Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Future Time Clauses
Transféré par
Radu BortesDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Future Time Clauses
Transféré par
Radu BortesDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
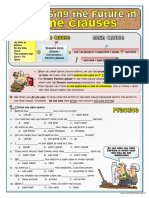
FUTURE TIME CLAUSES
When we describe events and actions expected to take place in the future, we use future tenses. Remember we have future simple, future progressive and future perfect tenses. When we have time clauses that refer to future time, the verb in the time clause is usually in the present tense not in the future tense. The time clauses in the English language are introduced by conjunctions such as after, as soon as, before, till, until, when, whenever, while or expressions such as the minute, the moment etc. The construction form is the same as the first conditional for the future. Read the example sentences WHEN When I finish writing the reports, I will go out with my friends. She will move to East Sarajevo when she finds a good job. When the party is over, well clean the house. BEFORE Before I go to Budva, Ill book a room. Milosh will visit all his relatives before he joins the army. They wont transfer any players before they sign the advertising agreement. AFTER After her sister prepares dinner, theyll invite their neighbours. My father will buy a new car after he saves enough money. What will you do after you finish the French course? AS SOON AS They will go to the beach as soon as they have their breakfast. All the players in the national team will go on holiday as soon as the Europian Championship is over. Dont worry mom. I will phone you as soon as I arrive Paris. UNTIL Will you wait for me until I get back? (refers to a point of time in the future) You can go out. I will wait until she calls. They wont start the match until the rain stops. I wont buy anything new until I pay all my debts. IF If I go home early tonight, I will watch the Olympic Games. Tara will buy a new TV set if the price goes down. If you pass the test, what will you do? HAVE YOU NOTICED THE STRUCTURE
when, after, before, as soon as, until, if are followed by SIMPLE PRESENT TENSE. Main clasuses in these sentences are followed by future will.
**PRACTICE** Fill in the blanks with the correct form of the verbs. 1) When the manager _____________ ( arrive ), they _______________ ( start ) the meeting. 2) If he _____________ ( reach ) the sales target this year, the company ____________ ( award ) him. 3) We _______________ ( start ) the construction of a shooping center as soon as the government __________( allow ) us to begin. 4) After she __________ ( find ) a good house in Karyaka, she_______________ ( buy ) some new furniture. 5) If Alex _______________ ( feel ) better at the weekend, he _______________ ( play ) in the match against Milan. 6) I will have to finish the reports before the manager _______________ ( call ). 7) She _______________( eat ) anything until the doctor_______________( tells ) her to eat. KEY: 1. arrives / will start 2. reaches / will award 3. will start / allows 4. finds / will buy 5. feels / will play 6. calls 7. wont eat / tells
Future in time clauses - grammar rules
Compare: I'll come back home and I'll do it. x I'll do it when I come back home. (when I come is the time clause) You will push this button and the door will open. x As soon as you push this button the door will open. Don't stand up. First I'll tell you. x Don't stand up till (until) I tell you. You'll need my car. Take it. x Whenever you need my car you can take it. You'll tidy up the house and I'll do the shopping. x You'll tidy up the house while I do the shopping. You will drop the bomb and it will explode. x The moment you drop the bomb it will explode. Similarly, other future forms also change to the present simple tense. He is going to leave. The room will be empty. x As soon as he leaves the room will be empty. We are moving next week. Then we'll call you. x When we move next week we'll call you.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- 2 - Fce - Conditional 0123 Rules 2015Document10 pages2 - Fce - Conditional 0123 Rules 2015Alba Fortuny HuetePas encore d'évaluation
