Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
5a - Boiler Construction Continued - Internals - Superheaters Locked
Transféré par
ganeshanTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
5a - Boiler Construction Continued - Internals - Superheaters Locked
Transféré par
ganeshanDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
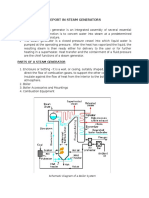
Main
Plant
Boilers
Main
Plant
Boilers
Feed water in
Economiser
Steam
drum
Water
drum
Superheater
Downcomers
Risers
Risers
Furnace
Casing
Superheated
steam out
Steam Drum
Steam Drum
The steam drum is designed to separate the steam from the
steam/water emulsion produced in the riser tubes.
It is important to ensure that no water is carried over into
the superheater. Separation is carried out by:-
Horizontal perforated plates acting as baffles.
A dry pipe situated at the top of the drum with slots
cut in to help prevent the passage of water. The dry
pipe carries the steam away from the drum to the
superheater.
The feed water pipe is submerged below the normal
working water level of the boiler.
Steam Drum Internals
Steam Drum Internals
Cyclone
Separators
Cyclone
Separators
Used in some makes
of boiler to give
improved separation of
steam/water.
Cyclone Separators
Cyclone Separators
Steam Drum
Steam Drum
Steam Drum
Steam Drum
Super-
heaters
Super-
heaters
The ESD III boiler
has an external
superheater that
uses the thermal
energy of the
combustion gasses
after passing
through the screen
wall
Superheater tubes are subject to very high temperatures
(510C) and full boiler pressure (65 bar) and are, therefore,
highly stressed.
Materials: Chrome/molybdenum steel.
Tube Diameter 53mm
The superheater tubes are welded on to stub pipes on the
headers, which are external to the gas passage.
The tube bends are supported by lugs which are welded to
the screen wall riser tubes in order to remove heat.
Superheaters
Superheaters
The superheater is set up as three separate banks of tubes.
The two top banks (furthest from the furnace) are set up as
the primary superheater.
The lower bank (closest to the furnace) is the secondary
superheater.
ALL steam flow from the boiler drum must pass through
ALL sections of the superheater continuously.
It is important to maintain maximum flow through the
superheater at all times in order to prevent overheating.
Superheaters
Superheaters
Superheaters
Superheaters
Superheaters
Superheaters
Superheaters
Superheaters
Steam Temperature Control
Steam Temperature Control
Air Attemporation
Steam Temperature Control
Steam Temperature Control
ESD II
Gas Flow Control
Steam Temperature Control
Steam Temperature Control
(
(
Attemporation
Attemporation
)
)
Superheat
Flow
Superheat
Superheat
Flow
Flow
Superheat Flow
Superheat Flow
Primary Superheater Contra flow
Secondary Superheater Parallel Flow
Attemporator
Attemporator
Attemporator
Attemporator
Water Spray
Water Spray
Attemporation
Attemporation
Feed water sprayed into steam path
Some of the superheated steam is de-superheated in order
to supply cooled saturated steam for lower quality heating
purpose e.g.
Steam/steam generators. Evaporators. De-aerators. Air
heaters. etc.
There are two main ways of de-superheating:-
Via a cooling coil in the water drum of the boiler.
Via a water spray de-superheater.
De-superheaters
De-superheaters
Spray De-superheater
Spray De-superheater
De-superheated
outlet
Superheated
inlet
Drain
Feed
water inlet
Feed
water flow
control
In order to improve the efficiency of the combustion
process and the overall efficiency of the boiler the
combustion air is pre-heated. This can be done in three
ways:-
A tube type air heater using de-superheated steam.
A rotary heat exchanger (Ljungstrom)
A double casing fitted round the boiler.
Air Heater
Air Heater
The combustion air is passed from the forced draught fan
into a double casing surrounding the furnace and
superheater.
The air is first heated by waste heat passing through the
riser tube wall and the refractory.
The air then passes through a tube type heat exchanger that
uses de-superheated steam to increase the temperature to
about 120C before the air passes to the burner registers.
Note that monowall boilers do not normally have double
casings.
