Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Antenatal Care
Transféré par
Annapurna DangetiTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Antenatal Care
Transféré par
Annapurna DangetiDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Antenatal Care Systematic supervision of a woman during pregnancy is called antenatal care.
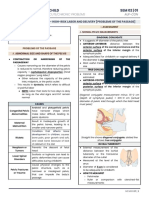
The supervision should be of a regular and periodic nature in accordance with the principles laid down or more frequently according to the need of the individual. It is the education, supervision and treatment to a pregnant woman so that her pregnancy and labour will terminate with delivery of a mature healthy living baby, without injury to the mind or body of the mother. The objective of Antenatal care is to ensure a normal pregnancy with delivery of a healthy baby from a healthy mother. Aims of antenatal care: 1. to monitor the progress of pregnancy in order to ensure maternal health and normal fetal development. . to recognise the deviation from the normal and provide management or treatment as required. !. to ensure that the woman reaches the end of her pregnancy physically and emotionally prepared for her delivery. ". to identify high ris# pregnancy and for their proper management. $. to reduce or prevent maternal and perinatal mortality and morbidity %. to help and support the mother in breast feeding and parenting. &. to offer family welfare advices on parenthood. Antenatal care comprises of: 1. 'egistration of pregnancy . (istory ta#ing !. Antenatal e)aminations *general and obstetrical+ ". (ealth education A. Registration of pregnancy: The registration of pregnancy must be done in an antenatal clinic within 1 wee#s. B. History taking: A complete history of the woman including the following is collected in the first visit. 1. ,emographic data -.ame, age, address, marital status, religion, education, occupation etc/ . 0enstrual history. !. 1ersonal history. ". 1ast medical and surgical history. $. 2amily history. %. (istory of present pregnancy -last menstrual period 301, 4)pected date of delivery 4,,, etc. &. 5bstetrical history -number of pregnancy, any abnormality in previous pregnancies and deliveries/. 6. 7alculation of e)pected date of delivery -4,,/8 4,, is calculated by adding nine calendar months and seven days to the date of first day of the woman9 s last menstrual period, provided the woman has a regular 6:day menstrual cycle. C. Antenatal examination:
A complete general e)aminations of the body is conducted, including 1. Height: The height is carefully recorded, as patients measuring $ feet or less is more li#ely to have a small pelvis that may cause difficulty during delivery. . Weight: ;eight should be regularly ta#en using an accurate weighing machine. 1eriodic and regular weight chec#ing helps in detecting abnormalities. !. Pallor: 7olour of conjuctiva, soft palate, tongue, and nail beds are to be noted. -1aleness indicates anemia/ ". Jaundice: 4yes and mouth are to be observed for yellow discolouration. -yellow discolouration indicates of jaundice/ $. ongue! teeth! gums: 5bserve for signs of infection and malnutrition. %. "egs: 3egs are to be e)amined for oedema. &. Breasts: 4)amination of the breasts is mandatory, to note the presence of pregnancy charges and condition of the nipples -crac#ed < depressed < inverted/. 6. A#dominal and $aginal examinations: 1osition of the uterus is noted in abdominal e)amination. =nless necessary, vaginal e)aminations is not routinely done e)cept for the first time when the woman attends the clinic to confirm pregnancy. "a#oratory in$estigations: %. 7omplete blood count including haemoglobin level, &. >lood grouping and 'h typing. '. >lood for ?,'3 (. =rine e)aminations8 ). =rine should be tested for albumin, sugar, pus cells, 5ne to two doses of tetanus to)oid is given to immuni@e against tetanus infection iron and folic acid supplements is given *u#se+uent $isits: =p to 6 wee# :: the antenatal chec# up should be done at an interval of " wee#s from the first visit. >eyond 6 wee#s, the antenatal chec# up should be done at interval of wee#s upto !