Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Sheet Metalworking: Review of Stress-Strain Relationships
Transféré par
dharshanaabDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Sheet Metalworking: Review of Stress-Strain Relationships
Transféré par
dharshanaabDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
21/9/2013
Review of stress-strain relationships
Tensile properties tensile test
Sheet metalworking
Review of Stress-strain Relationships
Chapters: 3.1.1, 3.1.4
Engineering stress = =
1
Gage marks
Applied force Original area of specimen F A0
Engineerin g strain =
L Lo Lo
Stages of tensile test
Maximum load Y = yield strength TS= tensile strength
TS Y
Elastic region - Elastic deformation i.e., material returns to its original length when the load is released
Fracture Necking Uniform elongation localised elongation
Elongation L f Lo = Lo
Plastic region - plastic deformation
3
i.e., material does not return to its original length when the load is released.
21/9/2013
Strain-hardening (work-hardening)
TS Y
Shear properties torsion test
Shear involves application of stresses in opposite directions on either side of a thin element.
Shear stress =
F , Shear strain = b A
Metal becomes stronger as the strain increases - this property is called strain hardening or work hardening.
Shear stress and strain are commonly tested in a torsion test.
5 6
Torsion test
L
A
Shear stress-shear strain curve
Shear strength S 0.7 (Tensile strength TS) t R
T Shear strength Fracture
Shear stress =
T 2R 2t
Shear strain = R L
7 8
21/9/2013
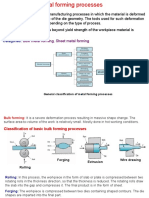
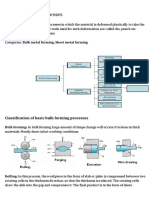
Overview of metal forming processes
Two main broad classifications: Bulk deformation processes Sheet metalworking processes Rolling
Bulk deformation processes
Slab
Plate, sheet Coil
10
Outline of sheet metalworking processes
Coil Plate, sheet
Punching Blanking Fine blanking Stamping Embossing Deburring Cleaning Coating Bending Roll forming Deep drawing Rubber forming Spinning Superplastic forming Explosive forming
Magnetic-pulse forming
11
Examples of parts produced by sheet metalworking processes
Sheet Plate
Shearing Cutting Sawing
Rolling
12
21/9/2013
Cutoff
Cutting line
Scrap Strip Blank
Parting
Nesting - for blanking
Cutting line
Blank Strip
Cutting line
Strip
Waste material
Scrap
Cutting line
Strip Blank
Cutting line
Scrap Strip Scrap
Difference from conventional shearing: 1. Cut edges not necessarily straight 2. Blanks can be nested - avoid scrap
13
Punch with 2 cutting edges that match the opposite sides of the blank - irregular shape. Scrap.
14
Redrawing
Drawn cup faced upwards on die
Drawn cup
F, v
Effect of Manufacturing Processes
Fh
Fh
Tolerance
Reverse drawing (is a redrawing process)
Drawn cup is placed face down on die Requires lower force than redrawing
Drawn cup
15 16
F, v
Fh
Fh
21/9/2013
Effect of Manufacturing Processes
Surface roughness
Hollow profiles such as tubes, straw Mandrel is used to give hollow shape.
Mandrel Air in
17
Air to maintain hollow form during hardening
18
Wires and cable coating
Production of sheet and film
Die opening is a narrow slit (as narrow as 0.4 mm). Thermoplastic sheet for thermoforming. Thin film for packaging e.g., grocery & garbage bags, product wrapping.
