Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Alternator Diagnostic
Transféré par
vickersDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Alternator Diagnostic
Transféré par
vickersDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Technical Procedure
Alternator Diagnostic Guide
Purpose:
The purpose of this technical procedure is to provide simple, easy-to-follow instructions on how to troubleshoot and isolate faults in the alternator used on CTD truck and trailer refrigeration equipment.
Scope:
This procedure covers alternator normal operation and fault-finding steps for improperly operating alternators. It applies to all CTD authorized dealer technicians responsible for repair of electrical systems on CTD truck and trailer refrigeration equipment.
Table of Contents 1. 2. 3. 4. Alternator And Related Component Part Numbers Normal Operation Common Malfunctions, Symptoms, Causes, And Repairs Component Testing Appendix A: Alternator Summary Information
Test Equipment Requirements 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Digital Multimeter Ammeter D.C. Ammeter D.C. Field Rheostat Carbon Pile Battery Hydrometer
- 0 to 10 amperes - 0 to 100 amperes - 0 to 50 ohms resistance, 50 watt capacity - capable of 0 to 150 ampere load - any commercial type, with temperature correction scale
62-50605-00 Rev B
7/23/99
Page 1 of 19
Technical Procedure
Alternator Diagnostic Guide
1. Alternator and Related Component Part Numbers Table 1 lists the most common and current production alternator and related component part numbers as used on CTD truck and trailer refrigeration equipment. Part Number 30-00409-00 through 13 50-01127-03 50-01127-05 50-01127-12 30-00409-43 30-00409-57 30-00306-14 30-00409-44 30-00409-30 Part Description 37, 65 and 105 amp alternators 3.08 inch alternator pulley 3.21 inch alternator pulley 3.58 inch alternator pulley CW fan CCW fan Bi-directional fan Voltage regulator Brushes
Table 1 Alternator and Related Component Part Numbers* *For a complete listing of all alternator and related component part numbers, including prior production models, see Appendix A (incorporates information previously released via Service Bulletin).
2. Normal Operation NOTE: The following information describes how the alternator should work under normal operating conditions. The unit examples referenced are the NDA94 Phoenix Ultra model with the factory installed alternator and pulley arrangement.
A. Alternator available amperage output is dependent upon the rpms that the alternator is turning. For example, an alternator rated at 65 amps when turning at 3000 rpms will be able to charge at a current rate of 60 amps. As the speed increases to 3300 rpms (normal operating speed when engine is running at 1900 rpms), the alternator reaches its maximum rated output. As ambient (or engine compartment) temperature increases, the available output amperage decreases. B. Alternator output voltage remains much more constant than amperage; alternator rpm has little affect on voltage output. Voltage is varied by ambient temperature and current load, meaning that if the current load is high, the voltage level is lower. For example, if the battery charge is low and requires charging, the current flow from the alternator is high and causes the voltage to drop slightly. NOTE: See Figures 1 and 2 on the following page for amperage and voltage levels at varied rpm and ambient temperatures.
C. Normal alternator operation is dependent upon proper alternator application. Major factors include good, clean, and tight alternator wiring connections at the alternator, unit ground, ammeter, and unit battery; proper belt tension and alternator rotation direction; and proper rpm levels.
62-50605-00 Rev B
7/23/99
Page 2 of 19
Technical Procedure
Alternator Diagnostic Guide
80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 0 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000 6000 7000 77F 199F
OUTPUT CURRENT (AMPERES D.C.)
ALTERNATOR SHAFT R.P.M.
Figure 1 65 AMP Alternator RPM / Output Chart
Figure 2 shows upper and lower voltage limits for all alternators using 30-00409-44 regulators.
15.5
ALTERNATOR VOLTAGE
15.0
14.5
14.0
13.5
-40 -20 0 20 40 60 80 100 120
REGULATOR TEMPERATURE (C)
Figure 2 Alternator Tolerance Band for Regulated Voltage
62-50605-00 Rev B
7/23/99
Page 3 of 19
Technical Procedure
Alternator Diagnostic Guide
3. Common Malfunctions, Symptoms, Causes, and Repairs Table 2 lists common malfunctions, symptoms, causes, and repairs.
MALFUNCTIONS ENG OIL (alarm message on micro) SYMPTOMS Output terminal D+ of the alternator supplies 12VDC to MPL3 at the microprocessor prior to the unit starting. When this occurs the unit will not be able to operate in the auto start mode and the alarm ENG OIL will be generated and displayed. (Note: The D+ output should not have voltage present until the alternator is turning at 600 rpms or higher). CAUSES Poor ground connection REPAIRS Broken or dirty alternator ground connection at alternator or starter ground stud - repair or clean Caution: always wear safety glasses. In order to remove any debris that may be causing a short circuit in the alternator, first attempt to blow it out with clean compressed air. It may be necessary to disassemble the alternator and completely clean it in order to remove all foreign material that may be causing a short circuit. Perform tests #1 & 2 Loose or worn belt or pulleys replace Loose or dirty battery connections or loose connections at the alternator or terminal MPL3 - repair or clean Worn brushes replace Perform tests #1 & 2 Replace oil pressure switch or check oil pressure switch wiring Replace worn component
Metal debris in alternator, causing a short circuit of the rectifier diode bridge
This malfunction is often intermittent and may be difficult to troubleshoot.
Defective alternator or voltage regulator ALT AUX (alarm message on micro) Unit running Low or no voltage on the alternator Aux terminal (D+) with unit running Or No voltage at microprocessor terminal MPL3 Belt or pulley
Wiring problem
Brush assembly Defective alternator or voltage regulator ALT AUX (alarm message on micro) Unit not running SLIPPING OR SQUEALING BELTS No voltage at microprocessor terminal MPL3 Defective engine oil pressure switch (stock closed/shorted) Alternator bearings worn Loose or worn belt Worn pulleys
Excessive noise Premature belt wear
NOTE: Tests and procedures referenced in above repairs section are described in the following pages.
