Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Types of Assisted Ventilation
Transféré par
Jerry G100%(2)100% ont trouvé ce document utile (2 votes)
7K vues1 pageComparison of CMV, SIMV, PSV, PCIR, PEEP and CPAP. Indications, contraindications, advantages, and miscellaneous notes. Print in landscape orientation.
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike (BY-NC-SA)
Formats disponibles
ODT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentComparison of CMV, SIMV, PSV, PCIR, PEEP and CPAP. Indications, contraindications, advantages, and miscellaneous notes. Print in landscape orientation.
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike (BY-NC-SA)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme ODT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
100%(2)100% ont trouvé ce document utile (2 votes)
7K vues1 pageTypes of Assisted Ventilation
Transféré par
Jerry GComparison of CMV, SIMV, PSV, PCIR, PEEP and CPAP. Indications, contraindications, advantages, and miscellaneous notes. Print in landscape orientation.
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike (BY-NC-SA)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme ODT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 1
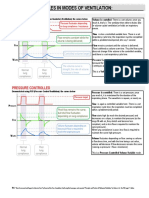
Types of Assisted Ventilation Jerry Goure
Ventilator Option Indications Contraindications Advantages Notes
Controlled Mandatory • No respiratory drive or • Hypovolemia • • Delivers preset volume at a preset rate.
Ventilation (CMV) effort
Assist Control Ventilation • Neuromuscular disorders • Hypovolemia • Allows spontaneous • Positive pressure during entire breath,
(ACV) (Guillain-Barré) breaths between ventilator- spontaneous or not.
• Pulmonary edema delivered breaths. • Delivers preset volume at a preset rate.
• Acute respiratory failure • When a spontaneous breath is detected,
the ventilator “pushes” the entire preset
volume into the patient.
Synchronized Intermittent • Weaning • Hypovolemia • Allows spontaneous • Delivers preset volume at a preset rate.
Mandatory Ventilation breaths between ventilator- • During a spontaneous breath, the pa-
(SIMV) delivered breaths. tient determines the volume delivered.
• Improved synchrony • The ventilator will “push” a minim-
between patient & ventilat- um volume into the patient, but the
or. patient can breathe deeper.
• Prevents atrophy of respir- • ↑ work of breathing for patient.
atory muscles. • Most common type of ventilation.
• Lower mean airway pres-
sure.
Pressure Support • Weaning (with SIMV) • Hypovolemia • Helps ↓ work of breathing • Patient controls the length of each
Ventilation (PSV) • Sole ventilatory and O2 demand. breath, the tidal volume, and the respir-
support for acute • ↑ endurance conditioning. atory rate.
respiratory failure. • Prevents atrophy of respir- • Delivers each breath with a preset (pos-
atory muscles. itive) pressure.
Pressure Controlled • ARDS • Hypovolemia • Keeps alveoli open longer. • I:E ratio is usually set to 2:1.
Inverse Ratio (PCIR) • Prolonged inspiratory time • Unnatural breathing pattern requires
may → “auto-PEEP.” sedation and/or paralysis.
Positive End-Expiratory • ARDS? • Hypovolemia • Keeps alveoli open during • Positive pressure applied to airway dur-
Pressure (PEEP) expiration. ing expiration.
• Limits O2 toxicity. • Mechanical equivalent to pursed-lip
breathing.
Continuous Positive • Apnea • Hypovolemia • • Positive pressure applied to airway dur-
Airway Pressure (CPAP) ing the entire breath.
• Mask must be tight-fitting over face.
