Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Megadiversity Countries PDF
Transféré par
ElektrocultureTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Megadiversity Countries PDF
Transféré par
ElektrocultureDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
www.biodiversitya-z.
org
Megadiversity Countries
Countries of the world with the greatest levels of biodiversity
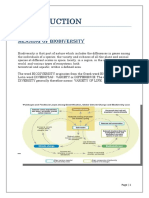
Description Megadiversity Countries is a term used to refer to the worlds top biodiversity-rich countries in the world. This country-based method raises national awareness for biodiversity conservation in nations with high biological diversity, with many species unique to a specific country. This concept complements that of biodiversity hotspots and high-biodiversity wilderness areas to achieve significant coverage of the worlds biological resources and was first proposed in 1988. The Megadiversity country concept is based on four premises:1 1. The biodiversity of each and every nation is critically important to that nations survival, and must be a fundamental component of any national or regional development strategy; 2. Biodiversity is by no means evenly distributed on our planet, and some countries, especially in the tropics, harbour far greater concentrations of biodiversity than others; 3. Some of the richest and most diverse nations also have ecosystems that are under the most severe threat; 4. To achieve maximum impact with limited resources, we must concentrate heavily (but not exclusively) on those countries richest in diversity and endemism and most severely threatened; investment in them should be roughly proportional to their overall contribution to global biodiversity. Supported by Conservation International Year of Creation
UNEP-WCMC
1/2
www.biodiversitya-z.org
1988 Coverage Global in extent covering 17 countries. 2 The identified Megadiverse countries are: United States of America, Mexico, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, Venezuela, Brazil, Democratic Republic of Congo, South Africa, Madagascar, India, Malaysia, Indonesia, Philippines, Papua New Guinea, China, and Australia. Criteria The principle criterion is endemism, first at the species level and then at higher taxonomic levels such as genus and family. To qualify as a Megadiverse country, a country must have at least 5000 of the worlds plants as endemics. 2 Management While there is no specific management associated with this concept, 17 countries rich in biological diversity and associated traditional knowledge have formed a group known as the Like Minded Megadiverse Countries.3 These include 12 of the above identified Megadiverse countries. This group was formed in 2002 under the Cancun Declaration to act as a mechanism of cooperation on the conservation of biological diversity and traditional knowledge. Business Relevance Legal and compliance Since this is a country based biodiversity prioritisation approach mainly to raise awareness, there is no legal protection or compliance associated with the designation itself. The legal and compliance requirements present within these countries will relate to other designations of biodiversity importance present within each country, such as legally protected areas. Biodiversity These countries are of global biodiversity value based on the number and the level of unique species present. They include areas of high biodiversity importance as well as degraded land and urban areas and therefore more detailed information is needed to locate the actual distribution of biodiversity within these countries for site-scale assessment and decision making. Socio-cultural As these areas include a variety of human land-uses, rural and urban, as well as protected areas under a range of possible governance types, many social and/or cultural values are likely to be present in some parts. Tools Reference/Websites 1. Mittermeier, R.A., Gil P.R. and Mittermeier, C.G. (1997) Megadiversity: Earths Biologically Wealthiest Nations. Conservation International, Cemex. 2. Mittermeier, R.A. 1988. Primate Diversity and the Tropical Forest: Case Studies from Brazil and Madagascar and the Importance of the Megadiversity Countries. In: Biodiversity (Ed. E.O. Wilson). National Academy Press, Washington, DC. 145-154. 3. Like-minded Megadiverse Countries website 4. Megadiversity website
