Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Icnd2 Course Labs RSTP Labs
Transféré par
aref12345Description originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Icnd2 Course Labs RSTP Labs
Transféré par
aref12345Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
ICND2
Rapid Spanning-Tree Protocol
TOPOLOGY 5x2950 (Layer 2 Switches) These exercises utilize build on the previous ones used in the last class sessions.
Lab Exercise 1: Rapid Spanning-Tree Configuration
Equipment Involved: SW1, SW2, SW3, SW4 & SW5 STEP 1: Verify 802.1d STP Operation on SW1 Double click on SW1 to open the command line interface window Press <enter> to get to user exec mode Type en and press <enter> to go into privileged mode (no password required)
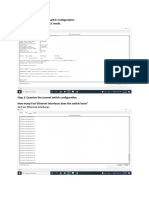
Type the word show spanning-tree to display the current 802.1d settings for SW1 o o o o Note the fact that STP is enabled and running (spanning tree enabled protocol ieee), which indicate a traditional Spanning-Tree operation (802.1d) Notice that the this bridge/switch is the root switch (This bridge is the root) All of the ports are in forwarding mode The typical timers for 802.1d are displayed: Hello: 2 seconds MaxAge: 20 seconds Forward Delay: 15 seconds
All of the displayed information indicates that Spanning-Tree Protocol is running as expected, in 802.1d mode
STEP 2: Change the Spanning-Tree mode on SW1 to Rapid Spanning-Tree Double click on SW1to open the command line interface window Press <enter> to get to user exec mode Type en and press <enter> to go into privileged mode (no password required)
Type config t to enter global configuration mode Type spanning-tree mode rapid-pvst to change from STP 802.1d to RSTP 802.1w Type exit to return to privileged exec mode Execute the show-spanning tree command again to verify the changes
Notice that the indicator that Spanning-Tree is functional has changed to the phrase protocol rstp from protocol ieee Almost all of the other settings appear unchanged Type copy running-config startup-config (or wr mem) to save the configuration to memory When finished, select File > Save on the main Packet Tracer screen in order to save your changes in the simulator file
STEP 3: Explore the Spanning-Tree Settings on SW2 Double click on SW2 to open the command line interface window Press <enter> to get to user exec mode Type en and press <enter> to go into privileged mode (no password required)
Type show-spanning tree and press <enter> to display spanning-tree data on SW3 You will notice that nothing has changed on SW3, and that it is still running in 802.1d STP mode (protocol ieee). This is because switches attached to 802.1w Rapid Spanning-Tree switches run in compatibility mode, using the older protocol on those links Type config t to enter global configuration mode Type spanning-tree mode rapid-pvst to change from STP 802.1d to RSTP 802.1w Type exit to return to privileged exec mode Execute the show-spanning tree command again to verify the changes Type exit to exit configuration mode completely Type copy running-config startup-config (or wr mem) to save the configuration to memory When finished, select File > Save on the main Packet Tracer screen in order to save your changes in the simulator file Repeat the process for all other switches
STEP 3: Simulate a link failure on SW4 to demonstrate the more efficient convergence process Double click on SW4 to open the command line interface window Press <enter> to get to user exec mode Type en and press <enter> to go into privileged mode (no password required)
Type show-spanning tree and press <enter> to display spanning-tree data on SW4 (see above) Notice several settings that indicate that SW4 is successfully running in RSTP mode: o o o Running protocol is RSTP (Spanning tree enabled protocol rstp) Fa0/3 is in blocking mode but is designated as an Alternate Port (secondary root port) Link types are identified as point-to-point (P2P)
Type config t to enter global configuration mode Enter interface configuration mode on the Fa0/1 root port using the command Type interface fa0/1 Type shutdown to simulate a link failure Type exit twice to return to privileged exec mode
Quickly execute the show-spanning tree command again to show the settings during the convergence process Note that the change to the new root port and the update process is remarkably brief
Restore the fa0/1 interface to service using the no shutdown command
