Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Parametric - Curves Beautiful Mathematics
Transféré par
amankapoor31Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Parametric - Curves Beautiful Mathematics
Transféré par
amankapoor31Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Section 9.
1 Parametric Curves
2010 Kiryl Tsishchanka
Parametric Curves
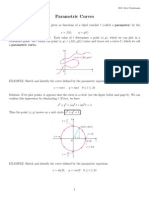
Suppose that x and y are both given as functions of a third variable t (called a parameter) by the equations x = f (t), y = g (t) (called parametric equations). Each value of t determines a point (x, y ), which we can plot in a coordinate plane. As t varies, the point (x, y ) = (f (t), g (t)) varies and traces out a curve C, which we call a parametric curve.
EXAMPLE: Sketch and identify the curve dened by the parametric equations x = cos t, y = sin t 0 t 2
Solution: If we plot points, it appears that the curve is a circle (see the gure below and page 6). We can conrm this impression by eliminating t. If fact, we have x2 + y 2 = cos2 t + sin2 t = 1 Thus the point (x, y ) moves on a unit circle x2 + y 2 = 1 .
EXAMPLE: Sketch and identify the curve dened by the parametric equations x = sin 2t, y = cos 2t 0 t 2
Section 9.1 Parametric Curves
2010 Kiryl Tsishchanka
EXAMPLE: Sketch and identify the curve dened by the parametric equations x = sin 2t, y = cos 2t 0 t 2
Solution: If we plot points, it appears that the curve is a circle (see the Figure below). We can conrm this impression by eliminating t. If fact, we have x2 + y 2 = sin2 2t + cos2 2t = 1 Thus the point (x, y ) moves on a unit circle x2 + y 2 = 1 .
EXAMPLE: Sketch and identify the curve dened by the parametric equations x = 5 cos t, y = 2 sin t 0 t 2
Solution: If we plot points, it appears that the curve is an ellipse (see page 8). We can conrm this impression by eliminating t. If fact, we have x2 y 2 ( x )2 ( y )2 + = + = cos2 t + sin2 t = 1 25 4 5 2 Thus the point (x, y ) moves on an ellipse x2 y 2 + =1. 25 4
x 5cos t , y 2sin t , 0 t 12Pi 6
2 1 4 2 1 2 2 4
EXAMPLE: Sketch and identify the curve dened by the parametric equations x = t cos t, y = t sin t t > 0
Section 9.1 Parametric Curves
2010 Kiryl Tsishchanka
EXAMPLE: Sketch and identify the curve dened by the parametric equations x = t cos t, y = t sin t t > 0
Solution: If we plot points, it appears that the curve is a spiral (see page 9). We can conrm this impression by the following algebraic manipulations: x2 + y 2 = (t cos t)2 + (t sin t)2 = t2 sin2 t + t2 cos2 t = t2 (sin2 t + cos2 t) = t2 To eliminate t completely, we observe that y t sin t sin t = = = tan t x t cos t cos t
2 2 2 2 2
x2 + y 2 = t2
=
2
t = arctan (y) x .
(y) x
Substituting this into x + y = t , we get x + y = arctan
x t cos t , y t sin t , 0 t 12Pi 4
10
10
10
10
EXAMPLE: Sketch and identify the curve dened by the parametric equations x = t2 + t, y = 2t 1
Section 9.1 Parametric Curves
2010 Kiryl Tsishchanka
EXAMPLE: Sketch and identify the curve dened by the parametric equations x = t2 + t, y = 2t 1
Solution: If we plot points, it appears that the curve is a parabola (see page 10). We can conrm this impression by eliminating t. If fact, we have ( )2 y+1 y+1 y+1 1 3 2 y = 2t 1 = t = = x = t + t = + = y2 + y + 2 2 2 4 4 1 3 Thus the point (x, y ) moves on a parabola x = y 2 + y + . 4 4
x t^2 t, y 2t 1, 2 t
2 1
2 12 4
0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 1 2 3 4 5
EXAMPLE: Sketch and identify the curve dened by the parametric equations x = sin2 t, y = 2 cos t
Solution: If we plot points, it appears that the curve is a restricted parabola (see page 11). We can conrm this impression by eliminating t. If fact, we have y2 4 We also note that 0 x 1 and 2 y 2. Thus the point (x, y ) moves on the restricted parabola y2 x sin^2 t , y 2cos t , 0 t 12Pi 6 x=1 . 4 2 y = 2 cos t = y 2 = 4 cos2 t = 4x + y 2 = 4 sin2 t + 4 cos2 t = 4 = x=1
0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 1.2
Section 9.1 Parametric Curves
2010 Kiryl Tsishchanka
The Cycloid
EXAMPLE: The curve traced out by a point P on the circumference of a circle as the circle rolls along a straight line is called a cycloid (see the Figure below). If the circle has radius r and rolls along the x-axis and if one position of P is the origin, nd parametric equations for the cycloid.