19
20
21/9/2013
Blow molding
Blow molding Produces one-piece hollow parts with thin walls: plastic bottles, hollow containers For thermoplastics only: PE (most common), PP, PVC
21
Extrusion blow molding
Extruder barrel Tube die v Parison Mold Blow pin Mold (closed) v Molded part v v
Air in
22
Compression molding
Widely used for thermosets (thermosetting plastics) & elastomers - phenolics, melamines, expoxies, urethanes Electric plugs, dinnerware plates (dishes)
Punch Cavity Heated mold Charge Heated mold Ejector pin v, F Molded part v
Compare compression with injection molding Simpler and less expensive mold- no sprue or runner (less scrap material) Limited to simple shape Mold must be heated Longer cycle time - lower production rate
Charge molding material (powder, pellet form)
Curing till part solidified. 0.5 to 5 mins
v
23 24
21/9/2013
Transfer molding
Used for thermosets & elastomers Modifed from compression molding Polymer melt enters mold cavity as a fluid
Transfer pot
Transfer molding
Pot transfer molding
v Transfer ram Charge (preform) Cavities Ejector pin v Charge heated until softened
25
v, F v Molded part
Cull Sprue
Pressure applied Curing in heated mold
26
Compare transfer with compression molding Can form intricate shape as polymer enters the cavity as a fluid Use for encapsulation, molding with metal/ceramic insert
Chip Bonds Lead frame Molded plastic body
Transfer molding with metal/ceramic
Leads
IC package
27
28
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Dimensions, Weights and Properties of Special and Standard Structural Steel Shapes Manufactured by Bethlehem Steel CompanyD'EverandDimensions, Weights and Properties of Special and Standard Structural Steel Shapes Manufactured by Bethlehem Steel CompanyPas encore d'évaluation
- GP Singapore Example BankDocument40 pagesGP Singapore Example BankdharshanaabPas encore d'évaluation
- HCI H2 Econs Prelim Essays Answers - SharingDocument22 pagesHCI H2 Econs Prelim Essays Answers - Sharingdharshanaab100% (1)
- Hungr Et Al 2005 - Landslide Travel DistanceDocument30 pagesHungr Et Al 2005 - Landslide Travel DistanceJosé Ignacio RamírezPas encore d'évaluation
- S406 Specifications For The Supply of Stone PDFDocument6 pagesS406 Specifications For The Supply of Stone PDFMfanelo MbanjwaPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Lab - Detailed - Answer KeyDocument6 pagesPhysics Lab - Detailed - Answer KeyJasdeepSinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Extrusion ProcessDocument24 pagesExtrusion Processchris mushunjePas encore d'évaluation
- Casting Forming Sheet Metal Processing Powder-And Ceramics Processing Plastics ProcessingDocument44 pagesCasting Forming Sheet Metal Processing Powder-And Ceramics Processing Plastics ProcessingRaj PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- Manufacturing Engineering II (ch3)Document111 pagesManufacturing Engineering II (ch3)AlemPas encore d'évaluation
- Manufacturing Engineering II (ch3)Document93 pagesManufacturing Engineering II (ch3)beila.amu.22Pas encore d'évaluation
- Rolling, Forging, Extrusion & DrawingDocument13 pagesRolling, Forging, Extrusion & DrawingMuhammad Ali AbroPas encore d'évaluation
- Sunu 1Document16 pagesSunu 1Ayca Betul BingolPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 4 Bulk Metal Forming (Extrusion)Document95 pagesLecture 4 Bulk Metal Forming (Extrusion)Anand P DwivediPas encore d'évaluation
- 4.3 ExtrusionDocument19 pages4.3 ExtrusionSiddharth RajendranPas encore d'évaluation
- Extrusión-Rolling and Forming ProcessDocument50 pagesExtrusión-Rolling and Forming Processquiron2010Pas encore d'évaluation
- MPP - SRS Class 6 Bulk Deforfmation Process - FinalDocument44 pagesMPP - SRS Class 6 Bulk Deforfmation Process - FinalSuk bahadur GurungPas encore d'évaluation
- Metal Forming ProcessesDocument91 pagesMetal Forming ProcessesSuneth TharakaPas encore d'évaluation
- L5 - Ta201p (05.07.2021)Document84 pagesL5 - Ta201p (05.07.2021)quick winnerPas encore d'évaluation
- Extrusion KM2833-20190917035934Document94 pagesExtrusion KM2833-20190917035934Sajjad0% (1)
- EMM 315 Materials Forming Processes - METAL FORMINGDocument91 pagesEMM 315 Materials Forming Processes - METAL FORMINGKimani JohnPas encore d'évaluation
- L8 - Bulk Deformation ProcessingDocument70 pagesL8 - Bulk Deformation ProcessingAstha PantPas encore d'évaluation
