Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
FINAL Drug Study
Transféré par
Kristen Leigh MarianoTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
FINAL Drug Study
Transféré par
Kristen Leigh MarianoDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
VII.
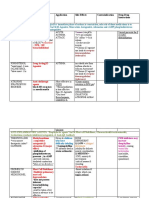
Drug Study: DRUG NAME Losartan Potassium Drug Class: Antihypertensive ARB MECHANISM OF ACTION Selectively blocks the binding of angiotensin II to specific tissue receptors found in the vascular smooth muscle and adrenal glands; this action block the vasoconstriction effect of the reninangiotensin system as well as the release of aldosterone leading to decreased BP. INDICATION Treatment of hypertension, alone or in combination with other antihypertensive. DOSAGE 50 mg tab OD in AM via NGT. SIDE EFFECTS Dizziness, headache, nauseas, vomiting, diarrhea, symptoms of upper respiratory tract infection, cough. CONTRAINDICATION Contraindicated with hypersensitivity to losartan, pregnancy (use during the second or third trimester can cause injury or even death to fetus), lactation. NURSING INTERVENTIONS Administer without regards to meal. Ensure that the patient is not pregnant before beginning therapy; suggest the use of barrier birth control while using losartan; fetal injury and deaths have been reported. Find an alternative method of feeding the baby if given to a nursing mother. Depression of reninangiotensin system in infant us potentially very dangerous. Alert surgeon and mark the patients chart with notice that losartan is being taken. The blockage of renin-angiotensin system following
Reduction of risk of CVA in patients with hypertension and left ventricular hypertrophy.
surgery can produce problems. Hypotension may be reversed with volume expansion. Monitor patient closely in any situation that may lead to decreased in BP secondary to reduction in fluid volume excessive perspiration, dehydration, vomiting, diarrhea excessive hypotension can occur.
DRUG NAME Amlodipine besylate Drug Class: Antianginal Antihypertensive Calcium Channel Blocker
MECHANISM OF ACTION Inhibits the movement of calcium ions across the membranes of cardiac and arterial muscle cells; inhibits transmembrane
INDICATION Essential hypertension, alone or in combination with other antihypertensives.
DOSAGE 10 mg tab OD at HS via NGT
SIDE EFFECTS Nausea, vomiting, headache.
CONTRAINDICATION Contraindicated with allergy to losartan, impaired hepatic or renal function, sick sinus syndrome, heart block, lactation.
NURSING INTERVENTIONS Monitor patients carefully (BP, cardiac rhythm, and output) while adjusting drug to therapeutic dose; use special caution if patient has heart failure.
calcium flow, which results in the depression of impulse formation in specialized cardiac pacemaker cells, slowing of the velocity of conduction of cardiac impulse, depression of myocardial contractility, and dilatation of coronary arteries and arterioles and peripheral arterioles; these effects lead to decreased cardiac work, decreased cardiac oxygen consumption, and in patients with vasospastic angina, increased delivery of oxygen to cardiac cells.
Monitor BP very carefully if patient is also in nitrates. Monitor cardiac rhythm regularly during stabilization of dosage and periodically during long term therapy. Administer drug without regards to meal. Report irregular heartbeat, shortness of breath, swelling of the hands or feet, pronounced dizziness, constipation.
DRUG NAME Simvastatin Drug class: Antihyperlipidemic HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitor
MECHANISM OF ACTION Inhibits HMG-CoA Reductase, the enzyme that catalyzes the first step in the cholesterol synthesis pathway, resulting in a decrease in serum cholesterol, serum LDLs, and either an increase or no change in serum HDLs.
INDICATION
DOSAGE
Adjunct to diet in 40 mg tab OD at the treatment of HS via NGT. elevated total cholesterol and LDL cholesterol with primary hypercholesterolem ia in those unresponsive to dietary restriction of saturated fat and cholesterol and other nonpharmacologic measures. To reduce the risk of coronary disease, mortality and CV events, including CVA, TIA, MI and reduction in need for bypass surgery and angioplasty in patients with coronary heart disease and hypercholesterolem ia.
SIDE EFFECTS Nausea, headache, muscle and joint aches and pains, sensitivity to light.
CONTRAINDICATION Contraindicated with allergy to simvastatin, fungal byproducts; active liver disease or unexplained, persistent elevation of serum transaminases; pregnancy, lactation.