Solution: We choose as parameter the angle of rotation of the circle ( = 0 when P is at the origin). Suppose the circle has rotated through radians. Because the circle has been in contact with the line, we see from the Figure below that the distance it has rolled from the origin is |OT | = arc P T = r
Therefore, the center of the circle is C (r, r). Let the coordinates of P be (x, y ). Then from the Figure above we see that x = |OT | |P Q| = r r sin = r( sin ) y = |T C | |QC | = r r cos = r(1 cos ) Therefore, parametric equations of the cycloid are x = r( sin ), y = r(1 cos ) R (1)
One arch of the cycloid comes from one rotation of the circle and so is described by 0 2 . Although Equations 1 were derived from the Figure above, which illustrates the case where 0 < < /2, it can be seen that these equations are still valid for other values of . Although it is possible to eliminate the parameter from Equations 1, the resulting Cartesian equation in x and y is very complicated and not as convenient to work with as the parametric equations: ( ) y 1 x y ( y )2 x + 2 2 2 1 = cos1 1 r 2 r r r r
Section 9.1 Parametric Curves
2010 Kiryl Tsishchanka
Unit Circle
Parametric equations: x = cos t, where t = k/6, k = 0, . . . , 12.
x cos t , y sin t , 0 t 1Pi 6
1.0
y = sin t
x cos t , y sin t , 0 t 2Pi 6
1.0
x cos t , y sin t , 0 t 3Pi 6
1.0
0.5
0.5
0.5
1.0
0.5
0.5
1.0
1.0
0.5
0.5
1.0
1.0
0.5
0.5
1.0
0.5
0.5
0.5
1.0
1.0
1.0
x cos t , y sin t , 0 t 4Pi 6
1.0
x cos t , y sin t , 0 t 5Pi 6
1.0
x cos t , y sin t , 0 t 6Pi 6
1.0
0.5
0.5
0.5
1.0
0.5
0.5
1.0
1.0
0.5
0.5
1.0
1.0
0.5
0.5
1.0
0.5
0.5
0.5
1.0
1.0
1.0
x cos t , y sin t , 0 t 7Pi 6
1.0
x cos t , y sin t , 0 t 8Pi 6
1.0
x cos t , y sin t , 0 t 9Pi 6
1.0
0.5
0.5
0.5
1.0
0.5
0.5
1.0
1.0
0.5
0.5
1.0
1.0
0.5
0.5
1.0
0.5
0.5
0.5
1.0
1.0
1.0
x cos t , y sin t , 0 t 10Pi 6
1.0
x cos t , y sin t , 0 t 11Pi 6
1.0
x cos t , y sin t , 0 t 12Pi 6
1.0
0.5
0.5
0.5
1.0
0.5
0.5
1.0
1.0
0.5
0.5
1.0
1.0
0.5
0.5
1.0
0.5
0.5
0.5
1.0
1.0
1.0
Section 9.1 Parametric Curves
2010 Kiryl Tsishchanka
Unit Circle
Parametric equations: x = sin t, where t = k/6, k = 0, . . . , 12.
