Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Phylum Protozoa Classification: Elementary Idea
Transféré par
Sudesh RathodCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Phylum Protozoa Classification: Elementary Idea
Transféré par
Sudesh RathodDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Course I: First semester
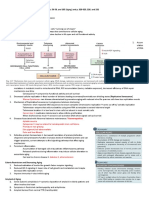
PHYLUM PROTOZOA
(Unicellular and most primitive animals) 1. These are the most primitive organisms (Protos = first; zoon = animal). 2. These are aquatic, microscopic, unicellular organisms. Class- Rhizopoda/ Sarcodina (bearing pseudopodia locomotory organelle.)
1. Locomotory organelles are pseudopodia which may be rhizome like called rhizopodium. Nucleus is single spherical or disc like. 2. The typical example of Class Rhizopoda is Amoeba. Amoeba: i. ii. iii. iv. Amoeba is fresh water form found in ponds and lakes. They are asymmetric in shape. Amoeba has pseudopodia for locomotion and feeding. Body consists of a single biconvex nucleus, ectoplasm, endoplasm, contractile vacuole and food vacuole. Reproduction is performed by binary fission, multiple fission and sporulation. Amoeba
v.
Class- Flagellata/ Mastigophora (bearing flagella as locomotory organelles.) 1. Locomotory organelles are long and ribbon like flagella which is used for locomotion and feeding 2. Most of them are colonial or solitary and free living and few are parasitic. 3. Nucleus is single and spherical; cytoplasm contains brown, yellow or green photosynthetic pigments. Fresh water forms have contractile vacuoles for osmoregulation. 4. The typical example of Class Flagellata is Euglena.
Prof. S. D. Rathod
Copy No II
Course I: First semester Euglena: i. ii. iii. iv. It is free living fresh water form found in ponds and lakes. Body is spindle shaped due to pellicle. Has single ribbon like flagellum performing feeding and locomotion. Has single spherical nucleus, and cytoplasm consists of ectoplasm, endoplasm, contractile vacuole, food vacuole and chloroplasts for photosynthesis.
Euglena
Class- Sporozoa (bearing no locomotory organelle.) 1. Locomotory organelles are absent in these animals as they are endoparasitic. They have a protective covering called cuticle around their body to protect against hazardous chemicals of their hosts. 2. Nutrition is saprophytic. Food is absorbed directly through body surface. 3. The typical example of Class Sporozoa is Plasmodium. Plasmodium: i. It is parasitic found in man as primary host and female anopheles as intermediate host. Body spherical with a nucleus, cytoplasm containing food and gas vacuoles. Contractile vacuole is absent.
ii.
Plasmodium
2
Prof. S. D. Rathod
Copy No II
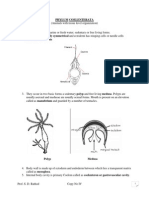
Course I: First semester Class- Ciliophora/ Ciliata (bearing cilia as locomotory organelle.) 1. Locomotory organelles are several hair-like cilia covering throughout the body; used for locomotion and feeding 2. Two nuclei; bigger kidney or horseshoe shaped called as meganucleus and a small micronuleus. Meganucleus controls all physiological activities whereas micronucleus performs reproductive activity. Fresh water forms have contractile vacuoles for osmoregulation. 3. The typical example of Class Ciliata is Paramecium. Paramecium: i. ii. It is free living fresh water form found in ponds or lakes. Body is slipper like due to presence of pellicle hence called as slipper cell animalcule. Ingests food through cytostome and cytopharynx whereas egests the undigested material through cytopyge. Body has two rosette shaped contractile vacuoles; one on each anterior and posterior ends. There are two nuclei; one kidney shaped and big meganucleus and another small micronucleus. Reproduction is carried by conjugation. Paramecium
iii.
iv.
v.