NURSING INTERVENTIONS Take drug in the evening. Highest rate of cholesterol synthesis are between midnight and 5 am. Do not drink grape juice while using this drug. Advise patient to have periodic blood test. Advise patient that this drug cannot be taken during pregnancy; using barrier contraception, is recommended.
DRUG NAME Mannitol Drug class: Diagnostic agent Osmotic diuretics Urinary irrigant
MECHANISM OF ACTION Elevates the osmolarity of the glomerular filtrate, thereby hindering the reabsorption of water and leading to a loss of water, sodium, chloride; creates an osmotic gradient in the eye between plasma and ocular fluids, thereby reducing IOP; creates an osmotic effect, leading to decreased swelling in posttransurethral prostatic resection.
INDICATION Prevention and treatment of the oliguric phase of renal failure. Reduction of intracranial pressure and treatment of cerebral edema; of elevated IOP when the pressure cannot be lowered by other means. Promotion of urinary excretion of toxic substances. Diagnostic use: Measurement of GFR.
DOSAGE 175cc every 4 hours
SIDE EFFECTS Increased urination; GI upset; dry mouth; headache, blurred vision.
CONTRAINDICATION Contraindicated with anuria due to severe renal disease.
NURSING INTERVENTIONS Do not give electrolyte free mannitol with blood. If blood must be given, add atleast 20mEq of sodium chloride to each liter of mannitol solution. Do not expose solutions to low temperatures; crystallization may occur. If crystals are seen, warm the bottle in a hot water bath, then cool to body temperature before administering. Make sure the infusion set contains a filter if giving concentrated mannitol. Monitor serum electrolytes
periodically with prolonged therapy.
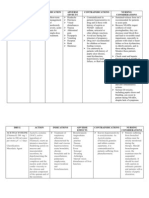
DRUG NAME Citicholine Drug class: CNS Stimulant, Peripheral Vasodilators, Cerebral Activators
MECHANISM OF ACTION Citicoline increases blood flow and O2 consumption in the brain. It is also involved in the biosynthesis action.
SIDE EFFECTS Citicoline is 500mg IV every 8 Fleeting and indicated in CVD hours discrete in acute recovery hypotension phase in severe s/sx effect, of cerebrovascular increased insufficiency and parasympathe in-cranial tic effects, traumatism and low blood their sequellae. pressure Citicoline in CVA, stimulates brain Itching or function. hives, swelling in face or hands, chest tightness, tingling in mouth and throat
INDICATION
DOSAGE
CONTRAINDICATION Any allergy or hypersensitivity to the drug Hypertonia of the parasympathetic nervous system
NURSING INTERVENTIONS Take Citicoline as prescribed Take Citicoline on time Monitor patients neurologic status Note if there are signs of slurring of speech Note for adverse reactions Titer medication when discontinuing Teach patient on how to take the drug Arrange for regular
follow-ups
DRUG NAME Lactulose Drug class: Ammonia reduction drug Laxative
MECHANISM OF ACTION Lactulose is a synthetic sugar used in the treatment of constipation and liver disease. It consists of the monosaccharides fructose and galactose. In the colon, lactulose is broken down primarily to lactic acid, and also to small amounts of formic and acetic acids, by the action of via evolved-beta galactosidase from colonic bacteria, which results in an increase in osmotic pressure and slight acidification of the
INDICATION Treatment of constipation. Prevention and treatment of portalsystemic encephalopathy.
DOSAGE 30 cc OD at HS
SIDE EFFECTS Abdominal fullness, flatulence, belching.
CONTRAINDICATION Contraindicated with allergy to lactulose, lowgalactose diet.
NURSING INTERVENTIONS Do not freeze laxative form. Extremely dark or cloudy syrup may be unsafe; do not use. Give laxative syrup orally with fruit juice, water, or milk to increase palatability. Administer retention enema using a rectal balloon catheter. Do not use cleansing enemas containing soapsuds or other alkaline drugs that counteract the effects of lactulose. Do not administer other laxatives while using lactulose.
colonic contents. This in turn causes an increase in stool water content and softens the stool. In treating heptic diseases (hepatic encephalopathy) it is thought that lactulose draws out ammonia from the body in the same way that it draws out water into the colon.
Monitor serum ammonia levels.