Type exit to exit configuration mode completely Type copy running-config startup-config (or wr mem) to save the configuration to memory When finished, select File > Save on the main Packet Tracer screen in order to save your changes in the simulator file
Lab Exercise 2: Per-VLAN Spanning-Tree Configuration
Equipment Involved: SW1, SW2, SW3, SW4 & SW5 STEP 1: Create two additional VLANs on all switches Double click on SW1 to open the command line interface window Press <enter> to get to user exec mode Type en and press <enter> to go into privileged mode (no password required)
Type config t and press <enter> to enter global configuration mode. Create an additional VLAN on SW1 using the command vlan 11 Create another VLAN on SW1 using the command vlan 111 Return to privileged command line mode by entering exit twice Execute the show vlan command to display all configured vlans, verifying that VLAN 11 and VLAN 111 appear in the output
Type exit to exit configuration mode completely Type copy running-config startup-config (or wr mem) to save the configuration to memory When finished, select File > Save on the main Packet Tracer screen in order to save your changes in the simulator file Repeat the process on SW2, SW3, SW4 & SW5 so that the same VLANs exist on all switches in the domain
STEP 2: Explore the changes created by separate Spanning-Tree instances for each VLAN Double click on SW2 to open the command line interface window Press <enter> to get to user exec mode Type en and press <enter> to go into privileged mode (no password required)
Type show spanning-tree and press <enter>, and press the spacebar to scroll down the output. Notice the following: o o o A separate Spanning-Tree instance is running for VLAN 1, VLAN 11, and VLAN 111 respectively SW1 is the root switch on the all STP instances SW2 is running in RSTP mode
Change the bridge priority for SW2 on VLAN 11 by entering the command spanning-tree vlan 11 root primary
Verify that SW1 is still the root switch on VLAN 1 by typing spanning-tree vlan 1 Verify that the phrase This bridge is the root is not present and that the MAC address of the root bridge is not the same as SW2
Type copy running-config startup-config (or wr mem) to save the configuration to memory When finished, select File > Save on the main Packet Tracer screen in order to save your changes in the simulator file
Lab Exercise 3: Voice VLAN Configuration
Equipment Involved: SW4 STEP 1: Add an IP Phone to the Lab Layout
Locate the Devices dialog on the lower left-hand corner of the screen (see image above) Click on the End Devices Icon to display endpoint devices that you can add to the network
Locate the IP Phone device on the devices menu (as displayed above), place the mouse over it, and click to drag the IP Phone next to SW4 (see below)
Locate the IP Phone device on the devices menu (as displayed above), place the mouse over it, and click to drag the IP Phone next to SW4 (see below) Next, create a connection between the IP Phone and SW4 by selecting the connections menu by clicking the straight-through cable Place the mouse over the IP Phone and left click over it, which will reveal a drop-down style menu with two selections, Switch and PC; select Switch Finally, move the mouse over SW4 (a line will start to drag from the IP Phone, this is normal), and left clock on SW4, which will display a drop-down style menu similar to the IP Phone. This time select Fa0/4 as the port When finished, select File > Save on the main Packet Tracer screen in order to save your changes in the simulator file
STEP 2: Configure the Fa0/4 port for Voice & Data VLAN Operation
Double click on SW4 to open the command line interface window Press <enter> to get to user exec mode Type en and press <enter> to go into privileged mode (no password required)
First, verify the presence of the IP Phone by executing the show cdp neighbors command from privileged mode on the CLI Verify the connection by finding the entry for IP Phone (as displayed above) Type config t and press <enter> to enter global configuration mode
Enter interface configuration mode by entering the command interface fa0/4 and press <enter> Set the port to access mode using the interface command switchport mode access Specify VLAN 11 as the data VLAN for the phone by using the command switchport access vlan 11 Set voice traffic to use a separate VLAN by typing the command switchport voice vlan 111 Return to privileged command line mode by entering exit twice Type copy running-config startup-config (or wr mem) to save the configuration to memory When finished, select File > Save on the main Packet Tracer screen in order to save your changes in the simulator file
