Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
HW3 2003
Transféré par
girithik14Description originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
HW3 2003
Transféré par
girithik14Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
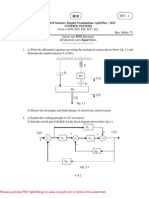
ECE 461 - Homework Set #3
EE 461 - Homework Set #3
Due Wednesday, September 17th
Transfer Function for Electrical Systems
2-Tank System
U X 1 X 2
Circuit Equivalent R1
X1
X2 +
U C1 C2
R2
Y -
1) 2-Tank System. C1 = C2 = 1F. R1 = 10, R2 = 100 1a) Write the node equations for the 2-tank system. 1b) Find the transfer function from U to Y 1c) What are the dominant pole(s) for this system? 1d) From the dominant pole(s), determine the systems response to a step input, including i) Steady-State value (DC gain), ii) Overshoot, iii) Settling Time
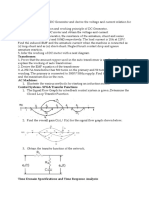
Temperature Along a Metal Bar U
Finite Elements T1
Mechanical System T2 Electrical Equivalent R T2
Y T3 T4
T1
T3
T4 +
+ C C C C
Y -
2) Temperature on a Metal Bar. R = 1.5M, C = 1uF. 2a) Write the node equations for the folowing circuit 2b) Find the transfer function from U to Y 2c) What are the dominant pole(s) for this system? 2d) From the dominant pole(s), determine the systems response to a step input, including i) Steady-State value (DC gain), ii) Overshoot, iii) Settling Time
ECE 461 - Homework Set #3
DC Servo Motor: Ra = 1 Ohm La = 50mH J = 0.1kg m2 B = 0.5Ns/m Kt = 5N/A = 5Vs 3a) Find the transfer function for a DC servo motor from Va (the voltage applied to the armature) to (the motor speed). 3b) What are the dominant pole(s) for this system?
Ra
La Ia W B J
Va
+ -
Kt W
+ -
Kt Ia
3c) From the dominant pole(s), determine the systems response to a step input, including i) Steady-State value (DC gain), ii) Overshoot, iii) Settling Time
4) For the DC servo motor, replace the voltage source with a current source. 4a) Find the transfer function from Ia to . 4b) What are the dominant pole(s) for this system? 4c) From the dominant pole(s), determine the systems response to a step input, including i) Steady-State value (DC gain), ii) Overshoot, iii) Settling Time
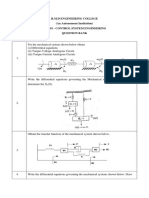
Mechanical Systems: 1/4 Car Model 5) The system to the right is called a 1/4 car model and is used to design the suspension of a car. 5a) Write the circuit equivalent for this system: 5b) Write the node equations for this system. 5c) Write the state-space equations which describe the dynamics of this system as
F
M (s 2 X) + B (sX) + K X = H F
6) Assume M1 = M2 = 1kg K1 = K2 = 100N/m B1 = 1Ns/m 6a) Find the transfer function from F ro X1 6b) Find the transfer function from F to (X1-X2) 6c) How do the poles change as you change what you define as the output?