DRUG NAME Omeprazole Drug class: Antisecretory drug Proton pump inhibitor
MECHANISM OF ACTION Gastric acid-pump inhibitor: Suppresses gastric acid secretion by specific inhibition of the hydrogenpotassium ATPase enzyme system at the secretory surface of the gastric parietal
INDICATION
DOSAGE
First-line therapy in 40 mg IV OD treatment of heartburn or symptoms of gastro esophageal reflux disease (GERD) Short-term treatment of active benign gastric ulcer
SIDE EFFECTS Dizziness, headache, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, symptoms of URI, cough.
CONTRAINDICATION Contraindicated with hypersensitivity to omeprazole or its components.
NURSING INTERVENTIONS Administer before meals. Caution patient to swallow capsules whole- not to open, chew, or crush them. If using oral suspension, empty packet into a small cup containing 2 tbsp of water. Stir and have patient drink
cells; blocks the final step of acid production.
GERD, severe erosive esophagitis, poorly responsive symptomatic GERD
immediately; fill cup with water and have patient drink this water. Do not use any other diluent. Administer antacids with, if needed.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Gem RemediesDocument49 pagesGem Remediesksrinivas9999100% (5)
- Drug Class:: Prototype (Generic/Trade) : Eskalith, LithobidDocument1 pageDrug Class:: Prototype (Generic/Trade) : Eskalith, LithobidAaLona Robinson100% (2)
- STUDENT Sepsis Rapid ReasoningDocument6 pagesSTUDENT Sepsis Rapid Reasoningghodghod123Pas encore d'évaluation
- CholestyramineDocument1 pageCholestyramineKatie McPeekPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharmacology MapsDocument18 pagesPharmacology MapsPERUBATAN Cawangan Zagazig100% (1)
- Drug Study: OmeprazoleDocument5 pagesDrug Study: Omeprazoleclau_latojaPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 10 HomeworkDocument10 pagesUnit 10 HomeworkKristen Leigh MarianoPas encore d'évaluation
- Medical-Surgical Nursing: (Prepared By: Prof. Rex B. Yangco)Document12 pagesMedical-Surgical Nursing: (Prepared By: Prof. Rex B. Yangco)Leilah Khan100% (1)
- Ivf Drug StudyDocument9 pagesIvf Drug StudyRyu Bomi0% (2)
- Pharma MnemonicsDocument10 pagesPharma MnemonicsMuhammad Ali Aziz100% (4)
- Aldactone SpironlactoneDocument1 pageAldactone SpironlactoneCassie100% (1)
- Drug Study Er MedsDocument12 pagesDrug Study Er MedsJerald S. OlaloPas encore d'évaluation
- Coreg (Carvedilol)Document1 pageCoreg (Carvedilol)Adrianne BazoPas encore d'évaluation
- AtivanDocument1 pageAtivanSheri490Pas encore d'évaluation
- Drug SuffixesDocument3 pagesDrug SuffixesjeromeasuncionPas encore d'évaluation
- Lopressor (Metoprolol) 100mgDocument2 pagesLopressor (Metoprolol) 100mgAdrianne Bazo100% (2)
- Drug Study For PneumoniaDocument15 pagesDrug Study For PneumoniaPrincess Pauline Abrasaldo100% (1)
- GIT DrugsDocument180 pagesGIT DrugsMaria Linevel Balderamos Dalida100% (1)
- DiltiazemDocument2 pagesDiltiazemE100% (1)
- Endocrine Drug ChartDocument1 pageEndocrine Drug ChartJessicaPas encore d'évaluation
- Anes Drugs TableDocument20 pagesAnes Drugs TableKathleen Grace ManiagoPas encore d'évaluation
- HHNK and DkaDocument4 pagesHHNK and Dkagoya100% (1)
- Pharmacology Respiratory DrugsDocument2 pagesPharmacology Respiratory DrugsM Youssif Elkady100% (1)
- PharmacologyDocument84 pagesPharmacologyhenrydycoco100% (1)
- DimenhydrinateDocument1 pageDimenhydrinateMichael KuzbytPas encore d'évaluation
- Chart Summary of Medications Affecting The Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument1 pageChart Summary of Medications Affecting The Autonomic Nervous Systemmadison61404100% (2)
- Drug StudyDocument15 pagesDrug StudyCheyee MaePas encore d'évaluation
