Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Tipos de Facilitacion
Transféré par
hheviaDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Tipos de Facilitacion
Transféré par
hheviaDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
8
Managing Facilitated Processes
Table 1.1
Types of Facilitated Processes
Process Type 1. Annual general meeting (AGM). A regular session with board members and general members of a not-for-profit group or other organization; focus is primarily on reporting on the past year and voting on key decisions for the future; usually chaired rather than facilitated. 2. Board meeting. A regular meeting of an organizations board of directors (and often some members) focused on the policies and related decisions required to manage the business or program as described in the organizations strategic plan; usually chaired rather than facilitated. 3. Charrette. A facilitated, collaborative, intensive work session that usually takes place over several days and with all interested parties as participants (National Charrette Institute, 2008). Deliverables Updates; issues analysis; report; decisions on key agenda items, based on voting Key Features Presentations enhance attendance or highlight business items or current issues. Often substantial audiovisual (AV) and technical support. Problem solving; policy development; strategic plan; ethical guidelines; decisions on strategic items, often with a confidential voting process Room setup often an open rectangle. Presentations by informants for educational purposes.
Problem identification and description; information sharing; consensus-based decision making focused on community ownership
Expert speakers as required to support decision making. A series of meetings and design sessions compressed into several days. Guests and new members may be included. Speakers bring interesting perspectives on new issues and approaches. Presentation outlines support technical discussions and note taking. Virtual and real-time discussions in small groups and plenary sessions.
4. Chartered forum. A membership-based assembly of like-minded individuals (for example, professionals) who meet virtually or in person through a regular forum (for example, biannually) or on an ongoing basis to discuss, coordinate, and promote common issues and areas of interest; may be chaired or facilitated.
Issues identification; analysis and resolution; practice guidelines; sometimes involves consensusbased decision making
5. Colloquium. An academic conference or seminar of interested participants, focused on dialogue and conversation; usually chaired.
Knowledge transfer and exchange; networking; community development
Speakers with academic expertise. Discussions in plenary session and informal small groups: for example, standing around caf tables during breaks. Copies of presentations often provided.
Initial Contact
Table 1.1
Types of Facilitated Processes, Contd.
Process Type 6. Community conversation. A discussionoften hosted over several meetingsthat is focused on building or enhancing a space for belonging and accountability in a community; the emphasis is on the various gifts that participants bring in relation to the future rather than on past problems. 7. Conference. A large (usually) gathering that brings together people who want to hear about, learn, or discuss important matters in a specific area; usually chaired; may be designed by a process consultant or meeting planner. Deliverables A community where people are committed and connected to each other and to a shared purpose Key Features Setup usually a circle of movable chairs, without tables. Meeting space setup and aesthetics reflect the intention of the community participants want to create. Participation open and based on interest or by invitation to members or specific groups. Inspiring, high-quality presentations a key success factor. Both large plenary and smaller concurrent sessions at various times and places and in both virtual and real time. 8. Consultation. A facilitated workshop or longer process (for example, a series of workshops or focus groups) where participants are encouraged to advocate their points of view, advise, consult with one another, or be consulted by another party, or perform some combination of these tasks. Information gathering; focused discussion; report; recommendations for action Participation usually by invitation but may also be open to interested individuals and groups. Focus on hearing participants opinions; decision making not involved. Speakers may enable discussion. Seating arranged to support maximum input; participant contact information important for follow-up purposes. 9. Forum. A formal meeting for public discussion; usually chaired; sometimes facilitated. Structured discussion; issues exploration; networking; question generation Participation open to interested parties or by invitation based on perspectives. Speakers, especially at the start. Room setup often theater style due to formality of session; usually involves a podium and microphone.
Information sharing; networking; product promotion
(continued on next page)
10
Managing Facilitated Processes
Table 1.1
Types of Facilitated Processes, Contd.
Process Type 10. Kickoff meeting. An initial session of a longer project or process where the focus is on building enthusiasm and understanding for an agenda, key themes, or issues; often half a day or less; usually facilitated. Deliverables Commitment to and buyin for an idea or project Key Features Participation by invitation to a specific group. Motivational speakers usually featured. Themed giveaways, videos, and special effects frequently employed. Input to decision making; question generation; information sharing; creative thinking Participants are experts, so few or no speakers required. Seating arrangement supports eye contact and equality of participants.