x sin t , y cos t , 0 t 1Pi 6
1.0
y = cos t
x sin t , y cos t , 0 t 2Pi 6
1.0
x sin t , y cos t , 0 t 3Pi 6
1.0
0.5
0.5
0.5
1.0
0.5
0.5
1.0
1.0
0.5
0.5
1.0
1.0
0.5
0.5
1.0
0.5
0.5
0.5
1.0
1.0
1.0
x sin t , y cos t , 0 t 4Pi 6
1.0
x sin t , y cos t , 0 t 5Pi 6
1.0
x sin t , y cos t , 0 t 6Pi 6
1.0
0.5
0.5
0.5
1.0
0.5
0.5
1.0
1.0
0.5
0.5
1.0
1.0
0.5
0.5
1.0
0.5
0.5
0.5
1.0
1.0
1.0
x sin t , y cos t , 0 t 7Pi 6
1.0
x sin t , y cos t , 0 t 8Pi 6
1.0
x sin t , y cos t , 0 t 9Pi 6
1.0
0.5
0.5
0.5
1.0
0.5
0.5
1.0
1.0
0.5
0.5
1.0
1.0
0.5
0.5
1.0
0.5
0.5
0.5
1.0
1.0
1.0
x sin t , y cos t , 0 t 10Pi 6
1.0
x sin t , y cos t , 0 t 11Pi 6
1.0
x sin t , y cos t , 0 t 12Pi 6
1.0
0.5
0.5
0.5
1.0
0.5
0.5
1.0
1.0
0.5
0.5
1.0
1.0
0.5
0.5
1.0
0.5
0.5
0.5
1.0
1.0
1.0
Section 9.1 Parametric Curves
2010 Kiryl Tsishchanka
Ellipse
Parametric equations: x = 5 cos t, where t = k/6, k = 0, . . . , 12. y = 2 sin t
x 5cos t , y 2sin t , 0 t 1Pi 6
2 1 4 2 1 2 2 4
x 5cos t , y 2sin t , 0 t 2Pi 6
2 1 4 2 1 2 2 4
x 5cos t , y 2sin t , 0 t 3Pi 6
2 1 4 2 1 2 2 4
x 5cos t , y 2sin t , 0 t 4Pi 6
2 1 4 2 1 2 2 4
x 5cos t , y 2sin t , 0 t 5Pi 6
2 1 4 2 1 2 2 4
x 5cos t , y 2sin t , 0 t 6Pi 6
2 1 4 2 1 2 2 4
x 5cos t , y 2sin t , 0 t 7Pi 6
2 1 4 2 1 2 2 4
x 5cos t , y 2sin t , 0 t 8Pi 6
2 1 4 2 1 2 2 4
x 5cos t , y 2sin t , 0 t 9Pi 6
2 1 4 2 1 2 2 4
x 5cos t , y 2sin t , 0 t 10Pi 6
2 1 4 2 1 2 2 4
x 5cos t , y 2sin t , 0 t 11Pi 6
2 1 4 2 1 2 2 4
x 5cos t , y 2sin t , 0 t 12Pi 6
2 1 4 2 1 2 2 4
Section 9.1 Parametric Curves
2010 Kiryl Tsishchanka
Spiral
Parametric equations: x = t cos t, where t = k/4, k = 0, . . . , 12.
x t cos t , y t sin t , 0 t 1Pi 4
1.5 1.0 1 0.5
y = t sin t
x t cos t , y t sin t , 0 t 2Pi 4
2
x t cos t , y t sin t , 0 t 3Pi 4
3 2 1
1.5
1.0
0.5 0.5
0.5
1.0
1.5
1 1
1 1 2
1.0 1.5 2
x t cos t , y t sin t , 0 t 4Pi 4
4
x t cos t , y t sin t , 0 t 5Pi 4
4
x t cos t , y t sin t , 0 t 6Pi 4
6 4
2 2
2 2 4
4 4 6
x t cos t , y t sin t , 0 t 7Pi 4
6 4 2
x t cos t , y t sin t , 0 t 8Pi 4
x t cos t , y t sin t , 0 t 9Pi 4
2 2 4 6
x t cos t , y t sin t , 0 t 10Pi 4
10
x t cos t , y t sin t , 0 t 11Pi 4
10
x t cos t , y t sin t , 0 t 12Pi 4
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
Section 9.1 Parametric Curves
2010 Kiryl Tsishchanka
Parabola
Parametric equations: x = t2 + t, where t = 2 + k/4, k = 0, . . . , 12.
