Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Neuro, GI, GU, MSK midterm and final review
Transféré par
jenn1722Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Neuro, GI, GU, MSK midterm and final review
Transféré par
jenn1722Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Eyes, ears, male, GU, musculoskeletal not on test.
Information from midterm on will be on final. Review last jeopardy game. Gall bladder/pancreas, gi, cerbrovasc ular disorders, neurologic trauma, neurologic inf.
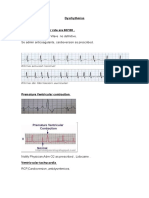
Pain with pancreatitis: epigastric pain radiating to back. Cholecystitis pain: right upper quadrant, radiating to right scapula and shoulder. EGD: check for return of the gag reflex. ERCP: Im glad I dont have to lie still for this procedure. Monitor lab detecting jaunidice for obstructed bile duct by bile stones: bilirubin Cholecystectomy: t tube drained 750 mL of green-brown drainage. After procedure it is bloody but turns green-brown. Document it as output. Never irriate t tube. Never clamp without dr. orders. If output is a liter, call doctor. Cholecystitis present to unit. Goals of treatment. Remove cause by pharmacologic endo and surgical reduce incidence of acute episodes of pain. Resuce acute episodes by dietary therapy. Spinal cord injusry of c6, most concern? Sever throbbing headache. Decreased sensation below waist, hypotensive, bradycxardic with warm extremities and sudden onset of fever. Type of shock? Neurogenic shock. Spinal cord injury to c 6. Diagnosis and highest priority? Autonomic dysreflexia: check the foley catheter for kinks to ensure patency. Bowel and bladder training. Interventions to prevent elevations in ICP: exhaling during repositioning. Vital signs indicate ICP: Inc. temp, dec pulse, dec RR, and inc. BP.
Spinal cord injury is prone to experience autonomic dysreflexia. What should be avoided to minimize risk of recurrence? Limiting blader catheritization to once every 12 hours. They should be catheterized q4-6 hrs. With basilar fracture bruising behind his ears is called? Battle sign. With basilar fracture periorbital ecchymosis around is eyes: raccoon mask. Three possible complications that can arrive from spinal cord injury: autonomic dysreflexia, orthostatic hypotension, and DVTS. No signs of autonomic dysreflexia: tachycardia, hypotension, dry nasal passages, tachypnea. With autonomic dysreflexia you should have nasal congestion, perfuse sweating, hypertension and piloerection. Surgery to releave ICP is craniotomy. Complications of craniotomy: infection, inc. in ICP, bleeding, hemorrhage, hydrocephalus, respiratory and neurologic problems, SIADH, hematoma, hypovolemic shock, diabetes insipidus. Check temperature with ICP. Inc. temperature can increase ICP. Suction as minimal as possible. Epidural hematoma, what nursing interventions should be implemented. Administer stool softeners daily, ensure pulse ox is reading higher than 93%, administer mild sedatives. Possible meningitis. Three signs could be possibly exhibit, nuchal rigidity, temperature, HA, positive Kernigs and Brudzinsky signs. Gullain Barre syndrome, what items should the nurse bring to the room: ECG monitoring electrodes and intubation tray. Trigeminal neuralgia: nerve 5, Bells Palsy is nerve 7
Lab to be monitored for a seizure on a anticonvulsant drug at risk for immune suppression: CBC. Causes of encephalitis: HSV TREAT WITH ZOVIRAX, FUNGAL TREAT WITH DIFLUCAN, VECTOR TREAT WITH AMPHOTERICIN B.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Hemodynamic Management Pocket Card PDFDocument8 pagesHemodynamic Management Pocket Card PDFjenn1722Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Anatomy of BreathingDocument6 pagesThe Anatomy of BreathingmihaiylaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ebook PDF The Phlebotomy Textbook 4th Edition PDFDocument41 pagesEbook PDF The Phlebotomy Textbook 4th Edition PDFmelody.bowers405100% (29)