% wee# and thereafter wee#ly, till the e)pected date of delivery. At each visit, the findings are to be recorded in the same card for better evaluation. ,. Health education: The antenatal education should include. ,iet The diet during pregnancy should be adequate to provide for a. the maintenance of maternal health. b. the needs of the growing fetus. c. the strength and vitality required during labour and d. the successful lactation. The pregnancy diet should be light, nutritious and easily digestible. It should be rich in protein, minerals vitamins and fibres and of the required calories. ,ietary advice should be given with due consideration to the socio:economic condition, food habits
and taste of the individual. Supplementary iron therapy is needed for all pregnant mothers from A wee#s onwards. Personal hygiene 1. Rest and sleep: The woman may continue her usual activities throughout pregnancy. (ard and strenuous wor# should be avoided. 5n an average, a patient should have 1A hours of sleep -6 hours at night and hours at noon/ . Bo-el: As there is a tendency of constipation during pregnancy, regular bowel movement may be facilitated by regulation of diet ta#ing plenty of fluids, vegetables and mil#. !. Bathing: ,aily baths and preferably twice a day are advised. ". Clothing: The patient should wear loose but comfortable dresses. (igh heel shoes are better avoided. $. ,ental hygiene: The dentist should be consulted at the earliest, if necessary. %. Care of the #reasts: 7leanliness of the breasts is maintained. If anatomical defects are present advise to see# medical help. &. Coitus: 7ontact with the husband to be avoided during the first trimester and last % wee#s. 6. ra$el: 3ong distance travel better to be avoided. 'ail route is preferable. B. *moking and alcohol: Smo#ing and alcohol are to be avoided totally during pregnancy as both cause variable injuries to the fetus. 1A. ,rugs8 The pregnant women should avoid over:the counter drugs -drugs without medical prescription/. The drugs may have teratogenic effects on the growing fetus especially during the first trimester -The first three months is the period of organogenesis. Teratogens will cause gross malformation or defects to the fetus. The common teratogens are drugs caffeine, e)posure to ):rays, alcohol, nicotine, etc/. .eneral ad$ice The patient should be persuaded to attend for antenatal chec#up positively on the scheduled date of visit. She is instructed to report to the doctor even at an early date and if the following untoward -warning signs and symptoms/ symptoms arise8 intense persistent headache severe oedema disturbed sleep with restlessness low urine output -less than $AA ml per day/ epigastric pain persistent vomiting painful uterine contractions sudden gush of watery fluid per vaginum active vaginal bleeding, etc.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Antenatal Care PPT EchyDocument14 pagesAntenatal Care PPT EchyYuliana alensi falloPas encore d'évaluation
- Antenatal CareDocument19 pagesAntenatal CareIshika RoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 3 Admission Procedure of Women in LabourDocument30 pagesUnit 3 Admission Procedure of Women in LabourNishaThakuriPas encore d'évaluation
- Postpartum Hemorrhage (PPH) : Prakash Thakulla InternDocument38 pagesPostpartum Hemorrhage (PPH) : Prakash Thakulla InternPrakash ThakullaPas encore d'évaluation
- Obstetric & Gynecology Nursing: Topic-Physiological Changes During LabourDocument54 pagesObstetric & Gynecology Nursing: Topic-Physiological Changes During LabourBhumi ChouhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Drugs Used IN Pregnancy, Labour, Puerperium & NewbornDocument42 pagesDrugs Used IN Pregnancy, Labour, Puerperium & NewbornSanjay Kumar SanjuPas encore d'évaluation
- A Study To Assess The Knowledge of Primi Gravida Mother Regarding Importance Colostrum at Selected Hospital Bagalkot Karnataka, IndiaDocument10 pagesA Study To Assess The Knowledge of Primi Gravida Mother Regarding Importance Colostrum at Selected Hospital Bagalkot Karnataka, IndiaInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyPas encore d'évaluation
