamakrishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- Nat Turner: The Complexity and Dynamic of His Religious Background - by Jakobi Williams, Ph.D.Document35 pagesNat Turner: The Complexity and Dynamic of His Religious Background - by Jakobi Williams, Ph.D.☥ The Drop Squad Public Library ☥0% (1)
- Theory VenturiDocument7 pagesTheory VenturiMahendranath RamakrishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- PartDocument9 pagesPartMahendranath Ramakrishnan0% (2)
- 30 2 CarsonDocument14 pages30 2 Carsonrussell_mahmoodPas encore d'évaluation
- Pale Blue Dot (Carl Sagan)Document201 pagesPale Blue Dot (Carl Sagan)Amanda Rutllant100% (5)
- 4 Oop 1Document12 pages4 Oop 1Mohammed AlnasharPas encore d'évaluation
- 5ET219Document4 pages5ET219Mahendranath RamakrishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- CAD Assignment QuestionsDocument1 pageCAD Assignment QuestionsMahendranath RamakrishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- M.J Deepak Reddy Satyabama University, Chennai: Aeronautical EngineeringDocument29 pagesM.J Deepak Reddy Satyabama University, Chennai: Aeronautical EngineeringMahendranath RamakrishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- Sampling Theory and Hypothesis TestingDocument21 pagesSampling Theory and Hypothesis TestingMahendranath RamakrishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 Oop 1Document12 pages4 Oop 1Mohammed AlnasharPas encore d'évaluation
- P442 CortecDocument6 pagesP442 CortecHari Krishna.MPas encore d'évaluation
- Get admission in computer courses and earn a degree after examsDocument2 pagesGet admission in computer courses and earn a degree after examsShahbaz HassanPas encore d'évaluation
- Sybase 12 Install InstructionsDocument29 pagesSybase 12 Install InstructionsJohn ThorntonPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment - ACCESSDocument19 pagesAssignment - ACCESSTeyhaPas encore d'évaluation
- 27.tacacs Configuration in Aci - Learn Work ItDocument8 pages27.tacacs Configuration in Aci - Learn Work Itravi kantPas encore d'évaluation
- Railway Resevration Python ProgrameDocument11 pagesRailway Resevration Python Programenishant raj100% (1)
- LTO and CPR ProcessingDocument2 pagesLTO and CPR Processingverkie100% (9)
- Computer Network Q - A Part-1Document7 pagesComputer Network Q - A Part-1Avi DahiyaPas encore d'évaluation
- 3DS 2017 GEO Surpac 5tips and Tricks Ebook Vol 1 PDFDocument13 pages3DS 2017 GEO Surpac 5tips and Tricks Ebook Vol 1 PDFAbush DestaPas encore d'évaluation
- Online ClassDocument5 pagesOnline ClassLokendra RathorePas encore d'évaluation
- En - Slide - CCNA 1 - Module 1 - Introduction To The NetworkDocument54 pagesEn - Slide - CCNA 1 - Module 1 - Introduction To The Networkcamarad77Pas encore d'évaluation
- DIALux Setup InformationÑLLDocument14 pagesDIALux Setup InformationÑLLJeckson FlorianPas encore d'évaluation
- SSH Key Generation ReferenceDocument6 pagesSSH Key Generation ReferenceBabjee ReddyPas encore d'évaluation
- Ora Net 1aDocument12 pagesOra Net 1aYulin LiuPas encore d'évaluation
- Manual Virex Pro 3.19r2 FR - 19!04!2012Document73 pagesManual Virex Pro 3.19r2 FR - 19!04!2012Lance Johnpaul SyPas encore d'évaluation
- System Requirements For DS Icem Surf 2017Document3 pagesSystem Requirements For DS Icem Surf 2017Hatim EddibPas encore d'évaluation
- Script MafiaDocument2 pagesScript MafiaHassan FethiPas encore d'évaluation
- CIE Lab Color SpaceDocument6 pagesCIE Lab Color SpaceOswaldo Cortés Vázquez0% (1)
- ControlNet and RSNetWorx Design GuideDocument160 pagesControlNet and RSNetWorx Design GuideGerman ParraPas encore d'évaluation
- MQ Managed File Transfer OverviewDocument72 pagesMQ Managed File Transfer OverviewfreddyandresPas encore d'évaluation
- Export Failed: The Data Cannot Be Displayed Because The Query Returned Too Many Records. Please Try Filtering Your Data in SAP Analytics CloudDocument2 pagesExport Failed: The Data Cannot Be Displayed Because The Query Returned Too Many Records. Please Try Filtering Your Data in SAP Analytics CloudVENKATESHPas encore d'évaluation
- The New Art of MemoryDocument514 pagesThe New Art of MemoryEduardo CostaPas encore d'évaluation
- JavaScript Print Version - Wikibooks Open Books For An Open World PDFDocument60 pagesJavaScript Print Version - Wikibooks Open Books For An Open World PDFsiriuslotPas encore d'évaluation
- Nemo Handy and Walker Air 3.40Document16 pagesNemo Handy and Walker Air 3.40miro1964Pas encore d'évaluation
- RobotShop Learning Center - Robotic TrendsDocument5 pagesRobotShop Learning Center - Robotic TrendsMC. Rene Solis R.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Project Proposal: Islamia College University PeshawerDocument8 pagesProject Proposal: Islamia College University PeshawerAmir Zeb JhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Canteen Management SystemDocument13 pagesCanteen Management SystemKay KaraychayPas encore d'évaluation
- CIS552 Indexing and Hashing 1Document56 pagesCIS552 Indexing and Hashing 1Vinay VarmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Data Structure NotesDocument171 pagesData Structure NoteskavirajeePas encore d'évaluation
- A Place of My Own: The Architecture of DaydreamsD'EverandA Place of My Own: The Architecture of DaydreamsÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (241)