• ↑ work of breathing for patient.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Advanced Cardiac Life Support Quick Study Guide 2015 Updated GuidelinesD'EverandAdvanced Cardiac Life Support Quick Study Guide 2015 Updated GuidelinesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (6)
- Cheatsheet 2Document1 pageCheatsheet 2Rick Frea86% (7)
- Cheat Sheet 1Document1 pageCheat Sheet 1Rick Frea100% (9)
- ABG InterpretationDocument1 pageABG Interpretationnulall100% (18)
- Bonehead Electrocardiography: The Easiest and Best Way to Learn How to Read Electrocardiograms—No Bones About It!D'EverandBonehead Electrocardiography: The Easiest and Best Way to Learn How to Read Electrocardiograms—No Bones About It!Évaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (2)
- CO2 Pocket GuideDocument2 pagesCO2 Pocket GuideDarryl Betts100% (7)
- Emergency Department Resuscitation of the Critically Ill, 2nd Edition: A Crash Course in Critical CareD'EverandEmergency Department Resuscitation of the Critically Ill, 2nd Edition: A Crash Course in Critical CarePas encore d'évaluation
- Vent Modes ChartDocument1 pageVent Modes Chartladyhavocinc100% (1)
- Back to Basics: Critical Care Transport Certification ReviewD'EverandBack to Basics: Critical Care Transport Certification ReviewPas encore d'évaluation
- Ventilation Cheat SheetDocument1 pageVentilation Cheat Sheetlizzy59683% (6)
- Arterial Blood Gas Analysis - making it easyD'EverandArterial Blood Gas Analysis - making it easyÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (4)
- Cheatsheet 5Document1 pageCheatsheet 5Rick Frea80% (5)
- Cheetsheet 6Document1 pageCheetsheet 6Rick Frea92% (12)
- The 12-Lead Electrocardiogram for Nurses and Allied ProfessionalsD'EverandThe 12-Lead Electrocardiogram for Nurses and Allied ProfessionalsPas encore d'évaluation
- Acid-Base WorksheetDocument2 pagesAcid-Base WorksheetMayer Rosenberg100% (18)
- Advance Cardiac Life Support: Short, Sweet and to the PointD'EverandAdvance Cardiac Life Support: Short, Sweet and to the PointÉvaluation : 3 sur 5 étoiles3/5 (2)
- Mechanical+Ventilation-Basics+for+Beginners (Unlocked by ComDocument49 pagesMechanical+Ventilation-Basics+for+Beginners (Unlocked by Comdokidok100% (14)
- Cheatsheet 3Document1 pageCheatsheet 3Rick Frea100% (1)
- Critical Care Survival GuideDocument2 pagesCritical Care Survival Guidetringalama100% (4)
- Haemodynamic Pocket GuideDocument2 pagesHaemodynamic Pocket GuideDarryl Betts85% (13)
- A Simplified ECG GuideDocument4 pagesA Simplified ECG Guidejalan_z96% (27)
- Cheatsheet 4Document1 pageCheatsheet 4Rick FreaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ventilation For DummiesDocument39 pagesVentilation For Dummiessuyalamit100% (6)
- Critical Care Intravenous DrugsDocument1 pageCritical Care Intravenous DrugsMarynel Dixie Izon Brao90% (10)
- Tidal Volumes Cheat SheetDocument1 pageTidal Volumes Cheat SheetRick Frea100% (1)
- Respiratory DysfunctionDocument1 pageRespiratory Dysfunctionoxidalaj100% (3)
- Critical Care NoteDocument10 pagesCritical Care NoteHanis Rozib99% (69)
- Icu GuidebookDocument43 pagesIcu Guidebookdrimran570100% (5)
- Lab CheatsheetDocument1 pageLab CheatsheetRick Frea86% (7)
- RT Consult Form Side #2Document1 pageRT Consult Form Side #2Rick Frea100% (1)
- ABG Made EasyDocument10 pagesABG Made EasyMayer Rosenberg100% (38)
- Electrolyte CompleteDocument6 pagesElectrolyte CompleteTofan Ana100% (2)
- Control of Mechanical VentilationDocument6 pagesControl of Mechanical VentilationMichael LevitPas encore d'évaluation
- ABG InterpretationDocument31 pagesABG Interpretationɹǝʍdןnos100% (12)
- Critical Care NotesDocument18 pagesCritical Care NotesjuliePas encore d'évaluation
- Boot Camp Hemodynamic MonitoringDocument37 pagesBoot Camp Hemodynamic MonitoringTinaHo100% (7)
- Risk For Diseases Cheat SheetDocument1 pageRisk For Diseases Cheat SheetRick Frea100% (5)
- @anesthesia - Books 2021 Respiratory Critical Care 1st EditionDocument964 pages@anesthesia - Books 2021 Respiratory Critical Care 1st EditionAlex Detick100% (1)