- Solucion Test 3 PDFDocument2 pagesSolucion Test 3 PDFYolanda Moya MartínezPas encore d'évaluation
- Relative ClausesDocument7 pagesRelative ClausesMuhammet ÜNLÜPas encore d'évaluation
- FUTURE TIME CLAUSES (When, Before, After, As Soon As, Until)Document2 pagesFUTURE TIME CLAUSES (When, Before, After, As Soon As, Until)Astarot VizjereiPas encore d'évaluation
- Future Time ClausesDocument1 pageFuture Time ClausesTiberiu CATALINAPas encore d'évaluation
- Future: 1. For Things That We Decide To Do Now. (Rapid Decisions)Document8 pagesFuture: 1. For Things That We Decide To Do Now. (Rapid Decisions)Darren OnlyPas encore d'évaluation
- Time Clauses WorkshopDocument6 pagesTime Clauses WorkshopCAROLINA DUQUE PÉREZPas encore d'évaluation
- Future Tenses and Time Clauses Practice-KeyDocument2 pagesFuture Tenses and Time Clauses Practice-KeyYunus Emre IsıktanPas encore d'évaluation
- Future Time Clauses: Expressing Future Time After 'When','before', 'After', 'As Soon As', 'Until'Document2 pagesFuture Time Clauses: Expressing Future Time After 'When','before', 'After', 'As Soon As', 'Until'Eduard SanduPas encore d'évaluation
- Exercise Future Perfect TenseDocument2 pagesExercise Future Perfect TenseKhalid Eka SaputraPas encore d'évaluation
- Future Time: Dragana FilipovicDocument43 pagesFuture Time: Dragana FilipovicTweetyandBeastPas encore d'évaluation
- Future Time: Dragana FilipovicDocument43 pagesFuture Time: Dragana FilipovicTweetyandBeastPas encore d'évaluation
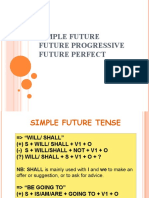
- Simple Future TensesDocument30 pagesSimple Future TensesKavitha Jeya MoorthiPas encore d'évaluation
- Future Time Clauses KDocument2 pagesFuture Time Clauses KAllinnaPas encore d'évaluation
- Future Time Clauses Grammar Drills - 96400Document4 pagesFuture Time Clauses Grammar Drills - 96400Tania Sarmiento CornesPas encore d'évaluation
- The Future - Infinitive of PurposeDocument24 pagesThe Future - Infinitive of PurposeSusaku KururugiPas encore d'évaluation
- English Class 13: Elementary LevelDocument18 pagesEnglish Class 13: Elementary LevelJesus CarreonPas encore d'évaluation
- INGLISHDocument4 pagesINGLISHJuan Pablo Arias VelasquezPas encore d'évaluation
- Future Time ClausesDocument4 pagesFuture Time ClausesRoxanaKwiekPas encore d'évaluation
- Mixed FuturesDocument7 pagesMixed FuturesVirginia JbPas encore d'évaluation
- Everything About The Future Tenses and Exercises PDFDocument33 pagesEverything About The Future Tenses and Exercises PDFGabriel Marchetto0% (1)
- Idoms and Present Simple in The FutuerDocument5 pagesIdoms and Present Simple in The FutuerEkbal RaghebPas encore d'évaluation
- Simple Future TensesDocument30 pagesSimple Future TensesElvis Aguilar JulcaPas encore d'évaluation
- 8.1. Uses and Meanings of Simple Future Tense and Continuous Future TenseDocument8 pages8.1. Uses and Meanings of Simple Future Tense and Continuous Future TenseAlina PetreaPas encore d'évaluation
- Inglés Instrumental: Unit 6. Time Clauses Subordinators Used To Introduce Time ClausesDocument4 pagesInglés Instrumental: Unit 6. Time Clauses Subordinators Used To Introduce Time ClausesclaudiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 8 VjezbeDocument8 pagesUnit 8 VjezbesophilauPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Bachillerato Extra Grammar Full With ExplanationDocument13 pages1 Bachillerato Extra Grammar Full With ExplanationAndreaTürmePas encore d'évaluation
- By Before (+time) : RememberDocument8 pagesBy Before (+time) : RememberfranosullivanPas encore d'évaluation
- Apuntes FUTURO PERFECTODocument5 pagesApuntes FUTURO PERFECTODarly MarquezPas encore d'évaluation
- Grammar English BookDocument44 pagesGrammar English Bookjohntheo94Pas encore d'évaluation
- Future Progressive Future Perfect....Document1 pageFuture Progressive Future Perfect....carlosPas encore d'évaluation
- GrammarDocument5 pagesGrammarЛиза ЛозновенкоPas encore d'évaluation
- Future Continuous Future Perfect Alternative Ways Referring To FutureDocument8 pagesFuture Continuous Future Perfect Alternative Ways Referring To FutureEnrique Gomez OrtegaPas encore d'évaluation
- Future Tenses: Ins Olivar GranDocument20 pagesFuture Tenses: Ins Olivar GranOmar Herrera RodríguezPas encore d'évaluation
- Engleski III k1Document24 pagesEngleski III k1DanijelaPas encore d'évaluation
