Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
GS104 - Exam I - Review
Transféré par
longlistCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
GS104 - Exam I - Review
Transféré par
longlistDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
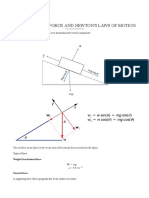
GS104 1st Test Major Topics for Review Format of the Test Multiple Choice (60 questions) Major
or Topics for Review (Chs 1-4) Motion Aristotle vs. Galileo Aristotle two kinds: Natural motion motion that is straight up or straight down Violent motion imposed motion resulting from an external push or pull Mass/Inertia G- Objects continue to move indefinitely Objects drop at the same time. Tendency of a moving body is natural. Inertia: property of things to resist change. Mass: Quantity of matter in an object. Measure of inertia or sluggishness that an object exhibits in response to any effort . Mass is greater than inertia. Smallaer mass smaller inertia Weight: amount of gravitational pull on an object proportional to mass. Mass involves how much matter an object contains. Volume involves how much space an object occupies. Density is the measure of how much mass occupies a given space. Equilibrium/Net force: Equilibirum is and object that moves at constant velocity. Two or more forces cancel at zero. Netforce: Combination of all forces that cat on an object. Changes an objects motion. Friction/Support force G- In the absence of friction, no force is necessary to keep a horizontally moving object moving. Friction: the resistive force that opposes the motion or attempted motion of an object through a fluid or past another object with which it is in contact and it is always acts in a direction to oppose motion Support force: is force that supports an object on the surface against gravity, and it is also normal force Velocity & Acceleration: Acceleration is the rate at which velocity changes with time. The change in velocity may be in magnitude, in direction, or both. Acceleration=change of velocity/time interval. Free fall: When the only force acting on a falling object is gravity Scalar vs. vector quantities: scalr has magnitude (speed), and vector has magnitude plus direction. (velocity Newtons Laws Newtons 1st/2nd/3rd Laws (be able to explain situations using all three laws) 1st. The law of inertia: Every object continues in a state of rest or of uniform speed in a straight line unless acted on by a nonzero force. 2nd. The law of acceleration: The acceleration produced by a net force on an object is directly proportional to the net force, is in the same direction as the net force, and is inversely proportional to the mass of the object Accerleration= net force/mass Smaller the force larger the mass small acceleration Large net force, mall mass large acceleration 3rd. Law of action and reaction: Whenever one object exerts a force on a second object, the second object exerts an equal and opposite force on the first. Free-Fall- An object in free fall accelerates toward Earth at 10 m/s per second. When the only force acting on a falling object is gravity, with negligible air resistance, the object is in free fall. Momentum & Energy Momentum: is inertia in motion defined as the product of mass and velocity: mv high mass high velocity -> high momentum and the higher Impulse: product of force and contact time equation: impulse = force time = Ft greater force for long time -> larger impulse Impulse = Change in momentum- decreases momentum over a longer time results in smaller force Conservation of momentum: momentum cannot change unless acted by an external force. Collisions: when objects collide in the absence of external force Elastic vs. Inelastic: is defined as a collision whereupon objects collide without permanent deformation or the generation of heat. Inelastic: is defined as a collision whereupon colliding objects become tangled or coupled together, generating heat. Energy: ability to do work Work: force applied over a distance Potential: stored energy due to position shape or state. Kinetic: defined as energy of a moving body. Work = Change in kinetic energy Conservation of energy: to save or remain unchanged Power: energy per unit time how fast work is done. Work/time interval. Machines/efficiency: