Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
EM Induction Mindmap
Transféré par
Julio Alvarez SDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
EM Induction Mindmap
Transféré par
Julio Alvarez SDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
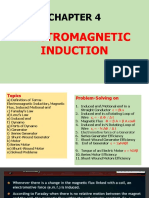
Electromagnetic Induction
www.TopPhysicsTuition.com Hp: 9620 7426 / Mr Tan Kheng Siang
Magnetic flux and the weber Wb The magnetic flux through a small plane surface is defined as the product of the magnetic flux density normal to the area and the area of the surface.
= (B cos )( A )
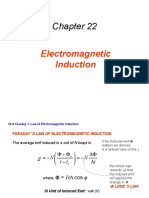
Lenzs law Lenz's law states that the direction of the induced current is such as to produce an effect that opposes the change of the magnetic flux that gives rise to it. The minus sign in the equation E = -
d (N) dt
expresses the Lenzs law.
Lenzs law is an example of the principle of the conservation of energy.
t NBA cos E = t B : A :
t
Normal B B cos B sin
N : E=
(BA cos )N t
or = (B sin )( A )
Faradays Law of EMI: E =
To induce emf, the numerator cannot be zero, hence at least one of the four quantities (N, B, A, ) must be a variable.
(cos ) :
Magnetic flux linkage () If a coil of N turns and area A is placed in a magnetic field of flux density B with its axis along the field, the total flux, known as flux linkage, is given by =N = N B A cos , where N: Number of turns of the coil The laws of electromagnetic induction Faradays law The magnitude of the induced electromotive force is directly proportional to the rate of change of flux linkage or the rate of flux cutting Induced e.m.f, | E |
d dt
E= (NA cos )B
S N
E=
(NB cos )A t
B (into page)
E=
(NBA )(cos ) t
B (into page)
v
Force Force
where is the flux linkage
d E=dt
Exerting a force on two ends of the coil, thus reducing the number of turns of the coil, N.
Removing the coil out of the B-Field, i.e. Bf = 0
/Wb
/Wb
t/s
t/s
E/V
E/V
The minus in the equation indicates the direction of the induced e.m.f. opposes the change of flux linkage. (Lenzs Law) For certain Calculations, Faradays law is expressed as
E =
t/s
t/s
, where : change t
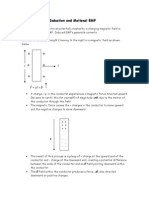
Eddy Current Small, circulating, unwanted currents generated by a magnetically induced electromotive force in a closed conductive path, such as a large metal plate, resulting in a waste of energy. If a large metal plate is moved through a magnetic field which intersects perpendicularly to the sheet, the magnetic field will induce small circulating current which will actually create internal magnetic fields opposing the change, thus slowing the object down. (Lenzs Law) In effect, the kinetic energy will go into driving small currents inside the metal which will give off that energy as heat as they push through the metal.
Bar magnet
For cutting of flux by a metal rod, E = BLv
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Chapter 21 Lecture Notes: FormulasDocument13 pagesChapter 21 Lecture Notes: Formulasapi-3710134Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter17 Electromagnetic Induction STPM PhsyicsDocument15 pagesChapter17 Electromagnetic Induction STPM PhsyicsSurianathPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4 - Electromagnetic Induction For SharingDocument42 pagesChapter 4 - Electromagnetic Induction For SharingTrisha Mae PerezPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 1 Formulae Electromagnetic InductionDocument6 pages4 1 Formulae Electromagnetic InductionNathanianPas encore d'évaluation
- (Y&F Chapters 30, 31 Ohanian Chapter 32) : Electromagnetic InductionDocument10 pages(Y&F Chapters 30, 31 Ohanian Chapter 32) : Electromagnetic InductionShootingStarPhotonsPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Electrical MachinesDocument63 pagesIntroduction To Electrical MachinessureshPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture - 13 and 14 Notes (1) - 1Document8 pagesLecture - 13 and 14 Notes (1) - 1Irene NziluPas encore d'évaluation