- Tuan 12Document5 pagesTuan 12Quyền NguyễnPas encore d'évaluation
- PPT. Expressing The FutureDocument53 pagesPPT. Expressing The FutureHanizar Rachman100% (1)
- Future Perfect Simple ModuleDocument6 pagesFuture Perfect Simple ModuleNathalie GarcíaPas encore d'évaluation
- Simple Future Future Progressive Future PerfectDocument14 pagesSimple Future Future Progressive Future PerfectLailanraPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 1. - The Future. ExercisesDocument12 pagesUnit 1. - The Future. ExercisesAntonio Sanchez LozanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Predict That STH Will Happen in The Future: Will and Going ToDocument9 pagesPredict That STH Will Happen in The Future: Will and Going ToJuan Carlos Briceño InciartePas encore d'évaluation
- Future Perfect Vs Future ContinuousDocument5 pagesFuture Perfect Vs Future ContinuousAryPas encore d'évaluation
- 2º Bach - Future Tenses Exercises With KeyDocument4 pages2º Bach - Future Tenses Exercises With Keypep_bep100% (1)
- FUTURE Tenses - PPTDocument37 pagesFUTURE Tenses - PPTi.diana100% (1)
- GramatykaDocument12 pagesGramatykaapi-3712805Pas encore d'évaluation
- Future Time ClausesDocument4 pagesFuture Time ClausesPamela GualdieriPas encore d'évaluation
- Quiz OnlingDocument22 pagesQuiz OnlingCristinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Future FormsDocument7 pagesFuture FormsSusana GarciaPas encore d'évaluation
- A. Circle The Correct For of The Verb To Complete Each SentenceDocument2 pagesA. Circle The Correct For of The Verb To Complete Each SentenceÇetin TemizelPas encore d'évaluation
- Simple Future TenseDocument7 pagesSimple Future TenseLuminitaCaciulaPas encore d'évaluation
- Homework Future Time ClausesDocument6 pagesHomework Future Time Clausesostz albanPas encore d'évaluation
- FutureDocument5 pagesFuture嘉惠Pas encore d'évaluation
- 1 ConditionalDocument9 pages1 ConditionalЛена ПетренкоPas encore d'évaluation
- Future Tenses ANSWERSDocument2 pagesFuture Tenses ANSWERSFrancisco Cañada Lopez100% (1)
- Underline The Most Suitable Future Form in Each SentenceDocument2 pagesUnderline The Most Suitable Future Form in Each SentenceCucPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Present Simple&ContDocument11 pages1 Present Simple&Contcrisboby80Pas encore d'évaluation
- Future All TypesDocument3 pagesFuture All TypesNoobgamer69Pas encore d'évaluation
- Grammar Reference: Future SimpleDocument13 pagesGrammar Reference: Future SimpleloredanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Grammar ExercisesDocument13 pagesGrammar ExercisesJoseph KennedyPas encore d'évaluation
- F. Scott Fitzgerald and The Jazz AgeDocument14 pagesF. Scott Fitzgerald and The Jazz AgeRadu BortesPas encore d'évaluation
- Word Order Rules and Exercises PDFDocument10 pagesWord Order Rules and Exercises PDFgabriella56Pas encore d'évaluation
- F. Scott Fitzgerald and The Jazz AgeDocument14 pagesF. Scott Fitzgerald and The Jazz AgeRadu BortesPas encore d'évaluation
- Upperintermediate b2 Advanced c1 Adult High SCDocument1 pageUpperintermediate b2 Advanced c1 Adult High SCRadu BortesPas encore d'évaluation
- Subiecte Oral Engleza BilingvDocument3 pagesSubiecte Oral Engleza BilingvRadu Bortes100% (1)
- Test Paper: 1. Complete With Present Simple or Present Continuous. (25x 2 50 Points)Document1 pageTest Paper: 1. Complete With Present Simple or Present Continuous. (25x 2 50 Points)Radu BortesPas encore d'évaluation
- Writing Subjanctive MoDocument1 pageWriting Subjanctive MoRadu BortesPas encore d'évaluation
- Islcollective Worksheets Intermediate b1 Upperintermediate b2 Advanced c1 Elementary School High School Reading Speaking 282504eeffca7b387b0 83201105Document3 pagesIslcollective Worksheets Intermediate b1 Upperintermediate b2 Advanced c1 Elementary School High School Reading Speaking 282504eeffca7b387b0 83201105Radu Bortes100% (1)
- About MyselfDocument1 pageAbout MyselfRadu BortesPas encore d'évaluation
- Rewrite Each Sentence Keeping The Meaning The SameDocument14 pagesRewrite Each Sentence Keeping The Meaning The SameRadu BortesPas encore d'évaluation
- Past-Simple Vs Past-ContinuousDocument3 pagesPast-Simple Vs Past-ContinuousRadu BortesPas encore d'évaluation