To verify the correct port settings, enter the command interface fa0/4 switchport and press <enter> In the command output, look for Access Mode VLAN 11 and Voice VLAN 111 to verify correct configuration Alternatively, you can use the command show running-config and look at the specific output under interface fa0/2
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Basic Switch ConfigDocument11 pagesBasic Switch Configm2incyberPas encore d'évaluation
- Laboratorio 3Document5 pagesLaboratorio 3Robinson DelgadoPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Switch ConfigurationDocument4 pagesBasic Switch ConfigurationanikajudyPas encore d'évaluation
- Technical Document Cisco 2960G, 2960S, and 2960X Configuration For Wheatnet-IpDocument6 pagesTechnical Document Cisco 2960G, 2960S, and 2960X Configuration For Wheatnet-IpRaneesh RamesanPas encore d'évaluation
- Initial Config of Switch Step by StepDocument20 pagesInitial Config of Switch Step by StepTolosa TafesePas encore d'évaluation
- S3900 Series Switches Configuration PreparationDocument6 pagesS3900 Series Switches Configuration PreparationmikemikelayPas encore d'évaluation
- LABDCT 2002 (Guide) Nexus.5020.Lab - GuideDocument52 pagesLABDCT 2002 (Guide) Nexus.5020.Lab - Guidekds20850Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2.2.3.3 Packet Tracer - Configuring Initial Switch SettingsDocument7 pages2.2.3.3 Packet Tracer - Configuring Initial Switch SettingsClareAustinPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3. Command Line Interface - Basics and Software ActualizationDocument24 pagesChapter 3. Command Line Interface - Basics and Software ActualizationCarlosPas encore d'évaluation
- How To Configure A Basic SwitchDocument11 pagesHow To Configure A Basic SwitchAlex BodeaPas encore d'évaluation
- Computernetworkingnotes Com Switching Vlan STP VTP DTP EtherDocument24 pagesComputernetworkingnotes Com Switching Vlan STP VTP DTP EtherNushran NufailPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Router and Switch Instructions (Cisco Devices)Document7 pagesBasic Router and Switch Instructions (Cisco Devices)h_lifemakerPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 8 - Switch ConfigurationDocument26 pagesChapter 8 - Switch ConfigurationMaxamed SaalaxPas encore d'évaluation
- Ccna Icnd2 Labs PDFDocument99 pagesCcna Icnd2 Labs PDFsousou2000Pas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment No. 4: Verify and Test Network Connectivity ODocument9 pagesExperiment No. 4: Verify and Test Network Connectivity ORana AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Router and Switch Instructions (Cisco Devices)Document7 pagesBasic Router and Switch Instructions (Cisco Devices)heruye mulugetaPas encore d'évaluation
- 3com 4400 ConfDocument26 pages3com 4400 ConfJuan José LopezPas encore d'évaluation
- Cisko Switch KomandeDocument6 pagesCisko Switch Komandegoran66bPas encore d'évaluation
- Laboratorio 2@Document5 pagesLaboratorio 2@carlosPas encore d'évaluation
- 01-Configuration PreparationDocument5 pages01-Configuration PreparationiwanbudakjambiPas encore d'évaluation
- ESwitching PTAct 2 5 1-Answer 3Document10 pagesESwitching PTAct 2 5 1-Answer 3Hari HermanPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 3Document8 pagesLab 3toto071902Pas encore d'évaluation
- Huawei: VRP User Manual - Configuration GuideDocument9 pagesHuawei: VRP User Manual - Configuration GuideBilly De NethersPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Switch Part1Document6 pagesBasic Switch Part1BasilPas encore d'évaluation
- 10G EPON OLT Quick Operation GuideDocument13 pages10G EPON OLT Quick Operation GuideStcAzad100% (1)
- CNs-Lab 9-Cisco Switch ConfigurationDocument8 pagesCNs-Lab 9-Cisco Switch ConfigurationHemin EssaPas encore d'évaluation
- Reset A Cisco 2960 Switch To Factory Default SettingsDocument7 pagesReset A Cisco 2960 Switch To Factory Default SettingsSuporte [CS Telecom]Pas encore d'évaluation
- How To Configure Cisco Switches - A Step by Step Guide - ComparitechDocument12 pagesHow To Configure Cisco Switches - A Step by Step Guide - ComparitechAbcxyz XyzabcPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 2 5 1 Basic Switch ConfigurationDocument14 pagesLab 2 5 1 Basic Switch ConfigurationChinh Nguyen0% (1)
