Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Final Paper
Transféré par
api-239711546Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Final Paper
Transféré par
api-239711546Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Griffin Moore Ninth Grade Literature Mrs.
White 7 March 2012
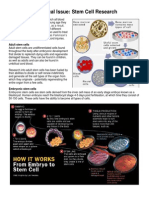
Why does the government give one billion dollars to the research of stem cells (Friedman 23)? In the past 22 years the controversy of stem cell research has been going on in countries like China, Japan, Germany, Israel, and many other countries (Friedman 18). As of this year there has been a delay in the United States for stem cell research. Much of the population in America thinks that it is morally wrong and is the destruction of life. Others think that this is the future and what science will come to be and will thrive on to build new and healthy organs. The United States is getting behind other countries with stem cell research, which can save lives. Stem cells are the beginning of the growth of a fetus (Basic Stem Cell Biology). Many cells have their own special job like working in the heart or the lungs, but with stem cells they can become any type of cell and work anywhere in the body. This tells the stem cells what to change to turn into an organ is the locus or location ("The Story of iPS Cells). This means if the stem cell is on the outside it might make the limbs or skin but if it is near the middle, it could be the heat or lungs. Stem cells are divided up into two groups. They are unspecialized cells capable of renewing themselves through cell division, sometimes after long periods of inactivity. Another is under certain physiologic or experimental conditions; they can be induced to become tissue- or organ-specific cells with special functions. There are two types of stem cells Embryonic and adult stem cells(Basic Stem Cell Biology). Many people think that embryonic stem cell research is morally wrong and is taking
a life. Once the sperm fertilizes the egg it forms a single cell called a zygote. But after around eight days it forms more and more cells and becomes an embryo. This is where it takes on the title of having a life. Many religious groups say those scientists who kill the embryo to take out stem cells are playing the role of god and that science and religion shouldnt mix. In the stem cells research scientist has been finding new ways to cure cancer and other diseases such as asthma and diabetes. Many people think that this is the new scientific revolution. These two types of stem cells are. There are Adult stem cells and embryonic stem cells. The adult stem cells are usually found in bone marrow and blood cells. They are not able to be changed into different types of cells and used to make other organs. Often after about sixty days if the body has not rejected the cells they are formed into as if they werent even transplanted. Embryonic stem cells are found after the zygote and before the embryo are formed. The scientist has to go into the embryo and eject the cells. These types of stem cells are able to be formed into different types of organs such as the heart, lungs, stomach, liver, and many other features on the body. Scientist thinks that they could cure cancer and other serious diseasesStem (Cells: Early Research). In the controversy of stem cell research, the United States Government needs to fund it for the health of people and to find new ways to keep us safe. As much as people against stem cell research have a good opinion about it, but its still the best way to go to study stem cells and learn more from what they are about and what we can do with them. We can learn more and figure out how to advance the way we heal and enhance our science department in the United States.
