Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
LDS Exam Notes
Transféré par
Nur AliaTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
LDS Exam Notes
Transféré par
Nur AliaDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
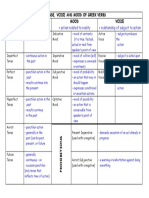
Word Class
Word Class Noun Pronoun Adjective Preposition Verb Adverb Conjunction Interjection Determiner
Verbs and Tenses Simple Present (SPr) Active: Base form, + s Passive: am/is/are + past participle Present Continuous (PrC) Active: am/is/are + present participle Passive: am/is/are + being + past participle Present Perfect (PrP) Active: has/have + past participle Passive: has/have + been + past participle Present Perfect Continuous (PrPC) Active: has/have + been + present participle Passive: rarely used
Example House, John Him, His Beautiful, stupid On, At Cooking, Running Nicely, wonderfully And, But Wow! The, that
Collapses, throws Is swept, are formed Are (you) listening, is living Are being eroded, is being built
Has done, has provided Have been questioned
Has been wanting, have been watching
Simple Past (SPs) Active: Simple past form (-ed) Passive: was/were + past participle Past Continuous (PsC) Active: was/were + present participle
Collided, failed Were killed, was passed Was speeding, was raining
Passive: was/were + being + past participle Past Perfect (PsP) Active: had + past participle Passive: had + been + past participle Past Perfect Continuous (PsPC) Active: had + been + present participle Passive: Rarely used Active (FA) will/shall + bare infinitive (base form) Passive (FP) will/shall + be + past participle Continuous (FC) will/shall + be + present participle Perfect (FPe) will/shall + have + past participle Perfect Continuous (FPC) will/shall + have + been + present participle
Was being cut, were being hanged
Had lived, had torn Had been lost, had been fixed Had been looking
Will announce Shall be done Will be sailing Will have spent Will have been looking
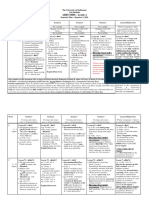
DIRECT SPEECH SPs Tom said, I saw Mike at the cinema. PrP Tom said, I have lost my watch. PrPC Joe said, I have been waiting for hours. PsC Kate said, I was trying to help.
-> -> -> ->
INDIRECT SPEECH PsP Sue said that she had seen Mike at the cinema. PsP Tom said that he had lost his watch. PsPC Joe said that he had been waiting for hours. PsPC Kate said that she had been trying to help.
Subject-Verb Agreement
1. Countable Nouns = Singular noun -> singular verb, Plural noun -> plural verb - A movie ticket costs RM8 on weekdays. - They leave their office at 7 p.m. everyday.
2. All uncountable nouns -> singular verb - Permission is granted for Air Force to land. - Evidence shows that the suspect was in the room with the victim.
3. Indefinite Pronoun (everyone, everybody) -> singular verb - Everyone associated with the project is proud to be part of the effort. - Someone has to be responsible.
4. Some phrases may contain plural words -> just focus on the subject pronoun - Each of the project partners is responsible for writing a chapter summary.
5. All, some -> refer back to the subject whether is countable or not - Some of the students in the class have voted already. *students is plural = plural verb have is used+ - Some of the grain was ruined by the flood. *grain is uncountable = singular verb was is used+ None can have both plural and singular verb
o None of us have any idea where did he went. *plural+ o None of us has any idea where did he went. *singular+
6. Fractional -> refer to subject whether it is countable or not - Two-fifth of the grain is ruined. *grain is uncountable = singular verb is is used+ - One-half of the students were convinced that there would be no final exam this year. *students is plural = plural verb were is used+
7. Phrases together with, along with, as well as -> can be ignored - Some of the hay in the barn, as well as some major pieces of farm equipment, was ruined in the flood. *hay is uncountable = singular verb was is used+
8. Either, Neither when stands alone -> singular verb - Neither of these choices appears to be satisfactory.
9. Eitheror, Neithernor (as correlative conjunction) -> refer to subject closer to the verb - Neither the principal nor the teachers are at fault. - Neither the teachers nor the principal is at fault.
