Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 5, RAID 10 Explained With Diagrams
Transféré par
pavankalluriTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 5, RAID 10 Explained With Diagrams
Transféré par
pavankalluriDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 5, RAID 10 Explained with Diagrams RAID stands for Redundant Array of Inexpensive (Independent) Disks.
On most situations you will be using one of the following four levels of RAIDs.
RAID 0 RAID 1 RAID 5 RAID 10 (also known as RAID 1+0)
This article explains the main difference between these raid levels along with an easy to understand diagram. In all the diagrams mentioned below:
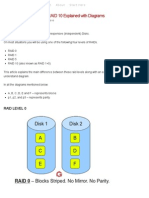
A, B, C, D, E and F represents blocks p1, p2, and p3 represents parity
RAID LEVEL 0
Following are the key points to remember for RAID level 0.
Minimum 2 disks. Excellent performance ( as blocks are striped ). No redundancy ( no mirror, no parity ). Dont use this for any critical system.
RAID LEVEL 1
Following are the key points to remember for RAID level 1.
Minimum 2 disks. Good performance ( no striping. no parity ). Excellent redundancy ( as blocks are mirrored ).
RAID LEVEL 5
Following are the key points to remember for RAID level 5.
Minimum 3 disks.
Good performance ( as blocks are striped ). Good redundancy ( distributed parity ). Best cost effective option providing both performance and redundancy. Use this for DB that is heavily read oriented. Write operations will be slow.
RAID LEVEL 10
Following are the key points to remember for RAID level 10.
Minimum 4 disks. This is also called as stripe of mirrors Excellent redundancy ( as blocks are mirrored ) Excellent performance ( as blocks are striped ) If you can afford the dollar, this is the BEST option for any mission critical applications (especially databases).
RAID 01
RAID 01 is also called as RAID 0+1 It is also called as mirror of stripes It requires minimum of 3 disks. But in most cases this will be implemented as minimum of 4 disks. To understand this better, create two groups. For example, if you have total of 6 disks, create two groups with 3 disks each as shown below. In the above example, Group 1 has 3 disks and Group 2 has 3 disks. Within the group, the data is striped. i.e In the Group 1 which contains three disks, the 1st block will be written to 1st disk, 2nd block to 2nd disk, and the 3rd block to 3rd disk. So, block A is written to Disk 1, block B to Disk 2, block C to Disk 3. Across the group, the data is mirrored. i.e The Group 1 and Group 2 will look exactly the same. i.e Disk 1 is mirrored to Disk 4, Disk 2 to Disk 5, Disk 3 to Disk 6. This is why it is called mirror of stripes. i.e the disks within the groups are striped. But, the groups are mirrored.
Main difference between RAID 10 vs RAID 01
Performance on both RAID 10 and RAID 01 will be the same. The storage capacity on these will be the same. The main difference is the fault tolerance level. On most implememntations of RAID controllers, RAID 01 fault tolerance is less. On RAID 01, since we have only two groups of RAID 0, if two drives (one in each group) fails, the entire RAID 01 will fail. In the above RAID 01 diagram, if Disk 1 and Disk 4 fails, both the groups will be down. So, the whole RAID 01 will fail. RAID 10 fault tolerance is more. On RAID 10, since there are many groups (as the individual group is only two disks), even if three disks fails (one in each group), the RAID 10 is still functional. In the above RAID 10 example, even if Disk 1, Disk 3, Disk 5 fails, the RAID 10 will still be functional. So, given a choice between RAID 10 and RAID 01, always choose RAID 10.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Raid Level & DetailsDocument9 pagesRaid Level & DetailsRAJARAMPas encore d'évaluation
