Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
ACC1002X Cheat Sheet 2
Transféré par
jieboCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
ACC1002X Cheat Sheet 2
Transféré par
jieboDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
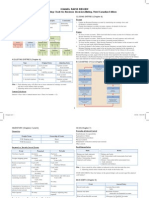
(1) Consolidated Statement of Income Operating Revenues Revenue from services Sales revenue Less: Credit Card Discount
Less: Sales Discount Less: Sales Returns & Allowances Total revenues Operating Expenses Cost of goods sold Salaries expense Rent expense Advertising expense General and administrative expenses Depreciation expense Other operating expenses Total expenses Operating Income Other Items Investment income Interest expense Loss on PPE sold Income before Income Taxes Income tax expense Net Income Earnings per Share (2) Consolidated Statement of SE Contributed Retained Total Capital Earnings SE Beginning, $0 $0 $0 date Additional X X contributions Net Income Dividends declared Ending, date X Y (Z) Y (Z)
(3) Consolidated Balance Sheet ASSETS Current Assets Cash and cash equivalents Short-term investments Inventories Supplies Accounts receivable Less: Allowance for doubtful account Short-term notes receivable Prepaid expenses Total current assets Properties, plants & equipment Less: Accumulated depreciation Goodwill Long-term investments Long-term notes receivable Intangibles Non-current deferred income taxes Total assets LIABILITIES AND SHAREHOLDERS EQUITY Current Liabilities: Accounts payable Dividends payable Accrued expenses payable Unearned revenue Short-term notes payable Total current liabilities Non-current liabilities Deferred lease credits Deferred taxes Non-current accrued income taxes Long-term notes payable Total non-current liabilities Total liabilities Shareholders equity Contributed capital Preferred stock Common stock Treasury stock Retained earnings Total shareholders equity Total liabilities and shareholders equity
(4) Consolidated Statement of Cash Flows Cash flows from operating activities: Net income Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by Operating Activities: Depreciation and amortization (expense) (+) Changes in assets and liabilities: (Decrease) Accounts receivable (Decrease) Inventory (Decrease) Prepaid expense (Decrease) Gains (Increase) Accounts payable (Increase) Accrued expenses (Increase) Losses Interest expense (-) Deduct if theres an increase in Assets Add if theres an increase in Liabilites Net cash provided (used) by operating activities Cash flows for investing activities: Purchase of PPE Proceeds from disposal of PPE Purchase of short-term investments Proceeds from short-term investments Sale of marketable securities Net cash provided (used) by investing activities Cash flows from financing activities: Borrowings under line of credit Payment on long-term debt Payment of dividends Purchase of treasury stock Proceeds from issuance of stock Net cash provided (used) by financing activities Net change in cash & cash equivalents: Cash & cash equivalents at beginning of period Cash & cash equivalents at end of period Indirect Method: Net Income Add: Depreciation Expense Decrease in Accounts Receivables Decrease in Inventories Increase in Accounts Payable Increase in Accrued Expenses Payable Non-operating Losses Net Cash provided (used) by Operating Activities Direct Method: Cash receipts from customers Cash payments to suppliers Cash payments for salary
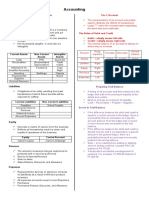
Definitions The Balance Sheet is a statement of financial position that reports dollar amounts assets, liabilities, and SE at a specific point in time The Income Statement is a statement of operations that reports revenues, expenses, and net income for a stated period of time. Statement of Retained Earnings explains changes to the retained earnings balance that occurred during the reporting period. The Statement of Cash Flows reports inflows and outflows of cash for a stated period of time. A Trial Balance is a list of ALL accounts with their balances to check on the equality of debits and credits Revenue Principle states that revenues are recognized when 1) delivery has occurred; 2) There is persuasive evidence of an arrangement for customer payment; 3) The price is fixed or determinable; 4) Collection is reasonably assured. The Matching Principle requires that expenses be recorded when incurred in earning revenue. Managers Choice of Inventory Methods 1) Net income effects (managers prefer to report higher earnings for the companies). 