Double Casing & Air Heater
Double Casing & Air Heater
LjungstromAir Heater
LjungstromAir Heater
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Evaluation of The Can Velocity Effect On A Bag Filter: Powder Technology August 2017Document5 pagesEvaluation of The Can Velocity Effect On A Bag Filter: Powder Technology August 2017Satrio FebriansyahPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 - Application of NOx Emissions Control Technologies To Achieve NOx Emission Less Than 200 MgNm3 On CoalDocument15 pages2 - Application of NOx Emissions Control Technologies To Achieve NOx Emission Less Than 200 MgNm3 On CoalStefanos GabalacPas encore d'évaluation
- Why Do Waste Heat Boilers Fail?: Excessive TemperatureDocument4 pagesWhy Do Waste Heat Boilers Fail?: Excessive TemperatureMaheesha GunathungaPas encore d'évaluation
- Air Monitoring Combustion Air Power BoilersDocument189 pagesAir Monitoring Combustion Air Power BoilersAnonymous zdCUbW8HfPas encore d'évaluation
- Air Venting Heat Loss and SummaryDocument9 pagesAir Venting Heat Loss and Summarysandeep kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Furnace Internal PressureDocument3 pagesFurnace Internal PressureskluxPas encore d'évaluation
- Air Heater Powermag 101 - CoalDocument36 pagesAir Heater Powermag 101 - CoalmasgrahaPas encore d'évaluation
- 12-Design Fundamentals of BoilerDocument12 pages12-Design Fundamentals of BoilerVishalVaishPas encore d'évaluation
- Boiler Excess Air Tune-UpDocument15 pagesBoiler Excess Air Tune-UpAlif Nur FirdausPas encore d'évaluation
- H Vs V CondensersDocument1 pageH Vs V CondensersParth PurohitPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 14Document23 pagesCH 14esojsuil_tgPas encore d'évaluation
- Condensate Cycle: Anshul Agarwal Engr (Opn)Document20 pagesCondensate Cycle: Anshul Agarwal Engr (Opn)Virendra AusarPas encore d'évaluation
- InTech Focus Final Control Elements Sept2019Document33 pagesInTech Focus Final Control Elements Sept2019luciaPas encore d'évaluation
- AccumulatorsDocument11 pagesAccumulatorsRufus D SPas encore d'évaluation
- PEPOI Condenser Performance BasicsDocument26 pagesPEPOI Condenser Performance BasicsFranz MonsantoPas encore d'évaluation
- Energy Savings in The HomeDocument27 pagesEnergy Savings in The Homeminorona2409100% (1)
- Performance Evaluation of Air PreheaterDocument8 pagesPerformance Evaluation of Air PreheaterAndria MatthewsPas encore d'évaluation
- 10 Ways To Make Your Compressor Installation More Energy EfficientDocument7 pages10 Ways To Make Your Compressor Installation More Energy EfficientKamel NefziPas encore d'évaluation
- Boiler Efficiency Combustion EfficiencyDocument8 pagesBoiler Efficiency Combustion EfficiencyBelalNorPas encore d'évaluation
- Pumpsandpumpingsystems 150309110148 Conversion Gate01Document58 pagesPumpsandpumpingsystems 150309110148 Conversion Gate01AltairPas encore d'évaluation
- Asme PTC-1-2011Document28 pagesAsme PTC-1-2011andhucaosPas encore d'évaluation
- Product Line Sulphur enDocument4 pagesProduct Line Sulphur enprgunjalPas encore d'évaluation
- Fuel FiringDocument39 pagesFuel Firingnetygen1Pas encore d'évaluation
- ID Fan BoilerDocument23 pagesID Fan BoilerAli BariPas encore d'évaluation
- Grundfos Category Heading Grundfos Boiler Feed ManualDocument32 pagesGrundfos Category Heading Grundfos Boiler Feed ManualTasawwur TahirPas encore d'évaluation
- Flue Gas System-2Document56 pagesFlue Gas System-2SamPas encore d'évaluation
- Boilerproblems 181026115558 PDFDocument23 pagesBoilerproblems 181026115558 PDFTaufiqTaufiqPas encore d'évaluation
- Loss Optimisation in BoilersDocument50 pagesLoss Optimisation in Boilersrashm006ranjanPas encore d'évaluation
