Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Cuestionario 13-Francia
Transféré par
Zlatan IbrahimovicDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Cuestionario 13-Francia
Transféré par
Zlatan IbrahimovicDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Recuerden que el numero de pagina es la de las hojas, no la que indica la aplicacin ok. Cuestionario 13 Todo de la lectura de Gallis,(2005) 1.
- la Pregunta 1 Belkin, P. (2011) Pgina 7 France, like the United States, believes that it has a special role in the world. The core perceptions of Frances role in the world stem from the Revolution that began in 1789. The Revolution was an event of broad popular involvement: widespread bloodshed, expropriation of property, and execution of the king fed the notion that there could be no turning back to monarchical government. Not only was the monarchy overthrown and a powerful church structure forcibly dismantled, but French armies, and ultimately French administrators in their wake, transformed much of the continent into societies where more representative, democratic institutions and the rule of law could ultimately take root. The Revolution was therefore a central, formative element in modern European history, notably in Europes evolution from monarchical to democratic institutions. The cultural achievements of France before and since the Revolution have added to French influence. French became the language of the lite in many European countries. By 1900, French political figures of the left and the right shared the opinion that France was and must continue to be a civilizing beacon for the rest of the world.13 The view that France has a civilizing mission (la mission civilisatrice) in the world endures today. For many years, the French government has emphasized the message of human rights and democracy, particularly in the developing world and in central Europe and Eurasia. Many French officials, particularly Gaullists,14 have been highly assertive in seeking to spread French values throughout the world. Dominique de Villepin, the last prime minister under Sarkozys predecessor Jacques Chirac, wrote that at the heart of our national identity, there is a permanent search for values that might be shared by others. 2.-pag5 parrafo2 lectura del 2005
France was one of the founding members of the European Union (initially known as the European Coal and Steel Community) in 1952. Improved trade and economic development were central objectives of member states in a Europe still struggling from the dislocation caused by the Second World War, but overarching objectives from the beginning were political rapprochement between Germany and its former enemies, and political stability on the continent. The EU was conceived in this context, with strong U.S. support.
3.-pag16 parrafo1 (subtema terrorismo) lectura 2005
Many U.S. and French officials believe that bilateral cooperation between the United States and France in law-enforcement efforts to combat terrorism since September 11 has been strong, but at the same time a range of political factors is complicating the relationship.41 France has long experience in combating terrorism, a tightly centralized system of law enforcement, and a far-reaching network that gathers information on extremist groups. Limits on resources and important social and political issues sometimes affect elements of Frances anti-terrorism policies
4.-pag8 parrafo2 lectura 2005
For the most part, Frances record over the past decade has been consistent in following the precept that the U.N. must endorse the use of force in a crisis. For
Recuerden que el numero de pagina es la de las hojas, no la que indica la aplicacin ok.
example, France, along with other countries, since 1990 has obtained a U.N. resolution for the potential or actual use of force for interventions in the first Gulf War, Bosnia, Afghanistan, Congo, the Ivory Coast, and Haiti. One notable exception came in 1999, when France joined its NATO allies in going to war against Serbia in an effort to prevent ethnic cleansing in Kosovo. In that case, until the eleventh hour, the French government sought a U.N. resolution for NATOs use of force. At the same time, in the face of an increasingly likely Russian veto, French officials and counterparts from several other European allies began indicating that Serbian actions had reached a stage where using force to prevent a humanitarian catastrophe in Kosovo would be justifiable without a U.N. resolution.16 When a Russian veto became certain, there was a consensus in NATO that the use of force was justifiable in this instance even in the absence of a U.N. resolution.
5.-pag8 parrafo3
The Chirac government and the Bush Administration and some of its supporters have clashed over Frances pursuit of multipolarity in economic, military, and political affairs. The French government has described multipolarity as a system of balance in international affairs, in part a natural outgrowth of trading blocs and regional global differences, in part a value that is in principled opposition to global domination by one power or bloc. Some Administration officials, notably Condoleezza Rice, have disparaged the concept as a means to thwart U.S. foreign policy. In June 2003, she said that it was troubling that some have spoken admiringly almost nostalgically of multipolarity, as if it were a good thing to be desired for its own sake. She said that France seemed intent upon checking the United States, and that France appeared to consider the United States more dangerous than Saddam Hussein.17 Some Administration supporters in the neoconservative movement are more pointed, and claim that France wishes to reclaim
6.- 12,13 donde dice France has a long history of religious violence. ....hasta Muslim world over the issue of
terrorism.