Table 2 Common Malfunctions, Symptoms, Causes, and Repairs 4. Component Testing 62-50605-00 Rev B 7/23/99 Page 4 of 19
Technical Procedure
Alternator Diagnostic Guide
The following flow charts (Figures 3 and 4) serve as guides to fault finding alternator-related malfunctions causing low or no battery charge or excessive battery charge. Test procedures 1 5 are included after the flow charts.
No/Low Battery "Charge" Condition Amp meter shows "no charge" or constant "discharge" with engine idling. (Symptoms: dim lights, hard starting, alt aux alarm, low battery voltage)
Broken/loose/slipping alternator belt OK Limited charging system operating time OK Loose, dirty, or corroded terminal connection at battery, alternator, ammeter, or unit ground OK
NOT OK
Adjust/replace belt
NOT OK
Charge battery as necessary
NOT OK
Clean, repair, replace as required
Battery condition OK Worn, broken brushes OK Perform test procedures 1 through 5 to determine cause of failure
NOT OK
Clean terminals, charge or replace Check fluid level
NOT OK
Replace brushes
Figure 3 No/Low Battery Charge Condition Flow Chart
62-50605-00 Rev B
7/23/99
Page 5 of 19
Technical Procedure
Alternator Diagnostic Guide
Excessive Battery "Charge" Condition Amp meter shows constant "charge" with engine idling. (Symptoms: frequent lamp burnout, excessive gasing, frequent water addition {in excess of approx. 2 oz. per cell per 1000 mi.})
Dirty, loose or corroded terminals at regulator battery, alternator, ammeter, or unit ground) OK Regulator is likely to be "shorted" Perform test procedure 4
NOT OK
Clean, repair & replace as necessary
NOT OK
Replace regulator
Figure 4 Excessive Battery Charge Condition Flow Chart
The following tests and related diagrams (Figures 5 - 9) serve as guides to fault-finding other types of alternator-related malfunctions.
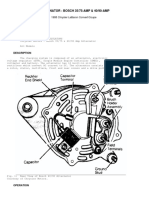
A. TEST NO. 1 ALTERNATOR/REGULATOR DEFECT ISOLATION TEST CONDITIONS: ENGINE NOT RUNNING This test will determine whether the alternator or regulator is the cause of the charging system failure. Disconnect battery. Remove the voltage regulator from the back of the alternator and disconnect both green regulator leads at alternator F1 and F2 brush terminals (see Figure 5). Connect a jumper lead from alternator brush terminal F2 to the alternator ground post. Set control knob of field rheostat in maximum position and connect in series to alternator brush terminal F1 as shown in Figure 5. The rheostat will protect the micro from any high voltages that may occur when performing this test. Reconnect battery. Connect a DC voltmeter to the alternator as shown in Figure 6. Measure and note output voltage with the engine off. Start and run engine in low speed (equivalent to approximately 2000 alternator rpm). Slowly reduce rheostat resistance, noting rise in voltage reading. (Stop test immediately if meter indicates more than 15.5 Volts.)
62-50605-00 Rev B
7/23/99
Page 6 of 19
Technical Procedure
Alternator Diagnostic Guide
Figure 5 Alternator/Regulator Defect Isolation Test If the output voltage increases over the initial value noted with engine stopped, the alternator is probably good and the regulator is defective (perform Alternator Excitation Voltage Test - Test No. 2). If entire rheostat resistance can be eliminated with no increase over initial voltage value, the alternator is probably defective and requires service. CAUTION: Limit time duration of charging test to less than one minute as relatively high voltages can quickly develop with subsequent harm to the system, and check battery condition before running this test. System damage can result by performing this test with poor batteries.
Figure 6 Alternator/Regulator Defect Isolation Test 62-50605-00 Rev B 7/23/99 Page 7 of 19
Technical Procedure
Alternator Diagnostic Guide
STOP HERE
At this point, if the alternator has been found to be faulty and should be replaced, and if the unit/alternator is under warranty, no further testing is required. The remaining steps included in this technical procedure are useful for diagnostic evaluations of individual alternator component failures and for instructions on repairing the alternator.
62-50605-00 Rev B
7/23/99
Page 8 of 19
Technical Procedure
Alternator Diagnostic Guide
B. TEST NO. 2 ALTERNATOR EXCITATION VOLTAGE TEST CONDITIONS: ENGINE RUNNING IN LOW SPEED EQUIVALENT TO 2000 ALTERNATOR RPM This test will determine if the regulator is faulty and if the excitation circuit within the alternator is functioning properly. 1) Prior to starting engine, connect an AC voltmeter across the two stator (phase) tap terminals as shown in Figure 7. 2) Start unit 3) If voltmeter indicates 0.05-1.50 volts for a no-charge condition, the alternator is probably good and the regulator may be defective (regulator check is indicated). Typically, a voltmeter should read 7-13 volts for a properly operating alternator.
Figure 7 Alternator Excitation Voltage Test
C. TEST NO. 3 SHORTED RECTIFIER DIODE TEST CONDITIONS: ENGINE NOT RUNNING Connect voltmeter as shown in Figure 8 (positive on terminal specified, negative on alternator ground). 1. Note battery voltage at alternator positive output terminal; should be approximately 12 volts (battery voltage). 2. Move positive voltmeter lead on either stator terminal. Correct voltmeter reading is zero volts. If higher, rectifier diode is shorted. The alternator must be removed from the unit for repair if a rectifier diode is shorted. Disconnect battery ground cable prior to removing alternator. 62-50605-00 Rev B 7/23/99 Page 9 of 19
Technical Procedure
Alternator Diagnostic Guide
Figure 8 Shorted Rectifier Diode Test
D. TEST NO 4 FIELD CIRCUIT TEST CONDITION: ENGINE NOT RUNNING
Disconnect battery. Remove the voltage regulator from back of the alternator and disconnect both green regulator leads at alternator F1 and F2 brush terminals (see Figure 9). Connect a jumper lead from alternator brush terminal F2 to the alternator ground post. Place test ammeter in low circuit, 1 to 10 amperes. Set control knob of field rheostat in maximum position and connect in series to alternator brush terminal F1 as shown in Figure 9. The rheostat will protect the ammeter from damage if the field circuit is shorted. Reconnect battery. Slowly reduce rheostat resistance, noting rise in ammeter reading. Stop test if meter indicates more than 3.7 amps for 37 amp unit or 3.5 amps for a 65 amp unit and 6.4 amps for a 105 amp alternator. If test ammeter goes over listed values, replace regulator.
