Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Comparison Table
Transféré par
Rodriguez Villalobos NelsonDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Comparison Table
Transféré par
Rodriguez Villalobos NelsonDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Comparison Table
This comparison summarize characteristics of all protection relay types described in previously published technical articles: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Using Protective Relay For Fighting Against Faults The Good Old Electromechanical Protective Relay The Solid State Relay (Static Relay) Overview Few Words About Digital Protection Relay Flexibility and Reliability of Numerical Protection Relay El. Mech. Relay 1st generation relays. Static Relay 2nd generation relays. Digital Relay Numerical Relay
Characteristic Technology Standard Operating Principle
Present Present generation relays. generation relays. They use They use microprocessor. microprocessor. Within built Within built software with software with predefined values predefined values Microprocessors, digital ICs, digital dignal processors A/D conversion, numerical algorithm techniques Microprocessors, digital ICs, digital signal processors A/D conversion, numerical algorithm techniques
They use principle In this relays of electromagnetic transistors and ICs principle. been used
Measuring elements/ Hardware Measuring method
Induction disc, electromagnets, induction cup, balance beam Electrical qtys converted intomechanical force, torque
R, L, C, transistors, analogue ICs comparators Level detects,comparison withreference value in analogue comparator
Surrounding Environment
Depend upon There value may gravitation and vary with respect to the value changes temperature also. to the surrounding magnetic fields also. El. Mech. Relay Bulky Slow Mechanical clock works, dashpot Temp. dependant High No Limited Required High 8 to 10 VA El. Mech. Relay Very High Required Limited Static Relay Small Fast Static timers Temp. dependant Low Yes Wide Required Low 1 VA Static Relay Less Required Wide Digital Relay Small Fast Counter Stable High Yes Wide Not required Low < 0.5 VA Digital Relay Less Required Wide Numerical Relay Compact Very fast Counter Stable High Yes Wide Not required Low < 0.5 VA Numerical Relay Less Required Wide
Characteristic Relay Size Speed of Response Timing function Time of Accuracy Reliability Vibration Proof Characteristics Requirement of Draw Out CT Burden CT Burden Characteristic Reset Time Auxiliary supply Range of settings
Isolation Voltage Function Maintenance Resistance Output Capacitance Characteristic Deterioration due to Operation Relay Programming SCADA Compatibility Operational value indication Visual indication Self monitoring Parameter setting Fault Disturbance Recording
Low Single function Frequent 100 mille ohms < 1 Pico Farad El. Mech. Relay Yes
High Single function Frequent 10 Ohms > 20 Pico Farads Static Relay No
High Multi function Low 10 Ohms > 20 Pico Farads Digital Relay No
High Single function Very Low 10 Ohms > 20 Pico Farads Numerical Relay No
No No Not Possible
Partially No Possible
Programmable Possible Possible
Programmable Yes Possible
Flags, targets No Plug setting, dial setting Not possible
LEDs Yes Thumb wheel, dual in line switches Not possible
LEDs, LCD Yes Keypad for numeric values, through computer Possible
LEDs, LCD Yes Keypad for numeric values, through computer Possible
Relays Nomenclature as per ANSI