x t^2 t, y 2t 1, 2 t
2 1
y = 2t 1
2 24 x t^2 t, y 2t 1, 2 t
2 1
2 14
x t^2 t, y 2t 1, 2 t
2 1
2 34
0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 5
0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 1 2 3 4 5
0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5
x t^2 t, y 2t 1, 2 t
2 1
2 44
x t^2 t, y 2t 1, 2 t
2 1
2 54
x t^2 t, y 2t 1, 2 t
2 1
2 64
0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 5
0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 1 2 3 4 5
0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5
x t^2 t, y 2t 1, 2 t
2 1
2 74
x t^2 t, y 2t 1, 2 t
2 1
2 84
x t^2 t, y 2t 1, 2 t
2 1
2 94
0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 5
0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 1 2 3 4 5
0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5
x t^2 t, y 2t 1, 2 t
2 1
2 10 4
x t^2 t, y 2t 1, 2 t
2 1
2 11 4
x t^2 t, y 2t 1, 2 t
2 1
2 12 4
0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 5
0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 1 2 3 4 5
0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5
10
Section 9.1 Parametric Curves
2010 Kiryl Tsishchanka
Restricted Parabola
Parametric equations: x = sin2 t, where t = k/6, k = 0, . . . , 12.
x sin^2 t , y 2cos t , 0 t 1Pi 6
2
y = 2 cos t
x sin^2 t , y 2cos t , 0 t 2Pi 6
2
x sin^2 t , y 2cos t , 0 t 3Pi 6
2
0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 1.2
0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 1.2
0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 1.2
x sin^2 t , y 2cos t , 0 t 4Pi 6
2
x sin^2 t , y 2cos t , 0 t 5Pi 6
2
x sin^2 t , y 2cos t , 0 t 6Pi 6
2
0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 1.2
0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 1.2
0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 1.2
x sin^2 t , y 2cos t , 0 t 7Pi 6
2
x sin^2 t , y 2cos t , 0 t 8Pi 6
2
x sin^2 t , y 2cos t , 0 t 9Pi 6
2
0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 1.2
0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 1.2
0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 1.2
x sin^2 t , y 2cos t , 0 t 10Pi 6
2
x sin^2 t , y 2cos t , 0 t 11Pi 6
2
x sin^2 t , y 2cos t , 0 t 12Pi 6
2
0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 1.2
0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 1.2
0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 1.2
11
Section 9.1 Parametric Curves
2010 Kiryl Tsishchanka
Buttery Curve
Parametric equations: [ ( )] t cos t 5 x = sin t e 2 cos(4t) + sin , 12 where t = k/6, k = 0, . . . , 12.
3 3 3
[ ( )] t cos t 5 y = cos t e 2 cos(4t) + sin 12
1 1
1 1
1 1
1 1
1 1
1 1
1 1
1 1
1 1
1 1
1 1
1 1
12
Section 9.1 Parametric Curves
2010 Kiryl Tsishchanka
Buttery Curve
Parametric equations: [ ( )] t cos t 5 x = sin t e 2 cos(4t) + sin , 12 where t = k/2, k = 0, . . . , 12.
3 3 3
[ ( )] t cos t 5 y = cos t e 2 cos(4t) + sin 12
1 1
1 1
1 1
1 1
1 1
1 1
1 1
1 1
1 1
1 1
1 1
1 1
13
Section 9.1 Parametric Curves
2010 Kiryl Tsishchanka
Parametric Curve
Parametric equations: x = t + 2 sin 2t, where t = 2 + k/3, k = 0, . . . , 12.