- Rolling Extrusion & DrawingDocument52 pagesRolling Extrusion & DrawingSpidyPas encore d'évaluation
- Metal Forming Processes - FullDocument64 pagesMetal Forming Processes - FullRohit Tamrakar100% (1)
- Metal Forming ProcessesDocument91 pagesMetal Forming ProcessesMalik IrfanPas encore d'évaluation
- Extrusion FundamentalsDocument5 pagesExtrusion FundamentalsJoPas encore d'évaluation
- Forging Design ConsiderationsDocument81 pagesForging Design ConsiderationssuneethaPas encore d'évaluation
- We Now Consider Some of These Ways and Their ConsequencesDocument6 pagesWe Now Consider Some of These Ways and Their ConsequencesConnor WalshPas encore d'évaluation
- Bulk Metal Forming, Sheet Metal FormingDocument6 pagesBulk Metal Forming, Sheet Metal FormingAbdulfattah TawfiqPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 05 (Metal Forming Processes)Document37 pagesLecture 05 (Metal Forming Processes)Mubashar ZahidPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 - Cold Working Processes of MetalsDocument13 pages4 - Cold Working Processes of MetalsHussein SaeedPas encore d'évaluation
- Mechanical Working of Materials: ExtrusionDocument10 pagesMechanical Working of Materials: ExtrusionSahil MaharPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 19-Bulk Deformation Processes IIDocument38 pagesChapter 19-Bulk Deformation Processes IIMuhammad Qasim QureshiPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 7 - Common Manufacturing Processes IIDocument41 pagesLecture 7 - Common Manufacturing Processes IIKamal SurenPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit - Iii: Metal Forming ProcessesDocument63 pagesUnit - Iii: Metal Forming ProcessesRohith RoPas encore d'évaluation
- Metal Forming ProcessesDocument120 pagesMetal Forming ProcessesAditya KoutharapuPas encore d'évaluation
- Metal Forming Processes - FullDocument5 pagesMetal Forming Processes - FullArjun NbPas encore d'évaluation
- Lec 6 Extrusion Metal WorkingDocument29 pagesLec 6 Extrusion Metal WorkingSidra SaeedPas encore d'évaluation
- ExtrusionDocument16 pagesExtrusionSourav Saha100% (1)
- Part B: Principles of Major Manufacturing Processes and Bulk FormingDocument49 pagesPart B: Principles of Major Manufacturing Processes and Bulk FormingsivaenotesPas encore d'évaluation
- 3.hot Working PDFDocument42 pages3.hot Working PDFkacangtim100% (1)
- Plastic Metal Forming of Metals and PowdersDocument20 pagesPlastic Metal Forming of Metals and Powdersيوسف عادل حسانينPas encore d'évaluation
- The Making of Coil Spring Uses The Extrusion Process. This Is A CompressionDocument3 pagesThe Making of Coil Spring Uses The Extrusion Process. This Is A Compressionnadia ayuningPas encore d'évaluation
- Revised Materials and Processes Sections 7 To 9Document207 pagesRevised Materials and Processes Sections 7 To 9Ameem TariqPas encore d'évaluation
- Sheet-Metal Forming Processes: Group 9 PresentationDocument90 pagesSheet-Metal Forming Processes: Group 9 PresentationjssrikantamurthyPas encore d'évaluation
- 4-BMCG 2323 Continous ProcessDocument34 pages4-BMCG 2323 Continous Processhemarubini96Pas encore d'évaluation
- Extrusion For ClassDocument49 pagesExtrusion For ClassNABIL HUSSAINPas encore d'évaluation
- Hot Cold WorkingDocument40 pagesHot Cold Workingpatel ketanPas encore d'évaluation
- Cold FormingDocument7 pagesCold FormingglaxionPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3 Metal Forming ProcessesDocument103 pagesChapter 3 Metal Forming Processesdagimawgchew777Pas encore d'évaluation
- 5 ExtrusionDocument19 pages5 ExtrusionManuel VillanuevaPas encore d'évaluation
- Metal Forming Processes - Full PDFDocument91 pagesMetal Forming Processes - Full PDFAnonymous 9xvU1F100% (2)
- Unit Iii Bulk Processes Bulk DeformationDocument77 pagesUnit Iii Bulk Processes Bulk DeformationAkash akPas encore d'évaluation
- Forging Die of SpannerDocument16 pagesForging Die of Spannervirendra pawarPas encore d'évaluation
- Forming & Shaping Processes For Plastics: Manufacturing Processes Manufacturing Processes ME ME - 222 222Document41 pagesForming & Shaping Processes For Plastics: Manufacturing Processes Manufacturing Processes ME ME - 222 222shahnawaz875Pas encore d'évaluation
- Polymer Processing: PDF File Can Be Downloaded atDocument66 pagesPolymer Processing: PDF File Can Be Downloaded atbibhu059Pas encore d'évaluation
