Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Counterbalance
Transféré par
cristi_amaCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Counterbalance
Transféré par
cristi_amaDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Service and Maintenance
Sun Counterbalance valves Settings and adjustments
INDEX
Section 1
Introduction
Section 2
Making Adjustments
Section 3
Troubleshooting
SECTION
Introduction
1
Figure 1.1
Counterbalance valves with pilot assist combine two valves; a check valve and a relief valve. The check valve allow free flow from the directional valve (port 2) to the load (port 1) while a direct acting, pilot-assisted relief valve controls flow from port 1 to port 2. Pilot assist at port 3 lowers the effective setting of the relief valve at a rate determined by the pilot ratio.
Rating for valve is stamped on hex section of valve in PSI .
The counterbalance valve will be on of the most difficult valves you will have to set on a piece of equipment. It is difficult to determine the setting of the valve while in the circuit in the usual manner. Because of this, the counterbalance valve has to be bench set off the machine with a special block for this purpose. You will need the following items to set the counterbalance valve: (See Figure 2.1 for set-up) - Pressure gauge that is suitable for the pressure involved. - A Sun Hydraulics P/N BCJ/S body with a T-2A cavity (Test Block). - Misc. hoses and fittings. - Hydraulic hand pump.
SECTION
Making Adjustments
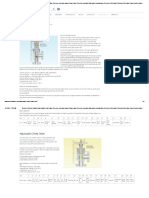
Figure 2.1 5000 psi Test Gauge
Line to Tank or Pail Counterbalance Valve
Line from Hand Pump
Adjusting Screw
Test Block Cap on Port Port not Used
Lock-nut
Before removing the counterbalance valve, ensure machines and loads (i.e.Top Drive) are mechanically held in position or at rest. Also make sure that the valve is not under pressure at the time of removal. Remove the counterbalance valve and install into testing block. Loosen lock-nut on counterbalance valve. Insert an allen key into the adjusting screw and turn out (counter-clockwise) to increase the pressure setting or in (clockwise) to reduce the pressure setting. While looking at gauge, pump up test system pressure with hand pump and set valve to relieve at recommended setting (see Figure 3.2 for location of setting on valve) . Repeat several times to ensure the consistency of the setting.
SECTION
Troubleshooting
The most common cause o f failure of a counterbalance valve cartridge is seal failure or contamination in the hydraulic fluid, which can then lodge in the working parts of the cartridge and interfere with their operation. The major symptom of a failed counterbalance valve is creeping in the cylinder. 1. Before removing the counterbalance valve, ensure machines and loads (i.e.Top Drive) are mechanically held in position or at rest. Also make sure that the valve is not under pressure at the time of removal. 2. Remove the cartridge from its Cavity. 3. Inspect the cartridge for visible contaminates, if found, carefully remove any obvious particles. 4. Flush the cartridge in clean mineral spirits and blow dry with clean dry air. 5. Replace any seals that are worn or damaged. 6. Dip the cartridge in clean hydraulic fluid and re-install the cartridge tightening to the specified torque. 7. If this procedure does not eliminate the operational problem, replace the malfunctioning cartridge with a new, factory tested cartridge.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Holland KingpinsDocument8 pagesHolland KingpinsPablo César Suárez NogalesPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapel Hydraulic ComponentsDocument76 pagesChapel Hydraulic ComponentsSaeed OsheePas encore d'évaluation