62-50605-00 Rev B
7/23/99
Page 10 of 19
Technical Procedure
Alternator Diagnostic Guide
Figure 9 Field Current Test E. TEST NO. 5 ALTERNATOR OUTPUT AND SYSTEM TEST CONDITIONS: ENGINE RUNNING - LOW SPEED This test requires the test ammeter to be switched to the 0-100 ampere scale and placed in series with the alternator positive output terminal and battery positive terminal, as shown in Figure 10. Place load control knob of carbon pile to the off position before connecting load leads to the battery terminals. Connect voltmeter as shown in Figure 10. Start engine; run a few minutes at high speed to stabilize component temperature. Set engine throttle to provide 3000 to 5000 alternator rpms. Apply carbon pile load to induce highest alternator current output. Note voltage at this point. See Table 3 below for the minimum acceptable (hot) output amperage and voltage. ALTERNATOR 12V, 37 Amp 12V, 65 Amp 12V, 105 Amp AMPERAGE 25-40 Amps 50-70 Amps 70-110 Amps VOLTAGE 13.0-15.0 Volts 13.0-15.0 Volts 13.0-15.0 Volts
Table 3 Minimum Acceptable Output If the alternator cannot provide the required output, it should be removed from the engine for overhaul service. Reduce carbon pile load on battery immediately after testing to avoid discharging battery. System voltage drop, between the alternator and the battery, is tested with the alternator producing 10 amperes (adjust carbon pile to attain 10 amps). The maximum allowable voltage drop between alternator and battery is .3 (three-tenths) volt. Excess voltage loss is generally corrected by cleaning and tightening all circuit connections or the use of heavier gauge output cables between the alternator and battery. 62-50605-00 Rev B 7/23/99 Page 11 of 19
Technical Procedure
Alternator Diagnostic Guide
Figure 10 Alternator Output And System Test
NOTE: A carbon pile tester can be obtained from many tool distributors such as Snap-On or NAPA. It must be rated at a minimum of 1200 cold cranking amps (CCA).
62-50605-00 Rev B
7/23/99
Page 12 of 19
Technical Procedure
Alternator Diagnostic Guide
Appendix A: Alternator Summary Information
The following pages incorporate alternator information presented in past Service Bulletins.
Carrier Transicold has used a variety of alternator models over the years on truck and trailer refrigeration equipment, which sometimes leads to confusion regarding application, installation, replacement parts, etc. In order to remedy this, a summary of information for these alternators has been gathered together in this bulletin. A-1 is a reference chart, sorted by alternator part number, which includes information regarding alternator specifications, primary serviceable parts, and supercedures. A-2 is a reference chart, sorted by pulley part number, which includes pulley dimensions and specifications. A-3 shows reference diagrams to be used during installation of any alternator included in the reference chart A-1.
Helpful Hints:
Serviceable Parts:
Continue to refer to the Service Parts manual for the particular model unit you are working on for alternator related part numbers (brushes, pulleys, belts, etc.). Then consult charts A-2 and A-3 for additional information. There are two different alternator shaft sizes. Always try to use the correct replacement alternator with the same shaft size, so that the pulley can be removed from the bad alternator and installed on the new one. When pulley replacement is required, refer to the particular units Service Parts manual, as well as charts A-1 and A-2, for assistance in pulley selection. Make certain of correct alternator fan rotation when selecting a replacement alternator for a particular unit. Chart A-1 indicates the correct fan rotation, as viewed from the shaft end of the alternator. If the fan rotation is incorrect, an opposite direction fan should be installed (refer to same chart for part numbers). To assist in replacement alternator installation, label the alternator wiring connections before removing the existing alternator. Do this by looking up the existing alternator installation diagram in A-3, and label the wires with the numbers 1 through 5 as shown. Then simply look up the installation diagram for the replacement alternator and connect the wires as shown. Remember that some alternators do not require an excitation connection, so cap off this wire (#3 on diagram) if it is not required on the replacement alternator.