x t 2sin 2t ,y t 2cos 5t , 2Pi t 2Pi 1Pi 3 x t 2sin 2t ,y t 2cos 5t , 2Pi t 2Pi 2Pi 3 x t 2sin 2t ,y t 2cos 5t , 2Pi t 2Pi 3Pi 3
y = t + 2 cos 5t
x t 2sin 2t ,y t 2cos 5t , 2Pi t
2Pi 4Pi 3
x t 2sin 2t ,y t 2cos 5t , 2Pi t
2Pi 5Pi 3
x t 2sin 2t ,y t 2cos 5t , 2Pi t
2Pi 6Pi 3
x t 2sin 2t ,y t 2cos 5t , 2Pi t
2Pi 7Pi 3
x t 2sin 2t ,y t 2cos 5t , 2Pi t
2Pi 8Pi 3
x t 2sin 2t ,y t 2cos 5t , 2Pi t
2Pi 9Pi 3
x t 2sin 2t ,y t 2cos 5t , 2Pi t
2Pi 10Pi 3
x t 2sin 2t ,y t 2cos 5t , 2Pi t
2Pi 11Pi 3
x t 2sin 2t ,y t 2cos 5t , 2Pi t
2Pi 12Pi 3
14
Section 9.1 Parametric Curves
2010 Kiryl Tsishchanka
Parametric Curves
Parametric equations: x = 1.5 cos t cos kt, where k = 1, . . . , 20.
x 1.5cos t cos 1t , y 1.5sin t sin 1t
2
y = 1.5 sin t sin kt
x 1.5cos t cos 3t , y 1.5sin t sin 3t
2
x 1.5cos t cos 2t , y 1.5sin t sin 2t
2
x 1.5cos t cos 4t , y 1.5sin t sin 4t
2
x 1.5cos t cos 5t , y 1.5sin t sin 5t
2
x 1.5cos t cos 6t , y 1.5sin t sin 6t
2
x 1.5cos t cos 7t , y 1.5sin t sin 7t
2
x 1.5cos t cos 8t , y 1.5sin t sin 8t
2
x 1.5cos t cos 9t , y 1.5sin t sin 9t
2
x 1.5cos t cos 10t , y 1.5sin t sin 10t
2
x 1.5cos t cos 11t , y 1.5sin t sin 11t
2
x 1.5cos t cos 12t , y 1.5sin t sin 12t
2
x 1.5cos t cos 13t , y 1.5sin t sin 13t
2
x 1.5cos t cos 14t , y 1.5sin t sin 14t
2
x 1.5cos t cos 15t , y 1.5sin t sin 15t
2
x 1.5cos t cos 16t , y 1.5sin t sin 16t
2
x 1.5cos t cos 17t , y 1.5sin t sin 17t
2
x 1.5cos t cos 18t , y 1.5sin t sin 18t
2
x 1.5cos t cos 19t , y 1.5sin t sin 19t
2
x 1.5cos t cos 20t , y 1.5sin t sin 20t
2
15
Section 9.1 Parametric Curves
2010 Kiryl Tsishchanka
Parametric Curves
Parametric equations: x = 1.5 cos t cos 3t, where k = 1, . . . , 20.