Prof. S. D. Rathod
Copy No II
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Unit:1 Kingdom Protista General Characters and Classification Upto Classes Locomotory Organelles and Locomotion in ProtozoaDocument34 pagesUnit:1 Kingdom Protista General Characters and Classification Upto Classes Locomotory Organelles and Locomotion in ProtozoaEgga AndiniPas encore d'évaluation
- Biodiversity Types and ImportanceDocument10 pagesBiodiversity Types and Importancekiran PoudelPas encore d'évaluation
- General Classification (All Phylum)Document16 pagesGeneral Classification (All Phylum)kiran PoudelPas encore d'évaluation
- 4.animalkingdom ResonanceDocument80 pages4.animalkingdom ResonanceEkta ManglaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Morphology and Physiology of Living Things: National Diploma in Science Laboratory TechnologyDocument99 pagesMorphology and Physiology of Living Things: National Diploma in Science Laboratory Technologyogbonna ebuka innocent100% (1)
- ZooLabParazoansSimpleMetazoansDocument8 pagesZooLabParazoansSimpleMetazoansAlexa Jean D. HonrejasPas encore d'évaluation
- ZOO211 MATERIALS With IntroductionDocument32 pagesZOO211 MATERIALS With IntroductionAdwale oluwatobi festusPas encore d'évaluation
- BIO 103 - All Notes-1 - Copy (2) - 1Document27 pagesBIO 103 - All Notes-1 - Copy (2) - 1judikidPas encore d'évaluation
- Njala University School of Environmental Sciences Department of Biological SciencesDocument52 pagesNjala University School of Environmental Sciences Department of Biological SciencesSheku KallonPas encore d'évaluation
- Survey of Protists: Protozoa and Slime MoldsDocument6 pagesSurvey of Protists: Protozoa and Slime MoldsGeorges SarkisPas encore d'évaluation
- Protozoa Definition: Protozoa May Be Defined As "Microscopic Acellular Animalcules Existing Singly or in ColoniesDocument13 pagesProtozoa Definition: Protozoa May Be Defined As "Microscopic Acellular Animalcules Existing Singly or in ColoniesRica NorcioPas encore d'évaluation
- Act. 1 - Animal-Like Protists - Instruction SheetDocument4 pagesAct. 1 - Animal-Like Protists - Instruction SheetMickeyPas encore d'évaluation
- Zoology (Book)Document26 pagesZoology (Book)sme olaplPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab Practical 1Document21 pagesLab Practical 1randy_sanchez_10Pas encore d'évaluation
- Invertebrate Biology: by Jane YaweDocument42 pagesInvertebrate Biology: by Jane YaweANYWAR SIMONPas encore d'évaluation
- Research No. 2Document46 pagesResearch No. 2Bai Putri Rohaina S. MalangPas encore d'évaluation
- Act.15 Animal-Like ProtistsDocument5 pagesAct.15 Animal-Like Protistsstudent10100Pas encore d'évaluation
- 7 Bio ClassificationDocument20 pages7 Bio ClassificationAuthor ClubPas encore d'évaluation
- TaxonomyDocument13 pagesTaxonomyDamilola NifemiPas encore d'évaluation
- Activity Animal KingdomDocument8 pagesActivity Animal KingdomGerald Agacid BangeroPas encore d'évaluation
- Protozoa Classification and CharacteristicsDocument3 pagesProtozoa Classification and CharacteristicsTrisha AlejandroPas encore d'évaluation
- Some Characteristics of The Phylum CnidariaDocument5 pagesSome Characteristics of The Phylum CnidariaTI Journals PublishingPas encore d'évaluation