ratio of input to output Sources of energy Gravity & Satellite Motion Universal Law of Gravity: Newtons Law of Universal Gravitation. Every body in the universe attracts every other body with a mutually attracting force. For 2 bodies, this force is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance separating them. Every mass pulls other mass. Inverse-square relationships: intensity of an object in inverse squares. Pull on by gravity. Weight & weightlessness- an illusion caused by the lack of support. Force or eg: free fall Projectile Motion: objects launched only under the influence of gravity Satellites: obejects that fall around an object eg. moon Circular vs. elliptical orbits: circular is around earth. Elliptical: is a path followed by a satellite. Orbital speed is 17500mph Escape Speed:The initial speed that an obeject must reach to escape gravitational influence of earth. 25000mph
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Science Reviewer 1st QuarterDocument21 pagesScience Reviewer 1st QuarterMarianne Asarez100% (1)
- MotionDocument51 pagesMotionJohanna Marie SorianoPas encore d'évaluation
- G9 Q2 W5 General Classes and Uses of Organic CompoundsDocument10 pagesG9 Q2 W5 General Classes and Uses of Organic CompoundsCherrilyn EnverzoPas encore d'évaluation
- As Level Physics Key WordsDocument6 pagesAs Level Physics Key Words林仁超Pas encore d'évaluation
- General Physics: Newton Law of MotionDocument4 pagesGeneral Physics: Newton Law of MotionJewel ValenciaPas encore d'évaluation
- Newton's Laws of MotionDocument29 pagesNewton's Laws of Motionpbayes83% (6)
- P6 Reviewer DefDocument5 pagesP6 Reviewer DefLexter AlteradoPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Fundamentals: Motion, Forces, Energy & MoreDocument10 pagesPhysics Fundamentals: Motion, Forces, Energy & MoreKatrina Anne Layson YeenPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4 PhysicDocument5 pagesChapter 4 PhysicWaleska MendezPas encore d'évaluation
- ForceDocument11 pagesForceAnastasia LarasatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics - Force and MotionDocument10 pagesPhysics - Force and MotionÅBanDonPas encore d'évaluation
- OCR A Level Physics Forces and Motion ConceptsDocument7 pagesOCR A Level Physics Forces and Motion ConceptsjmsonlPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Key Terms and Meaning-Semester-1Document6 pagesPhysics Key Terms and Meaning-Semester-1techzealPas encore d'évaluation
- Mechanics:-: AS Level Physics: Terms & DefinitionsDocument8 pagesMechanics:-: AS Level Physics: Terms & DefinitionsJenniferPas encore d'évaluation
- Laws of MotionDocument55 pagesLaws of MotionRalphNeilMarananPas encore d'évaluation
- AS Level Physics TermsDocument7 pagesAS Level Physics TermsJenniferPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 3 PhysciDocument124 pagesModule 3 Physciburner accPas encore d'évaluation
- Newton's Laws of Motion and ApplicationsDocument53 pagesNewton's Laws of Motion and Applicationsburner accPas encore d'évaluation
- Y10 Science Notes Semester 1Document3 pagesY10 Science Notes Semester 1Oscar ReinitzPas encore d'évaluation
- Science Grade 6 CDCDocument3 pagesScience Grade 6 CDCVlad VizcondePas encore d'évaluation
- Subject Grade 10 Physics NotesDocument1 pageSubject Grade 10 Physics Notesjordan.shapiroPas encore d'évaluation
- Newton's laws of motion explainedDocument6 pagesNewton's laws of motion explainedMohit ChokniwalPas encore d'évaluation
- Force and MotionDocument3 pagesForce and Motionapi-233366095Pas encore d'évaluation
- Forces, Newton's Laws, and DynamicsDocument10 pagesForces, Newton's Laws, and DynamicsCai MingleiPas encore d'évaluation
- Science Notes For Forces and MotionDocument6 pagesScience Notes For Forces and Motiontoe masterPas encore d'évaluation
- EASA Module 2 DictionaryDocument5 pagesEASA Module 2 DictionarySteven J. SelcukPas encore d'évaluation
- Physical Science Unit 9Document2 pagesPhysical Science Unit 9Bluematwo TwoPas encore d'évaluation
- Forces and MotionDocument2 pagesForces and Motionadivahussain2007Pas encore d'évaluation
- Forces and Friction: Nahdir Austin Honors Physics Period 2Document6 pagesForces and Friction: Nahdir Austin Honors Physics Period 2Asheesh KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Newton's Laws of Motion NotesDocument4 pagesNewton's Laws of Motion NotesSonicyBabaPas encore d'évaluation