- Preceptor Evaluation FormDocument2 pagesPreceptor Evaluation Formjenn1722Pas encore d'évaluation
- Dysrhythmia Recognition Pocket Reference Card PDFDocument14 pagesDysrhythmia Recognition Pocket Reference Card PDFjenn1722100% (2)
- Rounding Rules11!3!11Document1 pageRounding Rules11!3!11Sheldon SloanPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 09: Photo Atlas of Drug Administration Test Bank: Multiple ChoiceDocument8 pagesChapter 09: Photo Atlas of Drug Administration Test Bank: Multiple ChoicePrettygirl716Pas encore d'évaluation
- Droplet, Airborne, Contact Isolation PrecautionsDocument18 pagesDroplet, Airborne, Contact Isolation PrecautionsTommy GreenPas encore d'évaluation
- Surgical Hand Scrub Protocol UpdatesDocument22 pagesSurgical Hand Scrub Protocol UpdatesRex Lagunzad Flores100% (2)
- Hydroponics - Introduction To HydroponicsDocument91 pagesHydroponics - Introduction To HydroponicscorradiniaPas encore d'évaluation
- Atrial Fibrillation and Dysrhythmias GuideDocument10 pagesAtrial Fibrillation and Dysrhythmias Guideyaneidys perezPas encore d'évaluation
- Legal Issues in Nursing - With Class IntroductionDocument37 pagesLegal Issues in Nursing - With Class Introductionjenn1722Pas encore d'évaluation
- RN Thread NclexDocument21 pagesRN Thread NclexMaria Nadia MihalikPas encore d'évaluation
- Hyperemesis Gravidarum: Bleeding Complications of PregnancyDocument6 pagesHyperemesis Gravidarum: Bleeding Complications of PregnancykirbsPas encore d'évaluation
- Mapeh Grade 8 Third QuarterDocument4 pagesMapeh Grade 8 Third QuarterPhilip Jansen Guarin100% (2)
- FNP Final TestDocument10 pagesFNP Final TestNelson MandelaPas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced Med Surg Final Part 2 Everything ElseDocument25 pagesAdvanced Med Surg Final Part 2 Everything Elsejenn1722100% (1)
- Neuromuscular Blocking DrugsDocument23 pagesNeuromuscular Blocking DrugsRA TrancePas encore d'évaluation
- Exam ReviewDocument4 pagesExam ReviewMya Thomas100% (1)
- Reading and Writing: Quarter 3: Module 2 - Lesson 1Document13 pagesReading and Writing: Quarter 3: Module 2 - Lesson 1MELANIE IBARDALOZA100% (2)
- Positioning principles and protocols for common medical conditionsDocument48 pagesPositioning principles and protocols for common medical conditionsShazaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ethical Concepts in NursingDocument18 pagesEthical Concepts in Nursingjenn1722Pas encore d'évaluation
- DBQ FOCUS: Columbian Exchange: Document-Based Question FormatDocument5 pagesDBQ FOCUS: Columbian Exchange: Document-Based Question Formatbaruc barranco50% (2)
- Select All That ApplyDocument10 pagesSelect All That ApplyJohnasse Sebastian NavalPas encore d'évaluation
- Nclex RN Sata CompilationDocument10 pagesNclex RN Sata CompilationJanna mae PatriarcaPas encore d'évaluation
- NP4 Nursing Board Exam NotesDocument9 pagesNP4 Nursing Board Exam NotesNewb TobikkoPas encore d'évaluation
- Study Guide For Med Surg 1Document15 pagesStudy Guide For Med Surg 1desireemaenugentPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Academy Philippines Preboard ExamDocument10 pagesNursing Academy Philippines Preboard ExamCheng CapunoPas encore d'évaluation
- Medsurge RationaleDocument8 pagesMedsurge RationaleRose Anne AbivaPas encore d'évaluation
- Shock Types 141009102815 Conversion Gate01Document41 pagesShock Types 141009102815 Conversion Gate01Samjaisheel SamsonPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing BulletsDocument72 pagesNursing BulletsJoanna Mae Carolino100% (1)
- Medical Surgical ATI Proctored Exam 2019 Questions and Answers Verified 100Document7 pagesMedical Surgical ATI Proctored Exam 2019 Questions and Answers Verified 100ianshirow834Pas encore d'évaluation