- ANIMAL CLASSIFICATION GUIDEDocument22 pagesANIMAL CLASSIFICATION GUIDEAnne JoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Important Questions Class 11 Biology Chapter 6 Anatomy of Flowering PlantsDocument26 pagesImportant Questions Class 11 Biology Chapter 6 Anatomy of Flowering Plantsajinkyarsingh2006Pas encore d'évaluation
- Protozoans Chapter 11Document5 pagesProtozoans Chapter 11kingPas encore d'évaluation
- WameedMUCLecture 2021 92755384Document8 pagesWameedMUCLecture 2021 92755384rayankhan1290kPas encore d'évaluation
- Protozoans: Diverse Unicellular EukaryotesDocument45 pagesProtozoans: Diverse Unicellular EukaryotesStem 21 - Suyat, Justine Kay N.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Unicellular (Single-Celled) Protists - Eukaryotic Protozoan: EuglenaDocument3 pagesUnicellular (Single-Celled) Protists - Eukaryotic Protozoan: EuglenaEGSRHEtjykudli.u;Pas encore d'évaluation
- STUDY199@510614Document7 pagesSTUDY199@510614wanibilques1234Pas encore d'évaluation
- Phylum Protozoa-WPS OfficeDocument8 pagesPhylum Protozoa-WPS OfficeMark SudiePas encore d'évaluation
- Exam Additional NotsDocument31 pagesExam Additional NotsG MugzPas encore d'évaluation
- Pre-Lab Discussion of Activity 9-11Document7 pagesPre-Lab Discussion of Activity 9-11Maria HwasaPas encore d'évaluation
- Phylum PoriferaDocument18 pagesPhylum Poriferagonoles81Pas encore d'évaluation
- Kingdom AnimaliaDocument152 pagesKingdom AnimaliaS SPas encore d'évaluation
- P2C2 Group 3 Lab Report - Protozoa and PoriferaDocument7 pagesP2C2 Group 3 Lab Report - Protozoa and PoriferaAngela D.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Phylum PlatyhelminthesDocument11 pagesPhylum PlatyhelminthesasajumuthmainahPas encore d'évaluation
- Zoology Course OverviewDocument23 pagesZoology Course OverviewAbdirahman FarahPas encore d'évaluation
- MolluskDocument3 pagesMolluskJane ConstantinoPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 Animal KingdomDocument8 pages4 Animal KingdomPHANI KUMAR A.V.SPas encore d'évaluation
- Activity 15-23 SUMMARY UpdatedDocument7 pagesActivity 15-23 SUMMARY UpdatedZoe Kristeun GutierrezPas encore d'évaluation
- Kingdom: Protista: Protists Are Unicellular Organisms That Have A NucleusDocument48 pagesKingdom: Protista: Protists Are Unicellular Organisms That Have A NucleusYoumiePas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 3 - Sponges and Cnidaria PDFDocument47 pagesLecture 3 - Sponges and Cnidaria PDFJordan LewisPas encore d'évaluation
- ANIMAL SYMMETRY AND TISSUE GRADEDocument6 pagesANIMAL SYMMETRY AND TISSUE GRADERajdeep GhoshPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab Manual Animal Systematic II 2017 - Activity IDocument2 pagesLab Manual Animal Systematic II 2017 - Activity IVio Indah BudiartiPas encore d'évaluation
- BIOLOGYDocument11 pagesBIOLOGYSungdeok MinPas encore d'évaluation
- PLATYHELMINTHES AND MOLLUSCA LAB REPORTDocument7 pagesPLATYHELMINTHES AND MOLLUSCA LAB REPORTYasmine AurelliaPas encore d'évaluation
- BTM 111 22Document24 pagesBTM 111 22Toke SadockPas encore d'évaluation
- Kingdom: Protista: Protists Are Unicellular Organisms That Have A NucleusDocument61 pagesKingdom: Protista: Protists Are Unicellular Organisms That Have A NucleusYoumiePas encore d'évaluation
- Structure and FunctionDocument12 pagesStructure and FunctionJustine PamaPas encore d'évaluation
- LOPEZC - Biology NotesDocument11 pagesLOPEZC - Biology Notescasey lPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 33 Learning ObjectivesDocument7 pagesChapter 33 Learning ObjectivesMorgan MatthewsPas encore d'évaluation