x 1.5cos t cos 3t , y 1.5sin t sin 1t
2
y = 1.5 sin t sin kt
x 1.5cos t cos 3t , y 1.5sin t sin 3t
2
x 1.5cos t cos 3t , y 1.5sin t sin 2t
2
x 1.5cos t cos 3t , y 1.5sin t sin 4t
2
x 1.5cos t cos 3t , y 1.5sin t sin 5t
2
x 1.5cos t cos 3t , y 1.5sin t sin 6t
2
x 1.5cos t cos 3t , y 1.5sin t sin 7t
2
x 1.5cos t cos 3t , y 1.5sin t sin 8t
2
x 1.5cos t cos 3t , y 1.5sin t sin 9t
2
x 1.5cos t cos 3t , y 1.5sin t sin 10t
2
x 1.5cos t cos 3t , y 1.5sin t sin 11t
2
x 1.5cos t cos 3t , y 1.5sin t sin 12t
2
x 1.5cos t cos 3t , y 1.5sin t sin 13t
2
x 1.5cos t cos 3t , y 1.5sin t sin 14t
2
x 1.5cos t cos 3t , y 1.5sin t sin 15t
2
x 1.5cos t cos 3t , y 1.5sin t sin 16t
2
x 1.5cos t cos 3t , y 1.5sin t sin 17t
2
x 1.5cos t cos 3t , y 1.5sin t sin 18t
2
x 1.5cos t cos 3t , y 1.5sin t sin 19t
2
x 1.5cos t cos 3t , y 1.5sin t sin 20t
2
16
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesD'EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesPas encore d'évaluation
- Transformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankD'EverandTransformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankÉvaluation : 3 sur 5 étoiles3/5 (1)
- Parametric CurvesDocument16 pagesParametric CurvesSayan PalPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 6mm34 CasDocument15 pagesChapter 6mm34 CasEric MoralesPas encore d'évaluation
- MATH 265 - Final - 2012Document9 pagesMATH 265 - Final - 2012examkillerPas encore d'évaluation
- Applied Calculus: Credit Hour: 3Document39 pagesApplied Calculus: Credit Hour: 3bigbangmelvanPas encore d'évaluation
- Institut F Ur StochastikDocument15 pagesInstitut F Ur StochastikasdfPas encore d'évaluation
- Differential Calculus-I: Note: 1. If K ( 0) Is The Curvature of A Curve at P, Then The RadiusDocument28 pagesDifferential Calculus-I: Note: 1. If K ( 0) Is The Curvature of A Curve at P, Then The RadiustechzonesPas encore d'évaluation
- m7 REVIEW PDFDocument6 pagesm7 REVIEW PDFSkyezine Via Kit FoxPas encore d'évaluation
- Greens TheoremDocument9 pagesGreens TheoremAnonymous KIUgOYPas encore d'évaluation
- M 408M - Calculus Quest SolutionsDocument13 pagesM 408M - Calculus Quest Solutionsbrargolf50% (2)
- 11 6 Paramtrc DiffrntiatnDocument7 pages11 6 Paramtrc DiffrntiatnEbookcrazePas encore d'évaluation
- Review For Unit 3 - Chapter 3 Part 2: Sin Xisthesameas (Sinx) Know The Unit Circle!!Document16 pagesReview For Unit 3 - Chapter 3 Part 2: Sin Xisthesameas (Sinx) Know The Unit Circle!!Ian StantonPas encore d'évaluation
- 2010 Set B Paper 3 RVHS Promo (Solutions)Document12 pages2010 Set B Paper 3 RVHS Promo (Solutions)Lim Kew ChongPas encore d'évaluation
- 2014 H2 Maths Prelim Papers - NJC P1 SolutionDocument13 pages2014 H2 Maths Prelim Papers - NJC P1 Solutioncherylhzy0% (4)
- Problem Set 1Document7 pagesProblem Set 1alfonso_bajarPas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced DifferentiationDocument13 pagesAdvanced Differentiationangry_granPas encore d'évaluation
- Complex Numbers: N N N NDocument2 pagesComplex Numbers: N N N NxpgongPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 3.6: Variation of Parameters: T G y T Q y T P yDocument9 pagesCH 3.6: Variation of Parameters: T G y T Q y T P yPercdc DavaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Iit Jee 2004 MathDocument7 pagesIit Jee 2004 MathLokesh KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Calculus of VariationsDocument49 pagesCalculus of Variationsrahpooye31350% (2)
- Probleme de Program Are LiniaraDocument8 pagesProbleme de Program Are Liniaradanutzamihairo4738Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mathcad - Tarea Final EF3Document21 pagesMathcad - Tarea Final EF3EskorbutanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter Four: Curve FittingDocument58 pagesChapter Four: Curve FittingGirmole WorkuPas encore d'évaluation