2) Income tax effects (managers prefer to pay the least amount of taxes allowed by law as late as possible the least-latest rule). LIFO Conformity Rule: If LIFO is used on the income tax return, it must also be used to calculate inventory and cost of goods sold for the financial statements. When unit costs are rising, LIFO produces lower income and a lower inventory valuation than FIFO. First-In, First-Out assumes that the earliest purchased goods are sold first. Last-In, First-Out assumes that the most recently purchased units are sold first. Average Cost method uses the weighted average unit cost of the goods available for sale for both cost of goods sold and ending inventory. Profitability is a primary measure of overall success of a company. Several tests of profitability focus on measuring the adequacy of income by comparing it to other items reported on the financial statements. Liquidity refers to a companys ability to meet its maturing debts. Tests of liquidity focus on the relationship of current assets and current liabilities. Solvency refers to a companys ability to meet its long-term obligations. Tests of solvency are measures of a companys ability to meet these obligations. Market Tests relate the current price per share of stock to the return that accrues to investors. Stockholders can: (1) Vote in stockholders meeting on major issues w.r.t. management; (2) Participate proportionately in distribution of profits; (3) Share proportionately in the distribution of assets upon liquidation
Allowance for Doubtful Accounts | Beginning balance Write-offs | Bad debt expense | Ending balance Accounts Receivable Beginning balance | Write-offs Net Sales | Cash collections Ending balance |
Determine Bad Debt Expense 1) Use Aging Method to compute Allowance for Bad Debts, 2) Difference between and Beginning Balance of Allowance for Bad Debts is Bad Debt Expense 3) Net AR is AR less Allowance for Bad Debt
Cash payments for Other Expenses
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Accounting Cheat SheetDocument7 pagesAccounting Cheat Sheetopty100% (15)
- Federal Income Tax: a QuickStudy Digital Law ReferenceD'EverandFederal Income Tax: a QuickStudy Digital Law ReferencePas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Everyday Journal EntriesDocument2 pagesBasic Everyday Journal EntriesMary73% (15)
- Accounting Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesAccounting Cheat Sheetanoushes1100% (2)
- Ratios Used in Analysis of Financial StatementsDocument2 pagesRatios Used in Analysis of Financial StatementsMary100% (4)
- Intermediate Accounting 1: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideD'EverandIntermediate Accounting 1: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuidePas encore d'évaluation
- Accounting Cheat SheetsDocument4 pagesAccounting Cheat SheetsGreg BealPas encore d'évaluation
- Schaum's Easy Outline of Bookkeeping and Accounting, Revised EditionD'EverandSchaum's Easy Outline of Bookkeeping and Accounting, Revised EditionÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (3)
- Cheat Sheet - Financial STDocument2 pagesCheat Sheet - Financial STMohammad DaulehPas encore d'évaluation
- Cheat Sheet For AccountingDocument4 pagesCheat Sheet For AccountingshihuiPas encore d'évaluation
- Becker CPA BEC Review CheatsheetDocument6 pagesBecker CPA BEC Review CheatsheetGabrielPas encore d'évaluation
- Fnce 100 Final Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesFnce 100 Final Cheat SheetToby Arriaga100% (2)
- Closing Journal EntriesDocument1 pageClosing Journal EntriesMary91% (11)
- Accounting Journal Entries Flowchart PDFDocument1 pageAccounting Journal Entries Flowchart PDFMary75% (4)
- Instructions For A Classified Balance SheetDocument5 pagesInstructions For A Classified Balance SheetMary91% (11)
- Kelly's Finance Cheat Sheet V6Document2 pagesKelly's Finance Cheat Sheet V6Kelly Koh100% (4)
- Cheat Sheet Final - FMVDocument3 pagesCheat Sheet Final - FMVhanifakih100% (2)
- Intermediate Accounting 2: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideD'EverandIntermediate Accounting 2: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuidePas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Impact of Everyday Journal Entries On The Income StatementDocument2 pagesBasic Impact of Everyday Journal Entries On The Income StatementMary100% (1)