No 2 3 21 25 27 30 32 37 40 46 49 50 51 52 Time delay relay 3 Checking or Interlocking relay 21 Distance relay Check synchronizing relay Under voltage relay Annunciation relay Directional power (Reverse power) relay Low forward power relay Field failure (loss of excitation) Negative phase sequence relay Machine or Transformer Thermal relay Instantaneous Over current relay A.C. IDMT Over current relay Circuit breaker Type of Relay
52a Circuit breaker Auxiliary switch Normally open (a contact) 52b Circuit breaker Auxiliary switch Normally closed (b contact) 55 56 Power Factor relay Field Application relay
59 64 67 68 74 76 78 79 80 81
Overvoltage relay Earth fault relay Directional relay Locking relay Alarm relay D.C Over current relay Phase angle measuring or out of step relay AC Auto reclose relay Monitoring loss of DC supply Frequency relay
81 U Under frequency relay 81 O Over frequency relay 83 85 86 87 Automatic selective control or transfer relay Carrier or pilot wire receive relay Tripping Relay Differential relay
87G Generator differential relay 87G T Overall differential relay 87U UAT differential relay 87NT Restricted earth fault relay 95 99 Trip circuit supervision relay Over flux relay
186A Auto reclose lockout relay 186B Auto reclose lockout relay
Relays for Transmission and Distribution Lines protection
No 1 Line Protection
400 KV Main-I: Non switched or Numerical Distance Scheme Transmission Main-II: Non switched or Numerical Distance Scheme Line 220 KV Main-I : Non switched distance scheme (Fed from Bus PTs) Transmission Main-II: Switched distance scheme (Fed from line CVTs) With a changeover Line facility from bus PT to line CVT and vice-versa 132 KV Main Protection: Switched distance scheme (fed from bus PT). Transmission Backup Protection: 3 Nos. directional IDMT O/L Relays and Line 1 No. Directional IDMT E/L relay. 33 KV Lines Non-directional IDMT 3 Over Current and 1 Earth Fault relays 11KV Line Non-directional IDMT 2 Over Current and 1 Earth Fault relays
4 5
References: - Handbook of Switchgear Bhel - Digital/Numerical Relays - T.S.M. Rao
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Comparison of Protection Relay Types: Electromechanical, Static, Digital and NumericalDocument5 pagesComparison of Protection Relay Types: Electromechanical, Static, Digital and NumericalJeya KannanPas encore d'évaluation
- Comparison of Protection Relay TypesDocument5 pagesComparison of Protection Relay Typesasimnaqvi2003Pas encore d'évaluation
- Comparison of Protection Relay Types GuideDocument5 pagesComparison of Protection Relay Types GuideEuroSMC en América LatinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Comparison of Protection Relay Types: Characteristics and ApplicationsDocument6 pagesComparison of Protection Relay Types: Characteristics and ApplicationsVasudev AgrawalPas encore d'évaluation
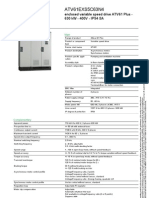
- Variable speed drive data sheetDocument13 pagesVariable speed drive data sheetMutu DanielPas encore d'évaluation
- Datasheet ATV61EXS5C63N4Document8 pagesDatasheet ATV61EXS5C63N4flake03Pas encore d'évaluation
- 7SG117 Argus 7: Answers For EnergyDocument10 pages7SG117 Argus 7: Answers For EnergygovindarulPas encore d'évaluation
- Altivar 71 ATV71HD11N4Document13 pagesAltivar 71 ATV71HD11N4Dagostino GigiPas encore d'évaluation
- Spaj160c Tob 750420encDocument12 pagesSpaj160c Tob 750420encqwkerbk090909Pas encore d'évaluation
- Protective Relays for Power SystemsDocument67 pagesProtective Relays for Power Systemsbasudev1978Pas encore d'évaluation
- Altivar 71 ATV71HU75N4Document4 pagesAltivar 71 ATV71HU75N4electrosysro8560Pas encore d'évaluation
- ATV32 variable speed drive 7.5 kW data sheetDocument11 pagesATV32 variable speed drive 7.5 kW data sheetbmshivakumarPas encore d'évaluation