11. Roundtable. A facilitated or chaired workshop where expert invitees share equal influence and status; most roundtables process information on a subject with a view toward decision making at the conclusion of the process. (King Arthur and his chosen knights are said to have sat at a round table so that none would have preference [see, for example, Timeless Myths, 2008].) 12. Search conference. A facilitated opportunity to discover common ground and imagine an ideal future; uses methods of discovery, analysis, and dialogue to broaden perspectives, expand horizons, and lead to committed action (Weisbord and others, 1992, p. xiii). 13. Seminar. A short (often a few hours), intensive course of study on a specific topic; often a meeting of specialists; usually small in size and chaired, not facilitated.
Decisions or recommendations on vision, strategic directions, community and network development, and next steps
Speakers may provide a focus for discussions that follow. Room layout corresponds to agenda; must support equitable and intensive discussion. Participation based on interest or restricted by invitation. Speakers are a highlight and focus on a specific topic. Room setup often theater style.
Informed speakers; knowledge transfer and exchange; critical reflection; presentation summaries
14. Summit. A facilitated conference where leading people in a topic area meet to discuss and come to agreement on key considerations for the future.
Informed speakers; technical background documents; conclusions and recommendations
Participation by invitation to current or future leaders in a field. High-profile speakers usually featured.
Initial Contact
11
Table 1.1
Types of Facilitated Processes, Contd.
Process Type 15. Symposium. An opportunity to learn from experts and discuss ideas with colleagues over a day or more; may, for example, be set up as a weeklong study tour focused on a specific topic; frequently chaired rather than facilitated. Deliverables Summary of expert presentations; problem solving; networking; report Key Features Participation by invitation to a profession or based on interest. Speakers a key part of the agenda. Room setup usually theater style. 16. Town hall meeting. A facilitated, open, informal gathering where general presentations are made and views on a subject are explored; usually half a day or less. Background documents; exploration of ideas and approaches Participation focuses on a specific community. Speakers usually leaders with accountability related to the topic. Room setup often informal; requires AV support for special presentations. 17. Think tank. A gathering where a group of experts, key informants, or opinion leaders provide advice and ideas on a specific topic; usually facilitated. Collaborative, creative thinking on an important topic; new ideas and options for action rather than decisions Participation by invitation to people with expertise. Speakers spark discussion and encourage creativity and innovation. Tools for working together creatively, such as poster walls and markers, may be used. 18. Workshop. A facilitated process with a specific purpose for a limited time period: for example, a few hours, a day, a weekend, or a week; participants are actively involved in doing work focused on outcomes. Conclusions, recommendations, or decisions related to objectives; report Effective room and group setups vary considerably; tables for taking notes helpful in some situations.
Decision Making After the Screen
The preliminary screening is an opportunity to assess the overall fit between what needs to be done with whom and to determine how people might work together to accomplish what needs to be done. This is the time to pause and reflect before making a decision about agreeing to the work. What are your thoughts and feelings telling you? Should this preliminary discussion move to the development of an agreement or not?