- 02 - Fundamentals of Physics - Naghi GasimovDocument16 pages02 - Fundamentals of Physics - Naghi GasimovKVP LyricsPas encore d'évaluation
- Big Idea 13 Forces and Change in MotionDocument7 pagesBig Idea 13 Forces and Change in Motionapi-291011460Pas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Newton'sLawsofMotionDocument44 pagesPhysics Newton'sLawsofMotionCamela LacsamaPas encore d'évaluation
- NoteDocument2 pagesNoteSudhanshu KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 2 MotionDocument4 pagesLecture 2 MotionAnne BautistaPas encore d'évaluation
- Force and Motion Review SheetDocument5 pagesForce and Motion Review Sheetnayrine shereenPas encore d'évaluation
- Motion and Design VocabDocument2 pagesMotion and Design Vocabapi-289447020100% (1)
- Group 4's Report on Newton's Laws of MotionDocument26 pagesGroup 4's Report on Newton's Laws of MotionSheralyne Daz PequinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 1 - Laws of MotionDocument66 pagesLesson 1 - Laws of MotionGianina De LeonPas encore d'évaluation
- Definitions - Topic 4 Mechanics and Materials - AQA Physics A-LevelDocument3 pagesDefinitions - Topic 4 Mechanics and Materials - AQA Physics A-LevelLaud FumhandaPas encore d'évaluation
- FORCE and MOTIONDocument3 pagesFORCE and MOTIONKristineMaeFernandezCarmeloPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics in Life Science: Force and Motion: Newton's LawsDocument40 pagesPhysics in Life Science: Force and Motion: Newton's LawssosatukiPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics ch-1.5 (Forces and Motion)Document3 pagesPhysics ch-1.5 (Forces and Motion)Safiul FaiyazPas encore d'évaluation
- DefinitionsDocument4 pagesDefinitionsmrshiviannaidooPas encore d'évaluation
- Scalar Quantities: Scalars 2. Vector Quantities: Vectors 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9Document2 pagesScalar Quantities: Scalars 2. Vector Quantities: Vectors 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9shayanPas encore d'évaluation
- Newton's First Law of Motion ExplainedDocument16 pagesNewton's First Law of Motion ExplainedJoelle PowePas encore d'évaluation
- ForcesDocument23 pagesForcesNancy Kawilarang100% (1)
- Inertia and Mass Newton's Laws of Motion Linear Momentum and Its Conservation Impulse Work and Energy Principle of Conservation of EnergyDocument39 pagesInertia and Mass Newton's Laws of Motion Linear Momentum and Its Conservation Impulse Work and Energy Principle of Conservation of EnergyZaforPas encore d'évaluation
- Laws of Motion ExplainedDocument44 pagesLaws of Motion Explainedmahsan abbasPas encore d'évaluation
- OCR G484 Definitions (The Newtonian World)Document3 pagesOCR G484 Definitions (The Newtonian World)Ashish ThakkarPas encore d'évaluation
- Contact Forces Action-at-a-Distance ForcesDocument6 pagesContact Forces Action-at-a-Distance ForcesBethlehem CuradaPas encore d'évaluation
- Motion & Forces: Kenneth Lester V. MarquezDocument29 pagesMotion & Forces: Kenneth Lester V. Marquezlachel joy tahinayPas encore d'évaluation
- Rotational Equilibrium and Rotational DynamicsDocument1 pageRotational Equilibrium and Rotational DynamicskaeppjangedPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics DefinitionsDocument15 pagesPhysics DefinitionsprintdaddyPas encore d'évaluation
- Kinematics and DynamicsDocument3 pagesKinematics and DynamicsmuhammadPas encore d'évaluation
- Forms of Energy Mechanical Energy Solar Energy Electrical Energy Chemical Energy Nuclear Energy Thermal Energy Sound Energy Light EnergyDocument7 pagesForms of Energy Mechanical Energy Solar Energy Electrical Energy Chemical Energy Nuclear Energy Thermal Energy Sound Energy Light EnergyAubry Grace PalconitePas encore d'évaluation
- Acceleration Due To Gravity ForcesDocument28 pagesAcceleration Due To Gravity Forcesfelipee20Pas encore d'évaluation
- CP Physics Ms. MorrisonDocument11 pagesCP Physics Ms. MorrisonDwight StephensonPas encore d'évaluation
- Science 8 1Document18 pagesScience 8 1Hannah Leigh CoronelPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 1 ScienceDocument38 pagesWeek 1 ScienceEyphrille UmandapPas encore d'évaluation
