Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Moss Ton
Transféré par
Tiang ElektrikCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Moss Ton
Transféré par
Tiang ElektrikDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
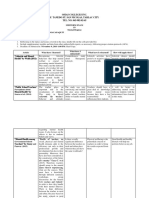
MOSSTONS CONTINUUM OF TEACHING STYLES
Teaching Style Description Example in your teaching?
Command
Teacher-centred. Teacher delivers knowledge; pupils remain passive
Practice
Pupils carry out tasks set by the teacher. Teacher may work with groups as the task is completed.
Reciprocal
Pupils work in pairs: a doer and teacher-partner who evaluates the doers work. Teacher works with the teacher-partner to improve their evaluative skills. Pupils learn to judge performance against criteria.
Self-check
Teacher sets the task; pupils complete it and evaluate their own performance; in collaboration with teacher, set new targets. Pupils move on when they are ready.
Inclusion
Differentiated tasks are set to ensure all pupils experience success and progress.
Guided discovery
Teacher sets individualised learning programmes for pupils based on their cognitive development; considered difficult in large groups, characteristic of SEN provision.
Convergent discovery
Teacher has a defined learning outcome in mind but pupils can decide the processes and presentation technique to reach that outcome. Teacher guides as required.
Divergent discovery
Multiple solutions are possible to a task (e.g. design problem) and pupils devise their own routes, with guidance, and assess the validity of their final solution.
Learner-designed
Pupil designs and carries out a programme or investigation to answer a particular question; requires knowledge and skills built up in earlier learning experiences.
Learner-initiated
Pupil provides a question for investigation as well as designing and carrying out the investigation.
From Mosston M. & Ashworth S. (2002) Teaching Physical Education, 5 ed. San Francisco: Benjamin Cummings
th
NB. A simpler categorisation you may prefer to use is the Closed Framed Negotiated definitions: The Closed Style A formal style in which the material of the lesson is tightly controlled by the teacher who directs pupils often in whole class work or individual tasks (e.g. teacher transmits facts didactically to pupils; teacher gives notes for pupils to write down or copy; pupils are given worksheets to complete with questions which have right answers determined by the teacher). The Framed Style A more pupil-centred style in which the teacher provides a structure for the lesson but pupils can contribute their own ideas and interpretations. This brings pupils into closer collaboration with the teacher (e.g. teacher sets up group problem-solving activities after an initial explanation: pupils are required to think their way towards conclusions). Negotiated Style The lesson is considerably dependent on pupil ideas and contributions. Pupils may be asked to identify needs which the teacher then supports on an individual/group basis (e.g. pupils plan and carry out project work tasks based on decisions made with the teacher and other pupils.)
From Mosston M. & Ashworth S. (2002) Teaching Physical Education, 5 ed. San Francisco: Benjamin Cummings
th
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5795)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- Lesson 4 - Mental, Emotional, and Social HealthDocument26 pagesLesson 4 - Mental, Emotional, and Social HealthAlvie Mae AlvarezPas encore d'évaluation
- Reflection On Micro TeachingDocument3 pagesReflection On Micro TeachingTiang ElektrikPas encore d'évaluation
- Ppat Task 4Document7 pagesPpat Task 4api-122157048100% (1)
- Spelling LessonDocument4 pagesSpelling Lessonapi-243039417Pas encore d'évaluation
- Multigrade TeachingDocument20 pagesMultigrade Teachingcsarali100% (2)
- Direct, Purposeful Experiences and BeyondDocument18 pagesDirect, Purposeful Experiences and BeyondMaria Mendoza AlejandriaPas encore d'évaluation
- 2018 PDPDocument4 pages2018 PDPapi-42001333750% (2)
