Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Speed and Control Methods in DC Motors and Transformers
Transféré par
Mehran Rahman DhrubaDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Speed and Control Methods in DC Motors and Transformers
Transféré par
Mehran Rahman DhrubaDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Chapter 30: (a)Write down the factors which control the motor speed.
Ans:Resistance Ra of armature circuit,flux/pole,applied voltage V.(article no:30.1) (b)Speed control of shunt motors: ( question:Describe the methods of speed control of dc shunt motor) (1)Flux control method(article no:30.2(1).(fig:30.1) (2)Armature or Rheostatic control method(fig:30.4). (c)Explain the necessity of a starter in a d.c. motor.(article no:30.19)(fig:30.37) (d) Describe the methods of speed control of series motors.(article no:30.3)..(class lecture a porano hoyechilo kina ta mone nai.but ata pora joruri.shunt motor porleseries o diye dite pare..jader important mone hobe tara poro.) (e)Three-point starte(article no:30.21) (PREVIOUS YEAR(2009) A ASECHE.ATA LECTURE A NAI)
Chapter:32 Transformer: ***Working principle of a transformer.(Article no:32.1) ***Definition(transformer:article:32.1( a transformer is a device that transfer electric power from one circuit to another). ****Derive e.m.f. equation of a transformer.(article no:32.6 page no:1122)..(fig:32.14) ***Voltage transformation ratio(article no:32.7).(physical significance of voltage transformation ratio) (a) ***Vector diagramfig:32.29) article no:32.14.(only figure) (very very important)(Resistive,capacitive & inductive load: konta resistive,konta capacitive agulo mne naivule gechiksto kre sure hoye niyo) (b) ***Equivalent circuit of a transformer(article no:32.18) fig:32.37(a),(b),32.38(a),(b),32.39,32.40,32.41(a),32.41(b)jegulo obossoi dite hobe32.37(a,b),32.38(b),32.40,32.41(a,b). (c) ***Why transformer rating in kva?(article no:32.23 page no:1151). (d) ***Losses in a transformer(article no:32.28). (e) ***Condition for maximum efficiency.(article no:32.30)( extra question ata.)
(f) ***Step-up & step-down transformer: article no:32.5(2 ta figure dewa ache & just definition .)
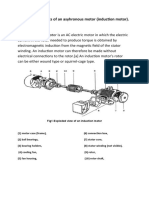
********** Chapter:34(Induction Motor): ***Why it is impossible for an induction motor to operate at synchronous speed?(ai question ta ami khuje pai nai..tomra pore niyo.previous year a aseche.r keu pele jodi possible hoy janaiyo) ***Advantages & disadvantages:(chapter:34 article no:34.3)(page:1245) Ans: Advantages: ----very simple ----low cost ----very reliable ----requires minimum of maintenance ----needs no extra starting motor. Disadvantages: ---Speed can't be varied without sacrificing some efficiency. ---speed decreases with increase in load. ******Construction of an induction motor: (a)stator & (b) rotor. (page no:1245-1247) article no:34.3(construction). Ans: Stator: Same as a synchronous motor.made up of a number of stampings.they are slotted to receive the windings.stator carries a 3-phase winding & is fed-from a 3-phase supply.it is wound for a definite number of poles.greater the number of poles,lesser the speed.(article no:34.3) Rotor: (1)Squirre-cage rotor: Almost 90 percent of induction motors are squirrel cage type.Rotor consists of a cylindrical laminated core with parallel slots for carrying the rotor conductors.( 7 line...1st r 7 line likhlei hobe).(article no:34.4) (2) phase-wound rotor: article no:34.5.
(figure: jodi paro,tobe diye diyo).
*****Article no:34.7 Three-phase supply(fig:34.11,34.12,34.13,34.14(4 ta figure)).....(proof:(1)Resultant flux is of constant value =(1.5* maximum value of flux). (2)& the resultant flux rotates around the stator at synchronous speed given by Ns=120f/p.)
