Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Drugs Study
Transféré par
Mark CapillanesCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Drugs Study
Transféré par
Mark CapillanesDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
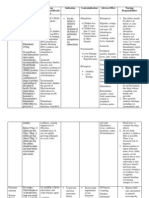
Generic Name: Brand name:
Furosemide Lasix
Classifications: Date ordered & dosage:
Diuretics, loop diuretic (6-16-13) stat 40 mg IV now (11:30am) (6-18-13) stat 20 mg IVTT now (6-21-13) stat 60 mg IVTT now (11:15pm) (6-23-13) 40 mg 1 tab OD (6pm)
Suggested dose:
20-80 mg/ day as a single dose initially, may repeat in 6-8 hours.
Indication:
Edema due to heart failure, hepatic impairment or renal disease. Hypertension.
Mode of Action:
Inhibits the reabsorption of sodium and chloride from the loop of Henle and distal renal tubule. Increases renal excretion of water, sodium, chloride, magnesium, potassium, and calcium. Decreases Blood pressure.
Contraindications:
Severe sodium and water depletion, hypersensitivity to sulphonamides and furosemide, hypokalaemia, hyponatraemia, precomatose states associated with liver cirrhosis, anuria or renal failure. Addison's disease.
Side effect:
CNS: blurred vision, dizziness, headache, vertigo EENT: hearing loss, tinnitus
Adverse Effects:
CV: hypotension GI: excessive urination Derm: photosensitivity, pruritis F&E: dehydration, hypochloremia, hypokalemia Endo: hyperglycemia, hyperuricemia Hemat: aplastic anemia, agranulocytosis, hemolytic anemia, leucopenia, thrombocytopenia
Drug interaction:
Analgesics reduce natriuretic action of furosemide. Antagoniseshypoglycaemic agents and drugs used for gout. Hyperglycaemia with antihypertensive agent diazoxide. Antagonises muscle relaxants. Increased risk of ototoxicity when used with aminoglycosides especially in renal impairment. May enhance nephrotoxicity of cephalosporins. Effects of antihypertensives enhanced. Action antagonised by corticosteroids. Phenytoin and indometacin may reduce effects of furosemide.
Nursing responsibilities:
- Assess fluid status. Monitor daily weight, intake and output ratios. - Monitor blood pressure and pulse before and during administration. Monitor frequency of prescription refills to determine compliance in patients treated for hypertension. - Geri: Diuretic use is associated with increased risk for falls in older adults. Keep patient safe at all times. - Monitor laboratory tests such as electrolytes, renal and hepatic function, serum glucose, etc. - PO: may be taken with food or milk to minimize gastric irritation. - Caution patient to change positions slowly to minimize orthostatic hypotension.
Generic Name: Brand name:
Acetamenophen Paracetamol
Classifications: Date ordered & dosage: Suggested dose: Indication: Mode of Action:
Antipyretics, Nonopioid Analgesics 6-18-13 1 tab 500 mg q4 PRN for fever 1 tab for mild to moderate pain and fever. Mild pain; fever Inhibits the synthesis of prostaglandins that may serve as mediators of pain and fever, primarily in the CNS. Has no significant anti-inflammatory properties or GI toxicity; Analgesia, antipyresis.
Contraindications:
Previous hypersensitivity; product containing alcohol, aspartame, saccharin, sugar or tartrazine should be avoided in patients who hypersensitivity or intolerance to these compounds. Use cautiously: Hepatic disease/ renal disease; chronic alcohol use/ abuse; malnutrition
Side effect:
CNS: confusion, headache GI: constipation nausea, vomiting
Adverse Effects:
GI: Hepatic failure, hepatotoxicity (overdose) GU: renal failure (high doses/chronic use); Heme: neutropenia, pancytopenia, leukopenia;
Drug interaction:
Drug-drug: chronic high-dose acetaminophen (>2g/day) may increase risk of bleeding with warfarin (PT should be monitored regularly and INR should not exceed 4); Hepatotoxicity is additive with other hepatotoxic substances including alcohol; concurrent use of sulfinpyrazone, isoniazid, rifampinrifabutin, phenytoin, barbiturates and carbamazepine may increase the risk of acetaminophen-induced liver damage; these agents will also decrease therapeutic effects of acetaminophen. Concurrent NSAIDs increase the risk of adverse renal effects; Propanolol decrease metabolism and may increase effects; may decrease effects of lamotrigine and zidovudine.
Nursing responsibilities:
- Assess overall health status and alcohol usage before administering acetaminophen. Patients who are
malnourished or chronically abuse alcohol are at higher risk of developing hepatotoxicity with chronic use of usual doses of this drug. - Asses fever; note presence of associated signs (diaphoresis, tachycardia and malaise). - If overdose occurs, acetylcysteine (Acetadote) is the antidote. When combined with opioids do not exceed the
maximum recommended daily dose of acetaminophen. - Advise patient to consult health care professional if discomfort or fever is not relieved by routine doses of this drug or if fever is greater than 39.5 C or lasts longer than 3 days.
Generic Name: Brand name:
Piperacillin + Tazobactam Tazovex
Classifications: Date ordered & dosage: Suggested dose: Indication:
Antibiotic, Penicillin 6-20-13 2.5 g IVTT q 6 ANST (-) (6-16-6-12) 3.75 4.5 grams q 6 Moderate to severe infections piperacillin-resistant, Blactamse producing strains causing infections in the respiratory, skin, urinary tract, bone, pneumonia.
Mode of Action:
This combination medication is an antibacterial agent, prescribed for various infections such as Nosocomial pneumonia. It blocks the bacteria's cell wall growth, which kills the bacteria. Tazobactam inhibits the action of bacterial beta-lactamases. It is added to the extended spectrum beta-lactam antibiotic piperacillin. It broadens the spectrum of piperacillin by making it effective against organisms that express beta-lactamase and would normally degrade piperacillin.
Contraindications: Side effect:
Hypersensitivity to penicillin, cephalosporin GI: Diarrhea, constipation, nausea and vomiting, dyspepsia, abdominal pain CNS: Headache, Insomnia, fever, dizziness, anxiety
Adverse Effects:
GI: PSEUDOMEMBRANOUS COLITIS , drug induced
hepatitis GU: interstitial nephritis Heme: leukopenia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia Other: phlebitis at IV site, ANAPHYLAXIS Drug interaction: Probenecid decrease renal excretion and increases blood levels. May alter excretion of lithium. Potassium-losing diuretics, corticosteroids, or amphotericin B. Increases risk of hepatotoxicity with other hepatotoxic agents. Nursing responsibilities: - Obtain a history before initiating therapy to determine previous use of and reactions to penicillins or cephalosporins. Persons with a negative history of penicillin sensitivity may still have an allergic response. - Assess patient for infection (vital signs; sputum, urine, and stool WBC) at beginning of and during therapy. - Obtain specimens for culture and sensitivity prior to initiating therapy. First dose may be given before receiving results. - Observe patient for signs and symptoms of anaphylaxis (rash, pruritus, laryngeal edema, wheezing). Discontinue the drug and notify the physician or other health care profession al immediately if these occur. Keep epinephrine, an antihistamine, and resuscitation equipment close by in the event of an anaphylactic reaction. - Check lab results to evaluate renal and hepatic function, CBC, serum potassium, and bleeding times prior to and routinely during therapy. - Advise patient to report signs of superinfection (black furry overgrowth on tongue, loose or foul-smelling stools) and allergy.