- Possessive Adjectives PronounsDocument4 pagesPossessive Adjectives PronounsRadu BortesPas encore d'évaluation
- Prepositions of Place, Furniture, Prepositions of PlaceDocument2 pagesPrepositions of Place, Furniture, Prepositions of PlaceRadu BortesPas encore d'évaluation
- Islcollective Worksheets Preintermediate A2 Intermediate b1 Upperintermediate b2 Adult High School Reading Speaking Rel 1126150f2eea61cf682 22220974Document5 pagesIslcollective Worksheets Preintermediate A2 Intermediate b1 Upperintermediate b2 Adult High School Reading Speaking Rel 1126150f2eea61cf682 22220974Radu BortesPas encore d'évaluation
- Possessive Pronouns 6ºanoDocument2 pagesPossessive Pronouns 6ºanoANAPas encore d'évaluation
- PEPDFDocument7 pagesPEPDFMarijaPas encore d'évaluation
- Noun ClauseDocument25 pagesNoun ClauseLorensa OktaviaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cut&PasteG1 3 LanguageArtsDocument98 pagesCut&PasteG1 3 LanguageArtsSong Nguyen100% (39)
- Clauses of ResultDocument4 pagesClauses of ResultBogdan MihăilăPas encore d'évaluation
- Algebra: Express Yourself: Mathematics As Language by Vicky BurkeDocument13 pagesAlgebra: Express Yourself: Mathematics As Language by Vicky BurkevickyburkePas encore d'évaluation
- Play English Sinapsis 4Document41 pagesPlay English Sinapsis 4Irina BorzaPas encore d'évaluation
- Barmina L A Verhovskaya I P Praktikum Po Angliiskomu YazykuDocument188 pagesBarmina L A Verhovskaya I P Praktikum Po Angliiskomu YazykuArcyom KaratchenyaPas encore d'évaluation
- English Language Tenses: Venetia Kimioni, Esl TeacherDocument14 pagesEnglish Language Tenses: Venetia Kimioni, Esl TeacherMon RojasPas encore d'évaluation
- Marven of The Great North WoodsDocument71 pagesMarven of The Great North WoodsSarah WilkersonPas encore d'évaluation
- Greek Frequency Dictionary 1 - Essential Vocabulary - 2500 Most Common Greek WordsDocument226 pagesGreek Frequency Dictionary 1 - Essential Vocabulary - 2500 Most Common Greek WordssemPas encore d'évaluation
- Discourse Markers For Addition, Cause and EffectDocument4 pagesDiscourse Markers For Addition, Cause and EffectClaudio ColussiPas encore d'évaluation
- Tips EnglishDocument11 pagesTips Englishvictoria castroPas encore d'évaluation
- Speaking For IELTS Teacher's NotesDocument32 pagesSpeaking For IELTS Teacher's Notesaeintyamincho4603Pas encore d'évaluation
- 7 Write Essay PTEA StrategiesDocument9 pages7 Write Essay PTEA StrategiesAbdullah Lazman100% (5)
- Purposive Communication Report July 2Document38 pagesPurposive Communication Report July 2Jericho MarianoPas encore d'évaluation
- Dhaka University5Document17 pagesDhaka University5Md Sifat KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Thesis On Multimodal Discourse AnalysisDocument4 pagesThesis On Multimodal Discourse Analysisgjcezfg9100% (2)
- Mipanda Yemazita (Noun Classes) : Mupanda 1Document33 pagesMipanda Yemazita (Noun Classes) : Mupanda 1Tboi Tboi100% (13)
- Rubrics Level 3Document3 pagesRubrics Level 3Carmen LuceroPas encore d'évaluation
- Automated Essay Evaluation With Semantic AnalysisDocument15 pagesAutomated Essay Evaluation With Semantic AnalysiscutestudentPas encore d'évaluation
- Present - Perfect - or - Past - Simple - 2-Đã G PDocument5 pagesPresent - Perfect - or - Past - Simple - 2-Đã G PTriết Dương Trần AnhPas encore d'évaluation
- The Lost Thing PPoint 2019Document52 pagesThe Lost Thing PPoint 2019Sunjit UppalPas encore d'évaluation
- Thunder Rose Family TimesDocument2 pagesThunder Rose Family Timesapi-296134556Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2020 HSC Chinese BeginnersDocument20 pages2020 HSC Chinese BeginnersPhoenixPas encore d'évaluation
- Prefijos y SufijosDocument5 pagesPrefijos y SufijosKatyana SilvaPas encore d'évaluation
- Self-Editing Worksheet 6 Chapter 6: Cause/Effect EssaysDocument2 pagesSelf-Editing Worksheet 6 Chapter 6: Cause/Effect EssaysDesi Fitria FajerinPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit Video/PPT LinkDocument89 pagesUnit Video/PPT LinkSRAPas encore d'évaluation
- 1MENTAL ABILITY PART - 1 of 4Document59 pages1MENTAL ABILITY PART - 1 of 4Barun SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Present Continuous TenseDocument6 pagesPresent Continuous TenseKhoerul AnwarPas encore d'évaluation