(page no:1250-1252).....(figure total-7ta).....(case 4 ta angle o,60,120,180 r jnno flex r obostha dekhate hobe.) (ata 99% probability ache asar....according to obaidur sir)
******Why does rotor rotate?(article no:34.9......) ******Definition:slip(article no:34.10)...(previous year a asche). Math:(2010 ) article no:34.4.
*****Draw & explain torque vs slip characteristic.(article no:34.22 Fig:34.21).(curve is a rectangular parabola).
****When & how an induction motor operates as a generator?(2010) (important) Article no:34.32 Fig:34.28 Fig:34.29..... Fig:34.30.....(When run faster than its synchronous speed ,an induction motor runs as a generator..called an induction generator.) how: article no:34.32 a describe kra ache. *******Proof: Rotor cu loss of an induction motor can be expressed as (s/1-s)*pm.(article no:34.37). (proof ta dekhi previous year a onnovabeo ase......so careful thako) Article no:34.37(Torque,mechanical power & rotor output). ******2008 a ai problem ta diyeche: Example:34.36.
Chapter :37 Alternators: ***Advantages of having stationary armature in alternators(article no:37.2).(4ta point )
***Describe the principle of operation of an alternator.(article no:37.1)(very very important) ****what r the conditions of parallel operation of alternator.(article no:37.30) (3 ta point ).((1),(2),(3))avabe dewa ache. ****Describe lamp bright method for synchronization of alternators.(article no:37.31fig;37.74,37.75,37.76). ***2006:Total maximum power output of the alternatorarticle no:37.42).(lecture a nai)(2006 a asche..).
Chapter 38: Synchronous motor: Power developed by a synchronous motor article no:38.12(fig:38.21) (2009 a 15 mark chilo atate(pm)max=EbV/Xs.where the symbols have their usual meaning. (page no:1502-1503 chapter:38). (very very important) Chapter 39:( previous year a question aschilo.but lecture a most probably porano hoy nai) Definition: Step angle(article no:39.2 definition:The angle through which the motor shaft rotates for each command pulse is called the stepangle. Applications: -----Operation control in (a) computer peripherals (b) textile industry (c) Robotics (d) IC fabrications ----Commercial ,military & medical applications. ----they also take part in production of science fiction movies. Article no:39.2(stepper motors:applications).
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Chapter ThreeDocument67 pagesChapter Threeetayhailu80% (5)
- 34.1. Classification of A.C. MotorsDocument7 pages34.1. Classification of A.C. Motorssabam boy marsius tampubolonPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction to Electrical Machines Chapter on Induction MachinesDocument64 pagesIntroduction to Electrical Machines Chapter on Induction MachinesTheødřøš ÄbPas encore d'évaluation
- 7 TransformadorDocument27 pages7 TransformadorMarkovic Ávila MartínezPas encore d'évaluation
- 315D L Excavator C4.2 Engine GuideDocument13 pages315D L Excavator C4.2 Engine GuideJose nildo lobato Mendes MendesPas encore d'évaluation
- RR420305 Robotics PDFDocument9 pagesRR420305 Robotics PDFSarath ChandraPas encore d'évaluation
- Mechatronics exam with questions on control systems and PLC applicationsDocument62 pagesMechatronics exam with questions on control systems and PLC applicationshaptooorPas encore d'évaluation
- RT31024052018Document1 pageRT31024052018Punya SekharPas encore d'évaluation
- RT31024112015Document8 pagesRT31024112015Punya SekharPas encore d'évaluation