- Key Concept in Magnetic FluxDocument25 pagesKey Concept in Magnetic FluxmvmbapplePas encore d'évaluation
- Electromagnetic InductionDocument8 pagesElectromagnetic InductionMAHESH DPas encore d'évaluation
- Electromanetic Induction Points To Remember: ElectromagneticsDocument8 pagesElectromanetic Induction Points To Remember: ElectromagneticsMAHESH DPas encore d'évaluation
- 6 - InductanceDocument10 pages6 - InductanceRichie BobbyPas encore d'évaluation
- E 59 Kbro 1 JHWPPD 4 XdvraDocument16 pagesE 59 Kbro 1 JHWPPD 4 XdvraNitinPas encore d'évaluation
- Faraday'S LAW: Emf Ve - D /DT ... (Xii)Document4 pagesFaraday'S LAW: Emf Ve - D /DT ... (Xii)ekta39Pas encore d'évaluation
- Emi NotesDocument30 pagesEmi NotesAdarsh DhawanPas encore d'évaluation
- Faradays Law of InductionDocument9 pagesFaradays Law of InductionaaaaPas encore d'évaluation
- Induction PowerpointDocument48 pagesInduction PowerpointIsaac DunkleyPas encore d'évaluation
- HET316 L11 Time Vaying B FieldsDocument41 pagesHET316 L11 Time Vaying B FieldsMohammed ZainPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter30 Induction and InductanceDocument46 pagesChapter30 Induction and InductanceAshish ParasharPas encore d'évaluation
- Electromagnetic Induction: Faraday's Law of InductionDocument10 pagesElectromagnetic Induction: Faraday's Law of InductionDisha KatariaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 34 Maxwell's Equations Electromagnetic WavesDocument15 pagesChapter 34 Maxwell's Equations Electromagnetic WavesAshok KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 10 Unit 4 - Electromagnetic Induction NotesDocument5 pagesGrade 10 Unit 4 - Electromagnetic Induction NotesAaron KebedePas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 19 - Chapter 29 Part 2Document27 pagesLecture 19 - Chapter 29 Part 2Mircea PanteaPas encore d'évaluation
- Handout 10Document6 pagesHandout 10Prabhakar KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 19 - Chapter 29 Part 2Document27 pagesLecture 19 - Chapter 29 Part 2Mircea PanteaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ch4 - PHY121 - Magnetic Field - InductionDocument8 pagesCh4 - PHY121 - Magnetic Field - Inductionrhrazz6Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 1 Induced EmfDocument64 pagesLesson 1 Induced Emfeisuhlaing8Pas encore d'évaluation
- Module 21: Faraday's Law of InductionDocument32 pagesModule 21: Faraday's Law of InductionMuhammad FayazPas encore d'évaluation
- 23 - EmiDocument16 pages23 - EmiPratima MondalPas encore d'évaluation
- Electromagnetic Induction CH6Document18 pagesElectromagnetic Induction CH6Rishab SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- 51 Ch29 InductionDocument37 pages51 Ch29 InductionKesalan TerasaPas encore d'évaluation
- FARADAYDocument6 pagesFARADAYoseisilasyawPas encore d'évaluation
- SAQ Ans 28Document2 pagesSAQ Ans 28harshanauocPas encore d'évaluation
- HW10Document18 pagesHW10Vinay Aanand AanandPas encore d'évaluation
- FaradayDocument3 pagesFaradaymadhavPas encore d'évaluation
- Notes For Chapter 20Document28 pagesNotes For Chapter 20edsoneiccPas encore d'évaluation
- p112 Lecture13 PDFDocument20 pagesp112 Lecture13 PDFGauravPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Electromagnetic InductionDocument20 pages1 Electromagnetic InductionRizan SaopPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment 11: Faraday's Law of InductionDocument3 pagesExperiment 11: Faraday's Law of InductionGabriel DavidPas encore d'évaluation
- Magnetic CircuitDocument29 pagesMagnetic Circuitsujalshirke1904Pas encore d'évaluation
- L2 2 Maxwell EquationsDocument37 pagesL2 2 Maxwell Equationskwaleed717Pas encore d'évaluation
- 20-21 Electromagnetism and Induced EMFDocument19 pages20-21 Electromagnetism and Induced EMFkw2533Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mid Term Exam: Fall Term 2002 Introduction To Plasma Physics I 22.611J, 6.651J, 8.613JDocument3 pagesMid Term Exam: Fall Term 2002 Introduction To Plasma Physics I 22.611J, 6.651J, 8.613JmkpsrtmPas encore d'évaluation