- Adjusting Ventilator SettingsDocument7 pagesAdjusting Ventilator SettingsSiva RamanPas encore d'évaluation
- Respiratory PathophysDocument1 pageRespiratory PathophysTori IkeharaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Ventilator BookDocument126 pagesThe Ventilator BookAlberto David100% (22)
- EKG Flash CardsDocument5 pagesEKG Flash CardsRyann Sampino FreitasPas encore d'évaluation
- Quick Reference SheetDocument2 pagesQuick Reference SheetCGdragonPas encore d'évaluation
- (SVR) Measures Systemic Resistance and Reflects Afterload of Left Ventricle Average Perfusion of A Cardiac CycleDocument1 page(SVR) Measures Systemic Resistance and Reflects Afterload of Left Ventricle Average Perfusion of A Cardiac Cyclesarah_stover_1100% (4)
- Pediatric Mechanical VentilationDocument36 pagesPediatric Mechanical VentilationrizalPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiac Study GuideDocument11 pagesCardiac Study Guidejenwiley318096% (73)
- Pharmacological Tools: Doses, Routes, and Uses of Common DrugDocument1 pagePharmacological Tools: Doses, Routes, and Uses of Common DrugApuntesdemedicinaa blogPas encore d'évaluation
- CCRN Sample QuestionsDocument5 pagesCCRN Sample Questionsgwapdose50% (2)
- Approach To ACLS RhythmDocument150 pagesApproach To ACLS RhythmChristine Bernadette Rapal Bollong100% (2)
- ICU Nurse Report SheetDocument1 pageICU Nurse Report SheetPuteri Hutami50% (4)
- CCRN PulmonaryDocument107 pagesCCRN PulmonaryCzarina Charmaine Diwa100% (4)
- Cardiac Meds ChartDocument1 pageCardiac Meds ChartCharlotte Louise75% (4)
- Hemodynamic Assessment ParametersDocument2 pagesHemodynamic Assessment ParametersalexPas encore d'évaluation
- Critical Care Calculations Study GuideDocument6 pagesCritical Care Calculations Study GuideAja Blue100% (2)
- The Intensive Care Unit at The Mid Yorkshire Hospitals NHS TrustDocument164 pagesThe Intensive Care Unit at The Mid Yorkshire Hospitals NHS TrustRajiv Srinivasa71% (7)
- Static Compliance & RSBI CheatsheetDocument1 pageStatic Compliance & RSBI CheatsheetRick FreaPas encore d'évaluation
- Critical CareDocument40 pagesCritical Carenkuligowski100% (6)
- Patient Worksheet - Postpartum 1-PatientDocument1 pagePatient Worksheet - Postpartum 1-PatientJerry G100% (1)
- Patient Worksheet - Pediatrics 1-PatientDocument1 pagePatient Worksheet - Pediatrics 1-PatientJerry G100% (1)
- Student Resource Nurse WorksheetDocument1 pageStudent Resource Nurse WorksheetJerry GPas encore d'évaluation
- Pediatric Developmental StagesDocument5 pagesPediatric Developmental StagesJerry G80% (5)
- Patient Worksheet - NICU 2-PatientDocument2 pagesPatient Worksheet - NICU 2-PatientJerry G75% (4)
- Patient Worksheet - MedSurg 3-PatientDocument1 pagePatient Worksheet - MedSurg 3-PatientJerry G100% (1)
- Creole Cornbread Stuffing RecipeDocument1 pageCreole Cornbread Stuffing RecipeJerry G100% (1)
- Patient Worksheet - MedSurg 2-PatientDocument1 pagePatient Worksheet - MedSurg 2-PatientJerry GPas encore d'évaluation
- Massage - Pre-Event Massage QuestionnaireDocument1 pageMassage - Pre-Event Massage QuestionnaireJerry GPas encore d'évaluation
- Amish Friendship Bread RecipeDocument1 pageAmish Friendship Bread RecipeJerry GPas encore d'évaluation
- Ethnic Art in The US - Sargent Johnson Preso NotesDocument2 pagesEthnic Art in The US - Sargent Johnson Preso NotesJerry GPas encore d'évaluation
- Microbiology - Bacteria TableDocument3 pagesMicrobiology - Bacteria TableJerry G100% (2)
- Ethnic Art in The US - Reading Summary - Lewis Ch. 2Document4 pagesEthnic Art in The US - Reading Summary - Lewis Ch. 2Jerry G100% (2)
- A&P - Muscle WorksheetDocument4 pagesA&P - Muscle WorksheetJerry GPas encore d'évaluation
- Warmup & Stretching: Pose Hold For RepeatDocument4 pagesWarmup & Stretching: Pose Hold For RepeatJerry G100% (2)
- Basic Chemistry - Final NotesDocument1 pageBasic Chemistry - Final NotesJerry G0% (1)
- The Party TwinsDocument136 pagesThe Party TwinsJerry G100% (3)