- Top Drive 500 TonDocument10 pagesTop Drive 500 TonImanPas encore d'évaluation
- Specifications: Pruebas y AjustesDocument5 pagesSpecifications: Pruebas y AjustesJuan FerPas encore d'évaluation
- Drilling Mud Pump Pump Fluid End PartsDocument2 pagesDrilling Mud Pump Pump Fluid End PartsleoPas encore d'évaluation
- Drawworks Disc Brake HPU Proportional ValveDocument4 pagesDrawworks Disc Brake HPU Proportional ValveNoureddine AdjPas encore d'évaluation
- Manual ENGDocument91 pagesManual ENGbrunosamaeianPas encore d'évaluation
- Accumulator CatalogueDocument280 pagesAccumulator CatalogueEdgar Allende ChavezPas encore d'évaluation
- PS15 Manually Operated Power Slip PS16 Pneumatically Operated Power SlipDocument52 pagesPS15 Manually Operated Power Slip PS16 Pneumatically Operated Power SlipAlas KHPas encore d'évaluation
- Drilling Rig PR-02 Specs: Trailer Rig, 1000HP, 8000ft DepthDocument17 pagesDrilling Rig PR-02 Specs: Trailer Rig, 1000HP, 8000ft DepthCaptain Nematollahi100% (1)
- E04 Using Kalsi Seals in Washpipe AssembliesDocument17 pagesE04 Using Kalsi Seals in Washpipe AssembliesSuresh Kumar MittapalliPas encore d'évaluation
- Drilling EquipmentDocument18 pagesDrilling EquipmentGhinet Teodor-ioanPas encore d'évaluation
- Rotary Checklist Rev4Document6 pagesRotary Checklist Rev4Shag ShaggyPas encore d'évaluation
- Threads and Sealing MethodsDocument80 pagesThreads and Sealing MethodsHuseyin TASKINPas encore d'évaluation
- Mud Pumps 1Document2 pagesMud Pumps 1John RongPas encore d'évaluation
- Operacion y Manual de HCR 5000 Psi (Actuador Hidraulico)Document22 pagesOperacion y Manual de HCR 5000 Psi (Actuador Hidraulico)Juan Miguel Robledo100% (2)
- Report No (1) Haydrulic MachinesDocument15 pagesReport No (1) Haydrulic MachinesWesame Shnoda100% (1)
- HAWE Proportional Directional Spool VALVEDocument28 pagesHAWE Proportional Directional Spool VALVECosma Petru-Raul100% (1)
- Lantec LW Series Winches Catalog PDFDocument16 pagesLantec LW Series Winches Catalog PDFFareedMohmed100% (1)
- WalvoilDocument64 pagesWalvoilSamad A BakarPas encore d'évaluation
- Onshore Product Reference Guide PDFDocument44 pagesOnshore Product Reference Guide PDFPedro RiveraPas encore d'évaluation
- PS 1000 ManualDocument117 pagesPS 1000 Manualnoormanmubarak100% (3)
- DL Bop BrochureDocument4 pagesDL Bop BrochurekrishnsgkPas encore d'évaluation
- Stress Analysis of Mast Structure For Water-Well Drilling MachineDocument8 pagesStress Analysis of Mast Structure For Water-Well Drilling MachineBruno Santos100% (1)
- 5-778-93 Hydraulic CylindersDocument8 pages5-778-93 Hydraulic CylindersJerry ZhangPas encore d'évaluation
- Hydraulic accumulators store fluid under pressureDocument39 pagesHydraulic accumulators store fluid under pressureRuben Dario Mata Romero50% (2)
- BARDEN Parts ListDocument20 pagesBARDEN Parts ListDwiki RamadhaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Osaka 2018 PDFDocument148 pagesOsaka 2018 PDFcmc261185Pas encore d'évaluation
- Denison Hydraulics Gold Cup Series Piston Pumps GuideDocument64 pagesDenison Hydraulics Gold Cup Series Piston Pumps Guideabuzer1981Pas encore d'évaluation
- 414 Centrifuge IOM Rev2Document104 pages414 Centrifuge IOM Rev2Giorgiana RosuPas encore d'évaluation
- CR191117 - E - Spare PartsDocument111 pagesCR191117 - E - Spare Partsandrea100% (1)
- Training ForajDocument150 pagesTraining ForajleoPas encore d'évaluation
- Data Sheet Brake MalacateDocument10 pagesData Sheet Brake MalacateAnonymous ciu3QEjuS100% (1)
- Bladder Accumulators HYDACDocument19 pagesBladder Accumulators HYDACPopescu Ioana CorinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Maintain and operate gate valvesDocument32 pagesMaintain and operate gate valvesNeilton Junior100% (2)