- ExtrusionDocument28 pagesExtrusionAkash SavaliyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 15Document17 pagesChapter 15Lhekha RaviendranPas encore d'évaluation
- A Technical Seminar Rreport On Extrusion: Prateek Raj Roll No.Document18 pagesA Technical Seminar Rreport On Extrusion: Prateek Raj Roll No.Sam SachanPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 5Document53 pagesWeek 5aqsa zahidPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 4 Sheet Metal ProcessDocument77 pagesUnit 4 Sheet Metal ProcessJackson ..100% (2)
- Extrusion LatestDocument27 pagesExtrusion LatestChanti ChaithanyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Mechanics of Sheet Metal FormingD'EverandMechanics of Sheet Metal FormingJack HuÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (3)
- Nov 2008Document13 pagesNov 2008dharshanaabPas encore d'évaluation
- Nov 2015Document54 pagesNov 2015dharshanaabPas encore d'évaluation
- 5-2-05 - The Wonder of Oobleck - Discrepant EventDocument4 pages5-2-05 - The Wonder of Oobleck - Discrepant EventdharshanaabPas encore d'évaluation
- (Easiest To Argue) Ongoing Tension and ConflictDocument1 page(Easiest To Argue) Ongoing Tension and ConflictdharshanaabPas encore d'évaluation
- StuffDocument1 pageStuffdharshanaabPas encore d'évaluation
- Prosper & Sucker RodDocument20 pagesProsper & Sucker RodOmar AbdoPas encore d'évaluation
- Data Download CMM366A-4G V1.0 enDocument16 pagesData Download CMM366A-4G V1.0 enSuramanPas encore d'évaluation
- Estimating QuotientsDocument7 pagesEstimating Quotientssheila mae neri100% (1)
- Me (3) - 2Document16 pagesMe (3) - 2aviralPas encore d'évaluation
- ECE ExperimentDocument13 pagesECE Experimentasm98090% (1)
- Final ProjectDocument4 pagesFinal ProjectChacho BacoaPas encore d'évaluation
- Partea I .60p I. Read The Text Below and Complete The Following Tasks. Write All Your Answers On The Answer SheetDocument4 pagesPartea I .60p I. Read The Text Below and Complete The Following Tasks. Write All Your Answers On The Answer SheetaaddniaPas encore d'évaluation
- Os ND06Document3 pagesOs ND06kevinbtechPas encore d'évaluation
- Presentation: Isa Test Sets Training Course - 2014Document5 pagesPresentation: Isa Test Sets Training Course - 2014Sultan Uddin KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Zbrush 4 ShortcutsDocument3 pagesZbrush 4 ShortcutsJPas encore d'évaluation
- Start Up and Commissioning of Chilled Water PumpsDocument6 pagesStart Up and Commissioning of Chilled Water PumpsAlaa AnwerPas encore d'évaluation
- Elecon GearboxDocument19 pagesElecon GearboxShirley Farrace100% (3)
- Fluid Mech. 2Document32 pagesFluid Mech. 2Leslie Owusu MensahPas encore d'évaluation
- Design and Development of An Additive Manufactured Component by Topology OptimisationDocument6 pagesDesign and Development of An Additive Manufactured Component by Topology OptimisationJon SnowPas encore d'évaluation
- PB152 - CJ60 GongDocument2 pagesPB152 - CJ60 GongJibjab7Pas encore d'évaluation
- D4304-Syllabus-Neural Networks and Fuzzy SystemsDocument1 pageD4304-Syllabus-Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systemsshankar15050% (1)
- Phrasal Verbs-Syntactic BehaviorDocument4 pagesPhrasal Verbs-Syntactic BehaviorAntonija KnezovićPas encore d'évaluation
- Creative Computing v06 n12 1980 DecemberDocument232 pagesCreative Computing v06 n12 1980 Decemberdarkstar314Pas encore d'évaluation
- Applications of Modern RF PhotonicsDocument213 pagesApplications of Modern RF PhotonicsrmcmillanPas encore d'évaluation
- Leading The Industry In: Solar Microinverter TechnologyDocument2 pagesLeading The Industry In: Solar Microinverter TechnologydukegaloPas encore d'évaluation
- Strain STREMADocument6 pagesStrain STREMAChavin StormPas encore d'évaluation
- 20CB PDFDocument59 pages20CB PDFChidiebere Samuel OkogwuPas encore d'évaluation
- Real Time Operating SystemsDocument15 pagesReal Time Operating SystemsSaro VrsPas encore d'évaluation
- Downloadble Science NotesDocument55 pagesDownloadble Science NotesJeb PampliegaPas encore d'évaluation
- B 1 1 4 Inplant Fluid FlowDocument5 pagesB 1 1 4 Inplant Fluid FlowBolívar AmoresPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 1 Engineering ScienceDocument38 pagesModule 1 Engineering ScienceLogan JessePas encore d'évaluation