7.- Pgina 15 donde
Sin embargo , grandes diferencias ocasionales en la OTAN entre Pars y Washington siguen apareciendo en el plano poltico . Por ejemplo , en febrero de 2003 , Francia ( y Alemania) intent bloquear un esfuerzo de EE.UU. en el NAC para discutir el envo de fuerzas de la OTAN para defender a Turqua en caso de que el inminente conflicto en Irak podra estimular el Bagdad de huelga Turqua. Pars y Berln afirmaron que el envo de fuerzas y equipos a Turqua constituira una aprobacin tcita de una decisin de EE.UU. de ir a la guerra, y sera un acto de provocacin . Francia y otros aliados , en lugar deseaban continuar las inspecciones de la ONU en Irak armas de destruccin masiva de armas ( se explica ms adelante ) . La Administracin Bush reaccion con enojo a los esfuerzos de Francia en la NAC . En abril de 2003 , el subsecretario de Defensa Wolfowitz dijo al Comit de Servicios Armados
Recuerden que el numero de pagina es la de las hojas, no la que indica la aplicacin ok.
del Senado que Francia haba " creado un gran problema " en la OTAN sobre la ayuda a Turqua. Ms tarde anunciar la decisin del Pentgono de excluir a empresas de Francia y otros pases se oponen a la guerra de Irak de los contratos para reconstruir Irak. Richard Perle , que forma parte del movimiento neo -conservador y asesor del Pentgono , dijo , " Francia ya no es el aliado que era. " El mes siguiente , algunos senadores propusieron alterar el proceso de toma de decisiones OTAN para frenar la voz de Francia
8.-pag 19 parrafo 4
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Eurozone Crisis: Greece, Ireland, Portugal, Italy, SpainDocument2 pagesEurozone Crisis: Greece, Ireland, Portugal, Italy, SpainZlatan IbrahimovicPas encore d'évaluation
- (114283684) Poland Country ReportDocument30 pages(114283684) Poland Country ReportZlatan IbrahimovicPas encore d'évaluation
- CRS Report For Congress: France: Factors Shaping Foreign Policy, and Issues in U.S.-French RelationsDocument32 pagesCRS Report For Congress: France: Factors Shaping Foreign Policy, and Issues in U.S.-French RelationsZlatan IbrahimovicPas encore d'évaluation
- (106927327) The Euro Debt Crisis and Germany's Euro TrilemmaDocument53 pages(106927327) The Euro Debt Crisis and Germany's Euro TrilemmaZlatan IbrahimovicPas encore d'évaluation
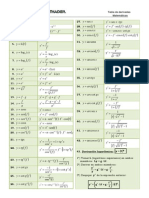
- ACADEMIA THADER DERIVADA FORMULASDocument1 pageACADEMIA THADER DERIVADA FORMULASJaneth Perez Armenta100% (1)
- Camtasia Getting Startedok GuideDocument5 pagesCamtasia Getting Startedok Guide,qwerty.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Formulas de Calculo Todas Derivadas Integrales LimitesDocument3 pagesFormulas de Calculo Todas Derivadas Integrales Limitesjorgejlhc100% (2)
- Armed Conflict in SyriaDocument54 pagesArmed Conflict in SyriaeanicolasPas encore d'évaluation
- BBC Tews 111 Every Tom Dick and Harry PDFDocument2 pagesBBC Tews 111 Every Tom Dick and Harry PDFmohsalehi1391Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5782)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (587)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (72)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Social Media LawsuitDocument39 pagesSocial Media LawsuitUnited Press InternationalPas encore d'évaluation
- Estonia Cyber Security StrategyDocument36 pagesEstonia Cyber Security StrategybobeczkoPas encore d'évaluation
- PSC Letter of 11 August (TIPS)Document182 pagesPSC Letter of 11 August (TIPS)Karin KunjaraPas encore d'évaluation
- PHD Proposal Media CensorshipDocument15 pagesPHD Proposal Media CensorshipCharbel Semaan Abi RachedPas encore d'évaluation