- Training ForajDocument150 pagesTraining ForajAlex ZamanPas encore d'évaluation
- D811001369 CL st-MAN-002 - Rev 05 - D811001369-MAN-002 - Rev05Document225 pagesD811001369 CL st-MAN-002 - Rev 05 - D811001369-MAN-002 - Rev05Daniel Matia Morla MichemPas encore d'évaluation
- M3036 Block 5861Document21 pagesM3036 Block 5861Gregory StewartPas encore d'évaluation
- One Company Unlimited SolutionsDocument20 pagesOne Company Unlimited SolutionsjobinjsPas encore d'évaluation
- RT Drive Device User ManualDocument13 pagesRT Drive Device User ManualJohn SimancaPas encore d'évaluation
- V5365 Z Ma 007 - 79445813Document26 pagesV5365 Z Ma 007 - 79445813peeps1980100% (1)
- Bladder-Type Accumulator HAB: RE 50170/03.2014, Bosch Rexroth AGDocument20 pagesBladder-Type Accumulator HAB: RE 50170/03.2014, Bosch Rexroth AGShariq KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Derrick, Crown & Accessories, National 516 HojasDocument516 pagesDerrick, Crown & Accessories, National 516 HojasMartin Guerrero100% (7)
- 10851186-MAN - Rev 01 - 10851186-MAN - Rev01Document296 pages10851186-MAN - Rev 01 - 10851186-MAN - Rev01Nehomar Jose Brito GuerraPas encore d'évaluation
- User Manual NovDocument578 pagesUser Manual Novgennaro100% (1)
- ParkerDocument600 pagesParkerSiddhant JoglekarPas encore d'évaluation
- Rollgliss 1Document425 pagesRollgliss 1Fabio Andrés CancinoPas encore d'évaluation
- 1562+Fz35 35闸板防喷器+用户手册a0 英文Document34 pages1562+Fz35 35闸板防喷器+用户手册a0 英文Jaya Manggala SaktiPas encore d'évaluation
- New TDS CourseDocument169 pagesNew TDS CourseNader abobakrPas encore d'évaluation
- Blohm+Voss PS 500 Technical DocDocument106 pagesBlohm+Voss PS 500 Technical Doc施咏胜100% (3)
- 750 HP Ideco Sbs h44 Drilling RigDocument22 pages750 HP Ideco Sbs h44 Drilling Riga. lekadirPas encore d'évaluation
- Cudd Pressure Control's 150K Modular Workover Snubbing SystemDocument15 pagesCudd Pressure Control's 150K Modular Workover Snubbing SystemAdolfo AnguloPas encore d'évaluation
- Manual Bba Triplex BD-85 BopDocument47 pagesManual Bba Triplex BD-85 BopwiloPas encore d'évaluation
- Rotary TableDocument1 pageRotary TableAek JayPas encore d'évaluation
- Sae j700 2011 King Pin Servicio RegularDocument4 pagesSae j700 2011 King Pin Servicio RegularCristian GordilloPas encore d'évaluation
- CVS Type 1051 Rotary Actuator: Instruction ManualDocument12 pagesCVS Type 1051 Rotary Actuator: Instruction Manualsalmo83:18Pas encore d'évaluation
- Valve Basics: 1.1 Actuating Force: Centre For Research and Industrial Staff PerformanceDocument6 pagesValve Basics: 1.1 Actuating Force: Centre For Research and Industrial Staff PerformanceSourabh KhandelwalPas encore d'évaluation
- A t3 Super Choke Operational Manual PDFDocument64 pagesA t3 Super Choke Operational Manual PDFMonica Caicedo100% (1)
- CFS PRV IOM Single PageDocument2 pagesCFS PRV IOM Single PageMazenPas encore d'évaluation
- AttTesting and AdjustingDocument8 pagesAttTesting and Adjustingchanlin100% (1)
- Reteta PaveleDocument6 pagesReteta Pavelecristi_amaPas encore d'évaluation
- Numatics Valve TrainingDocument57 pagesNumatics Valve TrainingRaymond EsmeraldaPas encore d'évaluation
- Concrete Block Egglayer EB12 - 10 OctDocument12 pagesConcrete Block Egglayer EB12 - 10 Octcristi_amaPas encore d'évaluation
- Garden Paving StonesDocument5 pagesGarden Paving Stonescristi_amaPas encore d'évaluation
- Improving Performance of An Energy Efficient Hydraulic Circuit PDFDocument175 pagesImproving Performance of An Energy Efficient Hydraulic Circuit PDFIjabiPas encore d'évaluation
- Overcenter ValvesDocument4 pagesOvercenter ValvesAnonymous jSTkQVC27b100% (1)