- Nuclear Energy in the 21st Century: World Nuclear University PressD'EverandNuclear Energy in the 21st Century: World Nuclear University PressÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (3)
- The Complete HVAC BIBLE for Beginners: The Most Practical & Updated Guide to Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning Systems | Installation, Troubleshooting and Repair | Residential & CommercialD'EverandThe Complete HVAC BIBLE for Beginners: The Most Practical & Updated Guide to Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning Systems | Installation, Troubleshooting and Repair | Residential & CommercialPas encore d'évaluation
- Piping and Pipeline Calculations Manual: Construction, Design Fabrication and ExaminationD'EverandPiping and Pipeline Calculations Manual: Construction, Design Fabrication and ExaminationÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (18)
- Building Construction Technology: A Useful Guide - Part 2D'EverandBuilding Construction Technology: A Useful Guide - Part 2Évaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Functional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsD'EverandFunctional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsPas encore d'évaluation
- An Architect's Guide to Construction: Tales from the Trenches Book 1D'EverandAn Architect's Guide to Construction: Tales from the Trenches Book 1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Civil Engineer's Handbook of Professional PracticeD'EverandCivil Engineer's Handbook of Professional PracticeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (2)
- An Introduction to the Periodic Table of Elements : Chemistry Textbook Grade 8 | Children's Chemistry BooksD'EverandAn Introduction to the Periodic Table of Elements : Chemistry Textbook Grade 8 | Children's Chemistry BooksÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- The Complete Guide to Alternative Home Building Materials & Methods: Including Sod, Compressed Earth, Plaster, Straw, Beer Cans, Bottles, Cordwood, and Many Other Low Cost MaterialsD'EverandThe Complete Guide to Alternative Home Building Materials & Methods: Including Sod, Compressed Earth, Plaster, Straw, Beer Cans, Bottles, Cordwood, and Many Other Low Cost MaterialsÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (6)
- How to Estimate with RSMeans Data: Basic Skills for Building ConstructionD'EverandHow to Estimate with RSMeans Data: Basic Skills for Building ConstructionÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (2)
- Pressure Vessels: Design, Formulas, Codes, and Interview Questions & Answers ExplainedD'EverandPressure Vessels: Design, Formulas, Codes, and Interview Questions & Answers ExplainedÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Trevor Kletz Compendium: His Process Safety Wisdom Updated for a New GenerationD'EverandTrevor Kletz Compendium: His Process Safety Wisdom Updated for a New GenerationPas encore d'évaluation
- The Complete Guide to Building Your Own Home and Saving Thousands on Your New HouseD'EverandThe Complete Guide to Building Your Own Home and Saving Thousands on Your New HouseÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (3)
- Building Construction Technology: A Useful Guide - Part 1D'EverandBuilding Construction Technology: A Useful Guide - Part 1Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (3)
- Practical Guides to Testing and Commissioning of Mechanical, Electrical and Plumbing (Mep) InstallationsD'EverandPractical Guides to Testing and Commissioning of Mechanical, Electrical and Plumbing (Mep) InstallationsÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (3)
- Field Guide for Construction Management: Management by Walking AroundD'EverandField Guide for Construction Management: Management by Walking AroundÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (3)
- Engineering Critical Assessment (ECA) for Offshore Pipeline SystemsD'EverandEngineering Critical Assessment (ECA) for Offshore Pipeline SystemsPas encore d'évaluation
- Process Engineering for a Small Planet: How to Reuse, Re-Purpose, and Retrofit Existing Process EquipmentD'EverandProcess Engineering for a Small Planet: How to Reuse, Re-Purpose, and Retrofit Existing Process EquipmentPas encore d'évaluation
- 1,001 Questions & Answers for the CWI Exam: Welding Metallurgy and Visual Inspection Study GuideD'Everand1,001 Questions & Answers for the CWI Exam: Welding Metallurgy and Visual Inspection Study GuideÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (7)
- How to Write Construction Programmes & SchedulesD'EverandHow to Write Construction Programmes & SchedulesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (9)
- Produced Water Treatment Field ManualD'EverandProduced Water Treatment Field ManualÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (5)
- An Applied Guide to Water and Effluent Treatment Plant DesignD'EverandAn Applied Guide to Water and Effluent Treatment Plant DesignÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (4)
- Guidelines for Chemical Process Quantitative Risk AnalysisD'EverandGuidelines for Chemical Process Quantitative Risk AnalysisÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)