- Lectrical Ngineering EpartmentDocument2 pagesLectrical Ngineering EpartmentBhargav PandyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ee-502 Unit - IDocument2 pagesEe-502 Unit - IVARAPRASADPas encore d'évaluation
- CH3 EditDocument46 pagesCH3 EditLetk ZelalemPas encore d'évaluation
- 2007 Anna University emDocument2 pages2007 Anna University emgnr12345Pas encore d'évaluation
- TP3: Characteristics of An Asyhronous Motor (Induction Motor) - 1) DefinitionDocument4 pagesTP3: Characteristics of An Asyhronous Motor (Induction Motor) - 1) DefinitionRedouane DaddiPas encore d'évaluation
- Rr312003 Turbo MachineryDocument8 pagesRr312003 Turbo MachinerySrinivasa Rao GPas encore d'évaluation
- PSD 2016Document8 pagesPSD 2016Kanisetty JanardanPas encore d'évaluation
- Mechtronics QBDocument8 pagesMechtronics QBKarthik Perumal SwamyPas encore d'évaluation
- 9A02303 Electrical & Mechanical TechnologyDocument4 pages9A02303 Electrical & Mechanical TechnologysivabharathamurthyPas encore d'évaluation
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument2 pagesGujarat Technological UniversityMitesh GandhiPas encore d'évaluation
- Maximizing Efficiency in Power Electronics and DrivesDocument34 pagesMaximizing Efficiency in Power Electronics and DrivesSaroj kumar BiswasPas encore d'évaluation
- 9A02303 Electrical & Mechanical TechnologyDocument4 pages9A02303 Electrical & Mechanical TechnologysivabharathamurthyPas encore d'évaluation
- نظرى معمل الات كهربيةDocument8 pagesنظرى معمل الات كهربيةAhmed HazemPas encore d'évaluation
- WWW - Manaresults.Co - In: Set - 1 Code No: RT32033Document8 pagesWWW - Manaresults.Co - In: Set - 1 Code No: RT32033Sai RamPas encore d'évaluation
- Question Bank Ac MachinesDocument4 pagesQuestion Bank Ac Machinesashwin paulPas encore d'évaluation
- Mechatronics Qp1Document6 pagesMechatronics Qp1Jegan ParamasivamPas encore d'évaluation
- Exam Ece 361 201920Document4 pagesExam Ece 361 201920WolfPas encore d'évaluation
- Turbomachinery Assignments Me 603 Me 6BDocument6 pagesTurbomachinery Assignments Me 603 Me 6Bd v rama krishnaPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical Mechanical Technology 1Document4 pagesElectrical Mechanical Technology 1Jyothsna VayyalaPas encore d'évaluation
- WWW - Manaresults.co - In: II B. Tech II Semester Supplementary Examinations, November - 2019 Electrical Machines-IiDocument2 pagesWWW - Manaresults.co - In: II B. Tech II Semester Supplementary Examinations, November - 2019 Electrical Machines-IiAbdullah MdPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter Three Induction Machines: Electromechanical ConversionDocument67 pagesChapter Three Induction Machines: Electromechanical ConversiontsegayPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 3 MachineDocument22 pagesCH 3 MachineTeshale AlemiePas encore d'évaluation
- Final Exam - 2021-FallDocument7 pagesFinal Exam - 2021-FallSrinivasa Rao DPas encore d'évaluation
- 100 Possible QuestionsDocument18 pages100 Possible Questionsdebadatta samalPas encore d'évaluation
- WWW - Manaresults.Co - In: Design of Machine Members - IiDocument8 pagesWWW - Manaresults.Co - In: Design of Machine Members - IigopichandallakaPas encore d'évaluation
- Super 30 EM-1 - QBDocument3 pagesSuper 30 EM-1 - QBmr.kaustubh1362Pas encore d'évaluation
- MechatronicsDocument7 pagesMechatronicsmuralmohanPas encore d'évaluation
- Cne Question BankDocument9 pagesCne Question BankrutujaraipurePas encore d'évaluation
- AC Motors, Motor Control and Motor ProtectionDocument25 pagesAC Motors, Motor Control and Motor Protectionwira eka0% (1)