- Counterterrorism Sanctions and War International Review of The Red Cross No 916 917Document772 pagesCounterterrorism Sanctions and War International Review of The Red Cross No 916 917puja sumantriPas encore d'évaluation
- 6 StahlDocument17 pages6 StahlijazPas encore d'évaluation
- Darko Trifunović: Origins of Terrorism in BosniaDocument40 pagesDarko Trifunović: Origins of Terrorism in BosniaNeverGiveUp ForTheTruePas encore d'évaluation
- PSR - Test - 6 - India and WorldDocument23 pagesPSR - Test - 6 - India and Worldshreyansh jainPas encore d'évaluation
- High Accuracy Location Information Extraction From Social Network Texts Using Natural Language ProcessingDocument12 pagesHigh Accuracy Location Information Extraction From Social Network Texts Using Natural Language ProcessingDarrenPas encore d'évaluation
- The Challenges of The Internet and Social Media in Public DiplomacyDocument16 pagesThe Challenges of The Internet and Social Media in Public DiplomacyThe American Security Project100% (4)
- Kata'Ib HezbollahDocument11 pagesKata'Ib HezbollahBogdan UrsuPas encore d'évaluation
- Download Testbook App to Learn About TerrorismDocument8 pagesDownload Testbook App to Learn About TerrorismmohankumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Pidato The Role of Pesantren in The Prevention of Terrorism and RadicalismDocument3 pagesPidato The Role of Pesantren in The Prevention of Terrorism and RadicalismFarah Nabila100% (1)
- Crisis ManagementDocument16 pagesCrisis Managementnikiniki9100% (1)
- International SecurityDocument5 pagesInternational SecurityMalik ZamanPas encore d'évaluation
- Fill in The Table Below. Minimum of 5 Sentences, Maximum of 7 SentencesDocument4 pagesFill in The Table Below. Minimum of 5 Sentences, Maximum of 7 SentencesJENIN SANTIAGOPas encore d'évaluation
- Effects of Terrorism on Community Safety and SecurityDocument1 pageEffects of Terrorism on Community Safety and SecurityDALE JERICH APAYORPas encore d'évaluation
- The Use of Media by ISIS in The Paris AttackDocument5 pagesThe Use of Media by ISIS in The Paris AttackHoàng LongPas encore d'évaluation
- Book MilitantgroupsDocument321 pagesBook MilitantgroupsSreoshi SinhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Revelation and Popular CultureDocument20 pagesRevelation and Popular Cultureapi-3735458100% (1)
- Pakistan Affairs by Asmatullah Junejo, PSP: Saturday, January 27, 2018Document41 pagesPakistan Affairs by Asmatullah Junejo, PSP: Saturday, January 27, 2018Ayaan KhaanPas encore d'évaluation
- Diploma Enforcement ManagementDocument18 pagesDiploma Enforcement ManagementSubaashine ArumugamPas encore d'évaluation
- Bombs and BalaclavasDocument52 pagesBombs and Balaclavasjvmarron100% (1)
- 2015 04 28 - Endurance International Group: A Web of DeceitDocument61 pages2015 04 28 - Endurance International Group: A Web of DeceitgothamcityresearchPas encore d'évaluation
- Comparison Table Goods in Transit Cover A and Annual Marine Cargo Icc ADocument6 pagesComparison Table Goods in Transit Cover A and Annual Marine Cargo Icc Apram006Pas encore d'évaluation
- 110 Islamic Travelogue 1427 8 - Imran HoseinDocument1 page110 Islamic Travelogue 1427 8 - Imran Hoseinspeed2kxPas encore d'évaluation
- Islamophobia Case Negative - DDI 2015 MMDocument40 pagesIslamophobia Case Negative - DDI 2015 MMJohnBoalsPas encore d'évaluation
- Democratic oversight of intelligence servicesDocument22 pagesDemocratic oversight of intelligence servicesVaz FolderPas encore d'évaluation
- Peace and Conflict Studies Fourth Edition Ebook PDF VersionDocument61 pagesPeace and Conflict Studies Fourth Edition Ebook PDF Versionedith.beltran702100% (36)
- Download Instructions Get Started Human SecurityDocument4 pagesDownload Instructions Get Started Human SecurityLalaine MolinaPas encore d'évaluation