M1 (Car)
X1
B1 (shocks)
K1 (springs)
M2 (tire)
X2
K2
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- ENT 300 Individual Assessment-Personal Entrepreneurial CompetenciesDocument8 pagesENT 300 Individual Assessment-Personal Entrepreneurial CompetenciesAbu Ammar Al-hakimPas encore d'évaluation
- DFo 2 1Document15 pagesDFo 2 1Donna HernandezPas encore d'évaluation
- AE6505 Control EngineeringDocument9 pagesAE6505 Control Engineeringsathesh waranPas encore d'évaluation
- Sheet 1 Process ControlDocument2 pagesSheet 1 Process ControlEng ForQ3Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sheet 1Document2 pagesSheet 1Eng ForQ3Pas encore d'évaluation
- 9A02503 Control SystemsDocument4 pages9A02503 Control SystemssivabharathamurthyPas encore d'évaluation
- QB BcsDocument10 pagesQB BcsKrishna Reddy Y.VPas encore d'évaluation
- IC6501-Control Systems EngineeringDocument16 pagesIC6501-Control Systems EngineeringragupaPas encore d'évaluation
- EC6405-Control Systems EngineeringDocument12 pagesEC6405-Control Systems EngineeringAnonymous XhmybK0% (1)
- Linear Control Engineering QBDocument11 pagesLinear Control Engineering QBAkizuki TakaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Question Bank: Unit I Systems and Their RepresentationDocument6 pagesQuestion Bank: Unit I Systems and Their RepresentationramyakalaPas encore d'évaluation
- TUTORIAL 6 - System ResponseDocument15 pagesTUTORIAL 6 - System ResponsetiraPas encore d'évaluation
- LCS Assignment-IDocument2 pagesLCS Assignment-IUnmesh PeriPas encore d'évaluation
- Dept of Aero: Unit I-Introduction PART - A (2 Marks)Document9 pagesDept of Aero: Unit I-Introduction PART - A (2 Marks)DeepakLingamoorthyPas encore d'évaluation
- EC602 Control Q Bank 2023Document9 pagesEC602 Control Q Bank 2023ROHAN CHOWDHURYPas encore d'évaluation
- QUESTION BANK of Control Systems Engineering PDFDocument12 pagesQUESTION BANK of Control Systems Engineering PDFMouhanit LimbachiyaPas encore d'évaluation
- II B.Tech II Semester, Regular Examinations, April/May - 2012 Control SystemsDocument8 pagesII B.Tech II Semester, Regular Examinations, April/May - 2012 Control SystemsViswa ChaitanyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Control SystemsDocument8 pagesControl Systemsvasantha_btechPas encore d'évaluation
- Final Exam - SampleDocument4 pagesFinal Exam - SampleAhmed MashhoorPas encore d'évaluation
- Control SystemsDocument8 pagesControl SystemsammukeeruPas encore d'évaluation
- DC MachinesDocument3 pagesDC Machines19euec154 - SUDARSAN PERUMAL VPas encore d'évaluation
- 208 - EC8391, EC6405 Control System Engineering - Important QuestionsDocument7 pages208 - EC8391, EC6405 Control System Engineering - Important QuestionsSagar Babu NandigamaPas encore d'évaluation
- Acs 2013s1 Assn1Document6 pagesAcs 2013s1 Assn1MiraelPas encore d'évaluation
- Kings: Department of Electronics and Communication EngineeringDocument12 pagesKings: Department of Electronics and Communication EngineeringLatosha FarrellPas encore d'évaluation
- VI Sem ECEDocument12 pagesVI Sem ECESenthil Kumar KrishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- 2008 ControlDocument3 pages2008 ControlPujan NarjinaryPas encore d'évaluation
- IC6501-Control Systems EngineeringDocument16 pagesIC6501-Control Systems EngineeringrameshsmePas encore d'évaluation
- EE404LinearSystemsAnalysis April2010 2006schemeDocument2 pagesEE404LinearSystemsAnalysis April2010 2006schemeAnith KrishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- Control System Question BankDocument12 pagesControl System Question Banksagar R RaoPas encore d'évaluation
- IAT SolutionsDocument13 pagesIAT Solutionsjay mehtaPas encore d'évaluation
- 3cs EceDocument3 pages3cs Ecekirankumar412Pas encore d'évaluation
- B. Tech Control SystemsDocument2 pagesB. Tech Control SystemsAnant VermaPas encore d'évaluation
- 130403control System - Unit12Document4 pages130403control System - Unit12Nitin GoyalPas encore d'évaluation
- Control System 2MARKSDocument16 pagesControl System 2MARKSSeekay Alais Karuppaiah CPas encore d'évaluation
- Control System Question BankDocument23 pagesControl System Question Bankdr mbaluPas encore d'évaluation
- Ece4 Lcs Dec09Document3 pagesEce4 Lcs Dec09MohitPas encore d'évaluation
- Cs April 2011Document8 pagesCs April 201129viswa12Pas encore d'évaluation