- Electromagnetic InductionDocument12 pagesElectromagnetic InductionLaila Nur AfiantiPas encore d'évaluation
- Electromagnetic Induction 2nd Year PhysicsDocument82 pagesElectromagnetic Induction 2nd Year PhysicsWafa Zainab67% (3)
- Topic 12 1 Induced Electromotive ForceDocument32 pagesTopic 12 1 Induced Electromotive ForceAli Qasim0% (1)
- Lne13 PDFDocument18 pagesLne13 PDFSahasrajit SarmasarkarPas encore d'évaluation
- Induction Motors Part ADocument88 pagesInduction Motors Part AArpit PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- Electromagnetic InductionDocument106 pagesElectromagnetic InductiondynamicranjanPas encore d'évaluation
- 6 Electromagnetic InductionDocument4 pages6 Electromagnetic InductionRajender ReddyPas encore d'évaluation
- Notes For Lecture #16: Electromagnetic Waves and ConductorsDocument8 pagesNotes For Lecture #16: Electromagnetic Waves and ConductorsJoanna Modupeh HodasiPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 19 - Chapter 29 Part 2Document36 pagesLecture 19 - Chapter 29 Part 2Mircea PanteaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture19 Faraday's Law Induction Lenz's Law Generators Motional EmfDocument76 pagesLecture19 Faraday's Law Induction Lenz's Law Generators Motional EmfTaqi ShahPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic ConceptDocument56 pagesBasic ConceptHarish KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Electromagnetic Induction by Naveed BalouchDocument5 pagesElectromagnetic Induction by Naveed BalouchHafiz AbdulRehman100% (1)
- Time Vaying FieldsDocument16 pagesTime Vaying FieldsPuneeth SiddappaPas encore d'évaluation
- AnswerDocument1 pageAnswerPM GBERPas encore d'évaluation
- Electromagnetic Induction and Motional EMFDocument18 pagesElectromagnetic Induction and Motional EMF140557Pas encore d'évaluation
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsD'EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsPas encore d'évaluation
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterD'EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterPas encore d'évaluation
- Interactions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsD'EverandInteractions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsPas encore d'évaluation
- LISTENING: Second Family Jessica Talks About Her Host Family in SpainDocument1 pageLISTENING: Second Family Jessica Talks About Her Host Family in SpainJulio Alvarez SPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic 2 - 2012/13 Writing Task 1 Personal InfoDocument2 pagesBasic 2 - 2012/13 Writing Task 1 Personal InfoJulio Alvarez SPas encore d'évaluation
- Speaing Interaction Going RestaurantDocument1 pageSpeaing Interaction Going RestaurantJulio Alvarez SPas encore d'évaluation
- PostcardsDocument4 pagesPostcardsJulio Alvarez SPas encore d'évaluation
- Talking About Your School DaysDocument2 pagesTalking About Your School DaysJulio Alvarez SPas encore d'évaluation
- Job and Work DialogueDocument2 pagesJob and Work DialogueJulio Alvarez S100% (1)
- Task 1 (Monologue) : Daily Routine: Read The Following Information and Talk About The Subject For Two MinutesDocument1 pageTask 1 (Monologue) : Daily Routine: Read The Following Information and Talk About The Subject For Two MinutesJulio Alvarez SPas encore d'évaluation
- In On atDocument1 pageIn On atJulio Alvarez SPas encore d'évaluation
- 07.12.2021 Maha+revisionDocument376 pages07.12.2021 Maha+revisionDeepak YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- CadiawnubnuawndaDocument4 pagesCadiawnubnuawndaCedric Jayme JordanPas encore d'évaluation
- 9792 PHYSICS: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2013 SeriesDocument13 pages9792 PHYSICS: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2013 SeriesKelvin SerimwePas encore d'évaluation
