Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Open Channel Problems
Transféré par
Mangam RajkumarDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Open Channel Problems
Transféré par
Mangam RajkumarDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
An open channel has a trapezoidal cross-section with a bottom width of 5 m and side slopes of 2:1 (H:V).
If the depth of flow is 2 m and the average velocity in the channel is 1 m/s, calculate the discharge in the channel.
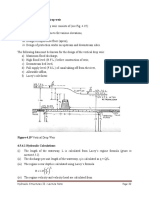
A trapezoidal channel is to be excavated at a site where permit restrictions require that the channel have a bottom width of 5 m, side slopes of 1.5:1 (H:V) and a depth of flow of 1.8 m. If the soil material erodes when the shear stress on the perimeter of the channel exceeds 3.5 N/m2, determine the appropriate slope and flow capacity of the channel. Use the DarcyWeisbach equation and assume that the excavated channel has an equivalent sand roughness of 3 mm.
Water flows at a depth of 2.20 m in a trapezoidal, concrete-lined section (ks = 2 mm) with a bottom width of 3.6 m and side slopes of 2:1 (H:V). The slope of the channel is 0.0006 and the water temperature is 20C. Assuming uniform-flow conditions, estimate the average velocity and flowrate in the channel. Use both the Darcy-Weisbach and Manning equations and compare your answers.
A trapezoidal irrigation channel is to be excavated to supply water to a farm. The design flowrate is 1.8 m3/s, the side slopes are 2:1 (H:V), the longitudinal slope of the channel is 0.1%, Mannings n is 0.025, and the geometry of the channel is to be such that the length of each channel side is equal to the bottom width. (a) Specify the dimensions of the channel required to accommodate the design flow under normal conditions; and (b) If the channel lining can resist an average shear stress of up to 4 Pa, under what flow conditions is the channel lining stable?
Water flows at 8.4 m3/s in a trapezoidal channel with a bottom width of 2 m and side slopes of 2:1 (H:V). Over a distance of 100 m, the bottom width expands to 2.5 m, with the side slopes remaining constant at 2:1. If the depth of flow at both of these sections is 1 m and the channel slope is 0.001, calculate the head loss between the sections. What is the power in kilowatts that is dissipated?
Determine the critical depth for 30 m3/s flowing in a rectangular channel with width 5 m. If the depth of flow is equal to 3 m, is the flow supercritical or subcritical?
A rectangular channel 2 m wide carries 3 m3/s of water at a depth of 1.2 m. If an obstruction 40 cm wide is placed in the middle of this channel, find the elevation of the water surface at the constriction. What is the minimum width of the constriction that will not cause a rise in the water surface upstream?
Water flows at 4.3 m3/s in a rectangular channel of width 3 m and depth of flow 1 m. If the channel width is decreased by 0.75 m and the bottom of the channel is raised by 0.25 m, what is the depth of flow in the constriction?
Water flows at 36 m3/s in a rectangular channel of width 10 m and a Manning n of 0.030. If the depth of flow at a channel section is 3 m and the slope of the channel is 0.001, classify the water-surface profile. What is the slope of the water surface at the observed section? Would the shape of the water-surface profile be much different if the depth of flow were equal to 2 m?
If 100 m3/s of water flows in a channel 8 m wide at a depth of 0.9 m, calculate the downstream depth required to form a hydraulic jump and the fraction of the initial energy lost in the jump.
Derive the hydraulic jump equation for a trapezoidal channel:
Water flows in a horizontal trapezoidal channel at 21 m3/s, where the bottom width of the channel is 2 m, side slopes are 1:1, and depth of flow is 1 m. Calculate the downstream depth required for a hydraulic jump to form at this location. What would be the energy loss in the jump?