- Hydraulic Proportional Servo TechnologiesDocument37 pagesHydraulic Proportional Servo Technologiescristi_amaPas encore d'évaluation
- Concrete Block MakerDocument3 pagesConcrete Block MakervbezuglyPas encore d'évaluation
- Concrete Bricks BlocksDocument6 pagesConcrete Bricks BlocksSalim ShPas encore d'évaluation
- Example Quality PlanDocument12 pagesExample Quality PlanZunair ShahidPas encore d'évaluation
- ATOS-Instr. Punere FCTDocument4 pagesATOS-Instr. Punere FCTcristi_amaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ec 0411Document7 pagesEc 0411cristi_amaPas encore d'évaluation
- Hydraulic Cylinder TroubleshootingDocument8 pagesHydraulic Cylinder Troubleshootingcristi_ama100% (1)
- 10 Metode de Marire Viteza Instalatii HidrauliceDocument4 pages10 Metode de Marire Viteza Instalatii Hidraulicecristi_amaPas encore d'évaluation
- Hydraulic SymbolsDocument1 pageHydraulic Symbolsshaken56Pas encore d'évaluation
- Accumulator CircuitsDocument2 pagesAccumulator Circuitscristi_amaPas encore d'évaluation
- Komatsu WA320 5Document7 pagesKomatsu WA320 5cristi_ama100% (2)
- Unionocel Big-New enDocument24 pagesUnionocel Big-New encristi_amaPas encore d'évaluation
- Dimensiuni Canale PanaDocument2 pagesDimensiuni Canale Panacristi_ama100% (1)
- SPECTRO iSORT 0412 Engl LowresDocument4 pagesSPECTRO iSORT 0412 Engl Lowrescristi_amaPas encore d'évaluation
- SPECTRO Mobile Metal Analyzers enDocument6 pagesSPECTRO Mobile Metal Analyzers enMahmoud FathyPas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding Schematics: (Return To Table of Contents) 123Document15 pagesUnderstanding Schematics: (Return To Table of Contents) 123bmrajahPas encore d'évaluation
- Ceed Mazda3 C4Document4 pagesCeed Mazda3 C4cristi_amaPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic 7 FF in Res 1Document18 pagesTopic 7 FF in Res 1Aneesch PreethaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 6: Supersonic AerodynamicsDocument94 pagesChapter 6: Supersonic AerodynamicsJohn Brennan100% (2)
- Accumulators and Intensifiers in Hydraulic SystemsDocument7 pagesAccumulators and Intensifiers in Hydraulic SystemsNimo NingthoujaPas encore d'évaluation
- Gas RegulatorDocument48 pagesGas RegulatorMahussienyPas encore d'évaluation
- Hyundai 210LC7 Hydraulic System DiagramDocument35 pagesHyundai 210LC7 Hydraulic System DiagramMarco Olivetto100% (6)
- Funcionamiento Hidraulico Cat 416D OrtogonalDocument23 pagesFuncionamiento Hidraulico Cat 416D OrtogonalMauriciow85% (20)
- Subm Mittal D Data - MD Outdo DV-V105 Oor Uni 5W/DVN IT N1: F FeaturesDocument2 pagesSubm Mittal D Data - MD Outdo DV-V105 Oor Uni 5W/DVN IT N1: F FeaturesJunior Pantaleon QuispePas encore d'évaluation
- Machine Component Locations: 793D Off-Highway Truck Hydraulic SystemDocument2 pagesMachine Component Locations: 793D Off-Highway Truck Hydraulic SystemИгорь Иванов0% (1)
- ManufacturerDocument2 pagesManufacturerchristianPas encore d'évaluation
- AA283 Aircraft and Rocket Propulsion: Chapter 3 - The Ramjet CycleDocument72 pagesAA283 Aircraft and Rocket Propulsion: Chapter 3 - The Ramjet CycleSaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Piping and Instrumentation DrawingDocument1 pagePiping and Instrumentation Drawingeke23Pas encore d'évaluation
- NPR080 Ratio Controller Model RCTDocument4 pagesNPR080 Ratio Controller Model RCTJorge VelasquezPas encore d'évaluation
- OZKAN Butterfly ValvesDocument11 pagesOZKAN Butterfly ValvesAhmed AbdelwaneesPas encore d'évaluation
- BS 6683 (1985) Installation and Use of ValvesDocument18 pagesBS 6683 (1985) Installation and Use of Valves김창배Pas encore d'évaluation
- KKS Designation System KKS Designation SystemDocument19 pagesKKS Designation System KKS Designation Systemdexter schmithPas encore d'évaluation