UNEP-WCMC
2/2
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Uncharted Eden: Preserving Life's Gems within Earth's Natural SanctuariesD'EverandUncharted Eden: Preserving Life's Gems within Earth's Natural SanctuariesPas encore d'évaluation
- Patana Bses 4C Midterms Biodiversity ConservationDocument4 pagesPatana Bses 4C Midterms Biodiversity ConservationSean Patrick ManlapazPas encore d'évaluation
- Miranda-C. Bses4c Midterms Biodversity-ConservationDocument4 pagesMiranda-C. Bses4c Midterms Biodversity-ConservationSean Patrick ManlapazPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio DiversityDocument71 pagesBio Diversityspecial officer office of CCLAPas encore d'évaluation
- Biodiversity: Life To Our Mother EarthDocument19 pagesBiodiversity: Life To Our Mother EarthAnil KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 2 BIODIVERSITYDocument13 pagesLesson 2 BIODIVERSITYIvan Ronald BragasPas encore d'évaluation
- Preserving Biodiversity in Forest EcosystemsDocument29 pagesPreserving Biodiversity in Forest EcosystemsSparsh TiwariPas encore d'évaluation
- Biodiversity HardDocument6 pagesBiodiversity HardJustinePas encore d'évaluation
- 13 Lopez Chap12Document30 pages13 Lopez Chap12Touhid AkramPas encore d'évaluation
- Biodiversity and Its ConservationDocument4 pagesBiodiversity and Its ConservationSoumam DieselPas encore d'évaluation
- Biodiversity EssayDocument10 pagesBiodiversity EssayWong Sun100% (2)
- Biodiversity and Its ConservationDocument26 pagesBiodiversity and Its ConservationMadhavi GawliPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio-Diversity Uses, Threats and Conservation: Dr. AnjayDocument23 pagesBio-Diversity Uses, Threats and Conservation: Dr. AnjayMayur KshirsagarPas encore d'évaluation
- Deputy Director (M & C), Press Information Bureau, New DelhiDocument4 pagesDeputy Director (M & C), Press Information Bureau, New DelhiakhiljindalPas encore d'évaluation
- Biodiversity Finance: Innovative Tools for a Flourishing PlanetD'EverandBiodiversity Finance: Innovative Tools for a Flourishing PlanetPas encore d'évaluation
- Forest Governance by Indigenous and Tribal Peoples. An Opportunity for Climate Action in Latin America and the CaribbeanD'EverandForest Governance by Indigenous and Tribal Peoples. An Opportunity for Climate Action in Latin America and the CaribbeanPas encore d'évaluation
- Conservation of BiodiversityDocument70 pagesConservation of BiodiversitynarasimhanpondyPas encore d'évaluation
- 15) Unit II - II (H) Biodiversity at Global Level, National Level and LocaDocument2 pages15) Unit II - II (H) Biodiversity at Global Level, National Level and LocavaishnaviPas encore d'évaluation
- Protection of Traditional Knowledge in The Present Ipr Regime: A Mirage or A RealityDocument42 pagesProtection of Traditional Knowledge in The Present Ipr Regime: A Mirage or A RealityAkshay ChadhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Biodiversity and Conservation Class 12 Notes CBSE Biology Chapter 15 (PDF)Document18 pagesBiodiversity and Conservation Class 12 Notes CBSE Biology Chapter 15 (PDF)Ritika LalPas encore d'évaluation
- Group-7-Biodiversity NewDocument2 pagesGroup-7-Biodiversity NewGina PiñeroPas encore d'évaluation
- Dr. Shivani Naik: Biodiversity and Its LevelsDocument9 pagesDr. Shivani Naik: Biodiversity and Its LevelsHeet DoshiPas encore d'évaluation
- Term Paper On AquacultureDocument14 pagesTerm Paper On AquacultureWilson EjercitoPas encore d'évaluation
- Policy Analysis of Biodiversity Protection in NepalDocument13 pagesPolicy Analysis of Biodiversity Protection in NepalAdarsh koiralaPas encore d'évaluation
- SustComm Bio DivDocument10 pagesSustComm Bio DivEstudios Rurales y Asesoría Campesina, A. C.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Convention On Biological DiversityDocument82 pagesConvention On Biological DiversityIkramuddin KamilPas encore d'évaluation
- NBSAP Canada EngDocument91 pagesNBSAP Canada Eng王也Pas encore d'évaluation
- BEVAE181 Solved AssignmentDocument32 pagesBEVAE181 Solved Assignmentparveen TanwarPas encore d'évaluation
- Agroforestry and Biodiversity Conservation in Tropical LandscapesD'EverandAgroforestry and Biodiversity Conservation in Tropical LandscapesPas encore d'évaluation