- Co2 Capture and Storage in IGCC PlantsDocument23 pagesCo2 Capture and Storage in IGCC PlantsAbhiram KukunuriPas encore d'évaluation
- Ref Pipe Sizing Ver 02 21 11Document12 pagesRef Pipe Sizing Ver 02 21 11Ahmef100% (1)
- Cooling Tower - Design ConsiderationsDocument6 pagesCooling Tower - Design Considerationsofelherrera77Pas encore d'évaluation
- Vacuum Pump SizingDocument1 pageVacuum Pump SizingAhmad Saiful AnwarPas encore d'évaluation
- Optimizing Pump and Fan ApplicationsDocument7 pagesOptimizing Pump and Fan Applicationsallahuakbar2011Pas encore d'évaluation
- CS46 - Basic Immersion Firetube ModelDocument22 pagesCS46 - Basic Immersion Firetube ModelYasin YILDIZPas encore d'évaluation
- NOx Burner ControlDocument14 pagesNOx Burner ControlsdgalaponPas encore d'évaluation
- Guide To Furnace SootblowingDocument40 pagesGuide To Furnace SootblowingnarayananalivePas encore d'évaluation
- Improving Energy Efficiency Boilers R1Document71 pagesImproving Energy Efficiency Boilers R1seif elsaiePas encore d'évaluation
- Coal-RDF Co-Firing Final ReportDocument19 pagesCoal-RDF Co-Firing Final ReportmjbotelhoPas encore d'évaluation
- Air CompreesorDocument59 pagesAir CompreesorramprakashpatelPas encore d'évaluation
- ENERGY AUDIT, CONSERVATION AND POWER FACTOR Improvement - Study NotesDocument6 pagesENERGY AUDIT, CONSERVATION AND POWER FACTOR Improvement - Study NotesRaghu Raman100% (1)
- Innovation For Boiler TubeDocument2 pagesInnovation For Boiler TubemasgrahaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cogenerations of Energy From Sugar Factory BagasseDocument8 pagesCogenerations of Energy From Sugar Factory BagasseTade GaromaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lec 3 BoilerDocument20 pagesLec 3 BoilerRajiv SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Presentation-4 - ESP Soot BlowerDocument19 pagesPresentation-4 - ESP Soot BlowerVaradPas encore d'évaluation
- System Curve Fan Curve Operating PointDocument45 pagesSystem Curve Fan Curve Operating PointAnonymous I0JAds2SP100% (1)
- Design of Air IDocument5 pagesDesign of Air IInvedePas encore d'évaluation
- Gas AnalyzerDocument5 pagesGas Analyzerengine5Pas encore d'évaluation
- Forced Draft BlowerDocument108 pagesForced Draft BlowerTrevor ChandlerPas encore d'évaluation
- Heat Rate of Thermal Power PlantDocument15 pagesHeat Rate of Thermal Power Plantsameer betal100% (1)
- Steam System Management-Six Sigma-Spirax SarcoDocument14 pagesSteam System Management-Six Sigma-Spirax SarcoJunghietu DorinPas encore d'évaluation
- Steam Table For Saturated Steam: (Continued)Document1 pageSteam Table For Saturated Steam: (Continued)ChristianGuerreroPas encore d'évaluation
- Air Cooled CondenserDocument7 pagesAir Cooled Condensermoreds1983Pas encore d'évaluation
- Rules of Thumb PDFDocument2 pagesRules of Thumb PDFHoney Tiwari100% (1)
- Properties of Saturated SteamDocument4 pagesProperties of Saturated SteamArif FaturohmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Part 1 - Fundamentals of Airflow, Fans & DuctDocument49 pagesPart 1 - Fundamentals of Airflow, Fans & Ductkhanh.vecPas encore d'évaluation
- Prof Ir Dr. Ab Saman B. Abd Kader, Peng, Miem, Mcit Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, UtmDocument21 pagesProf Ir Dr. Ab Saman B. Abd Kader, Peng, Miem, Mcit Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, UtmakusuperPas encore d'évaluation
- Boiler Accessories: Bibin ChidambaranathanDocument8 pagesBoiler Accessories: Bibin ChidambaranathanDr. BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANPas encore d'évaluation
- Report in Steam Generators: Schematic Diagram of A Boiler SystemDocument18 pagesReport in Steam Generators: Schematic Diagram of A Boiler SystemZa YonPas encore d'évaluation