- EzetimibeDocument3 pagesEzetimibeapi-3797941Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ranitidine, Acetaminophen, Albuterol Drug StudyDocument5 pagesRanitidine, Acetaminophen, Albuterol Drug StudyBea Andrea LarismaPas encore d'évaluation
- Generic and Trade Names, Mechanisms, InterventionsDocument4 pagesGeneric and Trade Names, Mechanisms, InterventionsSonia FernandesPas encore d'évaluation
- Anti-Infectives and AntibioticsDocument38 pagesAnti-Infectives and AntibioticsKarel Lu0% (1)
- Drug Name Mechanism Application Side Effects Contraindication Drug-Drug InteractionsDocument3 pagesDrug Name Mechanism Application Side Effects Contraindication Drug-Drug Interactionsazhar hussinPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharmacology & Parenteral TherapiesDocument44 pagesPharmacology & Parenteral Therapiesjennylyn guadalupePas encore d'évaluation
- Drugs acting on the Cardiovascular SystemDocument18 pagesDrugs acting on the Cardiovascular SystemIbrahem AlPas encore d'évaluation
- The 10 Most Common Emergency DrugsDocument28 pagesThe 10 Most Common Emergency DrugsKrishna BalsarzaPas encore d'évaluation
- Er-Drug StudyDocument41 pagesEr-Drug Studyrc_lacampuinganyahooPas encore d'évaluation
- EnalaprilDocument2 pagesEnalaprilAyah PaasaPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug PrilosecDocument1 pageDrug PrilosecSrkocher100% (1)
- Omeprazole DSDocument2 pagesOmeprazole DSjenniferducaoPas encore d'évaluation
- DRUG SUMMARY TABLE - Anticoagulantes y AntiagregantesDocument3 pagesDRUG SUMMARY TABLE - Anticoagulantes y AntiagregantesManuel BetancurPas encore d'évaluation
- Er DrugsDocument15 pagesEr DrugsDays AniarPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharmacology ReviewDocument28 pagesPharmacology ReviewKathy Wollschleger100% (1)
- Chest Tube ThoracostomyDocument7 pagesChest Tube Thoracostomyskyblueali100% (2)
- CeftriaxoneDocument2 pagesCeftriaxoneFlora Angeli PastoresPas encore d'évaluation
- Levaquin Drug CardDocument1 pageLevaquin Drug CardSheri490100% (1)
- Coreg (Carvedilol)Document3 pagesCoreg (Carvedilol)EPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyKristelle Joy MontesPas encore d'évaluation
- MorphineDocument2 pagesMorphineKatie McPeek100% (2)
- TrihexyphenidylDocument5 pagesTrihexyphenidylZepHemaPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug-Study PharmacologyDocument11 pagesDrug-Study PharmacologyEmmanuel CaracalPas encore d'évaluation
- Types of InsulinDocument1 pageTypes of InsulinSyed IbrahimPas encore d'évaluation
- Zoloft SertralineDocument1 pageZoloft SertralineAdrianne Bazo100% (1)
- Description: Congestive Heart FailureDocument22 pagesDescription: Congestive Heart FailurePinklet Arleena CubianPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Card MotrinDocument2 pagesDrug Card MotrinAdrianne BazoPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument14 pagesDrug StudyWendy EscalantePas encore d'évaluation
- Labs Drug Study 1Document17 pagesLabs Drug Study 1Drei LanuzoPas encore d'évaluation
- CVA Drug StudyDocument51 pagesCVA Drug StudyKarel LuPas encore d'évaluation
- Emergency DrugsDocument5 pagesEmergency DrugsArra PlacidesPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyMaurence John Feliciano LuluquisenPas encore d'évaluation
- Spironolactone: Generic Name Brand Name ClassificationDocument5 pagesSpironolactone: Generic Name Brand Name ClassificationShermalyn SalahuddinPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug Studyanon_11638632Pas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Action Indication Adverse Effects Contraindications Nursing Considerations Ketorolac TromethamineDocument8 pagesDrug Action Indication Adverse Effects Contraindications Nursing Considerations Ketorolac TromethamineAiryn CanonPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug RationaleDocument77 pagesDrug RationaleYolanda WilliamsPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument22 pagesDrug StudyColleen Fretzie Laguardia NavarroPas encore d'évaluation