Pulleys & Shaft Sizes:
Fan Direction:
Wiring Connections:
62-50605-00 Rev B
7/23/99
Page 13 of 19
Technical Procedure
Alternator Diagnostic Guide
A-1 Alternator Summary (Page 1 of 2)
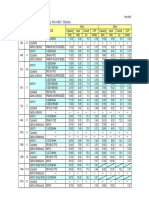
Part Number 30-00171-00 30-00171-11 30-00228-00 30-00281-00 30-00281-01 30-00281-02 30-00281-11 30-00306-00 30-00306-02 30-00306-03 30-00306-04 30-00306-05 30-00351-00 30-00351-02 30-00351-03 30-00351-04 30-00351-05 30-00355-00 30-00355-01 30-00355-02 30-00355-11 30-00355-11SV 30-00363-00 30-00363-01 30-00363-03 30-00363-04 30-00393-00 30-00393-00RM 30-00393-01 30-00393-02 30-00409-00 30-00409-01 30-00409-02 30-00409-03 30-00409-04 30-00409-05 30-00409-06 30-00409-07 30-00409-08 30-00409-09 30-00409-10 30-00409-11 30-00423-00 30-00423-00RM 30-50307-00 30-50323-00 30-50323-00RM 30-50324-00 30-50325-00 30-50326-00 Manufacturer Motorola or Prestolite Motorola or Prestolite Motorola or Prestolite Motorola or Prestolite Motorola or Prestolite Motorola or Prestolite Motorola or Prestolite Motorola or Prestolite Motorola or Prestolite Motorola or Prestolite Motorola or Prestolite Motorola or Prestolite Motorola or Prestolite Motorola or Prestolite Motorola or Prestolite Motorola or Prestolite Motorola or Prestolite Motorola or Prestolite Motorola or Prestolite Motorola or Prestolite Motorola or Prestolite Motorola or Prestolite Motorola or Prestolite Motorola or Prestolite Motorola or Prestolite Motorola or Prestolite Bosch Bosch Bosch Bosch Prestolite Prestolite Prestolite Prestolite Prestolite Prestolite Prestolite Prestolite Prestolite Prestolite Prestolite Prestolite Prestolite Prestolite Prestolite Prestolite Prestolite Prestolite Prestolite Prestolite Amperage 35 35 35 55 55 55 55 37 37 37 37 37 37 37 37 37 37 51 51 51 51 51 65 65 65 65 65 65 65 65 105 37 65 105 65 37 65 65 65 105 65 105 65 65 65 37 37 37 51 65 Fan 30-00306-14 30-00306-14 30-00306-14 30-00306-14 30-00306-14 30-00306-14 30-00306-14 30-00306-14 30-00306-14 30-00306-14 30-00306-14 30-00306-14 30-00306-14 30-00306-14 30-00306-14 30-00306-14 30-00306-14 30-00306-14 30-00306-14 30-00306-14 30-00306-14 30-00306-14 30-00306-14 30-00306-14 30-00306-14 30-00306-14 Not Included Not Included 30-00395-00 30-00395-01 30-00409-57 30-00409-43 30-00409-57 30-00409-57 30-00409-57 30-00409-43 30-00409-57 30-00409-57 30-00409-57 30-00409-57 30-00409-57 30-00409-57 30-00423-14 30-00423-14 30-00423-14 30-00306-14 30-00306-14 30-00306-14 Not Included Not Included Fan Direction
Bi-Directional Bi-Directional Bi-Directional Bi-Directional Bi-Directional Bi-Directional Bi-Directional Bi-Directional Bi-Directional Bi-Directional Bi-Directional Bi-Directional Bi-Directional Bi-Directional Bi-Directional Bi-Directional Bi-Directional Bi-Directional Bi-Directional Bi-Directional Bi-Directional Bi-Directional Bi-Directional Bi-Directional Bi-Directional Bi-Directional N/A N/A Clockwise Counter Clockwise Counter Clockwise Clockwise Counter Clockwise Counter Clockwise Counter Clockwise Clockwise Counter Clockwise Counter Clockwise Counter Clockwise Counter Clockwise Counter Clockwise Counter Clockwise Bi-Directional Bi-Directional Bi-Directional Bi-Directional Bi-Directional Bi-Directional N/A N/A
Regulator 30-00351-01 30-00351-01 30-00351-01 10-00265-01 10-00265-01 10-00265-01 10-00265-01 30-00306-01 30-00306-01 30-00306-01 30-00306-01 30-00306-01 30-00351-01 30-00351-01 30-00351-01 30-00351-01 30-00351-01 10-00265-01 10-00265-01 10-00265-01 10-00265-01 10-00265-01 30-00363-02 30-00363-02 30-00363-02 30-00363-02 30-00393-30 30-00393-30 30-00393-30 30-00393-30 30-00409-44 30-00409-44 30-00409-44 30-00409-44 30-00409-44 30-00409-44 30-00409-44 30-00409-44 30-00409-44 30-00409-44 30-00409-44 30-00409-44 30-00423-02 30-00423-02 30-00423-02 30-50324-01 30-50324-01 30-50324-01 30-50324-01 30-00423-02
Brushes 30-50001-01 30-50001-01 30-50001-01 30-50001-01 30-50001-01 30-50001-01 30-50001-01 30-50001-01 30-50001-01 30-50001-01 30-50001-01 30-50001-01 30-50001-01 30-50001-01 30-50001-01 30-50001-01 30-50001-01 30-50001-01 30-50001-01 30-50001-01 30-50001-01 30-50001-01 30-00363-05 30-00363-05 30-00363-05 30-00363-05 30-00393-30 30-00393-30 30-00393-30 30-00393-30 30-00409-30 30-00409-30 30-00409-30 30-00409-30 30-00409-30 30-00409-30 30-00409-30 30-00409-30 30-00409-30 30-00409-30 30-00409-30 30-00409-30 30-00409-30 30-00409-30 30-00409-30 30-00409-30 30-00409-30 30-00409-30 30-00409-30 30-00409-30
62-50605-00 Rev B
7/23/99
Page 14 of 19
Technical Procedure
Alternator Diagnostic Guide
A-1 Alternator Summary (Page 2 of 2)