10.Empty subject (there is, there are) -> refer to subject that comes after the verb - There are several explanations for the problem.
- Here come John and his two brothers. Phrases Phrases Noun Phrases (determiner + noun) Adjectival Phrases (intensifier + adjective) Adverbial phrases (adverb + intensifier / other noun) Prepositional Phrases (Prep + det + noun) More clearly, quickly to the rubbish bin To the school, in the bin, in the city Examples The school, the crazy man Very beautiful, very small
Clauses Noun Clause can be replaced by other pronouns a) Type of Clause - Start with these words that Wh-word (who, when, what, where, which, why, how) Wh-ever word The prince will marry whoever walks through that door. Whether If I dont know whether he will recover. I dont know if Fadzil has a job. He thinks that this audition is easy. Everybody wondered where he lives.
b) Function of clauses As subject of sentence That he has disappeared is a mystery. (can be replaced with it) Object of the sentence Her friends didnt like what she was saying. (can be replaced with that) Subject complement Her mistake was that she kept lying. (can be replaced with this) Object of preposition The search party looks into whatever is applicable. (can be replaced with it) Adjective complement She is afraid that the search is a failure.
Adverbial Clause (the function is usually adverbial too) - Answers questions of: Why? When? Where? How? How Long?
- Introduced by subordinating conjunctions as if he is so smart Wherever he likes
while she is free Adjectival Clause Pattern of clause - Relative Pronoun + Subject + Verb that she likes
although he loves her so much
(Rel. Pro) (Subject) (Verb)
- Relative Pronoun + Verb who sits beside me
(Rel. Pro) (Verb) Common relative pronouns and adverbs who that which where whom when Whose why
Function of Clause - Answers question: what kind? Which one? How many? - Provides extra information to the sentence - Subject complement Faiz, who scored high marks in the exam, lives in Selangor.
Cohesive Devices a) Logical connectors - Are usually conjunctions - Connects two ideas so they have a flow between them - FANBOYS, subordinating conjunctions, correlative conjunctions
The TV programme CSI is very popular among the young. As a result, many of them are interested in forensic science. b) Grammatical Devices - Are usually pronouns - This, That etc. Artists have great imagination. This helps them to produce amazing works. c) Lexical Devices - Words that replaces others - Synonyms, words that link to each other
Sentence Types a) Simple Sentence - One clause - Made up of 1 subject + 1 predicate - Noun phrase + Verb phrase - Only have 1 verb, but can have compound subject - E.g. Joe has two brothers. I wanted to have some cakes and sweets. The fish died.
b) Compound Sentence - Made up of two different simple sentences (independent clauses) - Have two subjects + two verbs - Joined by FANBOYS (for, and, nor, but, yet, so)
- E.g. I went to the market and bought some vegetables. Sally picked up the cat and stroked it gently.
c) Compound Sentences - Made up of 1 independent clause (main clause) + 1 dependant clause (subordinating clause) - Joined by subordinating conjunctions (because, since, after, although, before, if, while etc.) and relative pronouns (that, who, whom, which, whose etc.) - E.g. The earthquake struck while we were at the study hall. Although he had studied hard, he still fails the test. Sentence Patterns 1. Subject + Verb (SV) The chair breaks. The bird flies. Fahri smiles.
2. Subject + Verb + Object (SVO) Joseph kicked the ball. The boys build the tree-house. The men captured the thief.
3. Subject + Verb + Adverbial (SVA) My parents are at the bank. Miss Florence has been here before.
We were in the forest.
4. Subject + Verb + Complement (SVC) Miss Joanne was my music teacher. The boys are hungry. My sister is in a bad mood.
5. Subject + Verb + Object + Object (SVOO) *(2 objects = Indirect + Direct) I gave my mother a bouquet of flowers. Our boss gave us some bonus. Jimmy cooked some spaghetti for his guests.