- Cognitive Behavioural TherapyDocument5 pagesCognitive Behavioural TherapyAndi Firman MubarakPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 4 DLL SCIENCE 4 Q4 Week 2Document5 pagesGrade 4 DLL SCIENCE 4 Q4 Week 2Stephanie Marhen Abueva67% (3)
- Prac 1 Soil EcosystemsDocument8 pagesPrac 1 Soil EcosystemsTiang ElektrikPas encore d'évaluation
- Name: A) Circle The Correct AnswerDocument2 pagesName: A) Circle The Correct AnswerTiang ElektrikPas encore d'évaluation
- Teach Listening Skill: ActivitiesDocument2 pagesTeach Listening Skill: ActivitiesTiang ElektrikPas encore d'évaluation
- Prepared by Mohd Farahan Abdul Rahman Pismp Sem 5 124020Document9 pagesPrepared by Mohd Farahan Abdul Rahman Pismp Sem 5 124020Tiang ElektrikPas encore d'évaluation
- Ahmad Khairi Ahmad AzharDocument11 pagesAhmad Khairi Ahmad AzharTiang ElektrikPas encore d'évaluation
- Skip To Content en Español: in English - SearchDocument80 pagesSkip To Content en Español: in English - SearchTiang ElektrikPas encore d'évaluation
- Scid2 BPDDocument4 pagesScid2 BPDRamonaStereaPas encore d'évaluation
- Textbook Pages 4. Additional Materials From Learning Other Learning ResourcesDocument3 pagesTextbook Pages 4. Additional Materials From Learning Other Learning ResourcesKhim IlaganPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 9Document48 pagesChapter 9Rosalie RosalesPas encore d'évaluation
- 4th PE 2Document6 pages4th PE 2Ken Ken KenPas encore d'évaluation
- Staffing and LeadershipDocument15 pagesStaffing and LeadershipPratiksha SardaPas encore d'évaluation
- Adaptive and Assistive TechnologiesDocument17 pagesAdaptive and Assistive Technologiesapi-239695833Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mackenzie, G. (2018) - Building Resilience Among Children and Youth With ADHDDocument18 pagesMackenzie, G. (2018) - Building Resilience Among Children and Youth With ADHDjuanPas encore d'évaluation
- PrintDocument23 pagesPrintAnkush KharwalPas encore d'évaluation
- Empirically Supported Complexity: Rethinking Evidence-Based Practice in PsychotherapyDocument6 pagesEmpirically Supported Complexity: Rethinking Evidence-Based Practice in PsychotherapyPedro VargasPas encore d'évaluation
- Mental Health ExamDocument8 pagesMental Health Examdiona macasaquitPas encore d'évaluation
- SCIENCE DLL February 19-23, 2019Document2 pagesSCIENCE DLL February 19-23, 2019Geraldine Dioquino RosalesPas encore d'évaluation
- AndersonDocument14 pagesAndersonsskishore89Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pdev 111 2ND Grading Exam (Amaoedsources - Blogspot.com)Document122 pagesPdev 111 2ND Grading Exam (Amaoedsources - Blogspot.com)Keith Shimezu100% (2)
- Quality CirclesDocument14 pagesQuality Circlesedrich1932Pas encore d'évaluation
- How To Write Comments On Performance AppraisalDocument6 pagesHow To Write Comments On Performance AppraisalRay VictorPas encore d'évaluation
- Conceptual UnderstandingDocument22 pagesConceptual UnderstandingrishikeshPas encore d'évaluation
- M1 Kolb Learning Style InventoryDocument4 pagesM1 Kolb Learning Style Inventoryarhont1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Bsbldr801 Lead Personal and Strategic TransformationDocument5 pagesBsbldr801 Lead Personal and Strategic TransformationJoanne Navarro AlmeriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cyber Bullying 1Document5 pagesCyber Bullying 1api-241333093Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson Plan: Listen To Spoken Texts Constructed For Different Purposes, For Example ToDocument4 pagesLesson Plan: Listen To Spoken Texts Constructed For Different Purposes, For Example Toapi-283943860Pas encore d'évaluation
- Study Material-INTRODUCTION TO FACILITATING LEARNER-CENTERED TEACHINGDocument2 pagesStudy Material-INTRODUCTION TO FACILITATING LEARNER-CENTERED TEACHINGJosette BonadorPas encore d'évaluation
- Aims and Approaches: Task C: Check-List Check-List To Evaluate Teaching Learning Materials For EslDocument4 pagesAims and Approaches: Task C: Check-List Check-List To Evaluate Teaching Learning Materials For EslMohd Fauzi ZakariaPas encore d'évaluation