- GEA - Pump - NH3 - Data BookDocument69 pagesGEA - Pump - NH3 - Data BookThái Đạo Phạm LêPas encore d'évaluation
- TMM Hospital at Thiruvalla. Approved Make of Materials For Fire Protection SystemDocument2 pagesTMM Hospital at Thiruvalla. Approved Make of Materials For Fire Protection SystemMC EstimationPas encore d'évaluation
- Refrigeration COP and Heat CalculationsDocument19 pagesRefrigeration COP and Heat CalculationskelvinPas encore d'évaluation
- Start-Up Commissioning Specialist Compressor Station Operator Global Resume Kevin SheldonDocument5 pagesStart-Up Commissioning Specialist Compressor Station Operator Global Resume Kevin SheldonKevinSheldonPas encore d'évaluation
- 2-Port Self Acting Temp. Control Valve PDFDocument12 pages2-Port Self Acting Temp. Control Valve PDFbandithaguruPas encore d'évaluation
- Figure N.2: API STD 610 CENTRIFUGAL PUMP DATA SHEET (U.S. Customary Units) (Continued)Document1 pageFigure N.2: API STD 610 CENTRIFUGAL PUMP DATA SHEET (U.S. Customary Units) (Continued)jimmyboy1234Pas encore d'évaluation
- Series 5000 TexsteamDocument24 pagesSeries 5000 TexsteamDaniel Dambo100% (4)
- The Complete Product Range of Water ApplicationsDocument42 pagesThe Complete Product Range of Water Applicationsremus popescuPas encore d'évaluation
- Piping and Valves Spec SheetDocument2 pagesPiping and Valves Spec SheetДмитрий РыбаковPas encore d'évaluation
- الخليجDocument10 pagesالخليجmohamedPas encore d'évaluation
- Well Control NCR ClassificationDocument15 pagesWell Control NCR ClassificationwalidPas encore d'évaluation
- Nutech ControlsDocument5 pagesNutech ControlsmuralisunPas encore d'évaluation
- There Are 8 Basic Types of Fan Wheels PDFDocument3 pagesThere Are 8 Basic Types of Fan Wheels PDFAnonymous bHh1L1Pas encore d'évaluation
- 3.2.1. Water Supply Pipe Size Calculations: Step 1: Required DataDocument48 pages3.2.1. Water Supply Pipe Size Calculations: Step 1: Required DataazulaPas encore d'évaluation
- rr220301 Mechanics of FluidsDocument8 pagesrr220301 Mechanics of FluidsSRINIVASA RAO GANTAPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction to Petroleum Process SafetyD'EverandIntroduction to Petroleum Process SafetyÉvaluation : 3 sur 5 étoiles3/5 (2)
- Incidents That Define Process SafetyD'EverandIncidents That Define Process SafetyPas encore d'évaluation
- Functional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsD'EverandFunctional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsPas encore d'évaluation
- Implementing an Integrated Management System (IMS): The strategic approachD'EverandImplementing an Integrated Management System (IMS): The strategic approachÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (2)
- Asset Integrity Management for Offshore and Onshore StructuresD'EverandAsset Integrity Management for Offshore and Onshore StructuresPas encore d'évaluation
- The Grid: The Fraying Wires Between Americans and Our Energy FutureD'EverandThe Grid: The Fraying Wires Between Americans and Our Energy FutureÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (48)
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionD'EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Power of Habit: The Ultimate Guide to Forming Positive Daily Habits, Learn How to Effectively Break Your Bad Habits For Good and Start Creating Good OnesD'EverandPower of Habit: The Ultimate Guide to Forming Positive Daily Habits, Learn How to Effectively Break Your Bad Habits For Good and Start Creating Good OnesÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (21)