Part Number 30-00171-00 30-00171-11 30-00228-00 30-00281-00 30-00281-01 30-00281-02 30-00281-11 30-00306-00 30-00306-02 30-00306-03 30-00306-04 30-00306-05 30-00351-00 30-00351-02 30-00351-03 30-00351-04 30-00351-05 30-00355-00 30-00355-01 30-00355-02 30-00355-11 30-00355-11SV 30-00363-00 30-00363-01 30-00363-03 30-00363-04 30-00393-00 30-00393-00RM 30-00393-01 30-00393-02 30-00409-00 30-00409-01 30-00409-02 30-00409-03 30-00409-04 30-00409-05 30-00409-06 30-00409-07 30-00409-08 30-00409-09 30-00409-10 30-00409-11 30-00423-00 30-00423-00RM 30-50307-00 30-50323-00 30-50323-00RM 30-50324-00 30-50325-00 30-50326-00 Shaft Diameter 0.63" 0.63" 0.63" 0.63" 0.63" 0.63" 0.63" 0.63" 0.63" 0.63" 0.63" 0.63" 0.63" 0.63" 0.63" 0.63" 0.63" 0.63" 0.63" 0.63" 0.63" 0.63" 0.63" 0.63" 0.63" 0.63" 0.67" 0.67" 0.67" 0.67" 0.63" 0.63" 0.63" 0.63" 0.63" 0.63" 0.63" 0.63" 0.63" 0.63" 0.63" 0.63" 0.63" 0.63" 0.63" 0.63" 0.63" 0.63" 0.63" 0.67" Pulley 50-01127-00 Not Included 50-01127-01 50-01127-03 50-01127-00 50-01127-01 Not Included Not Included Not Included 50-01127-03 50-01127-00 50-01127-01 Not Included Not Included 50-01127-03 50-01127-00 50-01127-01 50-01127-03 50-01127-00 50-01127-01 Not Included Not Included Not Included Not Included Not Included Not Included Not Included Not Included 50-01127-07 50-01127-07 Not Included 50-01127-05 50-01127-03 Not Included 50-01127-12 50-01127-05 50-01127-03 Not Included 50-01127-12 50-01127-12 Not Included Not Included Not Included Not Included Not Included Not Included Not Included Not Included Not Included Not Included Comments Supercedures S/S by 30-50323-00 S/S by 30-50323-00 S/S by 30-50323-00 S/S by 30-50325-00 S/S by 30-50325-00 S/S by 30-50325-00 S/S by 30-50325-00 S/S by 30-50323-00 S/S by 30-50324-00 S/S by 30-50323-00 S/S by 30-50323-00 S/S by 30-50323-00 S/S by 30-50323-00 S/S by 30-50324-00 S/S by 30-50323-00 S/S by 30-50323-00 S/S by 30-50323-00 S/S by 30-50325-00 S/S by 30-50325-00 S/S by 30-50325-00 S/S by 30-50325-00 S/S by 30-50325-00 S/S by 30-00423-00 S/S by 30-00423-00 S/S by 30-00423-00 S/S by 30-00423-00 S/S by 30-50326-00 S/S by 30-50326-00 S/S by 30-50326-00 S/S by 30-00409-11 S/S by 30-00409-05 S/S by 30-00409-10 S/S by 30-00409-11 S/S by 30-00409-10 S/S by 30-00409-10 S/S by 30-00409-10 S/S by 30-00409-10 S/S by 30-00409-11
Less regulator, use pulley A,B,or C
Less regulator, use pulley A,B,or C Use pulley A,B,or C Less regulator, use pulley A,B,or C
Use pulley A,B,or C Less regulator, use pulley A,B,or C
Less regulator, use pulley A,B,or C Use pulley A,B,or C Use pulley A,B,or C Less regulator, use pulley A,B,or C Use pulley A,B,or C Less regulator, use pulley A,B,or C Less fan, use pulley E or F Less fan, use pulley E or F, remanufactured
Use pulley G or H
Use pulley G or H
Use pulley C or H
Use pulley C or H Use pulley G or H Use pulley A,B,or C Use pulley A,B,or C, remanufactured Use pulley A,B,or C S/S by 30-00423-00 Use pulley A,B,or C Use pulley A,B,or C, remanufactured Same as 30-50323-00, less regulator, use pulley A,B,or C Less fan, use 30-00306-14 Bi-Directional fan, use pulley A,B,or C Less fan, use fan from 30-00393, use pulley E or F
62-50605-00 Rev B
7/23/99
Page 15 of 19
Technical Procedure
Alternator Diagnostic Guide
A-2 Alternator Pulley Summary Pulley A B C D E F G H Part Number 50-01127-00 50-01127-01 50-01127-03 50-01127-05 50-01127-07 50-01127-09 50-01127-10 50-01127-12 Pulley Diameter 2.87" 2.62" 3.08" 3.21" 3.08" 3.21" 4.00" 3.58" Pulley Groove Shaft Bore Diameter 3/8" 0.63" 1/2" 0.63" 1/2" 0.63" 3/8" 0.63" 1/2" 0.67" 3/8" 0.67" 5/8" 0.63" 1/2" 0.63" Replacement For 30-00171-02 30-00228-12 30-00306-12 30-00393-38
62-50605-00 Rev B
7/23/99
Page 16 of 19
Technical Procedure
Alternator Diagnostic Guide
A-3 Alternator Installation Diagrams 30-00171 or 30-00228 30-00281
5 3
2 2 1
30-00306
30-00351
5 2
1 3 3 1 2
30-00355
4 3 4 5 5
30-00363
2 2 2 1
1 2 3 4 5 Positive Output (+) Ground (-) Excitation Ac Tap (Do Not Use) Indicator/Regulator (D+)
62-50605-00 Rev B
7/23/99
Page 17 of 19
Technical Procedure
Alternator Diagnostic Guide
30-00393
30-00409
5 2 1 3 2
30-00423
30-50307
3 4
1 2 3 4 5
Positive Output (+) Ground (-) Excitation Ac Tap (Do Not Use) Indicator/Regulator (D+)
62-50605-00 Rev B
7/23/99
Page 18 of 19
Technical Procedure 30-50323
Alternator Diagnostic Guide 30-50324
4 1
30-50325
30-50326
3 4 5 5
1 2 1 2
1 2 3 4 5
Positive Output (+) Ground (-) Excitation Ac Tap (Do Not Use) Indicator/Regulator (D+)
62-50605-00 Rev B
7/23/99
Page 19 of 19
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2D'EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Pas encore d'évaluation
- PGM Fi SystemDocument217 pagesPGM Fi Systemmkisa70Pas encore d'évaluation
- Transpo Testing Manual Prueba RelaysDocument425 pagesTranspo Testing Manual Prueba RelaysSixto Caira100% (1)