Generic Name: Brand name:
Potassium Chloride KaliumDurule
Classifications: Date ordered & dosage: Suggested dose: Indication:
Electrolyte, supplement (6-21-13) 2 tabs now (8:30 pm) (6-23-13) 1 tab TID x 3 days 2 durules bid or more until serum K is restored to normal Prevention and correction of potassium deficiency; when associated with alkalosis, use potassium chloride.
Mode of Action:
Potassium chloride is amajorcation of theintracellular fluid. It plays an active role in the conduction of nerve impulses in the heart, brain and skeletal muscle; contraction of cardiac skeletal and smooth muscles; maintenance of normal renal f unction, acidbase balance, carbohydrate metabolism and gastric secretion.
Contraindications:
Contraindicated with allergy to tartrazine, aspirin,severe renal impairment with oliguria, anuria, azotemia; untreated Addisons disease; hyperkalemia; adynamiaepisodicahereditaria; acute dehydration; heat cramps; GI disorders that delay passage in the GI tract. Use cautiously with cardiac disorders, especially if
treated with digitalis, pregnancy, lactation. Side effect: Adverse Effects: GI: Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal discomfort GI obstruction, GI bleeding, GI ulceration or perforation Hematologic: Hyperkalemiaincreased serum K+ Local: Tissue sloughing, local necrosis, local phlebitis. Drug interaction: Using potassium phosphate IV and products containing calcium or magnesium potassium sparing diuretics or other potassium products. Nursing responsibilities: - Assess vital signs of the patient specifically the cardiac status : Monitor pulse, blood pressure, and ECG - Tell patient not break, crush or chew tablets/capsule or enteric products. - If GI upset occurs, tell the patient that the medicine can be taken after meals or with food with a full glass of water. - Monitor serum potassium before and periodically during therapy, Monitor renal function, serum bicarbonate, and pH - Encourage patient and watcher to report hyperkalemia symptoms (lethargy, confusion, diarrhea, nausea and vomiting and decreased urine output.) - discontinue potassium, administration if hyperkalemia (slow, irregular heartbeat; fatigue; muscle weakness; paresthesia; confusion; dyspnea; peaked T waves; depressed ST segments; prolonged QT segments; widened QRS complexes; loss of P waves; and cardiac arrhythmias) occur.
Generic Name: Brand name:
Mucosta Rebapimide
Classifications: Date ordered & dosage: Suggested dose: Indication: Mode of Action:
Antacid, cytoprotective agent 6-12-13 1 tab TID (6-12-6) 1 tab orally 3 times daily. Peptic ulcer, acute gastritis Increasing the prostaglandin E2 content and exerting a cytoprotective effect on the gastric mucosa. The medicine also increases the amount of gastric mucus and stimulates gastric mucosal blood flow to improve impaired hemodynamics, thus helps to suppress inflammation and repair the gastric mucosa.
Contraindications:
Hypersensitivity and its components, pregnant, breatfeeding.
Side effect:
CNS: headache GI: abdominal pain, diarrhea, constipation, dyspepsia, flatulence, nausea, vomiting
Adverse Effects:
Heme: leukopenia, thrompocytopenia Other: anaphylaxis, hepatic dysfunction, shock
Drug interaction:
Increased risk of diarrhea with magnesium-containing
antacids. Nursing responsibilities: - Assess patient routinely for epigastric or abdominal pain and for frank or occult blood, in the stool, emesis, or gastric aspirate - Check CBC, serum ALT, AST if available - Administer medication with meals to reduce severity of diarrhea - Inform patient that side effects may occur such as diarrhea, constipations. - instruct to report to health care professional if diarrhea persists, Also ad vise patient to report onset of black, tarry, stools or severe abdominal pain
Amlodipine Generic Name: Amlodipine Brand name: Norvasc Classification: Anti-Anginal Drugs Calcium-channel blocker
Mode of Action: It works by relaxing blood vessels which allows blood to circulate more freely around your body. This lowers blood pressure, improves the efficiency of the heart and helps prevent chest pain associated with angina. Suggested dose: 5 mg daily Ordered Dose: 5 mg 1 tab OD Indication: Hypertension; chronic stable angina; vasospastic angina.
Contraindication: Sick sinus syndrome; second- or 3rd- degree AV block; except w/ a functioning pacemaker. Drug interaction: Drug-drug Beta blockers may cause increased adverse cardiac effect as a result of myocardial depression. Fentanyl -Severe hypotension or increased fluid volume requirements have occurred w/ similar drugs. Side effect: dizziness, headache, nausea and vomiting.
Adverse effect: Skin rash, allergic reaction, dyspnea and anaphylaxis.
Nursing Responsibilities: Caution patient to change positions slowly to minimize orthostatic hypotension. Monitor blood pressure and pulse prior to administering the drug. Report immediately and swelling, redness, burning, or pain at infusion site. Discontinue the infusion if the patient develops tachycardia or hypotension. Assess for hypersensitivity after giving medications. Advise patient that compliance of this medication is important.
Insulin Generic Name: Insulin Brand Name: Humulin (isophane neutral protamine hagedorn 70%,regular 30%) Classification: anti-diabetic hormone Mode of Action: Promotes glucose transport,which stimulates carbohydrate metabolism in skeletal and cardiac muscle and adipose tissue. Also promotes phosphorylation of glucose in liver, where its converted to glycogen. Directly affects fat and protein metabolism , stimulates protein synthesis , inhibits release of free fatty acids, and indirectly decreases phosphate and potassium. Suggested Dose: 0.2-0.5 unit/kg/day subcutaneously Ordered Dose: Indications: Type 1 (insulin dependent ) diabetes mellitus Type2 ( non-insulin-dependent)diabetes mellitus unresponsive to diet and oral hypoglycemic, diabetic ketoacidosis Contraindication: Hypersensitivity to drug or its components Hypoglycemia Insulin 70/30 18u SQ prebreakfast and predinner PRN- 6u CBG180 gm/dl
Side Effects: dry mucous membrane , hypoglycemia, headache ,fainting
Adverse Effects: extreme thirst , polyuria , kussmaul breathing ,dyspnea , rapid thready pulse ,brought about by the derangements of glucose and fat metabolism Drug Interactions: Alcohol, MAO inhibitors, beta-blockers, salicylates, and anabolic steroids= may lower blood glucose to a dangerous level (hypoglycemia) Tretracycline antibiotics, oral hypoglycemic drugs, Ace inhibitors= augment the blood glucose-lowering effect of insulin, but they are less likely to interact with insulin or have less of an effect
Dilitiazem, niacin, corticosteroids, thyroid hormones and, diuretics = decrease the effect of insulin
Nursing Responsibilities: Use the same type of and brand of syringe; use the same type and brand of insulin to avoid dosage errors. Do not change the order of mixing insulin. Rotate injection sites regularly to prevent breakdown at injection sites. Explain to patient that this medications controls hyperglycemia but does not cure diabetes. Monitor blood or urine glucose levels, and consult your health care provider if problems arise. Report fever, sore throat, vomiting, hypoglycaemic or hyperglycaemic reaction, rash
Generic Name: Brand Name: Date Ordered: Classification: Ordered Dose: Available Form:
Tranexamic acid Hemostan June 25, 2013 @ 3:30 pm Anti-fibrinolytic, antihemorrhagic 500 mg 1 capsule Adult: PO Short-term management of haemorrhage 1-1.5 g 2-3 times/day.Long-term management of hereditary angioedema 1-1.5 g 2-3 times/day. IVShort-term management of haemorrhage 0.5-1 g 3 times/day
Indication:
Medical: epistaxis, hemoptysis, hematuria, peptic ulcer
with hemorrhage and blood dyscrasias with hemorrhage
Management of hemophilic patients (those having Factor VIII or Factor IX deficiency) who have oral mucosal bleeding, or are undergoing tooth extraction or other oral surgical procedures.