- RAID 0, 1, 5, 10 Explained with DiagramsDocument5 pagesRAID 0, 1, 5, 10 Explained with DiagramsNavneetMishraPas encore d'évaluation
- DRBD-Cookbook: How to create your own cluster solution, without SAN or NAS!D'EverandDRBD-Cookbook: How to create your own cluster solution, without SAN or NAS!Pas encore d'évaluation
- Building a NAS Server with Raspberry Pi and OpenmediavaultD'EverandBuilding a NAS Server with Raspberry Pi and OpenmediavaultPas encore d'évaluation
- DB2 11 for z/OS: Intermediate Training for Application DevelopersD'EverandDB2 11 for z/OS: Intermediate Training for Application DevelopersPas encore d'évaluation
- SABSA IntroductionDocument51 pagesSABSA Introductionbobwillmore100% (1)
- IT46 en VoIP4D Laboratory Tutorial AsteriskNOWDocument31 pagesIT46 en VoIP4D Laboratory Tutorial AsteriskNOWictnewPas encore d'évaluation
- RAID 0, 1, 5, 10 ExplainedDocument4 pagesRAID 0, 1, 5, 10 ExplainedsoxxxxPas encore d'évaluation
- What is RAID? Guide to RAID levels and implementationsDocument10 pagesWhat is RAID? Guide to RAID levels and implementationsSrinivas GollanapalliPas encore d'évaluation
- RAID:-: Disk Drive Redundancy Parallel CommunicationDocument12 pagesRAID:-: Disk Drive Redundancy Parallel CommunicationSai PrasadPas encore d'évaluation
- Raid A: Redundant Array of Inexpensive DiscsDocument28 pagesRaid A: Redundant Array of Inexpensive DiscsDestiny HopesPas encore d'évaluation
- Explain RAID 10?: Raid Disk Mirroring Disk StripingDocument2 pagesExplain RAID 10?: Raid Disk Mirroring Disk Stripingprashant sharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- RaidDocument14 pagesRaidsini.laundry.ajaPas encore d'évaluation
- Simple RAID Cheat SheetDocument4 pagesSimple RAID Cheat Sheetdeserki20Pas encore d'évaluation
- What Is The Difference Between RAID 5 and RAID 10?: Linux Interview Questions & AnswersDocument1 pageWhat Is The Difference Between RAID 5 and RAID 10?: Linux Interview Questions & AnswersSantosh Kumar PandeyPas encore d'évaluation
- RAID 101 - Data Storage Technology That Combines DisksDocument25 pagesRAID 101 - Data Storage Technology That Combines DisksRahul DholePas encore d'évaluation
- RAID Technology White Paper: ImportantDocument14 pagesRAID Technology White Paper: Important_es__Pas encore d'évaluation
- Wiki RAIDDocument18 pagesWiki RAIDmshahomarPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is RAID Control PDFDocument6 pagesWhat Is RAID Control PDFAhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Raid ShivDocument17 pagesRaid Shivrajshivam833452Pas encore d'évaluation
- Raid X+Y vs. Raid Y+X: Nested ArraysDocument5 pagesRaid X+Y vs. Raid Y+X: Nested Arraysapi-26737619Pas encore d'évaluation
- RAID Overview:: Identifying What RAID Levels Best Meet Customer NeedsDocument10 pagesRAID Overview:: Identifying What RAID Levels Best Meet Customer NeedsRazz AmanPas encore d'évaluation
- RAID 50 and 60Document18 pagesRAID 50 and 60ice_coldPas encore d'évaluation
- Raid Technology: Seminar OnDocument33 pagesRaid Technology: Seminar OnPriti TripathyPas encore d'évaluation
- Session 3 RAID TECHNOLOGYDocument30 pagesSession 3 RAID TECHNOLOGYKelvin EliaPas encore d'évaluation
- Job Aid: RAID Cost, Performance, and Fault Tolerance ComparisonDocument2 pagesJob Aid: RAID Cost, Performance, and Fault Tolerance ComparisonvijitraiPas encore d'évaluation
- Term Paper On RaidDocument10 pagesTerm Paper On RaidEr RishabPas encore d'évaluation
- RAIDDocument6 pagesRAIDravimars22Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lab Activity #3 RAIDDocument1 pageLab Activity #3 RAIDYuvraj MPas encore d'évaluation
- RAID Types ExplainedDocument3 pagesRAID Types ExplainedBinu SivanPas encore d'évaluation
- RAID 13102022 045009pmDocument26 pagesRAID 13102022 045009pmSaira RiasatPas encore d'évaluation