- Harrop Lc200-1ur InstallDocument22 pagesHarrop Lc200-1ur InstallArtur ElectroMecânicoPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.troubleshoot Engine Crank But Cant StartDocument3 pages1.troubleshoot Engine Crank But Cant StartsyahrilPas encore d'évaluation
- Diagnosing Misfires: Steady MisfireDocument3 pagesDiagnosing Misfires: Steady MisfireDawood SubedarPas encore d'évaluation
- Circuit Description: o o o o o oDocument3 pagesCircuit Description: o o o o o oManabu WakisakaPas encore d'évaluation
- Military Tactical Wheeled Vehicle Technician Certification ProgramDocument20 pagesMilitary Tactical Wheeled Vehicle Technician Certification ProgramShawn HackPas encore d'évaluation
- Brake GuideDocument63 pagesBrake GuideainginerPas encore d'évaluation
- 88-02 Cummins Exhaust BrakeDocument24 pages88-02 Cummins Exhaust Brakemark_dayPas encore d'évaluation
- Ford Edge 2.0. U0402Document10 pagesFord Edge 2.0. U0402miguelPas encore d'évaluation
- 303-01A Engine - 6.2L V8, Removal and InstallationDocument31 pages303-01A Engine - 6.2L V8, Removal and InstallationAlexandru NicolaPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit Description SpecificationDocument11 pagesUnit Description SpecificationmanualPas encore d'évaluation
- Start No ClickDocument4 pagesStart No Clicklamping_apPas encore d'évaluation
- 2007 Ford Explorer Scheduled Maintenance GuideDocument48 pages2007 Ford Explorer Scheduled Maintenance Guideelcoma56Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2012 Fisker Karma Owner HandbookDocument152 pages2012 Fisker Karma Owner HandbookRitesh PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- Ford CrownVic 1998 ManualDocument160 pagesFord CrownVic 1998 ManualNasir AyubPas encore d'évaluation
- Alternator Transpo RegulatorDocument407 pagesAlternator Transpo Regulatoruli12345678100% (4)
- Installation Instructions: Nissan KA24DE Cylinder Head Kit Part Number 11061233Document7 pagesInstallation Instructions: Nissan KA24DE Cylinder Head Kit Part Number 11061233prosper shumbaPas encore d'évaluation
- Nissan Maxima A35 Wiper & WasherDocument100 pagesNissan Maxima A35 Wiper & WasherРомка ВоронинPas encore d'évaluation
- Fe05a PDFDocument72 pagesFe05a PDFvette512Pas encore d'évaluation
- Testing Lucas Alternators Aug 2013Document12 pagesTesting Lucas Alternators Aug 2013derryukPas encore d'évaluation
- Ac Compressor Oil CheckingDocument3 pagesAc Compressor Oil CheckingToua YajPas encore d'évaluation
- Kia Code RetrievalDocument2 pagesKia Code Retrievalandreisim80100% (1)
- Kipor - KDE7000T Generator-EnDocument20 pagesKipor - KDE7000T Generator-EnEzzadin Baban50% (4)
- Engine Valve Lash - Inspect/Adjust: Shutdown SIS Previous ScreenDocument4 pagesEngine Valve Lash - Inspect/Adjust: Shutdown SIS Previous ScreenbejoythomasPas encore d'évaluation
- 2003 GMC TAC ConnectorsDocument29 pages2003 GMC TAC ConnectorsfenkensteinPas encore d'évaluation
- 2013-01!26!194634 Peterbilt Model 387 Operators Manual Prior To 12-06 LowDocument188 pages2013-01!26!194634 Peterbilt Model 387 Operators Manual Prior To 12-06 LowyamilmrPas encore d'évaluation
- AL4000DDocument74 pagesAL4000Dtazjuan1Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Theory Behind The Engine BrakeDocument3 pagesThe Theory Behind The Engine BrakeJoseGarzaPas encore d'évaluation
- Snap On Meter TrainingDocument93 pagesSnap On Meter TrainingjoePas encore d'évaluation
- Alternator ManualDocument16 pagesAlternator Manualgraham4877Pas encore d'évaluation
- Op. Manual Smart Reefer enDocument32 pagesOp. Manual Smart Reefer envickers100% (1)
- Inspection Plug GuideDocument3 pagesInspection Plug GuideAbdul AzisPas encore d'évaluation
- Starter: 1991 Mitsubishi MonteroDocument9 pagesStarter: 1991 Mitsubishi MonteroAnimemanuel MuñozPas encore d'évaluation
- 2007 Allegro Motorhome Owners ManualDocument154 pages2007 Allegro Motorhome Owners ManualGF FranzoniPas encore d'évaluation
- Air Brake ManualDocument94 pagesAir Brake Manualfreeemeee.now130Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fullbay 2020 2021 State of Heavy Duty RepairDocument58 pagesFullbay 2020 2021 State of Heavy Duty RepairBilly SevernPas encore d'évaluation
- John Deere Z225 EZTrak Mower (North American Version) Service Repair Manual (Tm1477)Document15 pagesJohn Deere Z225 EZTrak Mower (North American Version) Service Repair Manual (Tm1477)zhuangfuqian31Pas encore d'évaluation
- Model FA (Vacuum Servo)Document54 pagesModel FA (Vacuum Servo)Komatsu Perkins Hitachi100% (1)
- Troubleshooting Fuel Dilution of Engine Oil PDFDocument2 pagesTroubleshooting Fuel Dilution of Engine Oil PDFmanu luvungaPas encore d'évaluation
- VOLTAGE DROP Testing Overview and Lab SheetDocument6 pagesVOLTAGE DROP Testing Overview and Lab SheetSabastian Edwards100% (1)
- 03 Features 1KD, 2KD PDFDocument2 pages03 Features 1KD, 2KD PDFCarlos QuispePas encore d'évaluation