Surgical: General surgical cases but most especially operative procedures on the prostate, uterus, thyroid, lungs, heart, ovaries, adrenals, kidneys, brain, tonsils, lymph nodes and soft tissues.
Obstetrical and gynecological: abortion, post-partum hemorrhage and menometrorrahgia, heavy menstrual bleeding
Effective in promoting hemostasis in traumatic injuries.
Mode of Action:
Tranexamic acid is a synthetic derivative of the amino acid lysine. It is an antifibrinolytic agent that competitively inhibits breakdown of fibrin clots. It blocks binding of plasminogen and plasmin to fibrin, thereby preventing haemostatic plug dissolution or prevents fibrinolysis and the breakdown of blood clots. The plasminogen-plasmin enzyme system is known to cause coagulation defects through lytic activity on fibrinogen, fibrin and other clotting factors.
Contraindications:
1. Severe renal failure, active intravascular clotting, thromboembolic disease, colour vision disorders, subarachnoid bleeding; 2. Pregnancy. Tranexamic acid crosses the placenta. Lactation. Tranexamic acid is distributed into breast milk; concentrations reach approximately 1% of the maternal plasma concentration.
Side and Adverse Effects:
CNS: headache, confusion, vision changes CV: hypotension, chest pain, dizziness Respi: shortness of breath GI: abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting Derm: rashes, itching, MS: body malaise, back pain Renal: decreased urine output
Interactions: Nursing Responsibilities:
Medicines containing estrogen 1. This medication can be administered with or without food. 2. Ensure clients safety by raising side rails, for the drug may headache and vision changes. 3. Monitor vital signs, especially the blood pressure and respirations of the client. 4. Assist client in activities and in ambulation to prevent injury. 5. Assess or instruct to report for severe allergic reactions such as rash, hives, itching, dyspnea, tightness in the chest, swelling of the mouth, face, lips or tongue. 6. Encourage to perform simple range of motion. 7. Instruct to use soft-bristled toothbrush to prevent gum bleeding. 8. May have ice chips in the mouth for active gum bleeding. 9. Instruct to avoid hard and hot foods. 10. Monitor intake and output.
Potassium chloride Generic Name: Potassium Chloride Brand Name: Kalium durule Classification: mineral and electrolyte replacements Mode of Action:
Maintain acid-base balance, isotonicity, and electrophysiologic balance of the cell
Activator in many enzymatic reactions; essential to transmission of nerve impulses; contraction of cardiac, skeletal, and smooth muscle; gastric secretion; renal function; tissue synthesis and carbohydrate metabolism
Suggested Dose: Ordered Dose: 2 tabs TID x 6 doses Indication: treatment of potassium depletion
Contraindications: Patients with oliguria, anuria, hyperkalemia and severe renal impairment.
Side/Adverse Effects: CNS: confusion, restlessness, weakness.
CV: arrhythmias, ECG changes.
GI: abdominal pain, diarrhea, flatulence, nausea, vomiting.
Neuro: paralysis, paresthesias.
Drug Interactions: Drug-Drug: Use with potassium sparring diuretics may lead to hyperkalemia.
Nursing Responsibilities: Monitor pulse, BP during therapy.
Assess for signs and symptoms of hypokalemia (weakness, fatigue, arrhythmia, polyuria, polydipsia) and hyperkalemia. Dissolve in at least one-half glass (4 ounces) of cold water or juice to reduce its possible stomach-irritating or laxative effect. Check with your doctor before starting any physical exercise program, exercise and certain medicines may increase the amount of potassium in the blood.
Check with your doctor at once if you notice blackish stools or other signs of stomach or intestinal bleeding. Monitor electrolyte results specifically potassium. Routine serum potassium test is indicated while administering this drug. Assess the patency of intravenous fluid. Potassium is vein irritant and is painful in peripheral vein when given.
Sultamicillin Generic Name: sultamicillin (sulbactam +ampicillin) Brand Name: Unasyn Classification: Anti-infectives (Penicillins) Mode of Action: Inhibits cell-wall synthesis during bacterial multiplication. Sultamicillin is hydrolyzed during absorption to provide sulbactam and ampicillin in the systemic circulation Suggested Dose: 375-750mg twice daily (IV/ PO) Ordered Dose: 750mg q8 IVTT Indication: intra-abdominal, gynecologic, and skin-structure infections caused by susceptible strains Contraindications: Contraindicated inpatients hypersensitive to drug or other penicillins Use cautiously in lactating and pregnant mothers Use cautiously inpatients with other drug allergies(especially to cephalosporins)because of possible cross-sensitivity and in those with mononucleosis because of high risk of maculopapular rash
Side Effects/Adverse Effects: CV: Thrombophlebitis, vein irritation GI: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, glossitis, stomatitis, enterocolitis, pseudo membranous colitis Hematologic: Anemia, thrombocytopenia, thrombocytopenic purpura, eosinophilia, leukopenia, agranulocytosis SKIN: Pain at injection site Other: Hypersensitivity reactions, anaphylaxis, overgrowth of non susceptible organisms Drug Interaction: Concurrent use increases risk of bleeding with warfarin and methotrexate toxicity decreases efficacy of oestrgen-containing oral contraceptives Excretion of ampicillin is reduced when used with probencid
Nursing Responsibilities: Assess for hypersensitivity to drug or other penicillin products. Decreased dosage in patient with renal failure. Monitor liver function test results during therapy,especially in patients with impaired liver functions. Advise patient to report rash, fever or chills. A rash is the most common allergic reactions. Protect solution from light and refrigerate ampules Instruct patient to promptly report signs of enterocolitis,vomiting, diarrhea and nausea
Generic Name:
Albumin
Brand name:
Plasbumin
Classifications: Date ordered & dosage: Suggested dose: Indication:
Volume expander, colloids 6-12-13 Albumin drip 25% 50cc to run for 6 hours 5075 g diluted or undiluted Expansion of plasma volume and maintenance fluid volume deficit, including shock, hemorrhage, and burns. Temporary replacement of albumin.