- Trigonometric Fourier Series: ECE 350 - Linear Systems I MATLAB Tutorial #6Document7 pagesTrigonometric Fourier Series: ECE 350 - Linear Systems I MATLAB Tutorial #6CatPas encore d'évaluation
- PEME200001 Mathematical Techniques 2Document10 pagesPEME200001 Mathematical Techniques 2Andrew AndersonPas encore d'évaluation
- Parametric Equations: Before You StartDocument20 pagesParametric Equations: Before You Startdotnetvenkat1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Higher Order DeterminantsDocument28 pagesHigher Order DeterminantsKanda Agung KusumaPas encore d'évaluation
- Rotation of AxesDocument9 pagesRotation of Axesapi-213604106Pas encore d'évaluation
- Polar CoordinatesDocument22 pagesPolar CoordinatesSyed Kamran HaiderPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 12 - Derivative of Inverse Trigonometric FunctionsDocument12 pagesLesson 12 - Derivative of Inverse Trigonometric FunctionsAlexander PiniliPas encore d'évaluation
- Trigonometric Formula Sheet: Definition of The Trig FunctionsDocument10 pagesTrigonometric Formula Sheet: Definition of The Trig Functionsmonelmetal100% (1)
- Cbse 2015 DelhiDocument10 pagesCbse 2015 Delhi-------hhhhhhhhhhhhhPas encore d'évaluation
- Ioannou Web Ch6Document27 pagesIoannou Web Ch6Yasemin BarutcuPas encore d'évaluation
- Polar Coordinates: R X y Tan y X X R Cos y R SinDocument8 pagesPolar Coordinates: R X y Tan y X X R Cos y R SinalfiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Liu2017 Article AFastAndStableAlgorithmForLineDocument31 pagesLiu2017 Article AFastAndStableAlgorithmForLineAman JalanPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 17 PDFDocument10 pagesChapter 17 PDFChirilicoPas encore d'évaluation
- Cubic Spline Tutorial v3Document6 pagesCubic Spline Tutorial v3Praveen SrivastavaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4.3 Part 1 Circular Functions PDFDocument4 pagesChapter 4.3 Part 1 Circular Functions PDFjiiPas encore d'évaluation
- EXERCISES MiscDocument11 pagesEXERCISES MiscMelissa San JoaquinPas encore d'évaluation
- Leep 214Document23 pagesLeep 214Koyal Gupta100% (1)
- MAM2085F 2013 Exam SolutionsDocument8 pagesMAM2085F 2013 Exam Solutionsmoro1992Pas encore d'évaluation
- E4Qdif XDocument9 pagesE4Qdif XRevelationPas encore d'évaluation
- m2 Rev4 - Stewart - PDFDocument2 pagesm2 Rev4 - Stewart - PDFSkyezine Via Kit FoxPas encore d'évaluation
- Using Parametric EquationsDocument5 pagesUsing Parametric EquationswolfretonmathsPas encore d'évaluation
- 8.2 Curve Representation - Implict Form and Parametric FormDocument23 pages8.2 Curve Representation - Implict Form and Parametric FormAlok SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- 2014 2 SARAWAK SMKStJoseph Kuching MATHS QADocument11 pages2014 2 SARAWAK SMKStJoseph Kuching MATHS QASK100% (3)
- Https Doc 00 7g Apps Viewer - GoogleusercontentDocument7 pagesHttps Doc 00 7g Apps Viewer - GoogleusercontentVignesh RavishankarPas encore d'évaluation
- Math 105 Practice Exam 3 SolutionsDocument3 pagesMath 105 Practice Exam 3 SolutionsexamkillerPas encore d'évaluation
- Review Exercises For Chapter 7: Integration Techniques, L'Hôpital's Rule, and Improper IntegralsDocument10 pagesReview Exercises For Chapter 7: Integration Techniques, L'Hôpital's Rule, and Improper IntegralsdeyanmgPas encore d'évaluation
- Volatility Swap Under The SABR Model: Simon Bossoney March 26, 2013Document10 pagesVolatility Swap Under The SABR Model: Simon Bossoney March 26, 2013Melissa AyquipaPas encore d'évaluation
- DeretDocument88 pagesDeretMuhammad WildanPas encore d'évaluation
- 11 6 PDFDocument7 pages11 6 PDFMayar ZoPas encore d'évaluation
- Application of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsD'EverandApplication of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsD'EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Factoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)D'EverandFactoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)Pas encore d'évaluation