- Global Nursing Pediatrics. Nclex - RNDocument14 pagesGlobal Nursing Pediatrics. Nclex - RNNANAPas encore d'évaluation
- Main drug therapy for ulcerative colitis is sulfa for one yearDocument4 pagesMain drug therapy for ulcerative colitis is sulfa for one yearcathyPas encore d'évaluation
- Fundamentals Quizzing TIPSDocument41 pagesFundamentals Quizzing TIPSmelissamichelllePas encore d'évaluation
- Medsurg 2007Document15 pagesMedsurg 2007WisdomIsMisery100% (1)
- DO NOT Delegate What You Can EATDocument1 pageDO NOT Delegate What You Can EATMerlin JosephPas encore d'évaluation
- NclexDocument4 pagesNclexihatetouPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 59 Care of Patients With Problems of The Biliary System and PancreasDocument28 pagesCH 59 Care of Patients With Problems of The Biliary System and Pancreasjrflores1284Pas encore d'évaluation
- Clinical Case Study - Online Discussion Form Fall 2020-1Document14 pagesClinical Case Study - Online Discussion Form Fall 2020-1Sabrina Odies100% (1)
- UWorld Critical CareDocument14 pagesUWorld Critical CareJohnasse Sebastian NavalPas encore d'évaluation
- Jennifer Portillo Health Assessment VocabularyDocument9 pagesJennifer Portillo Health Assessment VocabularyJennifer PortilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Immunity 1Document6 pagesImmunity 1Tori RolandPas encore d'évaluation
- Major Hormone Glands and Their FunctionsDocument5 pagesMajor Hormone Glands and Their FunctionsSTEFFI GABRIELLE GOLEZPas encore d'évaluation
- MS Final 46 Blood or Lymphatic DisorderDocument4 pagesMS Final 46 Blood or Lymphatic DisorderZachary T Hall0% (1)
- Chapter 55Document8 pagesChapter 55DelindaEvansPas encore d'évaluation
- VSim SARAH LIN For Nursing - Health Assessment POST QUIZDocument5 pagesVSim SARAH LIN For Nursing - Health Assessment POST QUIZWen RodsaPas encore d'évaluation
- Check My Twitter Account @nursetopia or IG @nursetopia1 For More Nursing Test Banks, Sample Exam, Reviewers, and NotesDocument5 pagesCheck My Twitter Account @nursetopia or IG @nursetopia1 For More Nursing Test Banks, Sample Exam, Reviewers, and NotesNurse UtopiaPas encore d'évaluation
- NCLEX Updates June 2010Document21 pagesNCLEX Updates June 2010erika_datu100% (1)
- Hesi Med Surg Study GuideDocument1 pageHesi Med Surg Study GuideGeorgePas encore d'évaluation
- Hesi Med Surg Study GuideDocument1 pageHesi Med Surg Study GuideGeorgePas encore d'évaluation
- Concept Map Et Al 11-04-15Document7 pagesConcept Map Et Al 11-04-15api-353656227Pas encore d'évaluation
- Medical Surgical Nursing - DiabetesDocument4 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing - Diabetestripj33100% (2)
- Flashcards 2601-2800Document191 pagesFlashcards 2601-2800kkenPas encore d'évaluation
- IV. Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument18 pagesIV. Multiple Choice Questionsycofel07Pas encore d'évaluation
- 52 Nclex ReviewDocument1 page52 Nclex ReviewedoblePas encore d'évaluation
- Medical-Surgical Nursing Review: 315 Key ConceptsDocument15 pagesMedical-Surgical Nursing Review: 315 Key ConceptsJap Avila BernasPas encore d'évaluation
- Respiratory meds guide for new nursesDocument2 pagesRespiratory meds guide for new nursesmlbrown8Pas encore d'évaluation
- Hesi Med Surg-14Document1 pageHesi Med Surg-14GeorgePas encore d'évaluation
- Renal & Urinary ATIDocument2 pagesRenal & Urinary ATIHelen Varela100% (1)
- Asthma That Disappears Between Ages 6-8 - Bronchioles Grew & Resolved The AsthmaDocument27 pagesAsthma That Disappears Between Ages 6-8 - Bronchioles Grew & Resolved The Asthmasimonedarling100% (1)
- Pharm Exam ReviewDocument13 pagesPharm Exam ReviewAshleyPas encore d'évaluation
- DelegationDocument3 pagesDelegationVanessa AbboudPas encore d'évaluation