Mode of Action:
Provides colloidal oncotic pressure, which serves to mobilize fluid from extravascular tissuesback into the intravascular space.
Contraindications:
Hypersensitivity, severe anemia, CHF, hepatic and renal impairement.
Side effect:
CNS: headache GI: increased salivation, nausea, vomiting
Adverse Effects:
CV: Pulmonary edema, fluid overload hypotension, tachycardia
Drug interaction: Nursing responsibilities:
None significant. - Monitor vital signs, if fever, tachycardia, hypotension occurs.
- Assess vascular overload (jugular vein distension, dyspnea, hypertension) during administration. - Check serum albumin result, after administration. -Assess for increased bleeding after administration caused by increased blood pressure and circulating blood. - Explain purpose and side effects, & instruct watcher to notify care giver if hypersensitivity reaction occurs. - Evaluate intake, output, & sodium level.
Generic name Brand name Classification
Furosemide Lasix Therapeutic: diuretics Pharmacologic: loop diuretics
Date Ordered/ Ordered Dose
February 2, 2012 Albumin 20% 50 cc 1 vial to run in 4 hrs OD (10pm) THEN Furosemide 20 g IVTT after albumin Edema
Suggested dose
PO (Adults): 20-80 mg/day as a single dose initially, may repeat in 6-8 hr; may increase dose by 20-40 mg q
6-8 hr until desired response. Maintenance doses may be given once or twice daily (doses up to 2.5 g/day have been used in patients with congestive heart failure or renal disease) IM, IV (Adults): 20-40 mg, may repeat in 1-2 hr and increase by 20 mg every 1-2 hr until response is obtained, maintenance dose may be given q 6-12 hr. Inhibits the reabsorption of sodium and chloride from the loop of Henle and distal renal tubule; Increases renal excretion of water, sodium, chloride, magnesium, potassium, and calcium. Effectiveness persists in Mode of action impaired renal function. Therapeutic Effects: Diuresis and subsequent mobilization of excess fluid (edema, fleural effusions). Decreased blood pressure. Edema due to hear failure, hepatic impairment or renal disease. Hypertension. Contraindicated in: Hypersensitivity; Cross-sensitivity with thiazides and sulfonamides may occur; hepatic coma or anuria; some liquid products may contain alcohol, avoid in patients with alcohol intolerance. Contraindications Use cautiously in: Severe liver disease (may precipitate hepatic coma; concurrent use with potassium-sparing & Precautions diuretics may be necessary); electrolyte depletion; Geri: geriatric patients may have increased of side effects, especially hypotension and electrolyte imbalance, at usual doses; diabetes mellitus; increase azotemia; pregnancy and lactation.
Indications
Drug-drug: Increase hypotension with anti hypertensives, nitrates, or acute ingestion of alcohol. Drug interaction Increase risk of hypokalemia with other diuretics, amphotericin B, stimulant laxatives, and corticosteroids. CNS: blurred vision, dizziness, headache, vertigo EENT: hearing loss, tinnitus CV: hypotension GI: excessive urination Derm: photosensitivity, pruritis, rash Endo: hyperglycemia, hyperuricemia Side effects / Adverse Effects F&E: dehydration, hypochloremia, hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, hyponatremia, hypovolemia, metabolic alkalosis and hypocalcemia Hemat: aplastic anemia, agranulocytosis, hemolytic anemia, leucopenia, thrombocytopenia MS: muscle cramps Neuro: paresthesia Misc: fever, increased BUN, nephrocalcinosis 1. Ensure that right drug with the right dosage is given to the right patient. 2. Assess fluid status. Monitor daily weight, intake and output ratios. Nursing Responsibilities 3. Monitor blood pressure and pulse before and during administration. Monitor frequency of prescription refills to determine compliance in patients treated for hypertension. 4. Geri: Diuretic use is associated with increased risk for falls in older adults. Keep patient safe at all times.
5. Asses patient for tinnitus or hearing loss. 6. Monitor laboratory tests such as electrolytes, renal and hepatic function, serum glucose, etc. 7. PO: may be taken with food or milk to minimize gastric irritation. 8. Caution patient to change positions slowly to minimize orthostatic hypotension.
Generic name Brand name Classification
Omeprazole Losec Therapeutic: antiulcer agents Pharmacologic: proton-pump inhibitors
Date Ordered/ Ordered Dose
2/4 - Omeprazole 40 mg IVTT OD once on NPO (6am)
PO (Adults): Suggested dose Gastric ulcer: 40 mg once daily for 4-6 wk Reduction of risk for GI bleeding in critically ill patients: 40 mg initially, then another 40 mg 6-8 hr later,
followed by 40 mg once daily up to 14 days. Binds on an enzyme on gastric parietal cells in the presence of acidic gastric pH, preventing the final transport of hydrogen ions into the gastric lumen. Mode of action Therapeutic Effect: Diminished accumulation of acid in the gastric lumen with lessened gastroesophageal reflux. Healing of duodenal ulcers. GERD/ maintenance of healing in erosive esophagitis. Indications Duodenal ulcers (with or without anti infectives for H. pylori). Short-term treatment of active benign gastric ulcer. Contraindicated in: Hypersensitivity; Metabolic alkalosis Contraindications and hypocalcemia. & Precautions Use cautiously in: Liver disease (dosage reduction may be necessary). CNS: dizziness, drowsiness, fatigue, headache, weakness Side effects / Adverse Effects CV: chest pain GI: abdominal pain, and regurgitation, constipation, diarrhea, flatulence, nausea, vomiting Derm: itching, rash 1. Ensure that right drug with the right dosage is Nursing Responsibilities given to the right patient. 2. Assess patient routinely for epigastric or abdominal pain and frank or occult blood in the stool, emesis, or gastric aspirate.
3. Lab tests considerations: Monitor CBC 4. PO: Administer doses before meals, preferably in the morning 5. May cause occasional drowsiness or dizziness. Provide safety for the client. 6. Advise patient to report onset of black tarry stools, diarrhea, abdominal pain.
Generic Name Brand Name Classification Date Ordered Ordered Dose
Omeprazole Omepron Anti-ulcer drug; Proton pump inhibitor 8/7/12 40 mg 1 cap OD P.O (6AM)
Suggested Dose Mode of Action
20 mg twice daily Binds to an enzyme on gastric parietal cells in the presence of acidic gastric pH, preventing the final transport of hydrogen ions into the gastric lumen.