- RA 9A02303 Electrical & Mechanical TechnologyDocument2 pagesRA 9A02303 Electrical & Mechanical TechnologysivabharathamurthyPas encore d'évaluation
- ST - Joseph'S College of Engineering, Chennai - 119 Model - Iii Examinations October 2010 Sub: Sub. Code: EI 2201 Branch: Semester: III Duration: 3 Hours Max - Marks: 100Document14 pagesST - Joseph'S College of Engineering, Chennai - 119 Model - Iii Examinations October 2010 Sub: Sub. Code: EI 2201 Branch: Semester: III Duration: 3 Hours Max - Marks: 100Senthil kumar BalakrishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- Mechanical Dissection Laboratory Power Hand DrillDocument38 pagesMechanical Dissection Laboratory Power Hand DrillIndu SekharPas encore d'évaluation
- NR-420301-Jet Propulsion & Rocket EngineeringDocument8 pagesNR-420301-Jet Propulsion & Rocket EngineeringSrinivasa Rao GPas encore d'évaluation
- 9A 02303 Electrical & Mechanical TechnologyDocument2 pages9A 02303 Electrical & Mechanical TechnologysivabharathamurthyPas encore d'évaluation
- EEE Questions Anna University ChennaiDocument42 pagesEEE Questions Anna University ChennaielectricalconsultantPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical Technology PDFDocument1 pageElectrical Technology PDFBibi Shama ShaikPas encore d'évaluation
- Synchronous Machines: ENGNG 2024 Electrical EngineeringDocument25 pagesSynchronous Machines: ENGNG 2024 Electrical Engineeringpham van duPas encore d'évaluation
- Induction MotorsDocument47 pagesInduction MotorsPurushothaman KannanPas encore d'évaluation
- Multiple Choice Question (MCQ) of Induction MotorsDocument18 pagesMultiple Choice Question (MCQ) of Induction Motorskibrom atsbha75% (4)
- Machine Design-I Exam Guide for University of Pune StudentsDocument56 pagesMachine Design-I Exam Guide for University of Pune Studentsavinash119870% (1)
- T.E. Electrical Sem II Exam 2009 Electrical Installation Maintenance and TestingDocument36 pagesT.E. Electrical Sem II Exam 2009 Electrical Installation Maintenance and TestingOmkar ShetePas encore d'évaluation
- Wound Rotor Induction MotorDocument4 pagesWound Rotor Induction MotorAnonymous zeISoBPas encore d'évaluation
- Beie Important Questions For Unit 3 and Unit 4Document5 pagesBeie Important Questions For Unit 3 and Unit 4vlkumashankardeekshithPas encore d'évaluation
- Mechatronics Systems Design and PLC ProgrammingDocument7 pagesMechatronics Systems Design and PLC ProgrammingVkrthirumalai RamanathanPas encore d'évaluation
- Comparative Analysis of Bearings For Micro-GT: An Innovative ArrangementDocument26 pagesComparative Analysis of Bearings For Micro-GT: An Innovative Arrangementbatu kuguPas encore d'évaluation
- EF 2 - Assignment # 3 - DC Motor RealDocument4 pagesEF 2 - Assignment # 3 - DC Motor RealWakwkaka JssjaaPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical Mechanical Technology 4Document1 pageElectrical Mechanical Technology 4Jyothsna VayyalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Design and Analysis of Centrifugal CompressorsD'EverandDesign and Analysis of Centrifugal CompressorsPas encore d'évaluation
- Common Rail Fuel Injection Technology in Diesel EnginesD'EverandCommon Rail Fuel Injection Technology in Diesel EnginesPas encore d'évaluation
- Hybrid Systems Based on Solid Oxide Fuel Cells: Modelling and DesignD'EverandHybrid Systems Based on Solid Oxide Fuel Cells: Modelling and DesignPas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced Electric Drives: Analysis, Control, and Modeling Using MATLAB / SimulinkD'EverandAdvanced Electric Drives: Analysis, Control, and Modeling Using MATLAB / SimulinkPas encore d'évaluation