- Bandstructure Lab FTUG EdtDocument42 pagesBandstructure Lab FTUG EdtAmol HPas encore d'évaluation
- Earthquake Resistance of Buildings With A First Soft StoreyDocument9 pagesEarthquake Resistance of Buildings With A First Soft StoreyZobair RabbaniPas encore d'évaluation
- (G. - P. - Motulevich) Optical Properties of Metals and Intermolecular InteractionsDocument234 pages(G. - P. - Motulevich) Optical Properties of Metals and Intermolecular Interactions张尚宇Pas encore d'évaluation
- 1.5 LipidsDocument19 pages1.5 Lipidsasifh76543Pas encore d'évaluation
- AP Bio NotesDocument2 pagesAP Bio Notestanu96tpPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemical Bath Deposition: Mark - Deguire@case - EduDocument21 pagesChemical Bath Deposition: Mark - Deguire@case - EduH Cuarto PeñaPas encore d'évaluation
- US8178353 - Method For Determination of Polymer Concentration in Water SystemsDocument15 pagesUS8178353 - Method For Determination of Polymer Concentration in Water SystemsKhanh Nguyen TuanPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Mechanics Hydraulics by Gillesania Chapter 1Document15 pagesFluid Mechanics Hydraulics by Gillesania Chapter 1Mary Grace BitantesPas encore d'évaluation
- Graphic OrganizerDocument3 pagesGraphic OrganizerSahira HerverPas encore d'évaluation
- Stator Tooth On Cogging TorqueDocument8 pagesStator Tooth On Cogging TorqueHoang Hoang LePas encore d'évaluation
- Preventing Generator Damage from Hydrogen MoistureDocument27 pagesPreventing Generator Damage from Hydrogen MoistureIskerPas encore d'évaluation
- download-Physics-A-level-Notes-Edexcel-IAL-Unit-4-Detailed-4.3. Further MechanicsDocument11 pagesdownload-Physics-A-level-Notes-Edexcel-IAL-Unit-4-Detailed-4.3. Further MechanicsTowsif HassanPas encore d'évaluation
- Eddy CurrentDocument9 pagesEddy Currentkrish_cvr2937Pas encore d'évaluation
- PN Junction Fabrication: Co-Ordinator DR Tarun ChaudharyDocument43 pagesPN Junction Fabrication: Co-Ordinator DR Tarun ChaudharyBIYYAPU SAI VAMSIPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 15 - Solutions Reading NotesDocument8 pagesChapter 15 - Solutions Reading Notescaffeinewriter100% (1)
- Metco 54NS-1 (Aluminum Seal Coat) PDFDocument3 pagesMetco 54NS-1 (Aluminum Seal Coat) PDFJ. BangjakPas encore d'évaluation
- 41.1.28 AOAC Official Method 969.33 Fatty Acids in Oils and FatsDocument1 page41.1.28 AOAC Official Method 969.33 Fatty Acids in Oils and FatsNguyễn Khang LuânPas encore d'évaluation
- ReportDocument41 pagesReportAli KakiPas encore d'évaluation
- FCJJ-16 Stoichiometry CH TeacherDocument7 pagesFCJJ-16 Stoichiometry CH TeacherHermes Polanco J.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Stability Indicating RP HPLC Method Development and Validation of Everolimus in Bulk and Pharmaceutical Dosage FormDocument9 pagesStability Indicating RP HPLC Method Development and Validation of Everolimus in Bulk and Pharmaceutical Dosage FormEditor IJTSRDPas encore d'évaluation
- NexSys® GEN1 Battery Installation, Operation and MaintenanceDocument4 pagesNexSys® GEN1 Battery Installation, Operation and MaintenanceEquipos CDCPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit IIDocument38 pagesUnit IIMugilPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 2 Version 1 EEE 471 Switchgear and Protection - NMKHANDocument12 pagesLecture 2 Version 1 EEE 471 Switchgear and Protection - NMKHANMortuzaPas encore d'évaluation
- GRAPHITEDocument1 pageGRAPHITEimpetuskolPas encore d'évaluation
- Diffusion and OsmosisDocument4 pagesDiffusion and OsmosisdetPas encore d'évaluation
- Atomic Particles: An Introduction to Water ReactorsDocument7 pagesAtomic Particles: An Introduction to Water ReactorsHamid OuchaghouiPas encore d'évaluation
- PAG 10.3 - Comparison of Methods of Determining Spring StiffnessDocument5 pagesPAG 10.3 - Comparison of Methods of Determining Spring StiffnessjmsonlPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2: Properties of Hydraulic Fluids Example 2.3Document13 pagesChapter 2: Properties of Hydraulic Fluids Example 2.3currjekPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction to Food Science and TechnologyDocument19 pagesIntroduction to Food Science and TechnologyAisha DollPas encore d'évaluation