- MatrixDocument37 pagesMatrixmssurajPas encore d'évaluation
- Grid Tied Solar Inverters Hitachi1250 KvaDocument4 pagesGrid Tied Solar Inverters Hitachi1250 KvaTejaswi ShuklaPas encore d'évaluation
- Hitachi Solar Inverters for Utility-Scale PV PlantsDocument8 pagesHitachi Solar Inverters for Utility-Scale PV PlantsBijuPas encore d'évaluation
- Solar PcsDocument6 pagesSolar Pcsharshad_soni7912Pas encore d'évaluation
- Altivar Lift ATV71LD17N4ZDocument4 pagesAltivar Lift ATV71LD17N4ZMelina LaborPas encore d'évaluation
- Analog Circuit Design: A Tutorial Guide to Applications and SolutionsD'EverandAnalog Circuit Design: A Tutorial Guide to Applications and SolutionsÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (6)
- ATV71H075N4: Product Data SheetDocument4 pagesATV71H075N4: Product Data SheetOtto AcnPas encore d'évaluation
- WIRE LESS Land Mine Detection Robo-VehicleDocument35 pagesWIRE LESS Land Mine Detection Robo-VehicleDebashish BeheraPas encore d'évaluation
- ATV32HD15N4Document12 pagesATV32HD15N4gasm22Pas encore d'évaluation
- PRODUCT ATV71HD15N4ZDocument4 pagesPRODUCT ATV71HD15N4ZSilas SilvaPas encore d'évaluation
- IRT-660G Automatic Relay Test Set PDFDocument98 pagesIRT-660G Automatic Relay Test Set PDFRonicel Caryl de RamosPas encore d'évaluation
- Energy Monitoring and Control PDFDocument33 pagesEnergy Monitoring and Control PDFDoravari LakshmiPas encore d'évaluation
- Digital Protective RelayDocument3 pagesDigital Protective RelayjannumitsPas encore d'évaluation
- Brochure Btl's AmetekDocument86 pagesBrochure Btl's AmetekGerardo Cruz EspinosaPas encore d'évaluation
- Automotive Electronics SolutionsDocument36 pagesAutomotive Electronics Solutionssorteabhay6877Pas encore d'évaluation
- Em 6400Document6 pagesEm 6400chetanmahulkar755374Pas encore d'évaluation
- Three-Phase Overcurrent Relay Spaj 131 C: Product GuideDocument12 pagesThree-Phase Overcurrent Relay Spaj 131 C: Product GuideSharaf Ali ZyoudPas encore d'évaluation
- Catalog ION 6200Document12 pagesCatalog ION 6200eltromePas encore d'évaluation
- ATV71HC20N4 DocumentDocument8 pagesATV71HC20N4 DocumentToth VasilePas encore d'évaluation
- Ad9851 Cmos 180 MHZ Dds/Dac SynthesizerDocument24 pagesAd9851 Cmos 180 MHZ Dds/Dac SynthesizerVijay VigneshPas encore d'évaluation
- Air Circuit Breakers-AHA TypeDocument8 pagesAir Circuit Breakers-AHA TypeanbarasubalayahoocomPas encore d'évaluation
- Altivar ATV61HU55N4 CatalogueDocument4 pagesAltivar ATV61HU55N4 CatalogueEugen Marius BadescuPas encore d'évaluation
- Himap BcsDocument22 pagesHimap Bcskhinmgsoe100% (1)
- MCDocument300 pagesMCdiegobenitezPas encore d'évaluation
- ATV61HD30N4Document4 pagesATV61HD30N4BlAdE 12Pas encore d'évaluation
- B 12 A 6Document8 pagesB 12 A 6Charles McNall100% (1)
- DG Application AMF / Synchroniser: Conzerv Systems PVT LTDDocument4 pagesDG Application AMF / Synchroniser: Conzerv Systems PVT LTDjaikolangaraparambilPas encore d'évaluation
- Description Power Range: Analog Servo DriveDocument8 pagesDescription Power Range: Analog Servo DriveElectromatePas encore d'évaluation
- 7sg118 Argus 8 Catalogue SheetDocument12 pages7sg118 Argus 8 Catalogue SheetCristi GrosuPas encore d'évaluation
- MCVG 61Document10 pagesMCVG 61Joel FigueroaPas encore d'évaluation
- ION8650 DatasheetDocument11 pagesION8650 DatasheetAlthaf Axel HiroshiPas encore d'évaluation
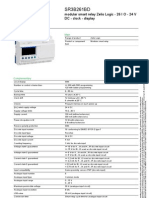
- Zelio Logic SR3B261BDDocument7 pagesZelio Logic SR3B261BDZoran SaricPas encore d'évaluation
- Model Sr850: DSP Lock-In AmplifierDocument290 pagesModel Sr850: DSP Lock-In AmplifieralexPas encore d'évaluation