- InfrastructureDocument1 pageInfrastructureKristen Leigh MarianoPas encore d'évaluation
- Nutrition and BPDocument1 pageNutrition and BPKristen Leigh MarianoPas encore d'évaluation
- 1application LetterDocument4 pages1application LetterKristen Leigh MarianoPas encore d'évaluation
- Couples Faith Tested by Alzheimer's in "A Vow to CherishDocument1 pageCouples Faith Tested by Alzheimer's in "A Vow to CherishKristen Leigh MarianoPas encore d'évaluation
- Enviro factors in HTNDocument2 pagesEnviro factors in HTNKristen Leigh MarianoPas encore d'évaluation
- Certificate SampleDocument1 pageCertificate SampleKristen Leigh MarianoPas encore d'évaluation
- Non Genetic Cellular Theory of AgingDocument2 pagesNon Genetic Cellular Theory of AgingKristen Leigh MarianoPas encore d'évaluation
- Non Genetic Cellular Theory of AgingDocument10 pagesNon Genetic Cellular Theory of AgingKristen Leigh MarianoPas encore d'évaluation
- Data Collection and InstrumentDocument1 pageData Collection and InstrumentKristen Leigh MarianoPas encore d'évaluation
- Uterine CancerDocument10 pagesUterine CancerKristen Leigh MarianoPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology of Uremic EncephalopathyDocument5 pagesPathophysiology of Uremic EncephalopathyKristen Leigh Mariano100% (1)
- Journal Report On Evidence Based Nursing: Far Eastern University Institute of NursingDocument4 pagesJournal Report On Evidence Based Nursing: Far Eastern University Institute of NursingKristen Leigh MarianoPas encore d'évaluation
- AbbreviationsDocument2 pagesAbbreviationslovely2886Pas encore d'évaluation
- Nutrition and BPDocument1 pageNutrition and BPKristen Leigh MarianoPas encore d'évaluation
- Past Tense Revision-DataCollectionDocument1 pagePast Tense Revision-DataCollectionKristen Leigh MarianoPas encore d'évaluation
- I NTRODUCTIONDocument1 pageI NTRODUCTIONKristen Leigh MarianoPas encore d'évaluation
- Normal Values of CSFDocument1 pageNormal Values of CSFKristen Leigh MarianoPas encore d'évaluation
- Who Is Your Hero?Document2 pagesWho Is Your Hero?Kristen Leigh MarianoPas encore d'évaluation
- Afterschool Red Into The Night SkyDocument3 pagesAfterschool Red Into The Night SkyKristen Leigh MarianoPas encore d'évaluation
- Figure 2. Frequency Distribution of The Respondents by Gender at Dapitan, Metro Manila, 2013Document1 pageFigure 2. Frequency Distribution of The Respondents by Gender at Dapitan, Metro Manila, 2013Kristen Leigh MarianoPas encore d'évaluation
- Who Is Your Hero?Document2 pagesWho Is Your Hero?Kristen Leigh MarianoPas encore d'évaluation
- Novel Technology Identifies Biomarkers for Ulcerative ColitisDocument1 pageNovel Technology Identifies Biomarkers for Ulcerative ColitisKristen Leigh MarianoPas encore d'évaluation
- Geno GramDocument2 pagesGeno GramKristen Leigh MarianoPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Out of 4 Pinoy Adults FatDocument7 pages1 Out of 4 Pinoy Adults FatKristen Leigh MarianoPas encore d'évaluation
- Tetanus Is Acquired When The Spores of The Bacterium Clostridium Tetani Infect A Wound or The Umbilical StumpDocument2 pagesTetanus Is Acquired When The Spores of The Bacterium Clostridium Tetani Infect A Wound or The Umbilical StumpKristen Leigh MarianoPas encore d'évaluation
- Head-To-Toe Physical Assessment Assessment Actual Findings Analysis Skin and NailsDocument8 pagesHead-To-Toe Physical Assessment Assessment Actual Findings Analysis Skin and NailsKristen Leigh MarianoPas encore d'évaluation