6. Subject + Verb + Object + Complement (SVOC) The warden found the prisoner dead. Everyone calls Fahri a genius. We elected her the president.
7. Subject + Verb + Object + Adverbial (SVOA) Mother cooks for us every day. John is baking some muffins for his children. Amy is donating some books for the new library.
Direct Speech -> Indirect Speech 1. Change in punctuation marks. 2. Change in reporting verbs. 3. Change in pronoun.
4. Change in tense DIRECT SPEECH SPs Tom said, I saw Mike at the cinema. PrP Tom said, I have lost my watch. PrPC Joe said, I have been waiting for hours. PsC Kate said, I was trying to help. INDIRECT SPEECH PsP Sue said that she had seen Mike at the cinema. PsP Tom said that he had lost his watch. PsPC Joe said that he had been waiting for hours. PsPC Kate said that she had been trying to help.
-> -> -> ->
5. Change in modal verb forms Direct Speech am/is/were was/were has/have will/shall can may Indirect Speech
-> -> -> -> -> ->
was/were had been had would could might
6. Change in time references Direct Speech tomorrow Today Indirect Speech
-> ->
the next day/the following day That day/the same day
Tonight Yesterday
That night The day before/ the previous day
Last night/week/month/year
->
The previous night/ week/month/year
Next night/week/month/year
The following night/ week/month/year
The day before yesterday The day after tomorrow Two days ago Now
-> -> -> ->
Two days before In two days time Two days before Then
Sentence Moods 1. Declarative mood - Stating facts to give details, facts, information - Ends with a period (.) - E.g. Bangkok is the capital of Thailand. I have completed my work.
2. Interrogative mood - To ask, to require information, to investigate, to request - Starts with modal verbs (will, should) or wh-questions (what, who etc.), ends with a question mark (?) - E.g. Is this your son? Do you need my help? What is happening?
3. Imperative mood - To instruct, give order, give command - Usually the subject of sentence is dropped Watch out! (You watch out!) - E.g. Let them go. Dont pluck the flowers! Do be careful.
4. Exclamatory mood - To express admiration, strong emotions and feelings - Ends with an exclamation mark (!) - E.g. How lovely you look! Isnt that a shame!
5. Subjunctive mood - Express doubt, conditions that may or may not happen - Express hope, suggestion - Usage of modal verbs (could, should, might, may, would) - Usage of subordinate conjunction if - E.g. If I should see her, I will tell her the decision. If I were you, I would be so happy. I wish that we will have a better leader.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Formation of Interrogative SentencesDocument7 pagesFormation of Interrogative SentencesAnonymous Fn7Ko5riKTPas encore d'évaluation
- E G E E G E: Nglish - Eneral Ducation Nglish - Eneral DucationDocument44 pagesE G E E G E: Nglish - Eneral Ducation Nglish - Eneral DucationKirito NajdPas encore d'évaluation
- PMR English Language ModulesDocument86 pagesPMR English Language Moduleshoneym694576100% (4)
- Whom, Whomever, and Why.: Nama Kelompok: PRICILLIA SITOMPUL 1901055115 Lesson: Paragraph Writing Class: 3DDocument10 pagesWhom, Whomever, and Why.: Nama Kelompok: PRICILLIA SITOMPUL 1901055115 Lesson: Paragraph Writing Class: 3Dcil laPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 2material - HS3252 - Professional English IiDocument15 pagesUnit 2material - HS3252 - Professional English Iikavishmasr2006Pas encore d'évaluation