- Account ClassificationDocument3 pagesAccount ClassificationUsama MukhtarPas encore d'évaluation
- Inbm 110 - Accounts Study Sheet: Chapter 1 & 2Document5 pagesInbm 110 - Accounts Study Sheet: Chapter 1 & 2Laura TaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Class of AccountsDocument5 pagesClass of AccountssalynnaPas encore d'évaluation
- 1040 Exam Prep Module III: Items Excluded from Gross IncomeD'Everand1040 Exam Prep Module III: Items Excluded from Gross IncomeÉvaluation : 1 sur 5 étoiles1/5 (1)
- ACCT 101 Cheat SheetDocument1 pageACCT 101 Cheat SheetAndrea NingPas encore d'évaluation
- Differentiation Cheat SheetDocument15 pagesDifferentiation Cheat SheetjieboPas encore d'évaluation
- FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING: Passbooks Study GuideD'EverandFINANCIAL ACCOUNTING: Passbooks Study GuidePas encore d'évaluation
- Cheat Sheet For Financial AccountingDocument1 pageCheat Sheet For Financial Accountingmikewu101Pas encore d'évaluation
- Module 2 Introducting Financial Statements - 6th EditionDocument7 pagesModule 2 Introducting Financial Statements - 6th EditionjoshPas encore d'évaluation
- Accouting Finals Cheat SheetDocument1 pageAccouting Finals Cheat SheetpinkrocketPas encore d'évaluation
- Financial Accounting 3Document47 pagesFinancial Accounting 3Roxana Istrate100% (1)
- Financial Accounting: Tools For Business Decision-Making, Third Canadian EditionDocument6 pagesFinancial Accounting: Tools For Business Decision-Making, Third Canadian Editionapi-19743565100% (1)
- Accounting: Assets Liabilities + Equity A L + EDocument4 pagesAccounting: Assets Liabilities + Equity A L + EjermainePas encore d'évaluation
- Tax Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesTax Cheat SheetJean Pingfang Koh100% (3)
- Ultimate Accounting Guide SheetDocument1 pageUltimate Accounting Guide SheetMD. Monzurul Karim Shanchay67% (6)
- Midterm Cheat SheetDocument4 pagesMidterm Cheat SheetvikasPas encore d'évaluation
- CheatDocument1 pageCheatIshmo KueedPas encore d'évaluation
- 2013 REG Last Minute Study Notes (Bonus)Document47 pages2013 REG Last Minute Study Notes (Bonus)olegscherbina100% (3)
- ST1131 Cheat Sheet Page 1Document1 pageST1131 Cheat Sheet Page 1jiebo0% (1)
- Integration Cheat SheetDocument7 pagesIntegration Cheat Sheetjiebo100% (1)
- BEC Notes Chapter 2Document7 pagesBEC Notes Chapter 2cpacfa100% (10)
- CPA Review Notes 2019 - FAR (Financial Accounting and Reporting)D'EverandCPA Review Notes 2019 - FAR (Financial Accounting and Reporting)Évaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (17)
- Use The Following Information For The Next Three Questions:: Activity 3.2Document11 pagesUse The Following Information For The Next Three Questions:: Activity 3.2Jade jade jadePas encore d'évaluation
- IS4241 - RevisionDocument13 pagesIS4241 - RevisionjieboPas encore d'évaluation
- BEC Notes Chapter 3Document6 pagesBEC Notes Chapter 3cpacfa90% (10)
- BEC Notes Chapter 3Document13 pagesBEC Notes Chapter 3bobby100% (1)
- BVA CheatsheetDocument3 pagesBVA CheatsheetMina ChangPas encore d'évaluation
- Inventory Turnover Cost of Sales / Avg Inventory High Is Effective Inv MGMT Days of Inventory On Hand (DOH) 365/inv TurnoverDocument3 pagesInventory Turnover Cost of Sales / Avg Inventory High Is Effective Inv MGMT Days of Inventory On Hand (DOH) 365/inv Turnoverjoe91bmwPas encore d'évaluation
- Journal Entries For Long Lived AssetsDocument2 pagesJournal Entries For Long Lived AssetsMary100% (20)
- Problem SolvingDocument10 pagesProblem SolvingRegina De LunaPas encore d'évaluation
- KRBL ReportDocument28 pagesKRBL ReportHardeep Singh SohiPas encore d'évaluation
- Equity Handout 4th YearDocument9 pagesEquity Handout 4th YearMildred Angela DingalPas encore d'évaluation
- Basics Accounting PrinciplesDocument22 pagesBasics Accounting PrincipleshsaherwanPas encore d'évaluation
- Creating Teams With An EdgeDocument8 pagesCreating Teams With An EdgejieboPas encore d'évaluation
- Gross Pay CalculationsDocument2 pagesGross Pay CalculationsMary100% (3)
- Fin Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesFin Cheat SheetChristina RomanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Financial Accounting and AnalysisDocument8 pagesFinancial Accounting and AnalysisRia LapizPas encore d'évaluation