- Demo AntenatalDocument26 pagesDemo AntenatalDeepika PatidarPas encore d'évaluation
- Normal PuerperiumDocument3 pagesNormal PuerperiumarunshreerajendranPas encore d'évaluation
- Abortion PP TDocument42 pagesAbortion PP TDivya ToppoPas encore d'évaluation
- Management of Cardiac Disease in PregnancyDocument7 pagesManagement of Cardiac Disease in PregnancyMegavarnen Gobinathan100% (1)
- Drugs Used in Pregnancy, Labour and Puerperium-PBBSc NSG PreviousDocument87 pagesDrugs Used in Pregnancy, Labour and Puerperium-PBBSc NSG PreviousDivya ToppoPas encore d'évaluation
- The Role of Magnesium Sulphate in Obstetrics: by Sneha Sehrawat M. C Nursing I YearDocument18 pagesThe Role of Magnesium Sulphate in Obstetrics: by Sneha Sehrawat M. C Nursing I YearRajaPas encore d'évaluation
- Third Stage of LabourDocument39 pagesThird Stage of LabourabydlPas encore d'évaluation
- Management of LabourDocument16 pagesManagement of LabourAlbert MusinguziPas encore d'évaluation
- Gestational Diabetes Mellitus (GDM)Document11 pagesGestational Diabetes Mellitus (GDM)Sadia YousafPas encore d'évaluation
- Labor and Birth Process 3 Stage & 4 Stage: RD THDocument23 pagesLabor and Birth Process 3 Stage & 4 Stage: RD THبشائر حمادةPas encore d'évaluation
- Minor Discomfort in PuerperiumDocument39 pagesMinor Discomfort in PuerperiumVarna MohanPas encore d'évaluation
- Uterine Prolaps1Document6 pagesUterine Prolaps1Ginsha GeorgePas encore d'évaluation
- Government College of Nursing Jodhpur (Raj.)Document5 pagesGovernment College of Nursing Jodhpur (Raj.)priyankaPas encore d'évaluation
- Diagnosis of PregnancyDocument25 pagesDiagnosis of PregnancyA suhasiniPas encore d'évaluation
- Partogram CORRECTEDDocument45 pagesPartogram CORRECTEDjayasankariPas encore d'évaluation
- Amnioscopy EnglishDocument2 pagesAmnioscopy EnglishAlya BudiPas encore d'évaluation
- New NORMAL PUERPERIUMDocument21 pagesNew NORMAL PUERPERIUMvarshaPas encore d'évaluation
- Amniotic Fluid EmbolismDocument5 pagesAmniotic Fluid EmbolismPatel AmeePas encore d'évaluation
- AbortionsDocument99 pagesAbortionsAGERI PUSHPALATHAPas encore d'évaluation
- Prostaglandins Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesProstaglandins Lesson PlanDelphy Varghese0% (1)
- Fluid Electrolyte ImbalanceDocument46 pagesFluid Electrolyte ImbalanceAxsa AlexPas encore d'évaluation
- CPD Book and Patient PictureDocument6 pagesCPD Book and Patient PicturePriyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture-4 Diagnosis of PregnancyDocument31 pagesLecture-4 Diagnosis of PregnancyMadhu Sudhan Pandeya100% (1)
- Health Care Delivery Sysytem in India-2020Document40 pagesHealth Care Delivery Sysytem in India-2020Sree LathaPas encore d'évaluation
- Review On Birth Asphyxia by TibinDocument22 pagesReview On Birth Asphyxia by Tibintibinj67Pas encore d'évaluation
- Placenta Previa: Introduction and DeffinitionDocument4 pagesPlacenta Previa: Introduction and DeffinitionPriyaPas encore d'évaluation
- OccipitoposteriorDocument11 pagesOccipitoposteriorVijith.V.kumar100% (1)
- BreastfeedingDocument9 pagesBreastfeedingPriyanjali SainiPas encore d'évaluation
- Preterm LabourDocument18 pagesPreterm LabourRutu RajPas encore d'évaluation
- Psychosocial and Cultural Aspects InpregnancyDocument2 pagesPsychosocial and Cultural Aspects InpregnancyKavitha p0% (1)
- HysterectomyDocument2 pagesHysterectomyJellou MacPas encore d'évaluation
- Hypothermia in NeonatesDocument7 pagesHypothermia in NeonatesBhawna Pandhu100% (2)
- Physiological Changes During Second Stage of LabourDocument44 pagesPhysiological Changes During Second Stage of LabourTami SelviPas encore d'évaluation
- Anemia in PregnancyDocument17 pagesAnemia in Pregnancytharmasilen100% (1)
- Physiology of Normal LabourDocument29 pagesPhysiology of Normal LabournamitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Stages of Labour: First StageDocument37 pagesStages of Labour: First StageJude Martin100% (1)
- JG College of Nursing, AhmedabadDocument13 pagesJG College of Nursing, AhmedabadVinayak Srivastava100% (1)