Indication
GERD/ maintenance of healing in erosive esophagitis. Duodenal ulcers (with or without anti-infectives for
Helicobacter pylori). Short-term treatment of active benign gastric ulcer. Pathologic hypersecretory conditions,
including Zollinger-Ellison syndrome. Reduction of risk of GI bleeding in critically ill patients.
Contraindication
Hypersensitivity; Metabolic alkalosis and hypocalcemia
Drug Interaction
Celexa, Valium, and iron supplements can alter the amounts of the medications in your blood, potentially increasing your risk of side effects or decreasing the effectiveness of the medications.
Side/Adverse effects
CNS: headache, dizziness, asthenia, vertigo, insomnia, apathy, anxiety Derm: rash, inflammation, uticaria, pruritus, alopecia, dry skin GI: diarrhea, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting,
constipation dry mouth Respi: URI symptoms, cough, epistaxis
Nursing Responsibilities
Administer before meals. Assess patient routinely for epigastric or abdominal pain. Administer dose before meals, capsule should be swallowed whole and not crushed. Monitor for severe headache, fever, and chills
9.
Generic Name Available forms Date ordered Classification
Magnesium sulfate Injection, premixed infusion 7/15/12 Therapeutic: mineral and electrolyte
replacements/supplements Pharmacologic: minerals/electrolytes Indications Treatment/ prevention of hypomagnesemia. Treatment of hypertension. Anticonvulsant associated with severe
eclampsia, pre-eclampsia, or active nephritis Action Essential for the activity of many enzymes. Plays an important role in neurotransmission and muscular excitability. Therapeutic effects: Replacement in deficiency states.
Resolution of eclampsia Ordered dose MgSO4 500 mg + 9cc PNSS slow IV via soluset to run in 5/10 minutes 6 hrs. x 3 doses Suggested dose IM, IV (Adults): severe deficiency: 8-12 g/day in divided doses Mild deficiency: 1 g q 6 hr for 4 doses or 250 mg/kg over 4 hr Seizures/hypertension: IM, IV (Adults): 1 g q 6 hr for 4 doses as needed Contraindications/ Precautions Contraindicated in: Hypermagnesemia, hypocalcemia, anuria, heart block
Use cautiously in: Any degree of renal insufficiency, digitalized
patients. Adverse reactions/ Side effects CNS: drowsiness Resp: decreased respiratory rate CV: arrhythmias, bradycardia, hypotension GI: diarrhea MS: muscle weakness Derm: flushing, sweating Metab: hypothermia Nursing responsibilities Explain the purpose of this medication to patient and family Monitor vital signs of patient specially, pulse rate, BP, and respirations Monitor neurologic status before each dose Institute seizure precautions, patellar reflex (knee jerk) should be tested before each parenteral dose of magnesium sulfate. Monitor intake and output ratios. Urine output should be maintained at a level of at least 100 ml/4hr. Direct IV: Diluent: 50% solution must be diluted in 0.9% NaCl or D5W to a concentration of 20% prior to administration
10.
Generic Name Brand Name Available forms Date ordered Classification Pregnancy category Indications
Furosemide Lasix Tablets, injection 7/14/12 10:35 Therapeutic: diuretics Pharmacologic: loop diuretics Edema due to heart failure, hepatic impairment or renal disease. Hypertension.
Action
Inhibits the reabsorption of sodium and chloride from the loop of Henle and distal renal tubule. Increases renal eexcretion of water, sodium, chloride, magnesium, potassium, and calcium
Ordered dose Suggested dose
Furosemide 40 mg IVTT now Edema: PO (Adults): 20-80 mg/day as a single dose initially, may repeat in 6-8 hr; may increase dose by 20-40 mg q 6-8 hr until desired response. IM,IV (Adults): 20-40 mg, may repeat in 1-2 hr and increase by 20 mg every 1-2 hr until response Is obtained, maintenance dose may given q6-12 hr
Contraindications/ Precautions
Contraindicated in: Hypersensitivity, history symptoms or findings consistent with ischemic heart disease, coronary artery vasospasm. Cerebrovascular syndromes including: strokes of any type, transient ischemic attacks, uncontrolled
hypertension.
Use cautiously in: Elderly patients (may be more susceptible to adverse cardiovasculareffects). Adverse reactions/ Side effects CNS: dizziness, drowsiness, fatigue CV: coronary artery vasospasm, MI, ventricular fibrillation, ischemia GI: dry mouth, dyspepsia, nausea Derm: flushing MS: skeletal pain Neuro: paresthesia Nursing responsibilities Assess fluid status, intake and output ratios, lung sounds, skin turgor, and mucous membranes. Notify health care professional if thirst, dry mouth, lethargy, weakness, hypotension or oliguria occurs Monitor blood pressure and pulse before and during administration. Geri: Diuretic use is associated with increased risk for falls in older adults. Implement fall prevention strategies Monitor electrolytes, renal and hepatic functions. Caution patient to change positions slowlyto minimize orthostatic hypotension.
2.
Generic Name
Ca polystyrene sulfonate
Brand Name Available forms Date ordered Classification
Kalimate Sachet (powder for oral suspension) 7/14/12 Electrolyte Serum potassium level lowering agent (treatment of hyperkalemia)
Indications
Prevention & treatment of hyperkalemia resulting from acute or chronic renal failure.
Action
Calcium ion of kalimate is exchanged for potassium ion in the intestinal tract, particularly around the colon, and the drug is excreted as unchanged polystyrene sulfonate resin into the feces without digestion and absorption. In consequence, potassium in the intestinal tracts excreted outside the body.
Ordered dose Suggested dose
Kalimate 3 sachets TID Adult: 15-30 g PO bid-tid, or 30 g by rectal route suspended in 100 mL water or 2% methylcellulose solution & left in the intestinal tract for 30 min-1 hr. Children: Acute Hyperkalemia: 1 g/kg body wt. daily in divided doses. Maintenance Therapy: 0.5 g/kg body wt daily in divided doses
Contraindications/ Precautions
Contraindicated in: Patients w/ intestinal obstruction & stenosis, constipation.
Use Cautiously in: Hyperparathyroidism & multiple myeloma. Monitor serum K &Ca levels regularly. Elderly, pregnancy, delivery & lactation Adverse reactions/ Side effects Constipation, anorexia & nausea
Nursing responsibilities
Intestinal perforation or intestinal obstruction may occur. If any abnormal findings such as severe constipation, prolonged abdominal pain, or vomiting, etc. are observed, administration of the drug should be discontinued and appropriate measures taken.
Patients should be instructed to pay attention to their feces Measurement of the serum potassium and serum calcium levels regularly to prevent the overdose Provide safety for the patient since one of its side effects is nausea
8.