- Transmisión Automática Nissan Titan 2004Document348 pagesTransmisión Automática Nissan Titan 2004Hendrick CepedaPas encore d'évaluation
- Symptoms of A Blown Head GasketDocument5 pagesSymptoms of A Blown Head GasketSandeep Swami G Elugu100% (2)
- Parasitic Draw ChartDocument9 pagesParasitic Draw Chartlionellin83Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ford Ranger Spare PartsDocument2 pagesFord Ranger Spare PartsNgila João AndréPas encore d'évaluation
- M116A2 Military Trailer Manual Number TM 5 6115 632 14Document119 pagesM116A2 Military Trailer Manual Number TM 5 6115 632 14GreenMountainGeneratorsPas encore d'évaluation
- Dobdsm971 PDFDocument25 pagesDobdsm971 PDFTecknobites VallenarPas encore d'évaluation
- VR-Vs V8 Distributor Remove-ReplaceDocument7 pagesVR-Vs V8 Distributor Remove-ReplaceJames MirfinPas encore d'évaluation
- JAC Light Truck HFC1040Document50 pagesJAC Light Truck HFC1040Jose Simonetti100% (1)
- Engine Electrical System (D4FA - DSL1.5) : General Charging System Starting SystemDocument28 pagesEngine Electrical System (D4FA - DSL1.5) : General Charging System Starting System2791957Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fluke - Troubleshooting Auto Electrical SystemsDocument23 pagesFluke - Troubleshooting Auto Electrical SystemsWesley YoungPas encore d'évaluation
- IM05805023K - XTJP - Op - Manual - RH2 - 06-07-12Document12 pagesIM05805023K - XTJP - Op - Manual - RH2 - 06-07-12melgarcia829Pas encore d'évaluation
- Troubleshooting VF DDocument7 pagesTroubleshooting VF DRichard BakerPas encore d'évaluation
- Lichtmaschine BoschDocument23 pagesLichtmaschine BoschJames PonzoPas encore d'évaluation
- Diesel Generator Set: Continuous Model:YM9-1P Standby Model:YM10S-1PDocument4 pagesDiesel Generator Set: Continuous Model:YM9-1P Standby Model:YM10S-1PYashveer TakooryPas encore d'évaluation
- B 12 A 6Document8 pagesB 12 A 6Charles McNall100% (1)
- 1g Charging Starting System-1Document21 pages1g Charging Starting System-1Anthony DizonPas encore d'évaluation
- Manual Generador ENGGADocument20 pagesManual Generador ENGGAmanuel100% (2)
- Danfoss Banana Ripening Application BrochureDocument6 pagesDanfoss Banana Ripening Application BrochurevickersPas encore d'évaluation
- ASHRAE Testing-Adjusting-Balancing-HVAC-Systems PDFDocument74 pagesASHRAE Testing-Adjusting-Balancing-HVAC-Systems PDFvickers100% (1)
- Danfoss Facts Worth Knowing About ACDrivesDocument208 pagesDanfoss Facts Worth Knowing About ACDrivesvickersPas encore d'évaluation
- Direct Expansion (DX) and Secondary Loop (SN) SystemsDocument2 pagesDirect Expansion (DX) and Secondary Loop (SN) SystemsvickersPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermal Applications CategoryDocument19 pagesThermal Applications CategoryvickersPas encore d'évaluation
- Building Sustainability AnalysisDocument25 pagesBuilding Sustainability AnalysisvickersPas encore d'évaluation
- Sanyo ScrollDocument24 pagesSanyo Scrollworker359567Pas encore d'évaluation
- Temperature To Resistance Chart NTC Thermistor: Temp C Temp F Resistance OhmsDocument1 pageTemperature To Resistance Chart NTC Thermistor: Temp C Temp F Resistance OhmsvickersPas encore d'évaluation
- Cooling Load Temperature Difference Calculation MethodDocument3 pagesCooling Load Temperature Difference Calculation Methodvickers50% (2)
- McQuay MCW-C-H Technical Manual EngDocument20 pagesMcQuay MCW-C-H Technical Manual EngCarlos Can PootPas encore d'évaluation
- Replacement Guideline For (ZR90K3, ZR11M3, ZR12M3, ZR16M3 and ZR19M3)Document10 pagesReplacement Guideline For (ZR90K3, ZR11M3, ZR12M3, ZR16M3 and ZR19M3)vickersPas encore d'évaluation
- 6 Adjustable Tripping Settings of A Circuit Breaker You MUST UnderstandDocument10 pages6 Adjustable Tripping Settings of A Circuit Breaker You MUST UnderstandvickersPas encore d'évaluation
- Fast, Easy Furnace TuningDocument2 pagesFast, Easy Furnace TuningvickersPas encore d'évaluation
- ThermostatCatalog 570-280Document12 pagesThermostatCatalog 570-280vickers0% (1)
- Cypetherm SuiteDocument72 pagesCypetherm SuitevickersPas encore d'évaluation
- Comparative Table of ScrollsDocument11 pagesComparative Table of ScrollsvickersPas encore d'évaluation
- Chiller Types and ApplicationsDocument73 pagesChiller Types and Applicationsvickers100% (3)
- Chiller CGA MInstallation, Operation, Air-Cooled Scroll Chillers 20-130 TonDocument152 pagesChiller CGA MInstallation, Operation, Air-Cooled Scroll Chillers 20-130 TonvickersPas encore d'évaluation
- INT69 KRIWAN Diagnosis SystemDocument6 pagesINT69 KRIWAN Diagnosis Systemvickers100% (1)
- Multi V Water PDB (08.04.10 - ) Final PDFDocument123 pagesMulti V Water PDB (08.04.10 - ) Final PDFMaxiaires RefrigeracionPas encore d'évaluation