- BiologyDocument12 pagesBiologyKamran SaleemPas encore d'évaluation
- Protista LaboratoryDocument22 pagesProtista LaboratoryRicardo RicoPas encore d'évaluation
- ProtozoaDocument26 pagesProtozoaAbul VafaPas encore d'évaluation
- Kingdom ProtistaDocument27 pagesKingdom ProtistaHELMA B. JABELLOPas encore d'évaluation
- ProtistDocument5 pagesProtistGerald Agacid BangeroPas encore d'évaluation
- Protista Written ReportDocument8 pagesProtista Written ReportLance RiveraPas encore d'évaluation
- Animal KingdomDocument47 pagesAnimal KingdomMeenal MeshramPas encore d'évaluation
- Characteristics of Animals-2Document23 pagesCharacteristics of Animals-2api-297087367Pas encore d'évaluation
- Correlation of Hepatosomatic Index I H ADocument15 pagesCorrelation of Hepatosomatic Index I H ASudesh RathodPas encore d'évaluation
- Qualitative Study of Fisheries Species DDocument8 pagesQualitative Study of Fisheries Species DSudesh RathodPas encore d'évaluation
- Feeding Habit and Pollution Indicating Food Items PDFDocument3 pagesFeeding Habit and Pollution Indicating Food Items PDFSudesh RathodPas encore d'évaluation
- Behavioural Studies of Boleophthalmus DussumieriDocument5 pagesBehavioural Studies of Boleophthalmus DussumieriSudesh RathodPas encore d'évaluation
- Surficial Emergence of Boleophthalmus Dussumieri (Val., 1837) Synchronized With Tidal Oscillation On The Silted Intertidal Mudflats of Ulhas RiverDocument5 pagesSurficial Emergence of Boleophthalmus Dussumieri (Val., 1837) Synchronized With Tidal Oscillation On The Silted Intertidal Mudflats of Ulhas RiverSudesh RathodPas encore d'évaluation
- The Relationship of Spatial Fisheries Diversity With Hydrological Conditions of Ulhas River EstuaryDocument11 pagesThe Relationship of Spatial Fisheries Diversity With Hydrological Conditions of Ulhas River EstuarySudesh RathodPas encore d'évaluation
- Artisanal Fisheries Landings During PreDocument10 pagesArtisanal Fisheries Landings During PreSudesh RathodPas encore d'évaluation
- Plastic Peril On Species Diversity and Fish CatchDocument7 pagesPlastic Peril On Species Diversity and Fish CatchSudesh RathodPas encore d'évaluation
- Levels of Organization in AnimalsDocument4 pagesLevels of Organization in AnimalsSudesh RathodPas encore d'évaluation
- Phylum Coelenterata ClassificationDocument3 pagesPhylum Coelenterata ClassificationSudesh Rathod100% (1)
- Comparative Embryology, Aspects of Human Reproduction Pollution and Its Effect On OrganismsDocument35 pagesComparative Embryology, Aspects of Human Reproduction Pollution and Its Effect On OrganismsSudesh RathodPas encore d'évaluation
- Phylum Porifera ClassificationDocument3 pagesPhylum Porifera ClassificationSudesh RathodPas encore d'évaluation
- Sybsc Sem III Course VII Unit1, ETHOLOGYDocument22 pagesSybsc Sem III Course VII Unit1, ETHOLOGYSudesh Rathod100% (1)
- Chronospatial Frequency of Fishing Gears Used Along The Ulhas River EstuaryDocument7 pagesChronospatial Frequency of Fishing Gears Used Along The Ulhas River EstuarySudesh RathodPas encore d'évaluation
- Qualitative Study of Fin Fish and Shell Fish Fauna of Thane Creek and Ulhas River EstuaryDocument8 pagesQualitative Study of Fin Fish and Shell Fish Fauna of Thane Creek and Ulhas River EstuarySudesh RathodPas encore d'évaluation