- Frequency Relay Spaf 140 C: Product GuideDocument10 pagesFrequency Relay Spaf 140 C: Product Guideමාධව නදුන්මල්.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Commander SE: Simple and EasyDocument8 pagesCommander SE: Simple and EasyRitesh SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Tech Characteristic VEGADocument16 pagesTech Characteristic VEGADark _Pas encore d'évaluation
- Under Voltage Over Voltage & ND RelayDocument2 pagesUnder Voltage Over Voltage & ND RelayDave Chaudhury100% (1)
- RPM 8Document3 pagesRPM 8pinku_thakkarPas encore d'évaluation
- AD9850Document20 pagesAD9850olopezPas encore d'évaluation
- Digital Automatic Voltage RegulatorDocument2 pagesDigital Automatic Voltage RegulatorPedro BancayanPas encore d'évaluation
- Altivar - 71 - ATV71HD11M3X User ManualDocument13 pagesAltivar - 71 - ATV71HD11M3X User Manualantothoppil001Pas encore d'évaluation
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2D'EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Pas encore d'évaluation
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1D'EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Évaluation : 2.5 sur 5 étoiles2.5/5 (3)
- Digital Power Electronics and ApplicationsD'EverandDigital Power Electronics and ApplicationsÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (3)
- Analog Circuit Design Volume Three: Design Note CollectionD'EverandAnalog Circuit Design Volume Three: Design Note CollectionÉvaluation : 3 sur 5 étoiles3/5 (2)
- Analog Circuit Design Volume 2: Immersion in the Black Art of Analog DesignD'EverandAnalog Circuit Design Volume 2: Immersion in the Black Art of Analog DesignPas encore d'évaluation
- AWEA 2005 Advanced Wake Model For Closely Spaced TurbinesDocument12 pagesAWEA 2005 Advanced Wake Model For Closely Spaced TurbinesRodriguez Villalobos NelsonPas encore d'évaluation
- Differential Bus ProtectionDocument14 pagesDifferential Bus ProtectionRodriguez Villalobos NelsonPas encore d'évaluation
- Active CoolDocument3 pagesActive CoolRodriguez Villalobos NelsonPas encore d'évaluation
- Flexible ConnectionsDocument13 pagesFlexible ConnectionsRodriguez Villalobos NelsonPas encore d'évaluation
- Integrated Finite Elements Analysis and Design of StructuresDocument50 pagesIntegrated Finite Elements Analysis and Design of Structuresaeiou321Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cable TutorialDocument22 pagesCable TutorialRodriguez Villalobos Nelson100% (4)
- Arc Busbar in SwitchboardDocument11 pagesArc Busbar in SwitchboardYudo Heru PribadiPas encore d'évaluation
- WhatsNew 15.1 en r1149Document33 pagesWhatsNew 15.1 en r1149Rodriguez Villalobos NelsonPas encore d'évaluation
- Ch.06 - Carrier Current Pilot and Microwave Pilot RelaysDocument10 pagesCh.06 - Carrier Current Pilot and Microwave Pilot Relays채대근Pas encore d'évaluation
- L90 - Guide Form Specification (Version 5.20) Specification For Transmission Line Current Differential Protection, Control and MonitoringDocument6 pagesL90 - Guide Form Specification (Version 5.20) Specification For Transmission Line Current Differential Protection, Control and MonitoringRodriguez Villalobos NelsonPas encore d'évaluation
- TechRef SEL DirectionalDocument10 pagesTechRef SEL DirectionalRodriguez Villalobos NelsonPas encore d'évaluation
- DIALux DXF InformationDocument1 pageDIALux DXF InformationLidia RaduPas encore d'évaluation
- OHSAS 18001-2007 Lead Auditor CourseDocument3 pagesOHSAS 18001-2007 Lead Auditor Coursesharaby81Pas encore d'évaluation