- A Poison Like No Other: How Microplastics Corrupted Our Planet and Our BodiesD'EverandA Poison Like No Other: How Microplastics Corrupted Our Planet and Our BodiesÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Flow Analysis for Hydrocarbon Pipeline EngineeringD'EverandFlow Analysis for Hydrocarbon Pipeline EngineeringPas encore d'évaluation
- Guidelines for Implementing Process Safety ManagementD'EverandGuidelines for Implementing Process Safety ManagementPas encore d'évaluation
- Idaho Falls: The Untold Story of America's First Nuclear AccidentD'EverandIdaho Falls: The Untold Story of America's First Nuclear AccidentÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (21)
- The Complete HVAC BIBLE for Beginners: The Most Practical & Updated Guide to Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning Systems | Installation, Troubleshooting and Repair | Residential & CommercialD'EverandThe Complete HVAC BIBLE for Beginners: The Most Practical & Updated Guide to Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning Systems | Installation, Troubleshooting and Repair | Residential & CommercialPas encore d'évaluation
- The New 3D Layout for Oil & Gas Offshore Projects: How to ensure successD'EverandThe New 3D Layout for Oil & Gas Offshore Projects: How to ensure successÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (3)
- Build Your Own Electric Vehicle, Third EditionD'EverandBuild Your Own Electric Vehicle, Third EditionÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (3)
- Renewable Energy: A Very Short IntroductionD'EverandRenewable Energy: A Very Short IntroductionÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (12)
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionD'EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionPas encore d'évaluation
- Nuclear Energy in the 21st Century: World Nuclear University PressD'EverandNuclear Energy in the 21st Century: World Nuclear University PressÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (3)
- OFF-GRID PROJECTS: A Comprehensive Beginner's Guide to Learn All about OffGrid Living from A-Z and Live a Life of Self-SufficiencyD'EverandOFF-GRID PROJECTS: A Comprehensive Beginner's Guide to Learn All about OffGrid Living from A-Z and Live a Life of Self-SufficiencyPas encore d'évaluation
- Shorting the Grid: The Hidden Fragility of Our Electric GridD'EverandShorting the Grid: The Hidden Fragility of Our Electric GridÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (2)
- Trevor Kletz Compendium: His Process Safety Wisdom Updated for a New GenerationD'EverandTrevor Kletz Compendium: His Process Safety Wisdom Updated for a New GenerationPas encore d'évaluation
- Handbook on Battery Energy Storage SystemD'EverandHandbook on Battery Energy Storage SystemÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (2)
- Industrial Piping and Equipment Estimating ManualD'EverandIndustrial Piping and Equipment Estimating ManualÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (7)
- Produced Water Treatment Field ManualD'EverandProduced Water Treatment Field ManualÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (5)
- Chemical Process Safety: Learning from Case HistoriesD'EverandChemical Process Safety: Learning from Case HistoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (14)
- ISO 50001: A strategic guide to establishing an energy management systemD'EverandISO 50001: A strategic guide to establishing an energy management systemPas encore d'évaluation
- Rules of Thumb for Maintenance and Reliability EngineersD'EverandRules of Thumb for Maintenance and Reliability EngineersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (12)
- Transmission Pipeline Calculations and Simulations ManualD'EverandTransmission Pipeline Calculations and Simulations ManualÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (10)