- LDCS QuestionsDocument10 pagesLDCS QuestionsRiya SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- IES Conventional Electrical Engineering 2012Document28 pagesIES Conventional Electrical Engineering 2012Srujan BobbyPas encore d'évaluation
- 9A19401 Control SystemsDocument5 pages9A19401 Control SystemssivabharathamurthyPas encore d'évaluation
- B. Tech Control SystemsDocument2 pagesB. Tech Control SystemsAnant VermaPas encore d'évaluation
- Code - No: 45106Document2 pagesCode - No: 45106Raj SamuelPas encore d'évaluation
- Acs 2012s2 Assn1Document6 pagesAcs 2012s2 Assn1MiraelPas encore d'évaluation
- Control SystemsDocument8 pagesControl SystemspadmajasivaPas encore d'évaluation
- Acs 2018s2 Assn1Document4 pagesAcs 2018s2 Assn1MiraelPas encore d'évaluation
- 45 37295 Ee311 2013 1 1 1 Ee311Document11 pages45 37295 Ee311 2013 1 1 1 Ee311Osama AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- R.M.D Engineering College (An Autonomous Institution) Ec8391 - Control System Engineering Question BankDocument6 pagesR.M.D Engineering College (An Autonomous Institution) Ec8391 - Control System Engineering Question Bankaarthir88Pas encore d'évaluation
- ACE EE Con-1Document8 pagesACE EE Con-1abishek_bhardwa8666Pas encore d'évaluation
- IES - Electronics Engineering - Control System PDFDocument66 pagesIES - Electronics Engineering - Control System PDFRod S Pangantihon Jr.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Gandhinagar Institute of Technology: Question BankDocument5 pagesGandhinagar Institute of Technology: Question BankvineetanishadPas encore d'évaluation
- Modeling and Experimental Validation of A First Order Plant Model: DC Servo MotorDocument17 pagesModeling and Experimental Validation of A First Order Plant Model: DC Servo Motormeghraj01Pas encore d'évaluation
- ExercisesDocument58 pagesExercisesmjdaleneziPas encore d'évaluation
- Control Syst Test IDocument4 pagesControl Syst Test IreporterrajiniPas encore d'évaluation
- Control System Short Answer Type QuestionsDocument1 pageControl System Short Answer Type QuestionsAlka GoyalPas encore d'évaluation
- Control Systems Unitwise Important Questions Unit 1 Part ADocument10 pagesControl Systems Unitwise Important Questions Unit 1 Part AChandra shekarPas encore d'évaluation
- B. Tech. (ME) IV-Semester, Sessional Test-Ii (2014-15) : Aligarh College of Engineering & Technology, AligarhDocument2 pagesB. Tech. (ME) IV-Semester, Sessional Test-Ii (2014-15) : Aligarh College of Engineering & Technology, AligarhamarPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment No.03: Mathematical Modeling of Physical System: ObjectiveDocument5 pagesExperiment No.03: Mathematical Modeling of Physical System: ObjectiveSao SavathPas encore d'évaluation
- Note: No Additional Answer Sheets Will Be Provided.: (An Autonomous Institution)Document3 pagesNote: No Additional Answer Sheets Will Be Provided.: (An Autonomous Institution)Rajesh AnugulaPas encore d'évaluation
- RegelTechniek1 2014Document3 pagesRegelTechniek1 2014John AppleseedPas encore d'évaluation
- Simulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetD'EverandSimulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetPas encore d'évaluation
- Simulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetD'EverandSimulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetÉvaluation : 2 sur 5 étoiles2/5 (1)
- Power Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 2: Power Converters and their ControlD'EverandPower Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 2: Power Converters and their ControlÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- CXA Series Signal AnalyzerDocument60 pagesCXA Series Signal Analyzergirithik14Pas encore d'évaluation
- SCADE Training Catalogue 2014Document33 pagesSCADE Training Catalogue 2014girithik14Pas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial Antenna Design CSTDocument37 pagesTutorial Antenna Design CSTLiz BenhamouPas encore d'évaluation
- AFDX Training October 2010 FullDocument55 pagesAFDX Training October 2010 FullHugues de PayensPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study DO-254Document9 pagesCase Study DO-254girithik14Pas encore d'évaluation