- Poetry in BrickDocument22 pagesPoetry in Brickakshata_dPas encore d'évaluation
- Landscape Architecture and WaterDocument8 pagesLandscape Architecture and WaterMehran Rahman DhrubaPas encore d'évaluation
- Persian Gardens Meanings Symbolism and DesignDocument19 pagesPersian Gardens Meanings Symbolism and DesignJairo Marin BarraganPas encore d'évaluation
- The Secret History of The MongolsDocument43 pagesThe Secret History of The Mongolsstebanoff100% (1)
- Arch ToonDocument1 pageArch ToonMehran Rahman DhrubaPas encore d'évaluation
- Universities in Ancient India by D.G. Apte PDFDocument68 pagesUniversities in Ancient India by D.G. Apte PDFHari KirupakarPas encore d'évaluation
- Mshyw - 301 (Wewa 13 ' Óe ) (150/-Uvkv G J I Bb-Rywwwkqvj ÷ V Ci Dci) BB Wgwbwu Eû (Mfxi Wfwë, Cvbwjs I em G U Gi RB )Document2 pagesMshyw - 301 (Wewa 13 ' Óe ) (150/-Uvkv G J I Bb-Rywwwkqvj ÷ V Ci Dci) BB Wgwbwu Eû (Mfxi Wfwë, Cvbwjs I em G U Gi RB )Mehran Rahman DhrubaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lyrics of The Paanch Adhyay Songs: All Songs Composed by Shantanu MoitraDocument8 pagesLyrics of The Paanch Adhyay Songs: All Songs Composed by Shantanu MoitraMehran Rahman DhrubaPas encore d'évaluation
- Werner Sobek r128 r129Document5 pagesWerner Sobek r128 r129Marco SpinelliPas encore d'évaluation
- University Admission and Requirements PDFDocument1 pageUniversity Admission and Requirements PDFMehran Rahman DhrubaPas encore d'évaluation
- Japanese DoctorDocument2 pagesJapanese DoctorMehran Rahman DhrubaPas encore d'évaluation
- Basement Parking Management PlanDocument2 pagesBasement Parking Management PlanMehran Rahman DhrubaPas encore d'évaluation
- Triniti Raashimala by Jafor IqbalDocument44 pagesTriniti Raashimala by Jafor IqbalMehran Rahman DhrubaPas encore d'évaluation
- Plea Brochure v2Document2 pagesPlea Brochure v2Mehran Rahman DhrubaPas encore d'évaluation
- Theory of design and the works of Balkrishna Vithaldas DoshiDocument20 pagesTheory of design and the works of Balkrishna Vithaldas DoshiMehran Rahman DhrubaPas encore d'évaluation
- Jazz PDFDocument6 pagesJazz PDFMehran Rahman DhrubaPas encore d'évaluation
- Design and Construction of Driven Pile FoundationsDocument14 pagesDesign and Construction of Driven Pile FoundationsMehran Rahman DhrubaPas encore d'évaluation
- Architecture - A Psychological History (Minus Images)Document47 pagesArchitecture - A Psychological History (Minus Images)Mehran Rahman DhrubaPas encore d'évaluation
- Public Toilet GuideDocument70 pagesPublic Toilet Guideshrikant100% (1)
- Kiln Shell Laser Manual 1Document24 pagesKiln Shell Laser Manual 1uddinsalahPas encore d'évaluation
- Yann Le Cun Conference Munich Artificial Intelligence "Autoregressive Models Suck"Document77 pagesYann Le Cun Conference Munich Artificial Intelligence "Autoregressive Models Suck"Frédéric BardeauPas encore d'évaluation
- International Journal of Computer Science and Security (IJCSS), Volume (3), IssueDocument153 pagesInternational Journal of Computer Science and Security (IJCSS), Volume (3), IssueAI Coordinator - CSC JournalsPas encore d'évaluation
- s4p2 PDFDocument12 pagess4p2 PDFAnh Do VoPas encore d'évaluation