- Insp Champs 2022 Modern - PhysicsDocument15 pagesInsp Champs 2022 Modern - Physicsdarling deanPas encore d'évaluation
- Dyna S Electronic Ignition Instructions: InstallationDocument5 pagesDyna S Electronic Ignition Instructions: InstallationAlejandro CardozoPas encore d'évaluation
- Microwave InspectionDocument10 pagesMicrowave InspectionZaid TariqPas encore d'évaluation
- Irradiance-Adaptive PV Module Integrated Converter For High Efficiency and Power Quality in Standalone and DC Microgrid ApplicationsDocument11 pagesIrradiance-Adaptive PV Module Integrated Converter For High Efficiency and Power Quality in Standalone and DC Microgrid ApplicationsTRIAD TECHNO SERVICESPas encore d'évaluation
- Course Code & Title Phy101EC-Physics Lecture MODULE 6: 5 Hrs. Waves and SoundDocument14 pagesCourse Code & Title Phy101EC-Physics Lecture MODULE 6: 5 Hrs. Waves and SoundBenedict SalazarPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Sciences 151. Electromagnetic Communication LaboratoryDocument5 pagesEngineering Sciences 151. Electromagnetic Communication LaboratorybaymanPas encore d'évaluation
- Chem Basic FB Answer Key CH 05 (06.13.16)Document6 pagesChem Basic FB Answer Key CH 05 (06.13.16)amalieroPas encore d'évaluation
- Electromagnetic Stress-Energy Tensor: SI UnitsDocument3 pagesElectromagnetic Stress-Energy Tensor: SI UnitsAmruta SadhuPas encore d'évaluation
- R. Harish (08011A0209) B.Tech (4/4) Dept. of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, JNTUH College of Engineering HyderabadDocument17 pagesR. Harish (08011A0209) B.Tech (4/4) Dept. of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, JNTUH College of Engineering HyderabadNagi NagPas encore d'évaluation
- Correspondence: Response of Grounding Electrodes To Impulsive Currents: An Experimental EvaluationDocument4 pagesCorrespondence: Response of Grounding Electrodes To Impulsive Currents: An Experimental EvaluationMaksimBarannikPas encore d'évaluation
- Speed and Acceleration MeasurementDocument38 pagesSpeed and Acceleration MeasurementAmit RegePas encore d'évaluation
- RRVV 65D R4 Product SpecificationDocument5 pagesRRVV 65D R4 Product SpecificationAngelPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2 Derivations Physics PDFDocument8 pagesChapter 2 Derivations Physics PDFSHAURYA SRIVASTAVAPas encore d'évaluation
- Self InductanceDocument3 pagesSelf Inductancesuhayb100% (1)
- Interview QuestionsDocument5 pagesInterview QuestionsShahed HussainPas encore d'évaluation
- P5 - Light ShadowDocument11 pagesP5 - Light ShadowHarshaWakodkarPas encore d'évaluation
- Yoga Maulana Putra (17063072)Document10 pagesYoga Maulana Putra (17063072)Yoga MaulanaPas encore d'évaluation
- HCV-2, HCV-4, HCV-8: Conventional Fire Alarm Control Panel Standard FeaturesDocument4 pagesHCV-2, HCV-4, HCV-8: Conventional Fire Alarm Control Panel Standard FeaturesVăn Tuấn NguyễnPas encore d'évaluation
- PhET - Electric Circuits - Virtual LabDocument5 pagesPhET - Electric Circuits - Virtual LabKelvin SmithPas encore d'évaluation
- S.6 Physics Trial Questions: Figure 6.23)Document6 pagesS.6 Physics Trial Questions: Figure 6.23)Mubiru IvanPas encore d'évaluation
- Handout Physics 101 ForceDocument12 pagesHandout Physics 101 ForceMary Grace AcostaPas encore d'évaluation
- Body PartsDocument3 pagesBody PartsKaren Molina AriasPas encore d'évaluation
- Force, Energy, and Momentum 3 QDocument28 pagesForce, Energy, and Momentum 3 QEses SPas encore d'évaluation
- Heaters For Contender EDS, EDS and N1 Series Manual Motor StartersDocument2 pagesHeaters For Contender EDS, EDS and N1 Series Manual Motor StartersMuhamad PriyatnaPas encore d'évaluation
- Final Sc. Ed. 422. Physics IIDocument15 pagesFinal Sc. Ed. 422. Physics IItikaram gautamPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Coulombs Law and Principle of SuperpositionDocument14 pages1 Coulombs Law and Principle of Superpositionpaulkani-ece100% (11)
- Eddy Current TestingDocument43 pagesEddy Current TestingkongsakuaiphonPas encore d'évaluation