- Predictor 6Document42 pagesPredictor 6Christine Ann GuinitaranPas encore d'évaluation
- Answer: CDocument34 pagesAnswer: CLola OladapoPas encore d'évaluation
- NCLEX Review NotesDocument20 pagesNCLEX Review Notesshaali86Pas encore d'évaluation
- Test QuestionsDocument2 pagesTest QuestionsLucille E. TesadoPas encore d'évaluation
- NursingDocument8 pagesNursingWen SilverPas encore d'évaluation
- Ignatavicius: Medical-Surgical Nursing, 7th EditionDocument9 pagesIgnatavicius: Medical-Surgical Nursing, 7th EditionGERALDE CHARLESPas encore d'évaluation
- HESI LPN ADN ENTRANCE EXAM MOBILITY EXAMS A GRADED 100 VERIFIED - pdf-1-33Document33 pagesHESI LPN ADN ENTRANCE EXAM MOBILITY EXAMS A GRADED 100 VERIFIED - pdf-1-33erick kanyiPas encore d'évaluation
- Emergent Care Clinic StudyDocument5 pagesEmergent Care Clinic StudyAna Bienne0% (1)
- NURSING CARE OF ADULTS II: Passbooks Study GuideD'EverandNURSING CARE OF ADULTS II: Passbooks Study GuidePas encore d'évaluation
- COMPREHENSIVE NURSING ACHIEVEMENT TEST (RN): Passbooks Study GuideD'EverandCOMPREHENSIVE NURSING ACHIEVEMENT TEST (RN): Passbooks Study GuidePas encore d'évaluation
- A Simple Guide to Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsD'EverandA Simple Guide to Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsPas encore d'évaluation
- The Limits of Off Shore BalancingDocument97 pagesThe Limits of Off Shore Balancingjenn1722Pas encore d'évaluation
- Future of US Strategic Rebalancing Toward Asia 2015Document10 pagesFuture of US Strategic Rebalancing Toward Asia 2015jenn1722Pas encore d'évaluation
- Common Medications: Uses, Questions & AnswersDocument1 pageCommon Medications: Uses, Questions & Answersjenn1722Pas encore d'évaluation
- Burn Injury Case Study Rule of Nines Calculation and Fluid ResuscitationDocument2 pagesBurn Injury Case Study Rule of Nines Calculation and Fluid Resuscitationjenn1722100% (11)
- Chapter 15 Key TermsDocument18 pagesChapter 15 Key Termsjenn1722Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 16 ReviewDocument21 pagesChapter 16 Reviewjenn1722Pas encore d'évaluation
- Home Health National Patient Safety GoalsDocument3 pagesHome Health National Patient Safety Goalsjenn1722Pas encore d'évaluation
- Black Box WarningDocument1 pageBlack Box Warningjenn1722Pas encore d'évaluation
- Final Copy Jenna PoemanalysisDocument6 pagesFinal Copy Jenna Poemanalysisjenn1722Pas encore d'évaluation
- FINAL COPY JENNA ShortStoryAnalysisLottery1Document10 pagesFINAL COPY JENNA ShortStoryAnalysisLottery1jenn1722Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ambulatory Health Care National Patiernt Safety GoalsDocument8 pagesAmbulatory Health Care National Patiernt Safety Goalsjenn1722Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 71, Karen2Document101 pagesChapter 71, Karen2jenn1722Pas encore d'évaluation
- Professional and Educational Development in NursingDocument30 pagesProfessional and Educational Development in Nursingjenn1722Pas encore d'évaluation
- Five RightsDocument2 pagesFive RightsPrasenjit RoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Quiz 2 Study Guide - SHOCK!!! 25 Questions READ BOOK!!! Know Charts Esp. Stages of Shock ChartDocument1 pageQuiz 2 Study Guide - SHOCK!!! 25 Questions READ BOOK!!! Know Charts Esp. Stages of Shock Chartjenn1722Pas encore d'évaluation
- Med Surg Quiz 1 Review.Document3 pagesMed Surg Quiz 1 Review.jenn1722Pas encore d'évaluation
- Clinical Worksheet: /var/www/apps/conversion/tmp/scratch - 2/182114054Document20 pagesClinical Worksheet: /var/www/apps/conversion/tmp/scratch - 2/182114054jenn1722Pas encore d'évaluation
- NUR 298 Role Transition MidtermDocument7 pagesNUR 298 Role Transition Midtermjenn1722Pas encore d'évaluation
- 298 Quiz 2 Study GuideDocument3 pages298 Quiz 2 Study Guidejenn1722Pas encore d'évaluation