- pm9sb 133Document0 pagepm9sb 133api-237494396Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 10Document30 pagesChapter 10Fernando Alcala Dela CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- Stats Workbook For College StudentsDocument337 pagesStats Workbook For College StudentsClifford CurtisPas encore d'évaluation
- ACT Prep Syllabus (Fall 2019)Document7 pagesACT Prep Syllabus (Fall 2019)Fallon HowePas encore d'évaluation
- Instrumentation Physics CurriculumDocument1 pageInstrumentation Physics CurriculumKen RubioPas encore d'évaluation
- 8 Antipatterns AssignmentDocument52 pages8 Antipatterns Assignmentdemelash kasayePas encore d'évaluation
- 3rd Periodic Test - Grade 9Document4 pages3rd Periodic Test - Grade 9sweetheart barrion43% (7)
- Schering BridgeDocument11 pagesSchering BridgePunithan RavichandranPas encore d'évaluation
- Write The Ratio, Decimal and Percent Equivalent of Each Picture. Write Your Answer On A Sheet of PaperDocument14 pagesWrite The Ratio, Decimal and Percent Equivalent of Each Picture. Write Your Answer On A Sheet of PaperMarlon Ursua BagalayosPas encore d'évaluation
- Pronominal Anaphora Resolution inDocument7 pagesPronominal Anaphora Resolution inijfcstjournalPas encore d'évaluation
- Pubali Bank Limited: Post NameDocument6 pagesPubali Bank Limited: Post NametitoPas encore d'évaluation
- Level-Ii: Sample PaperDocument5 pagesLevel-Ii: Sample PaperSeng SoonPas encore d'évaluation
- Nov 2005 4HDocument20 pagesNov 2005 4HpappadutPas encore d'évaluation
- Model - qp01 - Bmats201 For Computer Science StreamDocument3 pagesModel - qp01 - Bmats201 For Computer Science StreamVandana VandanagowdaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Potency of Using Math Educational Software in Teaching Business Mathematics CoursesDocument12 pagesThe Potency of Using Math Educational Software in Teaching Business Mathematics CoursesDUDE RYAN OBAMOSPas encore d'évaluation
- EthnomathematicsDocument9 pagesEthnomathematicsapi-256195037Pas encore d'évaluation
- Stein Corporation Wants To Find An Equation To Estimate Some of Their Monthly Operating Costs For The Operating Budget For 2018Document2 pagesStein Corporation Wants To Find An Equation To Estimate Some of Their Monthly Operating Costs For The Operating Budget For 2018Elliot RichardPas encore d'évaluation
- Course Syllabus For Math 231br Advanced Al - Quick, GereonDocument167 pagesCourse Syllabus For Math 231br Advanced Al - Quick, GereonLucas KevinPas encore d'évaluation
- Atomic HabitsDocument6 pagesAtomic HabitsTango1315100% (1)
- Trigonometryp1: (58 Marks)Document12 pagesTrigonometryp1: (58 Marks)mohammad maabrehPas encore d'évaluation
- AverageDocument4 pagesAveragerauf tabassumPas encore d'évaluation
- Measure of Dispersion and LocationDocument51 pagesMeasure of Dispersion and LocationTokyo TokyoPas encore d'évaluation
- Modeling of A Simple PendulumDocument9 pagesModeling of A Simple PendulumAnonymous Gmk3t4QPas encore d'évaluation
- (Made Simple Books) William R. Gondin, Bernard Sohmer - Advanced Algebra and Calculus Made Simple (1959, Doubleday) - Libgen - LiDocument228 pages(Made Simple Books) William R. Gondin, Bernard Sohmer - Advanced Algebra and Calculus Made Simple (1959, Doubleday) - Libgen - LiRodrigoPas encore d'évaluation
- Statistical Methods for Geography - A Student's Guide to Exploring Spatial PatternsDocument26 pagesStatistical Methods for Geography - A Student's Guide to Exploring Spatial PatternsMeenakshi MohanPas encore d'évaluation
- Homology Modeling Guide for Protein Structure PredictionDocument43 pagesHomology Modeling Guide for Protein Structure PredictionGaurabPas encore d'évaluation