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Department of Hydraulic &water Resource Engineering: Open Channel Hydraulics Chapter 1,2 and 3 Work SheetDocument5 pagesDepartment of Hydraulic &water Resource Engineering: Open Channel Hydraulics Chapter 1,2 and 3 Work SheetLemi100% (3)
- 10 - OPEN CHANNELS Sample ProblemsDocument13 pages10 - OPEN CHANNELS Sample ProblemsGray Fiore FullbusterPas encore d'évaluation
- Open Channel Notes - AnswersDocument39 pagesOpen Channel Notes - AnswersGertjan Duniceri100% (3)
- Slides 2 Uniform Flow in Open ChannelDocument54 pagesSlides 2 Uniform Flow in Open ChannelTing Wee Kiet100% (1)
- Irrigation EngineeringDocument20 pagesIrrigation EngineeringUmar Naveed100% (1)
- Chapter 3Document22 pagesChapter 3JommarVocalTagalog100% (1)
- Fluid Mechanics (Problem Solution)Document38 pagesFluid Mechanics (Problem Solution)Faruque AbdullahPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4 PART 2Document14 pagesChapter 4 PART 2Fetene Nigussie75% (8)
- Gradually-Varied FlowDocument43 pagesGradually-Varied FlowMe Kang He Kodos We Kang And Kodos80% (15)
- Chapter4 - Surface Irrigation NewDocument28 pagesChapter4 - Surface Irrigation NewMūssā Mūhābā ZēĒthiopiāPas encore d'évaluation
- Open ChannelDocument116 pagesOpen ChannelBřõwń MäņPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 5 Template PDFDocument15 pagesWeek 5 Template PDFAngelica LosaresPas encore d'évaluation
- Compilation Part 2 (11-19)Document100 pagesCompilation Part 2 (11-19)Joshua Zuniga50% (2)
- Design of Vertical Drop Weir PG, Example, 2020Document9 pagesDesign of Vertical Drop Weir PG, Example, 2020zelalemniguse75% (4)
- Solved Problems in Soil Mechanics: Ahmed S. Al-AghaDocument20 pagesSolved Problems in Soil Mechanics: Ahmed S. Al-AghaMemo LyPas encore d'évaluation
- 4.1 Open Channels - Uniform FlowDocument14 pages4.1 Open Channels - Uniform FlowJohn Reigh CatipayPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment 1 Hydrostatic Force and Center of Pressure: Lecturer: T.ADocument17 pagesExperiment 1 Hydrostatic Force and Center of Pressure: Lecturer: T.AeidalinPas encore d'évaluation
- Surveying Transpo and Ports PDFDocument25 pagesSurveying Transpo and Ports PDFJoy KathleenPas encore d'évaluation
- Practice ProblemsDocument19 pagesPractice Problemsgoddowon100% (1)
- To Investigate Relationship Between Specific Energy and Depth of FlowDocument9 pagesTo Investigate Relationship Between Specific Energy and Depth of FlowFaisal Sardar100% (12)
- Hydrostatic Force On Curved SurfacesDocument14 pagesHydrostatic Force On Curved Surfaceseric labordoPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Mechanics - Impact of Jet Vanes - ExperimentDocument4 pagesFluid Mechanics - Impact of Jet Vanes - ExperimentRavi Agarwal96% (24)
- Hydrostatic Force FinalDocument6 pagesHydrostatic Force FinalChala198979% (14)
- To Study Working and Different Parts of Hydraulic BenchDocument6 pagesTo Study Working and Different Parts of Hydraulic BenchaliPas encore d'évaluation
- Engg Hydrology Chapter - 3Document16 pagesEngg Hydrology Chapter - 3Abdu100% (1)
- Experiment 5 - FLUIDSDocument7 pagesExperiment 5 - FLUIDSJoePas encore d'évaluation
- Head and Cross RegulatorsDocument19 pagesHead and Cross RegulatorsEng Shakir H100% (1)
- Exercise Problems: Palara, Arman S. (Inc) SPL Ce 5BDocument23 pagesExercise Problems: Palara, Arman S. (Inc) SPL Ce 5BKristel LenonPas encore d'évaluation
- Open TutorialDocument2 pagesOpen Tutorialeph86% (7)
- 6.3.1 - Fluid Flow Measurement (Steady Flow)Document56 pages6.3.1 - Fluid Flow Measurement (Steady Flow)Kristoffer Villegas33% (3)
- Flow of Open ChannelDocument61 pagesFlow of Open Channelmr_sam91100% (1)
- Assignment 3 & 4 - AnswersDocument23 pagesAssignment 3 & 4 - Answersአድሜ ልስልሱ100% (2)
- Doe Hydraulics EngineeringDocument30 pagesDoe Hydraulics EngineeringMaster Pits100% (1)
- 44CDocument9 pages44Cjhacademyhyd100% (3)
- ORIFICE - Fluid MechanicsDocument7 pagesORIFICE - Fluid MechanicsWilliam67% (3)
- To Study The Flow Characteristics Over The Hump Orweir in A Rectangular ChannelDocument9 pagesTo Study The Flow Characteristics Over The Hump Orweir in A Rectangular ChannelFaisal Sardar100% (8)