- Biodiversity Notes For UPSC ExamDocument7 pagesBiodiversity Notes For UPSC ExamrohitPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio-Diversity Uses, Threats and Conservation: Dr. AnjayDocument23 pagesBio-Diversity Uses, Threats and Conservation: Dr. AnjaySoham Chakraborty100% (1)
- Biodiversity and Its ConservationDocument58 pagesBiodiversity and Its ConservationNishant Vinod Patil .Pas encore d'évaluation
- SM-Jul14-IPR-4 - SamanthaDocument24 pagesSM-Jul14-IPR-4 - SamanthaBipin RethinPas encore d'évaluation
- MalaysiaDocument20 pagesMalaysianizyatim6226Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mega Diversity CentreDocument12 pagesMega Diversity CentreVaibhav RohraPas encore d'évaluation
- Module PDFDocument10 pagesModule PDFGievel Enoroba LopezPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio Dis1pdfDocument12 pagesBio Dis1pdfAvinash JhaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Importance of Plant DiversityDocument3 pagesThe Importance of Plant Diversityakhileshmoney100% (5)
- Course Unit - Biodiversity and Healthy SocietyDocument10 pagesCourse Unit - Biodiversity and Healthy SocietyJules Alvarado100% (1)
- Lecture Note # 6 Biodiversity ConceptsDocument17 pagesLecture Note # 6 Biodiversity ConceptsBaucas, Rolanda D.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Module 5.2 BiodiversityDocument25 pagesModule 5.2 BiodiversityRodelLaborPas encore d'évaluation
- Summry 3rd 4th CHPTRDocument4 pagesSummry 3rd 4th CHPTRSadia AbbasiPas encore d'évaluation
- Conservation, Sustainable Use and Protection of Natural ResourcesDocument4 pagesConservation, Sustainable Use and Protection of Natural ResourcesKhairul ShahmiPas encore d'évaluation
- Biodiversity ProjectDocument19 pagesBiodiversity ProjectMadhurima khan92% (12)
- Power Point ProjectDocument51 pagesPower Point ProjectParthiv AnilPas encore d'évaluation
- Africa Regional Synthesis for the State of the World’s Biodiversity for Food and AgricultureD'EverandAfrica Regional Synthesis for the State of the World’s Biodiversity for Food and AgriculturePas encore d'évaluation
- Biodiversity: Made By: Roll No.: ClassDocument19 pagesBiodiversity: Made By: Roll No.: ClassChiranjiv KarkeraPas encore d'évaluation
- MSC Botnay Final Pap7 bl2Document46 pagesMSC Botnay Final Pap7 bl2Rekha guptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Day 3 FoodDocument50 pagesDay 3 FoodFitri AudiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Convention On Biological DiversityDocument7 pagesConvention On Biological DiversityKingsley 'kingsville' UdofaPas encore d'évaluation
- BiodiversityDocument21 pagesBiodiversitypadmashri67Pas encore d'évaluation
- Speech On International Biodiversity Conservation Day!Document5 pagesSpeech On International Biodiversity Conservation Day!LaalSinghChauhanPas encore d'évaluation
- 12 Biology Notes Ch15 Biodiversity and ConservationDocument4 pages12 Biology Notes Ch15 Biodiversity and ConservationMeenakshi VenkataramanPas encore d'évaluation
- Pacific Regional Synthesis for the State of the World’s Biodiversity for Food and AgricultureD'EverandPacific Regional Synthesis for the State of the World’s Biodiversity for Food and AgriculturePas encore d'évaluation
- Biodiversity and Its ConservationDocument12 pagesBiodiversity and Its ConservationhvrkPas encore d'évaluation
- BDDocument207 pagesBDGebretsadik Melak GionianPas encore d'évaluation
- Fungal Flora in The Philippines: Values and Conservation: Anjela J. LageraDocument19 pagesFungal Flora in The Philippines: Values and Conservation: Anjela J. LageraGerald GamboaPas encore d'évaluation
- Biodiversity Management in KenyaDocument8 pagesBiodiversity Management in KenyaEICQ/00154/2020 SAMUEL MWANGI RUKWAROPas encore d'évaluation
- Natural ResourcesDocument11 pagesNatural ResourcesBhavesh BhoeePas encore d'évaluation
- Present Problem and Future Prospect: Welcome To Our Presentation OnDocument16 pagesPresent Problem and Future Prospect: Welcome To Our Presentation OnprincedasPas encore d'évaluation
- Cost Element Accounting SAPDocument3 pagesCost Element Accounting SAPElektroculturePas encore d'évaluation
- Cost Element Accounting SAPDocument3 pagesCost Element Accounting SAPElektroculturePas encore d'évaluation