- Family Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesFamily Nursing Care PlanKristen Leigh MarianoPas encore d'évaluation
- Malnutrition FNCPDocument5 pagesMalnutrition FNCPKristen Leigh MarianoPas encore d'évaluation
- 11 Series TNCDocument32 pages11 Series TNCPoonam Yadav roll no.53Pas encore d'évaluation
- Biochemical Aspect of DiarrheaDocument17 pagesBiochemical Aspect of DiarrheaLiz Espinosa0% (1)
- Psychiatric History and Mental Status Examination GuideDocument7 pagesPsychiatric History and Mental Status Examination GuideGabriel Gerardo N. Cortez100% (1)
- The Over Training SyndromeDocument4 pagesThe Over Training SyndromeFilip ZalioPas encore d'évaluation
- Ocular Manifestations of HIV: A ReviewDocument33 pagesOcular Manifestations of HIV: A Reviewhenok birukPas encore d'évaluation
- 12 Physical Education Chapter 3Document24 pages12 Physical Education Chapter 3akanksha nayanPas encore d'évaluation
- Stress Managment ProjectDocument73 pagesStress Managment ProjectNagireddy KalluriPas encore d'évaluation
- Roth 10e NCLEX Chapter 10 Foodborne IllnessDocument4 pagesRoth 10e NCLEX Chapter 10 Foodborne IllnessjennaaahhhPas encore d'évaluation
- Foundation of Professional Nursing Practice Review (40Document25 pagesFoundation of Professional Nursing Practice Review (40Sittie Haya LazimPas encore d'évaluation
- Personal View: OnlineDocument9 pagesPersonal View: OnlineMaria YustinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Stenorol® Crypto - OS - Brochure - EN - v01 - 1020 PDFDocument2 pagesStenorol® Crypto - OS - Brochure - EN - v01 - 1020 PDFDrivailaPas encore d'évaluation
- The World Healthiest Foods Part III - FruitsDocument39 pagesThe World Healthiest Foods Part III - FruitsKyle J. NortonPas encore d'évaluation
- What Happens If Anal Fistula Is Not Treated On Time? - Dr. Samrat JankarDocument3 pagesWhat Happens If Anal Fistula Is Not Treated On Time? - Dr. Samrat JankarDr. Samrat JankarPas encore d'évaluation
- OSTEOARTHRITISDocument4 pagesOSTEOARTHRITISapi-3822433100% (2)
- Medical MarijuanaDocument4 pagesMedical MarijuanaDanielZepedaPereaPas encore d'évaluation
- Saudi ENT MCQ Exam 2010Document162 pagesSaudi ENT MCQ Exam 2010Hamada Hassan Alloq100% (1)
- MisoprostolDocument5 pagesMisoprostolkristenerika100% (2)
- End Stage Renal Disease Case StudyDocument8 pagesEnd Stage Renal Disease Case StudyNikko Dela CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2Document8 pagesChapter 2CLYDE ARIES TORCULASPas encore d'évaluation
- Isosorbide Mononitrate: Adult: PO Regular Release (ISMO, Monoket) 20 MG B.I.D. 7 H ApartDocument2 pagesIsosorbide Mononitrate: Adult: PO Regular Release (ISMO, Monoket) 20 MG B.I.D. 7 H ApartAubrey Unique EvangelistaPas encore d'évaluation
- 5 Natural Juices To Heal A Sore ThroatDocument5 pages5 Natural Juices To Heal A Sore Throatasset68Pas encore d'évaluation
- Great Plains LaboratoryDocument2 pagesGreat Plains LaboratoryLidia AgataPas encore d'évaluation
- AP Prefixes Suffixes Ebook 2016Document22 pagesAP Prefixes Suffixes Ebook 2016Jorge MarronePas encore d'évaluation
- Health - ALL ABT STRESSSSSSSSSDocument10 pagesHealth - ALL ABT STRESSSSSSSSSDennise Adrianne OfarilPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiology Workshop HighlightsDocument32 pagesCardiology Workshop HighlightsChristabella Natalia WijayaPas encore d'évaluation
- Vital Signs: Learning ObjectivesDocument35 pagesVital Signs: Learning ObjectivesVictoria TamayoPas encore d'évaluation
- Relationship Between Cigarette Smoking and Novel Risk Factors For Cardiovascular DiseaseDocument4 pagesRelationship Between Cigarette Smoking and Novel Risk Factors For Cardiovascular DiseaseInternational Medical PublisherPas encore d'évaluation