Works Cited Basic Stem Cell Biology. University of Wisconsin Stem Cells and Regenreration Medicine Center. 14 February 2012. 6 March 2012. <http://stemcells.wisc.edu/research/biology.html>. Friedman, Lauri S. and Hal Marcovitz. Is Stem Cell Research Necessary?. San Diego: Reference Point Press, 2010. Haerens, Margaret. Embryonic and Adult Stem Cells. Farmington Hills: Greenhaven Press, 2009. History of Stem Cell Research A Timeline. Childrens Hospital Boston. 2012. About Stem Cells. 28 February 2012 < http://stemcell.childrenshospital.org/about-stemcells/history/>. Stem Cells: Early Research. Online. NOVA science NOW, 2005. "The Story of iPS Cells." Genetic Science Learning Center. 2012.6 March 2012. <http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/tech/stemcells/ips/>.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Tissue EngineeringDocument32 pagesTissue Engineeringbrian3442Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Periodontal RegenerationDocument8 pagesMesenchymal Stem Cells and Periodontal Regenerationkishore KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- 7 Bioethical Issue - Stem CellsDocument4 pages7 Bioethical Issue - Stem Cellsapi-247725573Pas encore d'évaluation
- Alternatives To Animal ExperimentsDocument50 pagesAlternatives To Animal ExperimentsSyama J.SPas encore d'évaluation
- IF-2020 - Manual For EvaluatorsDocument58 pagesIF-2020 - Manual For EvaluatorsArchaeoAnalytics MeetingPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 2 - Stem Cells PPT NotesDocument8 pagesLesson 2 - Stem Cells PPT NotesJoseePas encore d'évaluation
- Stem Cells Therapy For Spinal Cord Injury 2018Document14 pagesStem Cells Therapy For Spinal Cord Injury 2018bhirau wilaksonoPas encore d'évaluation
- 12 TransplantationDocument137 pages12 TransplantationLee BoborasPas encore d'évaluation
- GEC STS - Finals ReviewerDocument17 pagesGEC STS - Finals ReviewerUrsula Grace LucaPas encore d'évaluation
- Current Status and Challenges of Stem Cell Treatment For Alzheimer's DiseaseDocument19 pagesCurrent Status and Challenges of Stem Cell Treatment For Alzheimer's DiseaseHelical Nail FemurPas encore d'évaluation
- Stem CellsDocument3 pagesStem Cellsapi-238545091Pas encore d'évaluation
- Stem Cell ProjectDocument6 pagesStem Cell Projectapi-133818838Pas encore d'évaluation
- ETHICS 2.2 FinalsDocument36 pagesETHICS 2.2 FinalsDenisse RoblesPas encore d'évaluation
- Stem Cells - Scribd PDFDocument7 pagesStem Cells - Scribd PDFBinusha ShabuPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 3 Lesson 11 Gene TherapyDocument10 pagesModule 3 Lesson 11 Gene TherapyJannie Rose MarquezPas encore d'évaluation
- A Project On Stem Cell Therapy: Submitted ToDocument35 pagesA Project On Stem Cell Therapy: Submitted ToLoks100% (1)
- GROUP 9 STS Research Term Paper On Stem CellDocument13 pagesGROUP 9 STS Research Term Paper On Stem Cellintroverted bossPas encore d'évaluation
- Soal News ItemDocument8 pagesSoal News ItemWiwin IsmailPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology of Stem Cells: An Overview: Pedro C. Chagastelles and Nance B. NardiDocument5 pagesBiology of Stem Cells: An Overview: Pedro C. Chagastelles and Nance B. NardiMayuri DuttaPas encore d'évaluation
- Science - 6 September 2013Document119 pagesScience - 6 September 2013martin.catalin1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Stem Cells Notes - BIO SUmmDocument3 pagesStem Cells Notes - BIO SUmmMuffaddal MustafaPas encore d'évaluation
- Stem Cell Therapy: Laguna State Polytechnic University San Pablo CityDocument12 pagesStem Cell Therapy: Laguna State Polytechnic University San Pablo CityAndromeda GalaxyPas encore d'évaluation
- Embryonic Stem CellsDocument6 pagesEmbryonic Stem CellsTakwa ShlakiPas encore d'évaluation
- General Biology AssignmentDocument3 pagesGeneral Biology AssignmentGladjeanwirl CañetePas encore d'évaluation
- Induced PluripotentDocument15 pagesInduced PluripotentmeghnaPas encore d'évaluation
- Stem Cells and Their ApplicationDocument16 pagesStem Cells and Their ApplicationRam Kewal TripathiPas encore d'évaluation
- Abstract BookDocument241 pagesAbstract BookMuhammad AsaduzzamanPas encore d'évaluation
- Tugas News Item KLS XiiDocument18 pagesTugas News Item KLS XiisuhaeniPas encore d'évaluation
- Embryonic Stem CellsDocument3 pagesEmbryonic Stem CellsRajPas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding Stem CellsDocument26 pagesUnderstanding Stem CellsNational Academies of Science, Engineering, and Medicine96% (23)