- Cost Element Accounting SAPDocument3 pagesCost Element Accounting SAPElektroculturePas encore d'évaluation
- Smart or Just LuckyDocument17 pagesSmart or Just LuckyGopi ParikhPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 Habits To A Lifetime of HappinessDocument12 pages4 Habits To A Lifetime of HappinessWilliam MolinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Change Your Life Before BreakfastDocument21 pagesChange Your Life Before BreakfastElektroculture100% (2)
- People vs. Samson, September 2, 2015Document5 pagesPeople vs. Samson, September 2, 2015Alpha Grace JugalPas encore d'évaluation
- Set 1 Questions 1-20Document10 pagesSet 1 Questions 1-20aeda80Pas encore d'évaluation
- Perfumery in Ancient IndiaDocument9 pagesPerfumery in Ancient IndiaRachel ChittilapillyPas encore d'évaluation
- Cryptocurrency: Presented By: Shashi KumarDocument15 pagesCryptocurrency: Presented By: Shashi KumaraabhasPas encore d'évaluation
- The Philippine Diary ProjectDocument37 pagesThe Philippine Diary ProjectLilibeth OchiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Fundamentals of Parenteral NutritionDocument4 pagesFundamentals of Parenteral NutritionankammaraoPas encore d'évaluation
- Matisse As Printmaker: Matisse'S Printmaking ProcessesDocument2 pagesMatisse As Printmaker: Matisse'S Printmaking ProcessesWriterIncPas encore d'évaluation
- Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) : Situation Report - 125Document17 pagesCoronavirus Disease (COVID-19) : Situation Report - 125CityNewsTorontoPas encore d'évaluation
- International Business of Pizza HutDocument13 pagesInternational Business of Pizza Hutpratikdotia9100% (2)
- FijiTimes - June 7 2013Document48 pagesFijiTimes - June 7 2013fijitimescanadaPas encore d'évaluation
- DerivativeDocument29 pagesDerivativeMohit AggarwalPas encore d'évaluation
- Gann Trding PDFDocument9 pagesGann Trding PDFMayur KasarPas encore d'évaluation
- UntitledDocument44 pagesUntitledDhvani PanchalPas encore d'évaluation
- Chitosan 55910823Document4 pagesChitosan 55910823sharemwPas encore d'évaluation
- A Natural Disaster Story: World Scout Environment BadgeDocument4 pagesA Natural Disaster Story: World Scout Environment BadgeMurali Krishna TPas encore d'évaluation
- Maternal Newborn Nursing The Critical Components of Nursing Care 2nd Edition Durham Test BankDocument32 pagesMaternal Newborn Nursing The Critical Components of Nursing Care 2nd Edition Durham Test Bankalicenhan5bzm2z100% (24)
- KWPL07 RankinDocument28 pagesKWPL07 RankinBoogy GrimPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Economics & Financial Accounting Two Mark Questions and AnswersDocument15 pagesEngineering Economics & Financial Accounting Two Mark Questions and AnswerspothigaiselvansPas encore d'évaluation
- Microsoft Lumia 950 XL - Unlocked (Black)Document8 pagesMicrosoft Lumia 950 XL - Unlocked (Black)Dawood AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Mao InoueDocument9 pagesMao InoueNemanja IlicPas encore d'évaluation
- IPTV-Bbc TVP What Is IptvDocument32 pagesIPTV-Bbc TVP What Is IptvSachin KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Scottish Myths and Legends (PDFDrive)Document181 pagesScottish Myths and Legends (PDFDrive)VeraPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 2 - Pure Substances and MixturesDocument41 pagesLesson 2 - Pure Substances and Mixturescecil tayagPas encore d'évaluation
- FM TransmitterDocument15 pagesFM TransmitterMuhammad Aiman AmranPas encore d'évaluation
- BHCS31352F Mentor ViQ Specsheet - R24Document8 pagesBHCS31352F Mentor ViQ Specsheet - R24Jocélio A. TavaresPas encore d'évaluation
- 4.08 Intermediate Category of Taxation and Attorney and Own Client CostsDocument4 pages4.08 Intermediate Category of Taxation and Attorney and Own Client CostsBarbraPas encore d'évaluation
- Deep Learning The Indus Script (Satish Palaniappan & Ronojoy Adhikari, 2017)Document19 pagesDeep Learning The Indus Script (Satish Palaniappan & Ronojoy Adhikari, 2017)Srini KalyanaramanPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4 The ProcessorDocument131 pagesChapter 4 The ProcessorAk GptPas encore d'évaluation
- APPELANTDocument30 pagesAPPELANTTAS MUNPas encore d'évaluation
- Quiz 4Document5 pagesQuiz 4Diegiitho Acevedo MartiinezPas encore d'évaluation