- Raid 5Document26 pagesRaid 5Ritu ShrivastavaPas encore d'évaluation
- Operating Systems: - Redundant Array of Independent DisksDocument26 pagesOperating Systems: - Redundant Array of Independent DisksAndrés PDPas encore d'évaluation
- 5.1 RaidDocument14 pages5.1 Raidgidum2007100% (1)
- Raid Concepts PDFDocument23 pagesRaid Concepts PDFMdlamini1984Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2-2 Raid TechnologiesDocument40 pages2-2 Raid TechnologiesAlberto SantosPas encore d'évaluation
- RAID LevelsDocument1 pageRAID LevelsTeja UppalapatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Raid TechnologyDocument6 pagesRaid Technologyzerihun2514Pas encore d'évaluation
- Raid Levels ExplainedDocument11 pagesRaid Levels ExplainedNagarjuna VelechetiPas encore d'évaluation
- HP Autoraid (Lecture 5,: Ion Stoica, UC Berkeley September 13, 2016Document25 pagesHP Autoraid (Lecture 5,: Ion Stoica, UC Berkeley September 13, 2016anirudhaPas encore d'évaluation
- RAID 10 vs RAID 5: Which is Best for Performance and Data SafetyDocument3 pagesRAID 10 vs RAID 5: Which is Best for Performance and Data SafetyphanisvnPas encore d'évaluation
- What is RAID? Guide to RAID levels 0-5 benefits and usesDocument25 pagesWhat is RAID? Guide to RAID levels 0-5 benefits and usesnarang24Pas encore d'évaluation
- R. A. I. D.: Edundant Rray Nexpensive IsksDocument6 pagesR. A. I. D.: Edundant Rray Nexpensive IsksAnonymous gdJiDHPas encore d'évaluation
- 3665 - Advanced Storage ManagementDocument13 pages3665 - Advanced Storage ManagementRoshan RaviPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 4Document19 pagesLecture 4Khaled AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Database RaidDocument9 pagesDatabase RaidShion K BabuPas encore d'évaluation
- RaidDocument148 pagesRaidsivaPas encore d'évaluation
- Raid ServerDocument1 pageRaid ServerAbhishek KadamPas encore d'évaluation
- RAID Concepts: Engenio Storage Group Internal RAID 2008Document21 pagesRAID Concepts: Engenio Storage Group Internal RAID 2008abhaysingh0100Pas encore d'évaluation
- Muhammad Imran: Created byDocument16 pagesMuhammad Imran: Created bym. imranPas encore d'évaluation
- A Case For Redundant Arrays of Inexpensive Disks (RAID)Document23 pagesA Case For Redundant Arrays of Inexpensive Disks (RAID)Sushil KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Data Warehousing PartitioningDocument7 pagesData Warehousing Partitioningtigistu wogayehu tigePas encore d'évaluation
- Dbms Chapter 6Document40 pagesDbms Chapter 6GplsHub.comPas encore d'évaluation
- RAID (Redundant Arrays of Independent Disks) - GeeksforGeeksDocument14 pagesRAID (Redundant Arrays of Independent Disks) - GeeksforGeeksprasannaharish26Pas encore d'évaluation
- RAID Level 0 - Striping: AdvantagesDocument19 pagesRAID Level 0 - Striping: AdvantagesoakkarPas encore d'évaluation
- RAID Technology: An Overview of the Different RAID LevelsDocument6 pagesRAID Technology: An Overview of the Different RAID Levelsmanivannan muruesanPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 5 Storage ExercisesDocument47 pagesLesson 5 Storage ExercisesManasjyoti BhuyanPas encore d'évaluation
- External Memory (Final)Document75 pagesExternal Memory (Final)AnamPas encore d'évaluation
- 02-04 RaidDocument26 pages02-04 RaidLadislauPas encore d'évaluation
- Data Protection: RAID: Section 1: Storage SystemDocument27 pagesData Protection: RAID: Section 1: Storage SystemAayush guptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Raid Technology ReportDocument11 pagesRaid Technology ReportpradhanhPas encore d'évaluation
- LaTeX TutorialDocument11 pagesLaTeX TutorialMarcelo Moya CajasPas encore d'évaluation
- আক_শ_র যত ত_র_ আইন_র তত_ ধ_র_Document3 pagesআক_শ_র যত ত_র_ আইন_র তত_ ধ_র_ictnewPas encore d'évaluation