- Induction of LabourDocument18 pagesInduction of LabourNihal ZaidiPas encore d'évaluation
- Era University / Era College of Nursing: Lesson Plan On-Abnormal Uterine BleedingDocument14 pagesEra University / Era College of Nursing: Lesson Plan On-Abnormal Uterine BleedingShreya Sinha100% (2)
- Thromboembolic DisordersDocument11 pagesThromboembolic Disordersannu panchalPas encore d'évaluation
- Antenatal Assessment of Foetal Wellbeing.Document30 pagesAntenatal Assessment of Foetal Wellbeing.Kavya S MohanPas encore d'évaluation
- Postnatal CareDocument26 pagesPostnatal CareShivani Shah100% (1)
- GDMDocument13 pagesGDMSharmistha DebnathPas encore d'évaluation
- Jaundice in PregnancyDocument32 pagesJaundice in PregnancyManoj Sankaranarayana100% (2)
- CPDDocument9 pagesCPDMeigy NitalessyPas encore d'évaluation
- Maternal and Perinatal Outcome in Jaundice Complicating PregnancyDocument10 pagesMaternal and Perinatal Outcome in Jaundice Complicating PregnancymanognaaaaPas encore d'évaluation
- EclampsiaDocument41 pagesEclampsiaNyshan KarkiPas encore d'évaluation
- Mechanism of LabourDocument16 pagesMechanism of LabourRadha SriPas encore d'évaluation
- Antenatal ExaminationDocument2 pagesAntenatal ExaminationJunaidahMubarakAliPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study On Fibroid UterusDocument68 pagesCase Study On Fibroid UterusSeenha DewanPas encore d'évaluation
- Antenatal AssessmentDocument16 pagesAntenatal AssessmentDevuchandana RPas encore d'évaluation
- TUBECTOMYDocument12 pagesTUBECTOMYkholifa s100% (1)
- Maternal and Child Health CareDocument12 pagesMaternal and Child Health CarePraachii SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Bleeding in Early PregnancyDocument25 pagesBleeding in Early PregnancyAnnapurna DangetiPas encore d'évaluation
- New Text DocumentDocument1 pageNew Text DocumentAnnapurna DangetiPas encore d'évaluation
- ObstetricsDocument5 pagesObstetricsAnnapurna Dangeti100% (1)
- Physical Examination MnemonicsDocument11 pagesPhysical Examination MnemonicsAnnapurna Dangeti100% (1)
- Pediatrics MnemonicsDocument11 pagesPediatrics MnemonicsAnnapurna Dangeti100% (1)
- Breastfeeding PositionsDocument2 pagesBreastfeeding PositionsAnnapurna DangetiPas encore d'évaluation
- Today Is The Big DayDocument9 pagesToday Is The Big DayAnnapurna DangetiPas encore d'évaluation
- Neurology MnemonicsDocument26 pagesNeurology MnemonicsAnnapurna DangetiPas encore d'évaluation
- Get Some Now": in Ascending Resistor Value OrderDocument5 pagesGet Some Now": in Ascending Resistor Value OrderAnnapurna DangetiPas encore d'évaluation
- Internal Medicine MnemonicsDocument23 pagesInternal Medicine MnemonicsAnnapurna Dangeti0% (1)
- Nephrology MnemonicsDocument5 pagesNephrology MnemonicsAnnapurna DangetiPas encore d'évaluation
- Microbiology MnemonicsDocument17 pagesMicrobiology MnemonicsAnnapurna Dangeti100% (2)
- Nephrology MnemonicsDocument5 pagesNephrology MnemonicsAnnapurna DangetiPas encore d'évaluation
- Gastroenterology MnemonicsDocument10 pagesGastroenterology MnemonicsAnnapurna DangetiPas encore d'évaluation
- MseDocument52 pagesMseAnnapurna DangetiPas encore d'évaluation
- Genetics MnemonicsDocument7 pagesGenetics MnemonicsAnnapurna Dangeti100% (1)
- Embryology MnemonicsDocument5 pagesEmbryology MnemonicsAnnapurna DangetiPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiology MnemonicsDocument18 pagesCardiology MnemonicsAnnapurna Dangeti100% (1)
- Signs in ObgyDocument2 pagesSigns in ObgyAnnapurna DangetiPas encore d'évaluation
- Emergency Medicine MnemonicsDocument18 pagesEmergency Medicine MnemonicsAnnapurna Dangeti100% (1)
- Biochemistry MnemonicsDocument20 pagesBiochemistry MnemonicsAnnapurna Dangeti100% (1)
- Psychiatric EmergenciesDocument25 pagesPsychiatric EmergenciesAnnapurna DangetiPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy MnemonicsDocument63 pagesAnatomy MnemonicsAnnapurna DangetiPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 1Document11 pagesUnit 1Annapurna DangetiPas encore d'évaluation
- Hand WashingDocument39 pagesHand WashingAnnapurna DangetiPas encore d'évaluation