- English Grammar GuideDocument44 pagesEnglish Grammar GuideJ MhheaPas encore d'évaluation
- TensesDocument35 pagesTensesTanuj DwivediPas encore d'évaluation
- The Past Simple Tense: Zion LanguagesDocument20 pagesThe Past Simple Tense: Zion LanguagesZion LanguagesPas encore d'évaluation
- The Past Simple Tense: Zion LanguagesDocument20 pagesThe Past Simple Tense: Zion LanguagesZion LanguagesPas encore d'évaluation
- TENSES IN ENGLISHDocument49 pagesTENSES IN ENGLISHPepy_GumilarPas encore d'évaluation
- Modul PMR (Jawab Untuk Semua Subjek A')Document87 pagesModul PMR (Jawab Untuk Semua Subjek A')mummyhartiniPas encore d'évaluation
- Articles and Pronouns GuideDocument8 pagesArticles and Pronouns GuideAdzimah ZullPas encore d'évaluation
- Makalah Bahasa Inggris 222 111Document9 pagesMakalah Bahasa Inggris 222 111cheese cakePas encore d'évaluation
- Grammar Guide to Subject-Verb AgreementDocument10 pagesGrammar Guide to Subject-Verb AgreementNathanaelPas encore d'évaluation
- English Class Part OneDocument19 pagesEnglish Class Part Onechristina ndong nkoghePas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Sentence StructuresDocument20 pagesBasic Sentence StructuresCarla GarciaPas encore d'évaluation
- Brown Aesthetic Group Project PresentationDocument44 pagesBrown Aesthetic Group Project Presentationmutiah mutiaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Verb Tense 1 SL PracticeDocument33 pagesVerb Tense 1 SL PracticecdivishyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Reported SpeechDocument24 pagesReported SpeechjuliareveronraPas encore d'évaluation
- Present Perfect Rules and ExplanationsDocument17 pagesPresent Perfect Rules and ExplanationsmanuelaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 1 TENSEDocument18 pagesLecture 1 TENSEKamran AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- ReviewDocument27 pagesReviewMārtiņš DriksnaPas encore d'évaluation
- Discussion Notes - Subject - Verb Agreement CompleteDocument3 pagesDiscussion Notes - Subject - Verb Agreement CompleteFrancis Guerrero TimbalPas encore d'évaluation
- Licence 1 English GrammarDocument28 pagesLicence 1 English GrammarAïda KouabenanPas encore d'évaluation
- Central University of Ecuador Faculty of Philosophy, Science and Letter of Education Semipresencial Subject: Morphology Name: Ana OrozcoDocument17 pagesCentral University of Ecuador Faculty of Philosophy, Science and Letter of Education Semipresencial Subject: Morphology Name: Ana OrozcoanyamorPas encore d'évaluation
- Grammar Review Part of Speech, Tenses, and Active and Passive VoiceDocument45 pagesGrammar Review Part of Speech, Tenses, and Active and Passive VoiceAmida UrfaPas encore d'évaluation
- Administración Inglés 3 Texto Paralelo FinalDocument29 pagesAdministración Inglés 3 Texto Paralelo FinalLN NLPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Sentence PatternDocument20 pagesBasic Sentence PatternShiella Monce AllawiganPas encore d'évaluation
- Reported SpeechDocument10 pagesReported SpeechNgọc TâmPas encore d'évaluation
- Reported SpeechDocument27 pagesReported SpeechOlga ChirondaPas encore d'évaluation