- Plate 4 Effective Stresses in SoilDocument14 pagesPlate 4 Effective Stresses in SoilSofia Isabelle GarciaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4Document34 pagesChapter 4BlueeeMoonZiahGracePas encore d'évaluation
- Computation of Water Surface Profiles: M S N Q yDocument36 pagesComputation of Water Surface Profiles: M S N Q yVivekka Olivia John100% (2)
- Board Reviewin Soil and Water Conservation EngineeringDocument13 pagesBoard Reviewin Soil and Water Conservation EngineeringKevin V LampaanPas encore d'évaluation
- LAB Hydrostatic PressureDocument7 pagesLAB Hydrostatic PressureomshakalocaPas encore d'évaluation
- Flow Through A Venturi FlumeDocument10 pagesFlow Through A Venturi Flumenaeem100% (1)
- Flow in Open Channel - Sample ProblemsDocument8 pagesFlow in Open Channel - Sample Problemsacurvz2005Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture#1 Guide BankDocument34 pagesLecture#1 Guide BankManamno Beza100% (1)
- Hydraulic Jump ConclusionDocument1 pageHydraulic Jump ConclusionWei SalinoPas encore d'évaluation
- Connect Intersecting Gradients in The Vertical PlaneDocument8 pagesConnect Intersecting Gradients in The Vertical PlaneuipohlklgfPas encore d'évaluation
- Activity 2Document4 pagesActivity 2VAN IRIAN GUERRERO0% (1)
- Soil and Water Conservation Engineering: Multiple ChoiceDocument6 pagesSoil and Water Conservation Engineering: Multiple ChoiceAbas Acmad100% (4)
- Unit Hydrograph Lecture NotesDocument12 pagesUnit Hydrograph Lecture NotesEpa Paul100% (1)
- Report HydrologyDocument56 pagesReport Hydrologydash1991Pas encore d'évaluation
- Worksheet - 143760187HS-II, TUTORIAL ON CH-5Document14 pagesWorksheet - 143760187HS-II, TUTORIAL ON CH-5A MusaverPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2 Part 1Document11 pagesChapter 2 Part 1virajain100% (3)
- HGE Preboard - 2 - SolutionsDocument20 pagesHGE Preboard - 2 - SolutionsRojane Flora100% (1)
- Problems 244 294Document14 pagesProblems 244 294Happy Feets50% (6)
- Classification of Open Channels: S R N V S R N VDocument11 pagesClassification of Open Channels: S R N V S R N VJireh LoquinarioPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 2-AnalysisofgravitydamDocument12 pages2 2-AnalysisofgravitydammorganPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3 Non-Uniform Flow TutorialDocument2 pagesChapter 3 Non-Uniform Flow TutorialFalahiah JudgePas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment and WorksheetDocument3 pagesAssignment and WorksheetHMAN OROMOPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter Eight Flow in Open Channels Practice Problems 1Document15 pagesChapter Eight Flow in Open Channels Practice Problems 1Jerle ParondoPas encore d'évaluation
- Irrigation Works: The Principles on Which Their Design and Working Should Be Based, with Special Details Relating to Indian Canals and Some Proposed ImprovementsD'EverandIrrigation Works: The Principles on Which Their Design and Working Should Be Based, with Special Details Relating to Indian Canals and Some Proposed ImprovementsPas encore d'évaluation
- Predicting Alcohol Levels: The ScienceDocument1 pagePredicting Alcohol Levels: The ScienceMangam RajkumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Navigating The Circle of FifthsDocument19 pagesNavigating The Circle of FifthsMangam RajkumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Sun Greatest Story Ever ToldDocument187 pagesSun Greatest Story Ever ToldMangam RajkumarPas encore d'évaluation
- WWW W WWW W WWW W WWW W .. .. .. .. WWW W # WWW W Œ Œ Œ Œ W Œ Œ Œ Œ W .. .. Œ Œ Œ Œ W Œ Œ Œ Œ W Œ Œ Œ Œ W # Œ Œ Œ Œ W C8-6-001Document1 pageWWW W WWW W WWW W WWW W .. .. .. .. WWW W # WWW W Œ Œ Œ Œ W Œ Œ Œ Œ W .. .. Œ Œ Œ Œ W Œ Œ Œ Œ W Œ Œ Œ Œ W # Œ Œ Œ Œ W C8-6-001Mangam RajkumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Westren Classical Music 1600-1899Document9 pagesWestren Classical Music 1600-1899Mangam RajkumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Em 1.4 RMDocument18 pagesEm 1.4 RMMangam RajkumarPas encore d'évaluation