- Spatio-Ecological Approach To Environmental Management of Three Neretic Ecosystems Along Maharashtra Coast, IndiaDocument2 pagesSpatio-Ecological Approach To Environmental Management of Three Neretic Ecosystems Along Maharashtra Coast, IndiaSudesh RathodPas encore d'évaluation
- Feeding Habits of Boleophthalmus Dussumieri (Cuv. & Val.) From Ulhas River Estuary Near Thane City, Maharashtra StateDocument7 pagesFeeding Habits of Boleophthalmus Dussumieri (Cuv. & Val.) From Ulhas River Estuary Near Thane City, Maharashtra StateSudesh RathodPas encore d'évaluation
- FYBSc Course-I, Semester-II, Ethology, Question Bank, SudeshrathodDocument2 pagesFYBSc Course-I, Semester-II, Ethology, Question Bank, SudeshrathodSudesh RathodPas encore d'évaluation
- Seasonal Assessment of Some Physico-Chemical Parameters of Ulhas River Estuary, in The Vicinity of Thane City, MaharashtraDocument1 pageSeasonal Assessment of Some Physico-Chemical Parameters of Ulhas River Estuary, in The Vicinity of Thane City, MaharashtraSudesh RathodPas encore d'évaluation
- Food and Feeding Habit of Boleophthalmus Dussumieri (Cuv. & Val.) From Ulhas River Estuary Near Thane City, Maharashtra StateDocument2 pagesFood and Feeding Habit of Boleophthalmus Dussumieri (Cuv. & Val.) From Ulhas River Estuary Near Thane City, Maharashtra StateSudesh RathodPas encore d'évaluation
- Effect of Pollution On Mudskipper Fishery of Ulhas River Estuary With A Special Reference To The Biology of Boleopthalmus Dussumieri (Cuv. & Val.)Document61 pagesEffect of Pollution On Mudskipper Fishery of Ulhas River Estuary With A Special Reference To The Biology of Boleopthalmus Dussumieri (Cuv. & Val.)Sudesh RathodPas encore d'évaluation
- Assessment of Pollution Status of Ambient Water Bodies Using Food Selection Habit of Mystus Gulio (Ham.) From Ulhas River Estuary and Thane Creek in The Vicinity of Thane, MaharashtraDocument1 pageAssessment of Pollution Status of Ambient Water Bodies Using Food Selection Habit of Mystus Gulio (Ham.) From Ulhas River Estuary and Thane Creek in The Vicinity of Thane, MaharashtraSudesh RathodPas encore d'évaluation
- Food and Feeding Habit of Mystus Gulio (Ham.) From Ulhas River Estuary and Thane CreekDocument1 pageFood and Feeding Habit of Mystus Gulio (Ham.) From Ulhas River Estuary and Thane CreekSudesh RathodPas encore d'évaluation
- Spatial Fin-Fishery Species Diversity of Ulhas River EstuaryDocument1 pageSpatial Fin-Fishery Species Diversity of Ulhas River EstuarySudesh RathodPas encore d'évaluation
- Assessment of Some Hydrological Parameters of Ulhas River Estuary, in The Vicinity of Thane City, Maharashtra State.Document6 pagesAssessment of Some Hydrological Parameters of Ulhas River Estuary, in The Vicinity of Thane City, Maharashtra State.Sudesh RathodPas encore d'évaluation
- Animal BehaviorFYBSc2004Document17 pagesAnimal BehaviorFYBSc2004Sudesh RathodPas encore d'évaluation
- Test I. Blood Puzzle: Find The Words Listed Below in The Word SearchDocument2 pagesTest I. Blood Puzzle: Find The Words Listed Below in The Word SearchPilarieBernalPas encore d'évaluation
- A New Evolutionary Law of Constant Extinction RatesDocument30 pagesA New Evolutionary Law of Constant Extinction RatesMarcos Vinicius Monteiro100% (1)
- Types of Culture MediaDocument39 pagesTypes of Culture Mediaw5waPas encore d'évaluation
- General Biology - q2 - Week 4Document33 pagesGeneral Biology - q2 - Week 4Renard JaenPas encore d'évaluation