- Tugas Remidial Bahasa Inggris: Oleh: SUIN - XI TKJA - 30Document24 pagesTugas Remidial Bahasa Inggris: Oleh: SUIN - XI TKJA - 30benpaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Text Completion Tips and StrategiesDocument86 pagesText Completion Tips and Strategiespain_rinneganPas encore d'évaluation
- AgreementDocument18 pagesAgreementnandaPas encore d'évaluation
- 1st Sem Functional Grammar Module 1 & 2 Notes - KrishtalkzDocument64 pages1st Sem Functional Grammar Module 1 & 2 Notes - Krishtalkzzayanmv7Pas encore d'évaluation
- Present Simple Grammar GuideDocument6 pagesPresent Simple Grammar GuideWill MillerPas encore d'évaluation
- Part of SpeechDocument7 pagesPart of Speechbarens soPas encore d'évaluation
- w3 English For Academic and Professional Purposes HandoutDocument107 pagesw3 English For Academic and Professional Purposes Handoutnathansola09Pas encore d'évaluation
- Tenses UsageDocument99 pagesTenses Usagemayank.singh.carePas encore d'évaluation
- Indirect Speech, Relative Clause, Passive VoiceDocument22 pagesIndirect Speech, Relative Clause, Passive VoiceFebby DwiPas encore d'évaluation
- C. Pre-IntermediateDocument13 pagesC. Pre-IntermediateJenelFernandezPas encore d'évaluation
- SUMMARY OF TENSES AND VERB FORMSDocument29 pagesSUMMARY OF TENSES AND VERB FORMSjojinjoPas encore d'évaluation
- AKPER TKT I - MATERI 2 & 3 Dan 4Document30 pagesAKPER TKT I - MATERI 2 & 3 Dan 4Ivy TangkabiringanPas encore d'évaluation
- Eng1 TopicsDocument5 pagesEng1 TopicsKatrina SantosPas encore d'évaluation
- Reported Speech CompleteDocument6 pagesReported Speech Completegloriasd2005Pas encore d'évaluation
- Reported Speech TheoryDocument4 pagesReported Speech TheoryanabelvilchesPas encore d'évaluation
- DsasdasDocument5 pagesDsasdasRizky GunawanPas encore d'évaluation
- Gcse French Complex Structures 1Document56 pagesGcse French Complex Structures 1api-24083262950% (2)
- Part of Speech RecoveredDocument17 pagesPart of Speech RecoveredMuhammad Primastri100% (1)
- GED Subject Verb AgreementDocument18 pagesGED Subject Verb Agreementhninthant83Pas encore d'évaluation
- Subject: 1. Basic English Sentence StructureDocument7 pagesSubject: 1. Basic English Sentence StructureMatthew de SouzaPas encore d'évaluation
- VERBS: FORMS AND FUNCTIONSDocument106 pagesVERBS: FORMS AND FUNCTIONSclaudia monroyPas encore d'évaluation
- USE FormDocument17 pagesUSE FormBernardo RochaPas encore d'évaluation
- Tenses of VerbsDocument26 pagesTenses of VerbsJeffry SalcedoPas encore d'évaluation
- English PortofoliuDocument22 pagesEnglish PortofoliuGataAlexandra100% (1)
- Annisa Alhamarini A1B021047 1B ING AdverbsDocument8 pagesAnnisa Alhamarini A1B021047 1B ING AdverbsAnnisa AlhamariniPas encore d'évaluation
- Prime Time 4 - 1Document53 pagesPrime Time 4 - 1MY GM 20Pas encore d'évaluation
- ESL - English as a Second Language - Verbs: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideD'EverandESL - English as a Second Language - Verbs: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuidePas encore d'évaluation
- Questions & Past YearsDocument20 pagesQuestions & Past YearsNur AliaPas encore d'évaluation
- Quiz on using prepositions "across" and "throughDocument2 pagesQuiz on using prepositions "across" and "throughNur AliaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Jungle Book: NAME: - YEAR: 4 MEGADocument1 pageThe Jungle Book: NAME: - YEAR: 4 MEGANur AliaPas encore d'évaluation
- Worksheet CDocument5 pagesWorksheet CNur AliaPas encore d'évaluation