- Normal Flora of The Human BodyDocument7 pagesNormal Flora of The Human Bodyshahbaz88% (16)
- First AidDocument5 pagesFirst AidAnnapurna DangetiPas encore d'évaluation
- Immunoglobulin GDocument1 pageImmunoglobulin GAnnapurna DangetiPas encore d'évaluation
- Slide 1Document20 pagesSlide 1Annapurna DangetiPas encore d'évaluation
- Drugs To Treat Endocrine System DisordersDocument2 pagesDrugs To Treat Endocrine System DisordersAnnapurna DangetiPas encore d'évaluation
- Super Sexual Orgasm - A Woman S Guide To Guaranteed SatisfactionDocument173 pagesSuper Sexual Orgasm - A Woman S Guide To Guaranteed SatisfactionSvedok Saradnik Milos61% (57)
- Chapter 15: Nursing Care of A Family During Labor and BirthDocument6 pagesChapter 15: Nursing Care of A Family During Labor and BirthAlyssaGrandeMontimorPas encore d'évaluation
- Abortion - A Philosophical Perspective: OpsommingDocument7 pagesAbortion - A Philosophical Perspective: OpsommingGeorge RaresPas encore d'évaluation
- Obs Gyn ClerkingDocument5 pagesObs Gyn ClerkingdonaldooiPas encore d'évaluation
- Wombtwin Survivors IntroDocument16 pagesWombtwin Survivors IntroAlthea hayton100% (2)
- 05.2 Problems of The PassageDocument5 pages05.2 Problems of The PassageJAN CAMILLE LENONPas encore d'évaluation
- Care of MotherDocument131 pagesCare of MotherBri ParalesPas encore d'évaluation
- 9 Myths and Facts About Domestic ViolenceDocument2 pages9 Myths and Facts About Domestic ViolenceRamonaStereaPas encore d'évaluation
- Diagnosis and Management of Adnexal MassesDocument6 pagesDiagnosis and Management of Adnexal MassesSebastianPas encore d'évaluation
- Manuskrip PDFDocument156 pagesManuskrip PDFFarhan FaturrohmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Abortion Position PaperDocument6 pagesAbortion Position PaperKylie100% (1)
- Newborn Physical AssessmentDocument7 pagesNewborn Physical AssessmentBinal JoshiPas encore d'évaluation
- Male Reproductive SystemDocument31 pagesMale Reproductive SystemKangeviyin Rong HueiPas encore d'évaluation
- PUERPERIUMDocument42 pagesPUERPERIUMKBDPas encore d'évaluation
- Barrier Contraceptive Method (Autosaved)Document12 pagesBarrier Contraceptive Method (Autosaved)Okera JamesPas encore d'évaluation
- Ovulation Pcos OhssDocument68 pagesOvulation Pcos OhssPrakash DhungelPas encore d'évaluation
- Hms Implementation GuideDocument122 pagesHms Implementation GuideShuaib KauchaliPas encore d'évaluation
- The Sexual Scripting of Oral Genital ContactsDocument25 pagesThe Sexual Scripting of Oral Genital Contactsmornlight1100% (2)
- Cephalopelvic DisproportionDocument3 pagesCephalopelvic DisproportionAira MiyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Intrauterine Growth RestrictionDocument21 pagesIntrauterine Growth Restrictionمصطفى محمدPas encore d'évaluation
- Namma Kalvi 12th Zoology Chapter 3 Sura English Medium GuideDocument9 pagesNamma Kalvi 12th Zoology Chapter 3 Sura English Medium GuideAakaash C.K.100% (1)
- IUFDDocument29 pagesIUFDfasyanneshaPas encore d'évaluation
- Unified Work Financial PlanDocument9 pagesUnified Work Financial PlanMarieta Alejo0% (1)
- Biological Development in Adolescent MalesDocument2 pagesBiological Development in Adolescent MalesrobertlordPas encore d'évaluation
- Kinship, Marriage, and The HouseholdDocument17 pagesKinship, Marriage, and The Householdmaxinejoyjuare100% (1)
- Health Puberty Changes Myths and MisconceptionsDocument20 pagesHealth Puberty Changes Myths and MisconceptionsJohn Kenneth NochePas encore d'évaluation
- ALISON - P - HENGEKA - ProposalDocument86 pagesALISON - P - HENGEKA - ProposalAlisonPas encore d'évaluation
- Female Infanticide: Mortality, Some Would Dispute The Assigning of Infanticide or Female Infanticide ToDocument14 pagesFemale Infanticide: Mortality, Some Would Dispute The Assigning of Infanticide or Female Infanticide ToViren SehgalPas encore d'évaluation
- Different Types of FamiliesDocument14 pagesDifferent Types of FamiliesJheanAlphonsineT.MeansPas encore d'évaluation
- Karakteristik Ibu Dan Berhubungan Dengan Terjadinya Ibu NifasDocument7 pagesKarakteristik Ibu Dan Berhubungan Dengan Terjadinya Ibu NifasPuskesmas PasarsimpangPas encore d'évaluation