- Cisco IOS Basic Switch Configuration PDFDocument8 pagesCisco IOS Basic Switch Configuration PDFArif KurniawanPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 2.5.1 - Basic Switch ConfigurationDocument15 pagesLab 2.5.1 - Basic Switch ConfigurationSarah Manich50% (2)
- Chapter One Lab-3 - Configure Initial Switch SettingsDocument5 pagesChapter One Lab-3 - Configure Initial Switch SettingsFedasa BotePas encore d'évaluation
- Win-Test Quick GuideDocument17 pagesWin-Test Quick GuideduoneudPas encore d'évaluation
- Name: Edi Purnomo/3311011003 Kelas: Karyawan: Lab 8.2.3 Configuring Static VlansDocument10 pagesName: Edi Purnomo/3311011003 Kelas: Karyawan: Lab 8.2.3 Configuring Static VlansCak LodhePas encore d'évaluation
- CCNA Lab Guide - Routing and SwitchingDocument151 pagesCCNA Lab Guide - Routing and SwitchingAnonymous 7QpTAo100% (4)
- Topic 7A. Configuring A CISCO IOS SwitchDocument20 pagesTopic 7A. Configuring A CISCO IOS SwitchsimonnjauPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.5.5 Packet Tracer - Configure Initial Switch SettingsDocument6 pages2.5.5 Packet Tracer - Configure Initial Switch SettingsБогдан МарчукPas encore d'évaluation
- Accessing The SwitchDocument29 pagesAccessing The SwitchZahid Nawaz AdilPas encore d'évaluation
- VLAN ConfigeDocument4 pagesVLAN Configehawariya abelPas encore d'évaluation
- Lan Switching and SecurityDocument13 pagesLan Switching and SecuritybikkerPas encore d'évaluation
- Taller Cisco 1Document8 pagesTaller Cisco 1Felipe TriviñoPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab - Initialize and Reload A Router and Switch - ILMDocument5 pagesLab - Initialize and Reload A Router and Switch - ILMDANIEL STEVEN ROMERO AGUIRREPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.5.5-Configuración de Los Parametros Iniciales Del SwitchDocument5 pages2.5.5-Configuración de Los Parametros Iniciales Del Switchpuyo.dc.22Pas encore d'évaluation
- Task 1: Verify The Default Switch Configuration Step 1: Enter Privileged EXEC ModeDocument20 pagesTask 1: Verify The Default Switch Configuration Step 1: Enter Privileged EXEC ModeAdnan YousafPas encore d'évaluation
- Dell Networking 6 4 2 8 Release NotesDocument16 pagesDell Networking 6 4 2 8 Release NotesIlhamSyuhadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Upgrading Dell Networking N1100-ON Series Switches To Version 6.8.1.2Document11 pagesUpgrading Dell Networking N1100-ON Series Switches To Version 6.8.1.2rudiansyah.ar313Pas encore d'évaluation
- TSHOOT Prep Guide v1.00Document25 pagesTSHOOT Prep Guide v1.00gogneyPas encore d'évaluation
- DI-1750 ManualDocument549 pagesDI-1750 ManualAmit VermaPas encore d'évaluation
- 01-03 Typical Basic ConfigurationDocument69 pages01-03 Typical Basic ConfigurationBarrymuyinda_2Pas encore d'évaluation
- IP6704A-QFXOA Operating TrainingDocument17 pagesIP6704A-QFXOA Operating TrainingAjay SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.5.5 Packet Tracer Configure Initial Switch Settings ConverterDocument6 pages2.5.5 Packet Tracer Configure Initial Switch Settings ConverterGiroPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.5.5 Packet Tracer - Configure Initial Switch SettingsDocument5 pages2.5.5 Packet Tracer - Configure Initial Switch Settingskds20850Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 04 Hardware Settings PDFDocument8 pagesChapter 04 Hardware Settings PDFsukandar sawidinPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 1 - Basic Router ConfigurationDocument3 pagesLab 1 - Basic Router ConfigurationazitaggPas encore d'évaluation
- CCNA Cheat SheetDocument23 pagesCCNA Cheat SheetzhenPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 SwitchingDocument60 pages1 SwitchingLoku BappaPas encore d'évaluation
- Network with Practical Labs Configuration: Step by Step configuration of Router and Switch configurationD'EverandNetwork with Practical Labs Configuration: Step by Step configuration of Router and Switch configurationPas encore d'évaluation
- WAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksD'EverandWAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksPas encore d'évaluation
- Cisco CCNA Command Guide: An Introductory Guide for CCNA & Computer Networking Beginners: Computer Networking, #3D'EverandCisco CCNA Command Guide: An Introductory Guide for CCNA & Computer Networking Beginners: Computer Networking, #3Pas encore d'évaluation
- Configuring Wireless Network ConnectionsDocument15 pagesConfiguring Wireless Network Connectionsaref12345100% (1)
- 6425CD ENU LabManualDocument414 pages6425CD ENU LabManualaniyisethPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 10 - 3 - 2 PDFDocument5 pagesLab 10 - 3 - 2 PDFaref12345Pas encore d'évaluation