- Accounting Cheat Sheet FinalsDocument5 pagesAccounting Cheat Sheet FinalsRahel CharikarPas encore d'évaluation
- Free BEC NotesDocument6 pagesFree BEC Notesxcrunner87Pas encore d'évaluation
- Accounting Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesAccounting Cheat SheetvgirotraPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Instructions For Retained Earnings StatementDocument1 pageBasic Instructions For Retained Earnings StatementMary100% (5)
- IS4203 - RevisionDocument37 pagesIS4203 - RevisionjieboPas encore d'évaluation
- IS2103 - SummaryDocument22 pagesIS2103 - SummaryjieboPas encore d'évaluation
- SSA2211 - Evolution of A Global City-StateDocument19 pagesSSA2211 - Evolution of A Global City-StatejieboPas encore d'évaluation
- GEM2900 Cheat Sheet 2Document2 pagesGEM2900 Cheat Sheet 2jieboPas encore d'évaluation
- GEM2900 ProbabilityDocument2 pagesGEM2900 ProbabilitywakakkaPas encore d'évaluation
- GEK2013 Real Estate FinanceDocument20 pagesGEK2013 Real Estate FinanceUnknown uploaderPas encore d'évaluation
- CS1231 Cheat Sheet Part 1Document1 pageCS1231 Cheat Sheet Part 1jieboPas encore d'évaluation
- ACC1002X Cheat Sheet 1Document2 pagesACC1002X Cheat Sheet 1jieboPas encore d'évaluation
- CS1231 Cheat Sheet 2Document2 pagesCS1231 Cheat Sheet 2jieboPas encore d'évaluation
- ST1131 Cheat Sheet Page 2Document1 pageST1131 Cheat Sheet Page 2jieboPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2 Joint ArrangementsDocument3 pagesChapter 2 Joint ArrangementsAngelica B. MartinPas encore d'évaluation
- WEEK 1 ReviewerDocument33 pagesWEEK 1 ReviewerFebemay LindaPas encore d'évaluation
- Zarrouk 2016Document22 pagesZarrouk 2016Aulya KiranaPas encore d'évaluation
- A Collection of Case Studies On Financial Accounting Concepts-YJKDocument65 pagesA Collection of Case Studies On Financial Accounting Concepts-YJKJkPas encore d'évaluation
- Colgate Estados Financieros 2021Document3 pagesColgate Estados Financieros 2021Lluvia RamosPas encore d'évaluation
- Acctg 115 - CH 5 SolutionsDocument11 pagesAcctg 115 - CH 5 SolutionsSharadPanchal100% (1)
- China Railway Construction Corporation Attaining Globalization Via HighDocument18 pagesChina Railway Construction Corporation Attaining Globalization Via HighCyril Ang-numbaalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chap 15Document17 pagesChap 15pdmallari12Pas encore d'évaluation
- ProfileDocument24 pagesProfilerajittillaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Caiib FM ModcDocument39 pagesCaiib FM ModcJenipher Carlos HosannaPas encore d'évaluation
- How The NSSF Has Grown Its Asset Base To Shs6 TrillionDocument2 pagesHow The NSSF Has Grown Its Asset Base To Shs6 TrillionjadwongscribdPas encore d'évaluation
- Template - Acctg. Major 3 Module 2Document7 pagesTemplate - Acctg. Major 3 Module 2Ryan PatitoPas encore d'évaluation
- CHAPTER 26 Statement of Comprehensive Income (Concept Map)Document1 pageCHAPTER 26 Statement of Comprehensive Income (Concept Map)kateyy99100% (1)
- Nike Case Study VrindaDocument4 pagesNike Case Study VrindaAnchal ChokhaniPas encore d'évaluation
- FOF Seminar Activities Topic 4 SolutionsDocument7 pagesFOF Seminar Activities Topic 4 Solutionsmuller1234Pas encore d'évaluation
- STRABAG - SE - Geschäftsbericht 2020 - E - ADocument264 pagesSTRABAG - SE - Geschäftsbericht 2020 - E - ASiddhartha ShekharPas encore d'évaluation
- Tata Steel Corus Acquisition Financial DetailsDocument6 pagesTata Steel Corus Acquisition Financial DetailsSandarbh Agarwal0% (1)
- Fabmi W3Document10 pagesFabmi W3rvinsmoke149Pas encore d'évaluation
- FAR - Becker To I75 WIPDocument18 pagesFAR - Becker To I75 WIPshobhitsPas encore d'évaluation
- Final CO of Corporate Valuation 2019 PDFDocument14 pagesFinal CO of Corporate Valuation 2019 PDF...ADITYA… JAINPas encore d'évaluation
- Student Copy Assignments On Money and Banking NewDocument12 pagesStudent Copy Assignments On Money and Banking Newtanishweta26Pas encore d'évaluation
- ACCT CH.2 HomeworkDocument13 pagesACCT CH.2 Homeworkj8noelPas encore d'évaluation
- Statement of The ProblemDocument24 pagesStatement of The ProblemLia AmmuPas encore d'évaluation
- The Little Book of Valuation: Cash FlowsDocument5 pagesThe Little Book of Valuation: Cash FlowsSangram PandaPas encore d'évaluation
- Group Work FA 1 - Group 7Document9 pagesGroup Work FA 1 - Group 7Tri HuynhPas encore d'évaluation
- Pre-Finals Act 1Document2 pagesPre-Finals Act 1Richard LamagnaPas encore d'évaluation