- CoalDocument41 pagesCoalKarthi KeyanPas encore d'évaluation
- How To Match Valves and Actuators 21990Document6 pagesHow To Match Valves and Actuators 21990ganeshan100% (1)
- Making Fire Systems Safe 21994Document11 pagesMaking Fire Systems Safe 21994ganeshanPas encore d'évaluation
- Compatibilidad Materiales Corrosion - TableDocument20 pagesCompatibilidad Materiales Corrosion - TableYaíma Casañola SuárezPas encore d'évaluation
- Bayer Process ChemistryDocument7 pagesBayer Process ChemistryganeshanPas encore d'évaluation
- Alumina Proses SistemDocument57 pagesAlumina Proses SistemSriyono NozbPas encore d'évaluation
- Bayer PaperDocument5 pagesBayer PaperMatt SalinovichPas encore d'évaluation
- Bauxite EIC1982Document4 pagesBauxite EIC1982ganeshanPas encore d'évaluation
- Dezurik V Port Ball Valves VPB Sales 15-00-1Document8 pagesDezurik V Port Ball Valves VPB Sales 15-00-1ganeshanPas encore d'évaluation
- Pondicherry IndustriesDocument13 pagesPondicherry IndustriesganeshanPas encore d'évaluation
- Vw0811 Actuation OxlerDocument2 pagesVw0811 Actuation OxlerganeshanPas encore d'évaluation
- Sodium Bisulphate 2011 MarchDocument9 pagesSodium Bisulphate 2011 MarchganeshanPas encore d'évaluation
- Why A Butterfly 1984Document2 pagesWhy A Butterfly 1984ganeshan100% (1)
- Explanation of IP RatingsDocument1 pageExplanation of IP RatingsganeshanPas encore d'évaluation
- Water Without A Pinch of Salt - Desalination Market in India - Post EditingDocument26 pagesWater Without A Pinch of Salt - Desalination Market in India - Post EditingganeshanPas encore d'évaluation
- Compatibilidad Materiales Corrosion - TableDocument20 pagesCompatibilidad Materiales Corrosion - TableYaíma Casañola SuárezPas encore d'évaluation
- Grayloc PictureDocument1 pageGrayloc PictureganeshanPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 Guidance On Valve Type SelectionDocument86 pages4 Guidance On Valve Type SelectionKrista OneillPas encore d'évaluation
- HobbsDocument41 pagesHobbsganeshanPas encore d'évaluation
- Isa Maharashtra Inteq Magazine July2012Document21 pagesIsa Maharashtra Inteq Magazine July2012ganeshanPas encore d'évaluation
- Listofitems RanipetDocument7 pagesListofitems RanipetganeshanPas encore d'évaluation
- Masala Dosa To Die For - NYTimesDocument13 pagesMasala Dosa To Die For - NYTimesganeshanPas encore d'évaluation
- NAF Unex Butterfly 4141 GB PDFDocument8 pagesNAF Unex Butterfly 4141 GB PDFganeshanPas encore d'évaluation
- FGD ValveDocument18 pagesFGD Valveganeshan100% (1)
- Pondicherry IndustriesDocument13 pagesPondicherry IndustriesganeshanPas encore d'évaluation
- Bluewater Website - Products and TechnologyDocument2 pagesBluewater Website - Products and TechnologyganeshanPas encore d'évaluation
- Kakinada PDFDocument30 pagesKakinada PDFSandeep Mandapaka100% (2)
- Bro Refining 20111025 01 PA4 2012427153825Document28 pagesBro Refining 20111025 01 PA4 2012427153825ganeshanPas encore d'évaluation
- Complete Valve Solutions: For The Refining and Petrochemical IndustriesDocument16 pagesComplete Valve Solutions: For The Refining and Petrochemical Industriesfranz_passariniPas encore d'évaluation
- Boiler CalculationsDocument16 pagesBoiler CalculationsBilly Moerdani100% (1)
- NJ Mpje PDFDocument168 pagesNJ Mpje PDFPatrick Mata100% (3)
- Improved Formation Programme For Lead Acid Batteries 1628828706Document9 pagesImproved Formation Programme For Lead Acid Batteries 1628828706ehsan453Pas encore d'évaluation
- Assay of Aspirin PDFDocument9 pagesAssay of Aspirin PDFyeleidispPas encore d'évaluation