Generic Name
calcium carbonate
Brand Name
Caltrate
Available forms Date ordered
Tablets, capsules 7/14/12
Classification Pregnancy category Indications
Therapeutic:
mineral
and
electrolyte
replacements/supplements Treatment and prevention of hypocalcemia PO: Adjunct in the prevention of post menopausal
osteoporosis Calcium carbonate: may be used as an antacids Action Essential for nervous, muscular, and skeletal systems. Maintain cell membrane and capillary permeability. Act as an activator in the transmission of nerve impulses and contraction of cardiac, skeletal, and smooth muscle. Essential for bone formation and blood coagulation
Therapeutic effects: Replacement of calcium in deficiency states. Control of hyperphosphatemia in end-stage renal disease without promoting aluminum absorption (calcium acetate) Ordered dose Suggested dose Caltrate 1 tab OD- 6am PO (Adults): Prevention of hypocalcemia, treatment of depletion, osteoporosis: 1-2 g/day Antacid: 0.5-1.5 g as needed (calcium carbonate only) Contraindications/ Precautions Contraindicated in: Hypercalcemia, renal calculi, Ventricular fibrillation
Use Cautiously in: Patients receiving digitalis glycosides, severe disease. Adverse reactions/ Side effects CNS: tingling CV: arrhythmias, bradycardia GI: constipation, nausea, vomiting GU: calculi, hypercalciuria Nursing Observe patient closely for symptoms of hypocalcemia respiratory insufficiency, renal disease, cardiac
responsibilities
(paresthesia, muscle twitching, colic, cardiac arrhythmias, Chvosteks or Trousseaus sign) Protect symptomatic patients by elevating and padding siderails and keeping bed in low position Monitor patients vital signs Assess patient for nausea, vomiting, anorexia, thirst, severe constipation, and bradycardia. Inform health care professional immediately Administer on an empty stomach before meals to optimize effectiveness. Administration with milk products may lead o milk-alkali syndrome (nausea, vomiting, confusion,headache) Advise patient that calcium carbonate may cause constipation. High fiber diet may be recommended and increasing oral fluid intake).
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Final NCPDocument5 pagesFinal NCPAce VirtusioPas encore d'évaluation
- KetorolacDocument5 pagesKetorolacMichelle Ann P. NacuaPas encore d'évaluation
- Emergency Drug StudyDocument3 pagesEmergency Drug StudyGrace Santos MirandaPas encore d'évaluation
- SimethiconeDocument1 pageSimethiconeDivine Dela PenaPas encore d'évaluation
- DrugStudy MetoclopramideDocument2 pagesDrugStudy MetoclopramideAshknee Khainna AlejoPas encore d'évaluation
- Amlodipine Drug StudyDocument1 pageAmlodipine Drug StudyEllePas encore d'évaluation
- Detrol (Tolterodine)Document1 pageDetrol (Tolterodine)EPas encore d'évaluation
- PrimaquineDocument3 pagesPrimaquineVijayakumar NsPas encore d'évaluation
- Mindanao State University - Iligan Institute of Technology Student: ALEXA MURIEL L. MOZAR Section: BLOCK 261Document2 pagesMindanao State University - Iligan Institute of Technology Student: ALEXA MURIEL L. MOZAR Section: BLOCK 261Alexandra AntondyPas encore d'évaluation
- Na HCO3Document2 pagesNa HCO3Niño Karol Zamora100% (1)
- Er Drug StudyDocument29 pagesEr Drug StudyMa Karenina DualanPas encore d'évaluation
- ZyvoxDocument1 pageZyvoxSheri490Pas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study NursingDocument27 pagesDrug Study Nursingbilliam123Pas encore d'évaluation
- NCP 6 CholesterolDocument2 pagesNCP 6 CholesterolAna P.100% (1)
- MetherginDocument2 pagesMetherginOtan Cuison100% (1)
- Drug Study: (Celecoxib)Document11 pagesDrug Study: (Celecoxib)Princess Brigitte R. PATE�APas encore d'évaluation
- Folic Acid Med CardDocument3 pagesFolic Acid Med CardDadybooboo2013Pas encore d'évaluation
- Calcium AcetateDocument3 pagesCalcium AcetateKIM NAMJOON'S PEACHES & CREAM100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument41 pagesDrug StudyCatherine PradoPas encore d'évaluation
- Atracurium BesylateDocument3 pagesAtracurium BesylateWidya WidyariniPas encore d'évaluation
- Assess Vital Signs For Baseline Data. Assess Vital Signs For Baseline Data. Directl y Affects NeuroreDocument14 pagesAssess Vital Signs For Baseline Data. Assess Vital Signs For Baseline Data. Directl y Affects NeuroreBianca Marithè RejanoPas encore d'évaluation
- AztreonamDocument2 pagesAztreonamHannahShaeHayesPas encore d'évaluation
- MetamucilDocument1 pageMetamucilSheri490Pas encore d'évaluation
- Diclofenac Sodium & Omeprazole Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDiclofenac Sodium & Omeprazole Drug StudyMelah MunchlaxPas encore d'évaluation
- Nifedipine Drug StudyDocument2 pagesNifedipine Drug StudyMary Shane MoraldePas encore d'évaluation
- Cervical Cancer Brochure (CFPNG)Document2 pagesCervical Cancer Brochure (CFPNG)Cancer Foundation PNGPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyCris SolisPas encore d'évaluation
- CeftriaxoneDocument5 pagesCeftriaxoneCastillo MikaellaPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study - CefradoxilDocument13 pagesDrug Study - CefradoxilJohara G'naid0% (1)
- VecuroniumDocument2 pagesVecuroniumAmanda La SalaPas encore d'évaluation
- KETOROLAC Drug StudyDocument3 pagesKETOROLAC Drug StudyChoox PriiPas encore d'évaluation
- Magnesium SulfateDocument2 pagesMagnesium SulfateKarla Karina Dela CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- CoversylDocument3 pagesCoversylianecunarPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudymYiE23Pas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyJonica CamposPas encore d'évaluation
- DP Discharge Plan@@@@@@@@Document6 pagesDP Discharge Plan@@@@@@@@Maemae SumalinogPas encore d'évaluation
- Brand Name: Generic Name: Drug ClassificationDocument2 pagesBrand Name: Generic Name: Drug ClassificationChristine Pialan SalimbagatPas encore d'évaluation
- Expanded Screening Fact Sheets - Doctors - 2019Document75 pagesExpanded Screening Fact Sheets - Doctors - 2019DadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyDimple calloPas encore d'évaluation
- DRUGSTUDY RANITIDINE, METRONIDAZOLE, CEFUROXIME, KEtorolac NUBainDocument7 pagesDRUGSTUDY RANITIDINE, METRONIDAZOLE, CEFUROXIME, KEtorolac NUBainKyle Cholo CholoPas encore d'évaluation
- As Pi LetDocument7 pagesAs Pi Letianecunar100% (1)
- Duty Drug Study'sDocument7 pagesDuty Drug Study'sGrape JuicePas encore d'évaluation
- GAT NCP Surgery WardDocument4 pagesGAT NCP Surgery WardDon Richard0% (1)
- CefuroximeDocument11 pagesCefuroximeAlmira Ballesteros CestonaPas encore d'évaluation