- Go Interviews - Top 100 PHP Interview Questions & AnswersDocument12 pagesGo Interviews - Top 100 PHP Interview Questions & AnswersictnewPas encore d'évaluation
- C Data Types:: Primary Data Types Derived Data Types User-Defined Data TypesDocument9 pagesC Data Types:: Primary Data Types Derived Data Types User-Defined Data TypesHarsha NaiduPas encore d'évaluation
- HSC Routine 2014Document2 pagesHSC Routine 2014Louis BerryPas encore d'évaluation
- Digital Forensics Research: The Next 10 Years: Simson L. GarfinkelDocument10 pagesDigital Forensics Research: The Next 10 Years: Simson L. Garfinkelsrahs1647Pas encore d'évaluation
- Top 25 Bank Interview QuestionDocument1 pageTop 25 Bank Interview QuestionictnewPas encore d'évaluation
- ScoresArrayDocument16 pagesScoresArrayPravallika ReddyPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 7Document27 pagesUnit 7Harsha NaiduPas encore d'évaluation
- Go Interviews - Top 100 Networking Interview Questions & AnswersDocument14 pagesGo Interviews - Top 100 Networking Interview Questions & AnswersictnewPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 8Document11 pagesUnit 8Harsha NaiduPas encore d'évaluation
- Typedef - To Define New Datatype BitfiedsDocument17 pagesTypedef - To Define New Datatype BitfiedsHarsha NaiduPas encore d'évaluation
- Modularizing and Reusing of Code Through FunctionsDocument9 pagesModularizing and Reusing of Code Through FunctionsHarsha NaiduPas encore d'évaluation
- Computer - Hardware: Arithmetic and Logic Unit Micro ProcessorDocument25 pagesComputer - Hardware: Arithmetic and Logic Unit Micro ProcessorMaheshpbk BmPas encore d'évaluation
- Go Interviews - Top 50 Oracle Interview Questions and AnswersDocument5 pagesGo Interviews - Top 50 Oracle Interview Questions and AnswersictnewPas encore d'évaluation
- Installation & Configuration of Mcafee Management Console (Epo 4.0)Document53 pagesInstallation & Configuration of Mcafee Management Console (Epo 4.0)ictnewPas encore d'évaluation
- Go Interviews - Top 50 OOPS Interview QuestionsDocument8 pagesGo Interviews - Top 50 OOPS Interview QuestionsictnewPas encore d'évaluation
- Go Interviews - Top 50 Operating System Interview QuestionsDocument8 pagesGo Interviews - Top 50 Operating System Interview QuestionsictnewPas encore d'évaluation
- Go Interviews - Top 50 Web Services Interview QuestionsDocument8 pagesGo Interviews - Top 50 Web Services Interview QuestionsictnewPas encore d'évaluation
- Go Interviews - Top 100 C Interview Questions & AnswersDocument17 pagesGo Interviews - Top 100 C Interview Questions & AnswersictnewPas encore d'évaluation
- Go Interviews - Top 50 SQL Question & AnswersvDocument7 pagesGo Interviews - Top 50 SQL Question & Answersvutop8Pas encore d'évaluation
- Go Interviews - Top 50 MySQL Interview Questions & AnswersDocument9 pagesGo Interviews - Top 50 MySQL Interview Questions & AnswersictnewPas encore d'évaluation
- Go Interviews - Top 50 Leadership Interview QuestionsDocument10 pagesGo Interviews - Top 50 Leadership Interview QuestionsictnewPas encore d'évaluation
- Go Interviews - Top 50 Management Interview QuestionsDocument9 pagesGo Interviews - Top 50 Management Interview QuestionsictnewPas encore d'évaluation
- Go Interviews - Top 50 HTML Interview QuestionsDocument8 pagesGo Interviews - Top 50 HTML Interview QuestionsictnewPas encore d'évaluation
- Go Interviews - Top 50 Business Analyst Interview QuestionDocument7 pagesGo Interviews - Top 50 Business Analyst Interview QuestionictnewPas encore d'évaluation
- Go Interviews - Top 50 Data Structure Interview QuestionsDocument8 pagesGo Interviews - Top 50 Data Structure Interview QuestionsictnewPas encore d'évaluation
- Go Interviews - Top 50 ASPDocument6 pagesGo Interviews - Top 50 ASPlaxmin1990Pas encore d'évaluation