- What Is A Solar Storm?Document2 pagesWhat Is A Solar Storm?Shawn SriramPas encore d'évaluation
- 56.vocal Warmup Log For Belt Your FaceDocument5 pages56.vocal Warmup Log For Belt Your FaceAlinutza AlinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Learners ' Health and Safety Practices and Their Academic PerformanceDocument10 pagesLearners ' Health and Safety Practices and Their Academic PerformanceHira SaddozaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Copd 9 027Document13 pagesCopd 9 027Yussuf MuhammadPas encore d'évaluation
- Questions To Client On SAP HCMDocument19 pagesQuestions To Client On SAP HCMeurofighterPas encore d'évaluation
- Reading Test - 3 Clinical Depression Text ADocument17 pagesReading Test - 3 Clinical Depression Text AJisha JanardhanPas encore d'évaluation
- CW Catalogue Cables and Wires A4 En-2Document1 156 pagesCW Catalogue Cables and Wires A4 En-2Ovidiu PuiePas encore d'évaluation
- Campus DrinkingDocument2 pagesCampus DrinkingLiHertzi DesignPas encore d'évaluation
- Evolution Practice Test 2 With AnswersDocument10 pagesEvolution Practice Test 2 With AnswersSuhani SinhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Report On Marketing of ArecanutDocument22 pagesReport On Marketing of ArecanutsivakkmPas encore d'évaluation
- Esomeprazol Vs RabeprazolDocument7 pagesEsomeprazol Vs RabeprazolpabloPas encore d'évaluation
- Education - Khóa học IELTS 0đ Unit 3 - IELTS FighterDocument19 pagesEducation - Khóa học IELTS 0đ Unit 3 - IELTS FighterAnna TaoPas encore d'évaluation
- An Agriculture Testament Albert HowardDocument297 pagesAn Agriculture Testament Albert Howardjagadeeshsunkad100% (1)
- Random FactsDocument353 pagesRandom FactsSergio Rivas100% (1)
- Pengaruh Pembangunan Center Point of IndDocument11 pagesPengaruh Pembangunan Center Point of IndSumitro SafiuddinPas encore d'évaluation
- Recognizing Fractures and Dislocations: Corpuz, Rachella Nicole PDocument46 pagesRecognizing Fractures and Dislocations: Corpuz, Rachella Nicole PRachella Nicole CorpuzPas encore d'évaluation
- 8582d Soldering Station English User GuideDocument9 pages8582d Soldering Station English User Guide1valdasPas encore d'évaluation
- Pelatihan Olahan Pangan Ukm LamselDocument6 pagesPelatihan Olahan Pangan Ukm LamselCalista manda WidyapalastriPas encore d'évaluation
- ECO-321 Development Economics: Instructor Name: Syeda Nida RazaDocument10 pagesECO-321 Development Economics: Instructor Name: Syeda Nida RazaLaiba MalikPas encore d'évaluation
- Good Laboratory Practice GLP Compliance Monitoring ProgrammeDocument17 pagesGood Laboratory Practice GLP Compliance Monitoring ProgrammeamgranadosvPas encore d'évaluation
- 01 Mono Channel BurnerDocument1 page01 Mono Channel BurnerSelwyn MunatsiPas encore d'évaluation
- Aircraft Noise Management: Graduation Project Defense For The Diploma of Air Traffic Management EngineerDocument46 pagesAircraft Noise Management: Graduation Project Defense For The Diploma of Air Traffic Management Engineerchouchou chamaPas encore d'évaluation
- Theory of Accounts On Business CombinationDocument2 pagesTheory of Accounts On Business CombinationheyPas encore d'évaluation
- Day Case Open Appendectomy: A Safe and Cost-Effective ProcedureDocument9 pagesDay Case Open Appendectomy: A Safe and Cost-Effective ProcedureAcademecian groupPas encore d'évaluation
- Radiador y Sus Partes, Motor Diesel 504BDTDocument3 pagesRadiador y Sus Partes, Motor Diesel 504BDTRamón ManglesPas encore d'évaluation
- AD Oracle ManualDocument18 pagesAD Oracle ManualAlexandru Octavian Popîrțac100% (2)
- Antiarrhythmic DrugsDocument56 pagesAntiarrhythmic DrugsHassan MohammadPas encore d'évaluation
- EdExcel A Level Chemistry Unit 4 Mark Scheme Results Paper 1 Jun 2005Document10 pagesEdExcel A Level Chemistry Unit 4 Mark Scheme Results Paper 1 Jun 2005MashiatUddinPas encore d'évaluation
- - 50 Đề Thi Học Sinh Gioi Lớp 12Document217 pages- 50 Đề Thi Học Sinh Gioi Lớp 12Nguyễn Thanh ThảoPas encore d'évaluation