- Antimalarial DrugsDocument7 pagesAntimalarial DrugsHilmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument15 pagesDrug StudyDon Laurence P. CasauayPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug - Htm#description.: Reference: Submitted By: Date Submitted: Submitted ToDocument2 pagesDrug - Htm#description.: Reference: Submitted By: Date Submitted: Submitted ToSHEILA MAE SACLOTPas encore d'évaluation
- Procreative Health Is The Moral Obligation of Parents To Have The Healthiest Children Through All Natural and Artificial Means AvailableDocument9 pagesProcreative Health Is The Moral Obligation of Parents To Have The Healthiest Children Through All Natural and Artificial Means AvailableShiela Mae GalisaPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study - CefotaximeDocument5 pagesDrug Study - CefotaximeAngel laurestaPas encore d'évaluation
- MG Drug StudyDocument3 pagesMG Drug StudySandra MedinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyJheryck SabadaoPas encore d'évaluation
- HEMOdrug Study (Jul 2013)Document7 pagesHEMOdrug Study (Jul 2013)Leoni HerreraPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study (MS)Document9 pagesDrug Study (MS)Kristine GallardoPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyEzshkha OnguePas encore d'évaluation
- MM MM MM MM MMM MMMMM M MM M MMMM MMMMM MMM MM MMM MM!M M!"M#MM MM M $M M %MMM MM "M "MM M MMM MDocument9 pagesMM MM MM MM MMM MMMMM M MM M MMMM MMMMM MMM MM MMM MM!M M!"M#MM MM M $M M %MMM MM "M "MM M MMM M배기숭Pas encore d'évaluation
- Labs Drug Study 1Document17 pagesLabs Drug Study 1Drei LanuzoPas encore d'évaluation
- CVA Drug StudyDocument51 pagesCVA Drug StudyKarel LuPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study ArvinDocument6 pagesDrug Study ArvinArvin BeltranPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyHelen ReonalPas encore d'évaluation
- Drugs Study of Omeprazole, Metoclopramide EtcDocument12 pagesDrugs Study of Omeprazole, Metoclopramide EtcMargaret Cortinas75% (4)
- Quizzes CompilationDocument7 pagesQuizzes CompilationMark CapillanesPas encore d'évaluation
- SyllabusDocument11 pagesSyllabusMark CapillanesPas encore d'évaluation
- IV Solutions Reference ChartDocument1 pageIV Solutions Reference ChartMark Capillanes100% (1)
- Final SyllabusDocument6 pagesFinal SyllabusMark CapillanesPas encore d'évaluation
- Comparison of Duodenal and Gastric Ulcers Duodenal Ulcer Gastric Ulcer IncidenceDocument1 pageComparison of Duodenal and Gastric Ulcers Duodenal Ulcer Gastric Ulcer IncidenceMark CapillanesPas encore d'évaluation
- Peptic Ulcer DiseaseDocument6 pagesPeptic Ulcer DiseaseMark CapillanesPas encore d'évaluation
- Test Print PageDocument1 pageTest Print PageMark CapillanesPas encore d'évaluation
- Test Print PageDocument1 pageTest Print PageMark CapillanesPas encore d'évaluation
- Comparison of Duodenal and Gastric Ulcers Duodenal Ulcer Gastric Ulcer IncidenceDocument1 pageComparison of Duodenal and Gastric Ulcers Duodenal Ulcer Gastric Ulcer IncidenceMark CapillanesPas encore d'évaluation
- Census: Date: Ward: Shift:: Endorsement SheetDocument1 pageCensus: Date: Ward: Shift:: Endorsement SheetMark CapillanesPas encore d'évaluation
- Crohn's DiseaseDocument5 pagesCrohn's DiseaseMark CapillanesPas encore d'évaluation
- List The 16 Documents of Vatican IIDocument4 pagesList The 16 Documents of Vatican IIMark Capillanes100% (2)
- ALL DiagramDocument3 pagesALL DiagramMark CapillanesPas encore d'évaluation
- Endorsement Sheet: Last Total: - Admissions: - Discharge: - Trans In/Out: - Present TotalDocument1 pageEndorsement Sheet: Last Total: - Admissions: - Discharge: - Trans In/Out: - Present TotalMark CapillanesPas encore d'évaluation
- Euthanasia DefinitionsDocument12 pagesEuthanasia DefinitionsMark CapillanesPas encore d'évaluation
- Case AnalysisDocument43 pagesCase AnalysisMark CapillanesPas encore d'évaluation
- ConsentDocument3 pagesConsentMark CapillanesPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyjchowkingPas encore d'évaluation
- June 20 (Transmittal Letters)Document5 pagesJune 20 (Transmittal Letters)Mark CapillanesPas encore d'évaluation
- CorrectsDocument46 pagesCorrectsnursing_hallPas encore d'évaluation
- Burns - Lewis Flashcards - QuizletDocument31 pagesBurns - Lewis Flashcards - QuizletNursyNursePas encore d'évaluation
- Electrolytes : Normal CHEM 10 ValuesDocument8 pagesElectrolytes : Normal CHEM 10 ValuesAmalPas encore d'évaluation
- Nutrition Therapy and Pathophysiology 3rd Edition Nelms Test BankDocument16 pagesNutrition Therapy and Pathophysiology 3rd Edition Nelms Test Bankrorybridgetewe100% (24)
- Case 9-2017: A 27-Year-Old Woman With Nausea, Vomiting, Confusion, and HyponatremiaDocument9 pagesCase 9-2017: A 27-Year-Old Woman With Nausea, Vomiting, Confusion, and HyponatremiaLindia PrabhaswariPas encore d'évaluation
- ESPGHAN - ESPEN - ESPR Guidelines On Pediatric Parenteral Nutrition FluidDocument10 pagesESPGHAN - ESPEN - ESPR Guidelines On Pediatric Parenteral Nutrition FluidPablo CamposPas encore d'évaluation
- Chronic Kidney Disease - ClinicalKeyDocument53 pagesChronic Kidney Disease - ClinicalKeyMariel Patricia CapunoPas encore d'évaluation
- Renal Pathophysiology PDFDocument52 pagesRenal Pathophysiology PDFzoher al naeemePas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Electrolyte Balances and ImbalanceDocument157 pagesFluid Electrolyte Balances and ImbalanceManisha Shakya0% (1)
- Acute Renal Failure and TreatmentDocument103 pagesAcute Renal Failure and TreatmentNathan AsinasPas encore d'évaluation
- Simple Nursing@Migrant NurseDocument679 pagesSimple Nursing@Migrant NurseHana kPas encore d'évaluation
- A1.Fundamentals - 25item With Rationale (NCLEX)Document5 pagesA1.Fundamentals - 25item With Rationale (NCLEX)Blardy Falking You Benchod BlardyPas encore d'évaluation
- D5 WATER Contents Per 100 ML DextroseDocument1 pageD5 WATER Contents Per 100 ML DextroseY_02_JPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plan: Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument10 pagesNursing Care Plan: Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationChamelli RobinPas encore d'évaluation
- Renal Tubular Acidosis: ObjectivesDocument11 pagesRenal Tubular Acidosis: Objectivesms khanPas encore d'évaluation
- Medical-Surgical Nursing 1Document332 pagesMedical-Surgical Nursing 1KoRnflakes93% (15)
- Acute Renal FailureDocument21 pagesAcute Renal Failureاحمد الهاشميPas encore d'évaluation
- 021290gapuz Notes Day 1 7Document158 pages021290gapuz Notes Day 1 7Joan Manabat BugnaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ka-En MimsDocument7 pagesKa-En MimsMFWPPas encore d'évaluation
- Renal Disease: Acute Kidney Injury (AKI)Document5 pagesRenal Disease: Acute Kidney Injury (AKI)api-142637023Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid and Electrolyte ImbalanceDocument82 pagesFluid and Electrolyte ImbalanceMinlik-alew Dejenie67% (3)