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- PC Hardware Servicing Teacher's GuideDocument7 pagesPC Hardware Servicing Teacher's GuidedanballaisPas encore d'évaluation
- Discovery Doodles Sketchbook Basics V2.1Document46 pagesDiscovery Doodles Sketchbook Basics V2.1hhevia100% (25)
- Troublshooting For PET PreformDocument5 pagesTroublshooting For PET PreformSteven Cheng75% (4)
- Substation Construction MethodologyDocument23 pagesSubstation Construction Methodologyhusktech67% (15)
- Clean Energy Council Installers Checklist PDFDocument3 pagesClean Energy Council Installers Checklist PDFAndre SPas encore d'évaluation
- Oracle Mid Exam Sem 1Document2 pagesOracle Mid Exam Sem 1Ardie Gucci100% (1)
- Sense Amplifier For SRAMDocument28 pagesSense Amplifier For SRAMPrateek AgrawalPas encore d'évaluation
- 3.1 Turbine and GoverningDocument90 pages3.1 Turbine and GoverningYudo Heru PribadiPas encore d'évaluation
- Ballastless TracksDocument20 pagesBallastless TracksYacoub Cheikh67% (3)
- Dlms DocumentDocument71 pagesDlms DocumentSudarshan ReddyPas encore d'évaluation
- Santiago & Elmore HER ArticleDocument22 pagesSantiago & Elmore HER ArticlehheviaPas encore d'évaluation
- You Too Can SketchDocument17 pagesYou Too Can SketchhheviaPas encore d'évaluation
- Building Effective Community PartnershipsDocument40 pagesBuilding Effective Community PartnershipsmutaijPas encore d'évaluation
- 7 2-ChaordicDocument8 pages7 2-ChaordichheviaPas encore d'évaluation
- Complexity Theory Realism and Path DependencyDocument22 pagesComplexity Theory Realism and Path DependencyhheviaPas encore d'évaluation
- Complexity Theory Realism and Path DependencyDocument22 pagesComplexity Theory Realism and Path DependencyhheviaPas encore d'évaluation
- Naruto - NagareboshiDocument2 pagesNaruto - NagareboshiOle HansenPas encore d'évaluation
- 14 QuestionnaireDocument14 pages14 QuestionnaireEkta SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Motor Driver Board Tb6560-5axisDocument14 pagesMotor Driver Board Tb6560-5axisAli Asghar MuzzaffarPas encore d'évaluation
- Silabus Reading VDocument4 pagesSilabus Reading VAndi AsrifanPas encore d'évaluation
- Tubewell Energy Audit PDFDocument172 pagesTubewell Energy Audit PDFshaheerdurrani100% (1)
- GSB (Coarse Graded) Summary Sheet: Physical PropertiesDocument10 pagesGSB (Coarse Graded) Summary Sheet: Physical PropertiesjitendraPas encore d'évaluation
- 165 NebulizerDocument2 pages165 NebulizerLotfi BahriPas encore d'évaluation
- Dokumen - Tips Cfm56 7 B AnswerbookDocument75 pagesDokumen - Tips Cfm56 7 B AnswerbookOnur YayPas encore d'évaluation
- Angoca Db2 Cheat Sheet For DevelopmentDocument3 pagesAngoca Db2 Cheat Sheet For DevelopmentTanveer AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- ABB Surge Arrester MWK - Data Sheet 1HC0075865 E01 ABDocument5 pagesABB Surge Arrester MWK - Data Sheet 1HC0075865 E01 ABsriniPas encore d'évaluation
- HCF Spec 190 1.0 PDFDocument31 pagesHCF Spec 190 1.0 PDFvikulovPas encore d'évaluation
- Lexium Motion Control 200401Document130 pagesLexium Motion Control 200401Mohamed Elsayed HasanPas encore d'évaluation
- Is 15462 2004 Modified Rubber BItumen PDFDocument16 pagesIs 15462 2004 Modified Rubber BItumen PDFrajeshji_000100% (3)
- Eletrical Motor OffshoreDocument38 pagesEletrical Motor OffshoreandreisraelPas encore d'évaluation
- Dap 018 ADocument28 pagesDap 018 AajoaomvPas encore d'évaluation
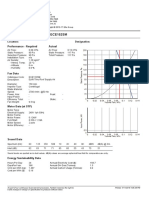
- Technical Data - Fan Model ECE152SM: Location: Designation: Performance - Required ActualDocument2 pagesTechnical Data - Fan Model ECE152SM: Location: Designation: Performance - Required ActualJPas encore d'évaluation
- Altman Fall Winter 2012 Product Showcase FlyerDocument32 pagesAltman Fall Winter 2012 Product Showcase FlyerИлия ГеоргиевPas encore d'évaluation
- Mech Bicycle RimsDocument8 pagesMech Bicycle Rimsharish rajputPas encore d'évaluation
- Der 484Document84 pagesDer 484Rohit SainiPas encore d'évaluation
- Manufacturing Systems-Fleximble Manufacturing Application-Case Study of ZimbabweDocument5 pagesManufacturing Systems-Fleximble Manufacturing Application-Case Study of Zimbabwejosphat muchatutaPas encore d'évaluation
- Sp. Reserve MagazineDocument21 pagesSp. Reserve MagazineViraf DasturPas encore d'évaluation