- Wonka Posters PrintDocument9 pagesWonka Posters PrintNur AliaPas encore d'évaluation
- Revision NotesDocument2 pagesRevision NotesNur AliaPas encore d'évaluation
- Revision QuestionsDocument2 pagesRevision QuestionsNur AliaPas encore d'évaluation
- Reflective Essay CurriculumDocument2 pagesReflective Essay CurriculumNur Alia100% (6)
- Bountiful Harvest - Story, Little Red Hen, Writing, ReadingDocument6 pagesBountiful Harvest - Story, Little Red Hen, Writing, Readingtoaster91Pas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial Task 3 Topic 1: By: Wardani X Rabiatul X Saranya X AliaDocument19 pagesTutorial Task 3 Topic 1: By: Wardani X Rabiatul X Saranya X AliaNur AliaPas encore d'évaluation
- Worksheet A: Instructions: Read The Sentences Below. Circle The Main Idea and Underline The DetailsDocument3 pagesWorksheet A: Instructions: Read The Sentences Below. Circle The Main Idea and Underline The DetailsNur AliaPas encore d'évaluation
- Clap Your HandsDocument2 pagesClap Your HandsFifah FiffyPas encore d'évaluation
- Main Ideas & Supporting Details ExplainedDocument22 pagesMain Ideas & Supporting Details ExplainedNur AliaPas encore d'évaluation
- Notes For Romantic (Radical) DesignDocument1 pageNotes For Romantic (Radical) DesignNur Alia67% (3)
- Banana Leaf Restaurant Lunch Deal RM9Document2 pagesBanana Leaf Restaurant Lunch Deal RM9Nur AliaPas encore d'évaluation
- BooksDocument7 pagesBooksNur AliaPas encore d'évaluation
- Importance of 3 T's for well-conducted speaking lessonsDocument3 pagesImportance of 3 T's for well-conducted speaking lessonsNur AliaPas encore d'évaluation
- Portfolio of Songs and Poetry For Young LearnersDocument10 pagesPortfolio of Songs and Poetry For Young LearnersNur AliaPas encore d'évaluation
- TSL3073 Teaching Writing ISL TasksDocument2 pagesTSL3073 Teaching Writing ISL TasksNur AliaPas encore d'évaluation
- Template Lesson PlanDocument1 pageTemplate Lesson PlanNur AliaPas encore d'évaluation
- Songs For Year 1Document6 pagesSongs For Year 1Nur AliaPas encore d'évaluation
- EDU3104 2012 Structure PaperDocument6 pagesEDU3104 2012 Structure PaperNur AliaPas encore d'évaluation
- Reading Activity For Primary School ClassroomDocument3 pagesReading Activity For Primary School ClassroomNur AliaPas encore d'évaluation
- Maroon 5 - Map LyricsDocument2 pagesMaroon 5 - Map LyricsNur AliaPas encore d'évaluation
- EDU3104 2012 Structure PaperDocument6 pagesEDU3104 2012 Structure PaperNur AliaPas encore d'évaluation
- Graphic Organisers For Reading ArticlesDocument4 pagesGraphic Organisers For Reading ArticlesNur AliaPas encore d'évaluation
- Example of Handouts For Language ArtsDocument4 pagesExample of Handouts For Language ArtsNur AliaPas encore d'évaluation
- EDU3104 Task 1 Characteristics of A Good TeacherDocument2 pagesEDU3104 Task 1 Characteristics of A Good TeacherNur AliaPas encore d'évaluation
- AssessmentsDocument1 pageAssessmentsNur AliaPas encore d'évaluation
- Example Ideas For Reading Activity in ClassroomDocument3 pagesExample Ideas For Reading Activity in ClassroomNur AliaPas encore d'évaluation
- Theoretical Grammar - Answers For The ExamDocument27 pagesTheoretical Grammar - Answers For The ExamOksana Pimenova100% (1)
- Italian NotesDocument44 pagesItalian NotesJas A.100% (1)