- Supco TimersDocument7 pagesSupco Timersvickers100% (1)
- HVACR Service Trobleshooting With The Professor John TomczykDocument48 pagesHVACR Service Trobleshooting With The Professor John TomczykvickersPas encore d'évaluation
- Fasco Full Catalog PDFDocument184 pagesFasco Full Catalog PDFvickersPas encore d'évaluation
- 30RB Opt28B Low Ambient OperationDocument1 page30RB Opt28B Low Ambient OperationvickersPas encore d'évaluation
- Unilever Solar Assisted Ice Cream Cabinet With Danfoss Direct Current Operated Propane CompressorDocument2 pagesUnilever Solar Assisted Ice Cream Cabinet With Danfoss Direct Current Operated Propane CompressorvickersPas encore d'évaluation
- R-22 en ChillersDocument4 pagesR-22 en ChillersvickersPas encore d'évaluation
- Bul-30RB Brine OptionDocument1 pageBul-30RB Brine OptionvickersPas encore d'évaluation
- Template Manual Abb Ret 670 v1.1 Enu Tu2.22 v1.000Document18 pagesTemplate Manual Abb Ret 670 v1.1 Enu Tu2.22 v1.000m_dh87129100% (1)
- Physics Master PDF - JEE Main 2021 - 19 Chapter-WiseDocument1 306 pagesPhysics Master PDF - JEE Main 2021 - 19 Chapter-WiseShubh Agarwal100% (1)
- Ersa Soldering Station PDFDocument22 pagesErsa Soldering Station PDFtodorloncarskiPas encore d'évaluation
- Construction of Alternator - Electrical4uDocument5 pagesConstruction of Alternator - Electrical4uM Kumar MarimuthuPas encore d'évaluation
- Newton-Raphson State Estimation Solution Employing Systematically Constructed Jacobian MatrixDocument5 pagesNewton-Raphson State Estimation Solution Employing Systematically Constructed Jacobian MatrixMuhudin Mohammed SemanPas encore d'évaluation
- Ee 2027Document1 pageEe 2027thattskavasPas encore d'évaluation
- Service Manual: PPP P PDocument185 pagesService Manual: PPP P PLaurent CAUFRIEZPas encore d'évaluation
- GA500 Data SheetDocument27 pagesGA500 Data SheetAtoumane DiengPas encore d'évaluation
- Joystick System OperationDocument3 pagesJoystick System OperationHusi NihaPas encore d'évaluation
- Electro-Hydraulic Actuator Type PVEP / PVEP-F TechDocument16 pagesElectro-Hydraulic Actuator Type PVEP / PVEP-F TechHYDRAULICGURUPas encore d'évaluation
- Servo Vexta Kblm460-Am P 4lwfqDocument49 pagesServo Vexta Kblm460-Am P 4lwfqDimas SetiajiPas encore d'évaluation
- Stepper Motor ControllerDocument3 pagesStepper Motor Controllerelfrich100% (3)
- Engine Out 3Document178 pagesEngine Out 3Mohamed Mahrous100% (1)
- Series: Aluminum Electrolytic CapacitorsDocument4 pagesSeries: Aluminum Electrolytic Capacitorsyo mismoPas encore d'évaluation
- 3B ACCP Technical SpecificationDocument5 pages3B ACCP Technical SpecificationPraveen KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Surge Arresters: Varistar Storm Trapper High Energy Mov Arrester Installation InstructionsDocument2 pagesSurge Arresters: Varistar Storm Trapper High Energy Mov Arrester Installation InstructionsAgussalim AddinPas encore d'évaluation
- Electric Force & Electric Field IDocument60 pagesElectric Force & Electric Field IImran ParvezPas encore d'évaluation
- U.S. Pat. 4,809,336, Semiconductor Amplifier With Tube Amplifier Characteristics, Pritchard, 1989.Document10 pagesU.S. Pat. 4,809,336, Semiconductor Amplifier With Tube Amplifier Characteristics, Pritchard, 1989.Duane BlakePas encore d'évaluation
- Teac MC-D95Document32 pagesTeac MC-D95Djalma MilanPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Physics (14BT1BS01)Document4 pagesEngineering Physics (14BT1BS01)Pavan KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Applied Electricity PHY 222 2.0 Tutorial Number 01Document3 pagesApplied Electricity PHY 222 2.0 Tutorial Number 01c nnPas encore d'évaluation
- Capitol Drive, Capitol Compound City of Balanga 2100 Bataan PhilippinesDocument1 pageCapitol Drive, Capitol Compound City of Balanga 2100 Bataan PhilippinesWilson Domingo LazartePas encore d'évaluation
- 55-2-1 PhysicsDocument11 pages55-2-1 PhysicsSezein DuaPas encore d'évaluation
- Operating Manual: Air Band TransceiverDocument40 pagesOperating Manual: Air Band TransceiverПросто СлесарьPas encore d'évaluation
- Lec 21 PDFDocument8 pagesLec 21 PDFVictor CantuárioPas encore d'évaluation
- Neetpassionate Aiats 1 2021Document26 pagesNeetpassionate Aiats 1 2021Hasmukh Ravat100% (1)
- Electronic and Medical Instrumentation-1Document1 pageElectronic and Medical Instrumentation-1Mady BuzeaPas encore d'évaluation
- NR Jed 316708 enDocument64 pagesNR Jed 316708 enSalvador Santos RomeroPas encore d'évaluation
- Class 5 - Node Voltage AnalysisDocument22 pagesClass 5 - Node Voltage AnalysisSwayam Tejas PadhyPas encore d'évaluation
- BEEE Unit I MaterialDocument93 pagesBEEE Unit I MaterialK Praveen KumarPas encore d'évaluation