- Secret Scents 1Document78 pagesSecret Scents 1RiazBasrahPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture Note 2. Familiarization With ApparatusesDocument28 pagesLecture Note 2. Familiarization With ApparatuseskkkPas encore d'évaluation
- Cder Guidance AmethDocument9 pagesCder Guidance Amethdrs_mdu48Pas encore d'évaluation
- Artículo para ForoDocument7 pagesArtículo para ForoJuan MendozaPas encore d'évaluation
- Phoenicia University Department of Engineering Faculty of Petroleum Engineering Petroleum Fluid Properties Laboratory PENG212L Dean Stark Plug SizeDocument14 pagesPhoenicia University Department of Engineering Faculty of Petroleum Engineering Petroleum Fluid Properties Laboratory PENG212L Dean Stark Plug SizeEmanuelta NaibahoPas encore d'évaluation
- MeasureMaster Dual Chamber Orifice FittingDocument6 pagesMeasureMaster Dual Chamber Orifice FittingirfanPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio FertilizerDocument15 pagesBio FertilizerAamir SajjadPas encore d'évaluation
- IMF PogilDocument6 pagesIMF PogilsungminindiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Notes - Respiratory SystemDocument9 pagesBiology Notes - Respiratory SystemnoorbdeirPas encore d'évaluation
- ReviewerDocument19 pagesReviewerCarlos Miguel Dacaimat100% (1)
- Waste-Management EDITEDDocument20 pagesWaste-Management EDITEDpshantanu123Pas encore d'évaluation
- Practise School - ChemistryDocument64 pagesPractise School - ChemistrySonakshi BhatiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Portfolio - Biological Cell Prepared by 1st Year Mbbs Student-LekshmiDocument10 pagesPortfolio - Biological Cell Prepared by 1st Year Mbbs Student-Lekshmispillai11Pas encore d'évaluation
- In-Vitro Antimicrobial Activity of Nano-Chitosan Hydroxyapatite Against Streptococcus Mutans On Biofilm FormationDocument8 pagesIn-Vitro Antimicrobial Activity of Nano-Chitosan Hydroxyapatite Against Streptococcus Mutans On Biofilm FormationInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Industrial BiotechnologyDocument29 pagesBasic Industrial BiotechnologyBharathiPas encore d'évaluation
- Influence of Adding Short Carbon Fibers On The Flexural Behavior of Textile-Reinforced Concrete One-Way SlabDocument18 pagesInfluence of Adding Short Carbon Fibers On The Flexural Behavior of Textile-Reinforced Concrete One-Way SlabShaker QaidiPas encore d'évaluation
- Polypro VC 17Document2 pagesPolypro VC 17hauvuPas encore d'évaluation
- TopyDocument64 pagesTopyChristiano Calijorne de BarrosPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug CalculationsDocument6 pagesDrug CalculationsLighto RyusakiPas encore d'évaluation
- Titration Strong Weak Acids BasesDocument6 pagesTitration Strong Weak Acids Basesapi-309713761Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ammonia Waste WaterDocument19 pagesAmmonia Waste WaterAnonymous GfPSYi4nPas encore d'évaluation
- Pressurised Mud Cap Drilling Paper (Spe-125311-By Dany)Document7 pagesPressurised Mud Cap Drilling Paper (Spe-125311-By Dany)Hammad KhalidPas encore d'évaluation
- T0-1-PAA-S0001-00-Talin-Specification Attachments-21250w - EN (0630) - Rev1 PDFDocument43 pagesT0-1-PAA-S0001-00-Talin-Specification Attachments-21250w - EN (0630) - Rev1 PDFdang2172014Pas encore d'évaluation
- Essential Molecular BiologyDocument19 pagesEssential Molecular BiologySandra JelynPas encore d'évaluation
- NEET TEst PapaerDocument11 pagesNEET TEst PapaerBiswajit ChangkakotyPas encore d'évaluation
- ASTM D7393-07 (2012) Standard Practice For Indicating Oil in AbrasivesDocument2 pagesASTM D7393-07 (2012) Standard Practice For Indicating Oil in Abrasivesalexander zuritaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry of Kupipakwa RasayanasDocument7 pagesChemistry of Kupipakwa RasayanasSrinivas Naik0% (1)