- Conditional SentencesDocument14 pagesConditional SentencesShabira NadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Uses of Modals May, Might and CouldDocument6 pagesUses of Modals May, Might and CouldJhoi Enriquez Colas Palomo70% (10)
- Express modals in daily situationsDocument5 pagesExpress modals in daily situationsKristy Mae Pascua MuhammadPas encore d'évaluation
- Greek Verbs - Tense, Mood, VoiceDocument1 pageGreek Verbs - Tense, Mood, VoiceEstevan MorducPas encore d'évaluation
- Systemic Functional GrammarDocument42 pagesSystemic Functional GrammarArchettePas encore d'évaluation
- Shona-Grammar - DocxDocument33 pagesShona-Grammar - DocxMufaro Nyamutora100% (1)
- Grammar FinalDocument27 pagesGrammar Finalhuonglanle1230% (1)
- Prelim Reviewer Engl 111Document7 pagesPrelim Reviewer Engl 111STEM 12- Cruz, SarahPas encore d'évaluation
- Mini-Lesson - SmileDocument5 pagesMini-Lesson - Smileapi-325261291Pas encore d'évaluation
- Learn Punjabi Lesson OneDocument25 pagesLearn Punjabi Lesson OneSharan SethiPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 10 UBD FIRST QUARTER (2019-2020)Document38 pagesGrade 10 UBD FIRST QUARTER (2019-2020)Donna GeonzonPas encore d'évaluation
- ARBC10006 Arabic 2 Semester Plan-2Document7 pagesARBC10006 Arabic 2 Semester Plan-2Lily RobinsonPas encore d'évaluation
- Interpersonal Analysis of Imran Khan's Speech: A Study Based On SFGDocument7 pagesInterpersonal Analysis of Imran Khan's Speech: A Study Based On SFGAJHSSR JournalPas encore d'évaluation
- German For ReadingDocument499 pagesGerman For ReadingRacsono100% (3)
- University Grammar of English Workbook R A CloseDocument92 pagesUniversity Grammar of English Workbook R A CloseAndrea Mijatovic93% (15)
- Mood, Modality and Modal VerbsDocument31 pagesMood, Modality and Modal Verbsfluffehmoon100% (1)
- Contrastive GrrammarDocument152 pagesContrastive GrrammarKendra WalkerPas encore d'évaluation
- Sentence Moods - Definitions and UsesDocument3 pagesSentence Moods - Definitions and UsescandilanglitPas encore d'évaluation
- 1st Term Planning Division LessonsDocument5 pages1st Term Planning Division LessonsHadjraPas encore d'évaluation
- English Syntax I: An Analysis of MoodDocument16 pagesEnglish Syntax I: An Analysis of MoodVictoria Del Rosario Maidana100% (1)
- THE Subjunctive Mood: Pages 134-136Document16 pagesTHE Subjunctive Mood: Pages 134-136Andrea Jane PalaroanPas encore d'évaluation
- Short Syntax NunnDocument200 pagesShort Syntax NunnDavid BaileyPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 1 - Teaching Portfolio A Dios Le Pido LessonDocument6 pagesLesson 1 - Teaching Portfolio A Dios Le Pido LessonaguasamargasPas encore d'évaluation
- A Pali PracticeDocument311 pagesA Pali PracticePmsakda HemthepPas encore d'évaluation
- Situations: HG2002 Semantics and PragmaticsDocument47 pagesSituations: HG2002 Semantics and PragmaticsNurul MaskanaPas encore d'évaluation
- The First Conditional GrammarDocument4 pagesThe First Conditional GrammarLaura GPPas encore d'évaluation
- Hebrew I Barrick Notes 10 24Document74 pagesHebrew I Barrick Notes 10 24kyyeungPas encore d'évaluation
- Evert Van Emde Boas, Albert Rijksbaron, Luuk Huitink, Mathieu de Bakker - The Cambridge Grammar of Classical Greek-Cambridge University Press (2019)Document856 pagesEvert Van Emde Boas, Albert Rijksbaron, Luuk Huitink, Mathieu de Bakker - The Cambridge Grammar of Classical Greek-Cambridge University Press (2019)Fatih Yılmaz100% (2)