- ECG Manifestations of Multiple Electrolyte Imbalance: Peaked T Wave To P Wave ("Tee Pee Sign")Document5 pagesECG Manifestations of Multiple Electrolyte Imbalance: Peaked T Wave To P Wave ("Tee Pee Sign")Mohammad AlzawiPas encore d'évaluation
- MCQs For Prometric Examination PDFDocument155 pagesMCQs For Prometric Examination PDFYacine Tarik AizelPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid and Electrolytes - Balance and DisturbancesDocument129 pagesFluid and Electrolytes - Balance and DisturbancesEmmy SaPas encore d'évaluation
- RESUS 8904 Special CircsDocument68 pagesRESUS 8904 Special CircsCroBranPas encore d'évaluation
- Medical Terms in Lay LanguageDocument7 pagesMedical Terms in Lay LanguageMavra zPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study Case PresentationDocument5 pagesDrug Study Case PresentationRobert MedinaPas encore d'évaluation
- (JURNAL, Eng) A Retrospective Cohort Review of Prescribing in Hospitalised Patients With Heart Failure Using Beers Criteria and STOPP RecommendationsDocument7 pages(JURNAL, Eng) A Retrospective Cohort Review of Prescribing in Hospitalised Patients With Heart Failure Using Beers Criteria and STOPP RecommendationsAurellia Annisa WulandariPas encore d'évaluation
- SodiumDocument4 pagesSodiumsandeep4485Pas encore d'évaluation
- POTASIODocument2 pagesPOTASIOJohann PalaciosPas encore d'évaluation
- The Perspective Drawing Guide: Simple Techniques for Mastering Every AngleD'EverandThe Perspective Drawing Guide: Simple Techniques for Mastering Every AngleÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1)
- The Botanical Hand Lettering Workbook: Draw Whimsical & Decorative Styles & ScriptsD'EverandThe Botanical Hand Lettering Workbook: Draw Whimsical & Decorative Styles & ScriptsÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (2)
- The Beginner's Guide to Watercolor: Master Essential Skills and Techniques through Guided Exercises and ProjectsD'EverandThe Beginner's Guide to Watercolor: Master Essential Skills and Techniques through Guided Exercises and ProjectsPas encore d'évaluation
- Creative Abstract Watercolor: The beginner's guide to expressive and imaginative paintingD'EverandCreative Abstract Watercolor: The beginner's guide to expressive and imaginative paintingPas encore d'évaluation
- Celtic Line Drawing - Simplified InstructionsD'EverandCeltic Line Drawing - Simplified InstructionsÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (4)
- Drawing and Sketching Portraits: How to Draw Realistic Faces for BeginnersD'EverandDrawing and Sketching Portraits: How to Draw Realistic Faces for BeginnersÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (5)
- Art Models AnaRebecca009: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceD'EverandArt Models AnaRebecca009: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5)
- Art Models KatarinaK034: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceD'EverandArt Models KatarinaK034: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceÉvaluation : 3 sur 5 étoiles3/5 (2)
- Acrylic Painting: Learn How to Paint Easy Techniques with Acrylic Paint (with photos)D'EverandAcrylic Painting: Learn How to Paint Easy Techniques with Acrylic Paint (with photos)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (4)
- Watercolor For The Soul: Simple painting projects for beginners, to calm, soothe and inspireD'EverandWatercolor For The Soul: Simple painting projects for beginners, to calm, soothe and inspireÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (6)
- Painting Perspective, Depth & Distance in WatercolourD'EverandPainting Perspective, Depth & Distance in WatercolourÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (2)
- 15-Minute Watercolor Masterpieces: Create Frame-Worthy Art in Just a Few Simple StepsD'Everand15-Minute Watercolor Masterpieces: Create Frame-Worthy Art in Just a Few Simple StepsÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (7)
- Art Models 10: Photos for Figure Drawing, Painting, and SculptingD'EverandArt Models 10: Photos for Figure Drawing, Painting, and SculptingÉvaluation : 2.5 sur 5 étoiles2.5/5 (6)
- Beginner's Guide To Procreate: Characters: How to create characters on an iPad ®D'EverandBeginner's Guide To Procreate: Characters: How to create characters on an iPad ®3dtotal PublishingÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1)
- Art Models Adrina032: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceD'EverandArt Models Adrina032: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (2)
- Draw Every Little Thing: Learn to Draw More Than 100 Everyday Items, From Food to FashionD'EverandDraw Every Little Thing: Learn to Draw More Than 100 Everyday Items, From Food to FashionÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (4)
- How To Draw Chibi: Learn Drawing Supercute Chibi Characters for Kids and Beginners - Easy Step-By-Step TutorialsD'EverandHow To Draw Chibi: Learn Drawing Supercute Chibi Characters for Kids and Beginners - Easy Step-By-Step TutorialsÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (4)
- The Fundamentals of Watercolour Landscapes: Paintings for all seasonsD'EverandThe Fundamentals of Watercolour Landscapes: Paintings for all seasonsÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1)
- Art Models AnaIv309: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceD'EverandArt Models AnaIv309: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceÉvaluation : 3 sur 5 étoiles3/5 (2)
- Art Models Sam074: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceD'EverandArt Models Sam074: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1)
- Art Models Becca425: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceD'EverandArt Models Becca425: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (3)
- David Bellamy's Seas & Shorelines in WatercolourD'EverandDavid Bellamy's Seas & Shorelines in WatercolourÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1)
- Living Color: Painting, Writing, and the Bones of SeeingD'EverandLiving Color: Painting, Writing, and the Bones of SeeingÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (4)
- Art Models Felicia016: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceD'EverandArt Models Felicia016: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceÉvaluation : 3 sur 5 étoiles3/5 (2)
- Watercolor Botanical Garden: A Modern Approach to Painting Bold Flowers, Plants, and CactiD'EverandWatercolor Botanical Garden: A Modern Approach to Painting Bold Flowers, Plants, and CactiÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (2)