- Citrix Desktop Server Administrator's Guide PDFDocument68 pagesCitrix Desktop Server Administrator's Guide PDFaref12345Pas encore d'évaluation
- Classless SubnettingDocument27 pagesClassless Subnettingaref12345Pas encore d'évaluation
- Server Virtualization Seminar PresentationDocument39 pagesServer Virtualization Seminar Presentationaref12345Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fast Track Data Warehouse For SQL Server 2012: Eric Kraemer Senior Program ManagerDocument12 pagesFast Track Data Warehouse For SQL Server 2012: Eric Kraemer Senior Program Manageraref12345Pas encore d'évaluation
- 98 361 (Actual Test)Document48 pages98 361 (Actual Test)aref1234557% (7)
- GE 7 ReportDocument31 pagesGE 7 ReportMark Anthony FergusonPas encore d'évaluation
- Maritime Academy of Asia and The Pacific-Kamaya Point Department of AcademicsDocument7 pagesMaritime Academy of Asia and The Pacific-Kamaya Point Department of Academicsaki sintaPas encore d'évaluation
- 2-1. Drifting & Tunneling Drilling Tools PDFDocument9 pages2-1. Drifting & Tunneling Drilling Tools PDFSubhash KediaPas encore d'évaluation
- PE MELCs Grade 3Document4 pagesPE MELCs Grade 3MARISSA BERNALDOPas encore d'évaluation
- FE CH 5 AnswerDocument12 pagesFE CH 5 AnswerAntony ChanPas encore d'évaluation
- BSBITU314 Assessment Workbook FIllableDocument51 pagesBSBITU314 Assessment Workbook FIllableAryan SinglaPas encore d'évaluation
- Aakriti 1Document92 pagesAakriti 1raghav bansalPas encore d'évaluation
- Electronic Spin Inversion: A Danger To Your HealthDocument4 pagesElectronic Spin Inversion: A Danger To Your Healthambertje12Pas encore d'évaluation
- Faa Data On B 777 PDFDocument104 pagesFaa Data On B 777 PDFGurudutt PaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Walking in Space - Lyrics and Chord PatternDocument2 pagesWalking in Space - Lyrics and Chord Patternjohn smithPas encore d'évaluation
- IcarosDesktop ManualDocument151 pagesIcarosDesktop ManualAsztal TavoliPas encore d'évaluation
- Guardcam InstructionsDocument12 pagesGuardcam InstructionsCompuFix RepairsPas encore d'évaluation
- Binary OptionsDocument24 pagesBinary Optionssamsa7Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sankranthi PDFDocument39 pagesSankranthi PDFMaruthiPas encore d'évaluation
- Disclosure To Promote The Right To InformationDocument11 pagesDisclosure To Promote The Right To InformationnmclaughPas encore d'évaluation
- Knee JointDocument28 pagesKnee JointRaj Shekhar Singh100% (1)
- Codan Rubber Modern Cars Need Modern Hoses WebDocument2 pagesCodan Rubber Modern Cars Need Modern Hoses WebYadiPas encore d'évaluation
- Wallem Philippines Shipping Inc. v. S.R. Farms (Laxamana)Document2 pagesWallem Philippines Shipping Inc. v. S.R. Farms (Laxamana)WENDELL LAXAMANAPas encore d'évaluation
- BIAN How To Guide Developing Content V7.0 Final V1.0 PDFDocument72 pagesBIAN How To Guide Developing Content V7.0 Final V1.0 PDFميلاد نوروزي رهبرPas encore d'évaluation
- Cyclic MeditationDocument8 pagesCyclic MeditationSatadal GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment - 1: Batch (Differential) Distillation: 1. ObjectiveDocument30 pagesExperiment - 1: Batch (Differential) Distillation: 1. ObjectiveNaren ParasharPas encore d'évaluation
- Gomez-Acevedo 2010 Neotropical Mutualism Between Acacia and Pseudomyrmex Phylogeny and Divergence TimesDocument16 pagesGomez-Acevedo 2010 Neotropical Mutualism Between Acacia and Pseudomyrmex Phylogeny and Divergence TimesTheChaoticFlamePas encore d'évaluation
- M. Ircham Mansyur 07224005 Microprocessor-2 (H13)Document7 pagesM. Ircham Mansyur 07224005 Microprocessor-2 (H13)emiierPas encore d'évaluation
- Airport & Harbour Engg-AssignmentDocument3 pagesAirport & Harbour Engg-AssignmentAshok Kumar RajanavarPas encore d'évaluation
- How To Convert Files To Binary FormatDocument1 pageHow To Convert Files To Binary FormatAhmed Riyadh100% (1)
- ENT 300 Individual Assessment-Personal Entrepreneurial CompetenciesDocument8 pagesENT 300 Individual Assessment-Personal Entrepreneurial CompetenciesAbu Ammar Al-hakimPas encore d'évaluation
- HepaDocument1 pageHepasenthilarasu5100% (1)
- Signature Object Detection Based On YOLOv3Document4 pagesSignature Object Detection Based On YOLOv3Lý Khánh NhưPas encore d'évaluation
- Soil NailingDocument6 pagesSoil Nailingvinodreddy146Pas encore d'évaluation
- Data Asimilasi Untuk PemulaDocument24 pagesData Asimilasi Untuk PemulaSii Olog-olog PlonkPas encore d'évaluation