- Department of Education: Tle-Cookery Assessment - Grade 10 Quarter 1 Week 1Document2 pagesDepartment of Education: Tle-Cookery Assessment - Grade 10 Quarter 1 Week 1IvyRoseBarcilloAlivioPas encore d'évaluation
- Kementerian Agama Republik Indonesia: Penilaian Akhir Semester Ganjil Madrasah Aliyah TAHUN PELAJARAN 2020-2021Document7 pagesKementerian Agama Republik Indonesia: Penilaian Akhir Semester Ganjil Madrasah Aliyah TAHUN PELAJARAN 2020-2021Aisyah DPas encore d'évaluation
- The Weekly Time Table For Year I Semester II of 2016 - 2017 FinalDocument26 pagesThe Weekly Time Table For Year I Semester II of 2016 - 2017 FinalsoePas encore d'évaluation
- Walk-In-Interview in CRPFDocument1 pageWalk-In-Interview in CRPFDevi PrasadPas encore d'évaluation
- Cancer and The Cell CycleDocument42 pagesCancer and The Cell CycleBrayan CuevasPas encore d'évaluation
- Ginther, 1998 Equine PregnancyDocument32 pagesGinther, 1998 Equine PregnancyAdrian Ayala GutierrezPas encore d'évaluation
- Sexual Reproduction in PlantsDocument23 pagesSexual Reproduction in PlantsStephen AreriPas encore d'évaluation
- DP1 BIO - Test - Topic 1 Paper 1 PDFDocument6 pagesDP1 BIO - Test - Topic 1 Paper 1 PDFSaima SyedaPas encore d'évaluation
- LMRP Physio, BiochemistryDocument5 pagesLMRP Physio, BiochemistryAzhar MohamadPas encore d'évaluation
- Gender Is It A Social Construct or A Biological InevitabilityDocument5 pagesGender Is It A Social Construct or A Biological InevitabilitySaurabhChoudharyPas encore d'évaluation
- Secondary Structure of ProteinDocument3 pagesSecondary Structure of ProteinSahrEmmanuelJr.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Tackling heat stress in poultry production with ImmunotechDocument2 pagesTackling heat stress in poultry production with ImmunotechAbtl Enzymes100% (2)
- RFLP Teaching KitDocument5 pagesRFLP Teaching Kitkuldip.biotechPas encore d'évaluation
- Synaptic IntegrationDocument3 pagesSynaptic IntegrationOmar AlemánPas encore d'évaluation
- Muscle FibresDocument3 pagesMuscle FibresOliviaMcCarthy6100% (1)
- Drug DesignDocument38 pagesDrug DesignPhArMaCyGrAdUaTeSPas encore d'évaluation
- Plant Anatomy: Structure and FunctionsDocument8 pagesPlant Anatomy: Structure and FunctionsWimartama WayanPas encore d'évaluation
- IBO 2005 Pract Part 4Document14 pagesIBO 2005 Pract Part 4pdbiocompPas encore d'évaluation
- Histologi Usus Ikan NilaDocument14 pagesHistologi Usus Ikan NilaOnnaSafuraPas encore d'évaluation
- Robbins Notes: Aging, Radiation, and Inflammation Self StudyDocument44 pagesRobbins Notes: Aging, Radiation, and Inflammation Self StudyJustine HungPas encore d'évaluation
- Patent EsDocument10 pagesPatent Esalcorrea2009Pas encore d'évaluation
- Starch and Microbial α-Amylases: From Concepts to Biotechnological ApplicationsDocument30 pagesStarch and Microbial α-Amylases: From Concepts to Biotechnological ApplicationsIndrayana PratamaPas encore d'évaluation
- Effects of High Temperature On Nodulation and Nitrogen Fixation byDocument8 pagesEffects of High Temperature On Nodulation and Nitrogen Fixation byFábio Luís MostassoPas encore d'évaluation
- Primary Assignment 1 Science 1Document15 pagesPrimary Assignment 1 Science 1IslamBachaMkdPas encore d'évaluation
- Konsep Dasar ToksikologiDocument63 pagesKonsep Dasar ToksikologiSaber LohengarmPas encore d'évaluation
- Dna Sequencing ThesisDocument7 pagesDna Sequencing Thesisdwndnjfe100% (2)