- Quiz 2 and Midterm Study BankDocument19 pagesQuiz 2 and Midterm Study Bankjenn1722Pas encore d'évaluation
- PP T 0000041Document54 pagesPP T 0000041jenn1722Pas encore d'évaluation
- Microbiology exam study guide digestive and urinary diseasesDocument2 pagesMicrobiology exam study guide digestive and urinary diseasesjenn1722Pas encore d'évaluation
- Review Lab TableDocument4 pagesReview Lab Tablejenn1722Pas encore d'évaluation
- BIO 260 SU 12 Exam 4 Study Tables A & BDocument3 pagesBIO 260 SU 12 Exam 4 Study Tables A & Bjenn1722Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Mpact: Smok NGDocument1 pageThe Mpact: Smok NGsabaPas encore d'évaluation
- Community WrittenDocument23 pagesCommunity WrittenImPrint CenterPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Report VTDocument12 pagesCase Report VTAnonymous ZbhBxeEVPas encore d'évaluation
- Snow White - Abnormal Psychology PaperDocument6 pagesSnow White - Abnormal Psychology PaperNicky JosephPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 4 Di Nitro Chloro BenzeneDocument9 pages2 4 Di Nitro Chloro BenzeneKannan NainarPas encore d'évaluation
- Preconception Care: Maximizing The Gains For Maternal and Child HealthDocument15 pagesPreconception Care: Maximizing The Gains For Maternal and Child HealthAnita Rezeki Carolina100% (1)
- IPA 8 Legend GuideDocument7 pagesIPA 8 Legend GuideAdrien JeanniardPas encore d'évaluation
- Leading Cause of Death by State: Allison Sandys, Graham Vogtman, Madison MannDocument10 pagesLeading Cause of Death by State: Allison Sandys, Graham Vogtman, Madison MannGrahamVogtmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Investigation of Blood Culture Using BACTEC SystemsDocument36 pagesInvestigation of Blood Culture Using BACTEC SystemsGregorio De Las CasasPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1-5 PDFDocument77 pagesChapter 1-5 PDFEstebanPas encore d'évaluation
- Judi Januadi Endjun: Gatot Soebroto Army Central Hospital/ Medical Faculty, University of Indonesia ISUOG, Bali, 2009Document66 pagesJudi Januadi Endjun: Gatot Soebroto Army Central Hospital/ Medical Faculty, University of Indonesia ISUOG, Bali, 2009Judi Januadi Endjun, MD, ObsGynPas encore d'évaluation
- Physical and Mental Health of The Workers in The Readymade Garment Industry of BangladeshDocument10 pagesPhysical and Mental Health of The Workers in The Readymade Garment Industry of BangladeshDr. Nazrul IslamPas encore d'évaluation
- 07 DR Ismat Mohd SulaimanDocument21 pages07 DR Ismat Mohd SulaimanGiles Ching100% (1)
- Essay in MapehDocument4 pagesEssay in MapehJane Ikan AlmeroPas encore d'évaluation
- 12 Biology Notes Ch11 Biotechnology Principles and ProcessesDocument9 pages12 Biology Notes Ch11 Biotechnology Principles and ProcessesAnkit YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- Annual Accomplishment Report (Aar) S.Y. 2016 - 2017: Maligaya High SchoolDocument3 pagesAnnual Accomplishment Report (Aar) S.Y. 2016 - 2017: Maligaya High SchooljeneferPas encore d'évaluation
- Physiology of ReproductionDocument34 pagesPhysiology of ReproductionCalcium QuèPas encore d'évaluation
- Fundamentals of Epidemiology (EPID 610) Exercise 12 Screening Learning ObjectivesDocument4 pagesFundamentals of Epidemiology (EPID 610) Exercise 12 Screening Learning Objectiveswelcome martin100% (1)
- Global Food Problems and SolutionsDocument21 pagesGlobal Food Problems and SolutionsMd Umar HaadPas encore d'évaluation
- A Case Report - Ayurvedic Management of Pariplutayonivyapada W.S.R To Pelvic Inflammatory DiseaseDocument6 pagesA Case Report - Ayurvedic Management of Pariplutayonivyapada W.S.R To Pelvic Inflammatory DiseaseIJAR JOURNALPas encore d'évaluation
- UB HSPED Differential Diagnosis of Lower Back PainDocument62 pagesUB HSPED Differential Diagnosis of Lower Back PainJolaine ValloPas encore d'évaluation