- Toyota TVIP System ProgrammingDocument11 pagesToyota TVIP System Programmingcheerios353Pas encore d'évaluation
- Seven QC Tools Tool #5: Part 1-Run ChartDocument6 pagesSeven QC Tools Tool #5: Part 1-Run ChartAnkur DhirPas encore d'évaluation
- Action Paper g2 Final OutputDocument67 pagesAction Paper g2 Final Outputjay diazPas encore d'évaluation
- 05 Allama Ibn e Nujaim or Un Ki Kitab PDFDocument20 pages05 Allama Ibn e Nujaim or Un Ki Kitab PDFFk imaginaryPas encore d'évaluation
- Culligan o Ring DirectoryDocument30 pagesCulligan o Ring DirectoryCarl Schleif0% (1)
- BE Semester-VIII (Civil Engineering) Question Bank (Design of Steel Structures)Document2 pagesBE Semester-VIII (Civil Engineering) Question Bank (Design of Steel Structures)Suresh RajuPas encore d'évaluation
- Antipsychotic DrugsDocument2 pagesAntipsychotic DrugsDana Mae AfanPas encore d'évaluation
- PL SQLDocument53 pagesPL SQLKarthik100% (1)
- Chapter 10 Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument12 pagesChapter 10 Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction: Multiple Choice Questionsquiet19Pas encore d'évaluation
- What I Know: Directions: Read and Analyze The Following Questions. Choose The LetterDocument12 pagesWhat I Know: Directions: Read and Analyze The Following Questions. Choose The LetterArym Sherwin R. VendiolaPas encore d'évaluation
- (Franziska Bieri) From Blood Diamonds To The KimbeDocument226 pages(Franziska Bieri) From Blood Diamonds To The KimbeMona SaidPas encore d'évaluation
- Opti PlexDocument4 pagesOpti PlexshailendrabachalPas encore d'évaluation
- Notes 2. Decision Theory - ToDocument13 pagesNotes 2. Decision Theory - Tostephen mwendwaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ariston Ecosf109 19509154400 - GB CZ SK GRDocument60 pagesAriston Ecosf109 19509154400 - GB CZ SK GRionPas encore d'évaluation
- The Deer and The CrocodilesDocument4 pagesThe Deer and The CrocodilesM Rifky FauzanPas encore d'évaluation
- Informatica Bhaskar20161012Document90 pagesInformatica Bhaskar20161012Bhaskar ReddyPas encore d'évaluation
- EGRA Phil IRi ResultsDocument9 pagesEGRA Phil IRi Resultsjuvelyn abuganPas encore d'évaluation
- Infinite SummerDocument145 pagesInfinite SummermarcelbocalaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Tools and MaterialsDocument71 pagesTools and MaterialsMahardikaPas encore d'évaluation
- JSA For MPIDocument3 pagesJSA For MPIMohammed MinhajPas encore d'évaluation
- Literature Study of HospitalDocument18 pagesLiterature Study of HospitalJasleen KaurPas encore d'évaluation
- Aeon Trinity - Field Report - Corporate LifeDocument19 pagesAeon Trinity - Field Report - Corporate Lifekrwull100% (1)
- How to love and understand the independent ISTP personality typeDocument4 pagesHow to love and understand the independent ISTP personality typeKingwaKamencuPas encore d'évaluation
- Alcohol-Related DiseaseDocument18 pagesAlcohol-Related DiseaseSPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson Plan Financial LiteracyDocument1 pageLesson Plan Financial Literacyapi-438803241Pas encore d'évaluation
- Book QuantLibDocument40 pagesBook QuantLibPradeep Srivatsava ManikondaPas encore d'évaluation
- Company Profile NecarrDocument10 pagesCompany Profile Necarranescobar0001Pas encore d'évaluation
- 425 TR - Chiller Data SheetSpecDocument2 pages425 TR - Chiller Data SheetSpecjohnsvjPas encore d'évaluation
- Standoblue Base Coat Colors With Use of Mix 130 Silk Silver: Working Process: Special Effect Standoblue BasecoatDocument3 pagesStandoblue Base Coat Colors With Use of Mix 130 Silk Silver: Working Process: Special Effect Standoblue BasecoatMee MeePas encore d'évaluation