- SCF Flute Book PDFDocument28 pagesSCF Flute Book PDFSebastián GómezPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Mechanics: Module1, 2, 3 Week 1Document7 pagesFluid Mechanics: Module1, 2, 3 Week 1Mangam RajkumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Em 1.3 RMDocument12 pagesEm 1.3 RMMangam RajkumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Mechanics / Unit 1/ Module 1 Introduction of MechanicsDocument4 pagesEngineering Mechanics / Unit 1/ Module 1 Introduction of MechanicsMangam RajkumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Projection of LinesDocument7 pagesProjection of LinesMangam RajkumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Orthographic ProjectionsDocument4 pagesOrthographic ProjectionsMangam RajkumarPas encore d'évaluation
- DynamicsDocument2 pagesDynamicsMangam RajkumarPas encore d'évaluation
- P-2/D:/N-fluid/Fld11-1: Flow PipeDocument1 pageP-2/D:/N-fluid/Fld11-1: Flow PipeMangam Rajkumar100% (1)
- Meteorology And: "Gmiy UnsiaoieDocument1 pageMeteorology And: "Gmiy UnsiaoieMangam RajkumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Sustainable Performance in The Construction Industry: CEMEX STUDY 18/5/10 14:34 Page 1Document4 pagesSustainable Performance in The Construction Industry: CEMEX STUDY 18/5/10 14:34 Page 1Nikhil SatavPas encore d'évaluation
- TUV Manual IEC2016 2022.04.11 PDFDocument69 pagesTUV Manual IEC2016 2022.04.11 PDFFriedrichPas encore d'évaluation
- WB146 5 PDFDocument10 pagesWB146 5 PDFLuisAlbertoVerdejoTapia100% (1)
- Chapter 1 Solutions Modern Physics 4th EditionDocument30 pagesChapter 1 Solutions Modern Physics 4th EditionDaniele CastroPas encore d'évaluation
- Charge Performance DataDocument8 pagesCharge Performance Datasamin0Pas encore d'évaluation
- Heat Exchange PDFDocument3 pagesHeat Exchange PDFmunhPas encore d'évaluation
- Heat TransferDocument382 pagesHeat TransferManish Chouhan100% (1)
- Pravin ResumeDocument3 pagesPravin ResumeSatyajeet ReddyPas encore d'évaluation
- JodhpurDocument2 pagesJodhpurPranita ShandilyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ifa 3 - Students Pack Extra ExercisesDocument28 pagesIfa 3 - Students Pack Extra ExercisesSusana Castro Gil0% (1)
- Open Ended LabDocument6 pagesOpen Ended LabVishal DhimanPas encore d'évaluation
- SCG-SH-0201 Lockout Tagout (LOTO) FinalDocument52 pagesSCG-SH-0201 Lockout Tagout (LOTO) FinalThái TrầnPas encore d'évaluation
- Raku Kei Reiki MudrasDocument4 pagesRaku Kei Reiki Mudrasmajadb100% (1)
- Sitrans T: Unrestricted © Siemens AG 2016 Siemens - Tld/keywordDocument56 pagesSitrans T: Unrestricted © Siemens AG 2016 Siemens - Tld/keywordfredyPas encore d'évaluation
- Roomie Dylon MannualDocument25 pagesRoomie Dylon MannualJanePas encore d'évaluation
- Arc Welding: Assignment in Ce12Document5 pagesArc Welding: Assignment in Ce12Analyn NatividadPas encore d'évaluation
- Catalogo Invt gd100 PVDocument10 pagesCatalogo Invt gd100 PVSergio RecabarrenPas encore d'évaluation
- Advance Retrofitting India Central Business DistrictsDocument14 pagesAdvance Retrofitting India Central Business DistrictsKarn KhandelwalPas encore d'évaluation
- Objective: "Spiritalia Seu Pneumatica," Describes A Number of Contrivances Which Either Had Then LongDocument15 pagesObjective: "Spiritalia Seu Pneumatica," Describes A Number of Contrivances Which Either Had Then Longmohamad_shukor_5Pas encore d'évaluation
- Manual de Usuario Succionador 2Document36 pagesManual de Usuario Succionador 2Wilmer CaicedoPas encore d'évaluation
- 2018 JC2 H2 Physics SA2 Anglo Chinese Junior College PDFDocument109 pages2018 JC2 H2 Physics SA2 Anglo Chinese Junior College PDFeternal vorcePas encore d'évaluation
- Corrosion of Carbon Steels in Caustic SodaDocument5 pagesCorrosion of Carbon Steels in Caustic SodamasilamaniPas encore d'évaluation
- LPI® Copper & Stainless Steel Earth Rods: o o o oDocument3 pagesLPI® Copper & Stainless Steel Earth Rods: o o o oCecep NanuPas encore d'évaluation
- Coulson MethodDocument17 pagesCoulson MethodSanjeeb SutradharPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 28 Ground GRDocument3 pagesChapter 28 Ground GRmanirup_tcePas encore d'évaluation
- Cooling SystemDocument14 pagesCooling SystemSteven AmadorPas encore d'évaluation
- AOYG 18 LAC2 - Outdoor PCB DiagramsDocument4 pagesAOYG 18 LAC2 - Outdoor PCB DiagramsJack BilyPas encore d'évaluation
- Sheer Driving PleasureDocument25 pagesSheer Driving Pleasuremst317Pas encore d'évaluation
- P300 2Document4 pagesP300 2Kevin LoayzaPas encore d'évaluation
- A.s.t.m.22 Manual On The Use of ThermocouplesDocument312 pagesA.s.t.m.22 Manual On The Use of ThermocouplesAR RmsPas encore d'évaluation