- Safety-Critical Software Development: DO-178B: Prof. Chris Johnson, School of Computing Science, University of GlasgowDocument38 pagesSafety-Critical Software Development: DO-178B: Prof. Chris Johnson, School of Computing Science, University of Glasgowgirithik14Pas encore d'évaluation
- Orbital Rendezvous Using An Augmented Lambert Guidance SchemeDocument0 pageOrbital Rendezvous Using An Augmented Lambert Guidance Schemegirithik14Pas encore d'évaluation
- EE 461 - Homework Set #4Document4 pagesEE 461 - Homework Set #4girithik14Pas encore d'évaluation
- Experimental Design, Sensitivity Analysis, and OptimizationDocument24 pagesExperimental Design, Sensitivity Analysis, and Optimizationgirithik14Pas encore d'évaluation
- ECE 461: Homework #5: Water Level Control: 1) The Dynamics of A 2-Tank System With Proportional (P K) Feedback AreDocument1 pageECE 461: Homework #5: Water Level Control: 1) The Dynamics of A 2-Tank System With Proportional (P K) Feedback Aregirithik14Pas encore d'évaluation
- Seabank Statement 20220726Document4 pagesSeabank Statement 20220726Alesa WahabappPas encore d'évaluation
- Pulmonary EmbolismDocument48 pagesPulmonary Embolismganga2424100% (3)
- 1B20 40Document4 pages1B20 40Electrival TcatallerPas encore d'évaluation
- National Football League FRC 2000 Sol SRGBDocument33 pagesNational Football League FRC 2000 Sol SRGBMick StukesPas encore d'évaluation
- Bcci ScandalDocument6 pagesBcci ScandalNausaf AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Guardcam InstructionsDocument12 pagesGuardcam InstructionsCompuFix RepairsPas encore d'évaluation
- 1995 Biology Paper I Marking SchemeDocument13 pages1995 Biology Paper I Marking Schemetramysss100% (2)
- BIAN How To Guide Developing Content V7.0 Final V1.0 PDFDocument72 pagesBIAN How To Guide Developing Content V7.0 Final V1.0 PDFميلاد نوروزي رهبرPas encore d'évaluation
- Soil NailingDocument6 pagesSoil Nailingvinodreddy146Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fundamentals of Signal and Power Integrity PDFDocument46 pagesFundamentals of Signal and Power Integrity PDFjaltitiPas encore d'évaluation
- Surgery - 2020 With CorrectionDocument70 pagesSurgery - 2020 With CorrectionBaraa KassisPas encore d'évaluation
- Concrete Repair Manual (2017)Document59 pagesConcrete Repair Manual (2017)Fernando EscriváPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is Universe?Document19 pagesWhat Is Universe?Ruben M. VerdidaPas encore d'évaluation
- Random Variables Random Variables - A Random Variable Is A Process, Which When FollowedDocument2 pagesRandom Variables Random Variables - A Random Variable Is A Process, Which When FollowedsdlfPas encore d'évaluation
- M. Ircham Mansyur 07224005 Microprocessor-2 (H13)Document7 pagesM. Ircham Mansyur 07224005 Microprocessor-2 (H13)emiierPas encore d'évaluation
- Dreaded Attack - Voyages Community Map Rules v1Document2 pagesDreaded Attack - Voyages Community Map Rules v1jPas encore d'évaluation
- Comparative Study Between Online and Offilne Learning With Reference of Tutedude E-LearningDocument61 pagesComparative Study Between Online and Offilne Learning With Reference of Tutedude E-LearningDeeksha Saxena0% (2)
- This Study Resource Was: For The Next 6 ItemsDocument9 pagesThis Study Resource Was: For The Next 6 ItemsJames CastañedaPas encore d'évaluation
- JFC 180BBDocument2 pagesJFC 180BBnazmulPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment - 1: Batch (Differential) Distillation: 1. ObjectiveDocument30 pagesExperiment - 1: Batch (Differential) Distillation: 1. ObjectiveNaren ParasharPas encore d'évaluation
- Conservation Assignment 02Document16 pagesConservation Assignment 02RAJU VENKATAPas encore d'évaluation
- 10 Killer Tips For Transcribing Jazz Solos - Jazz AdviceDocument21 pages10 Killer Tips For Transcribing Jazz Solos - Jazz Advicecdmb100% (2)
- in 30 MinutesDocument5 pagesin 30 MinutesCésar DiazPas encore d'évaluation
- (Campus of Open Learning) University of Delhi Delhi-110007Document1 page(Campus of Open Learning) University of Delhi Delhi-110007Sahil Singh RanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Acc116 Dec 2022 - Q - Test 1Document6 pagesAcc116 Dec 2022 - Q - Test 12022825274100% (1)
- Final WMS2023 HairdressingDocument15 pagesFinal WMS2023 HairdressingMIRAWATI SAHIBPas encore d'évaluation
- Santu BabaDocument2 pagesSantu Babaamveryhot0950% (2)
- Bba VDocument2 pagesBba VkunalbrabbitPas encore d'évaluation