Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Max16820 24v Hb-Led PWM 1-10v Dimming
Transféré par
Ovidiu FratuDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Max16820 24v Hb-Led PWM 1-10v Dimming
Transféré par
Ovidiu FratuDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
High-brightness LEDs (HBLEDs) are making inroads into more traditional lighting applications that include a dc distribution system
(for example, !-" #$-%& track lights) . HBLEDs are more efficient, and they have a potentially longer lifespan than do halogen or xenon lamps. Because hysteretic controllers are inexpensive, simplify lighting designs, and require no compensation networks, they re well!suited for driving HBLEDs. Hysteretic controllers usually have a pulsewidth! modulator "#$%& input that ena'les a pulse train of varying duty cycle to provide the dimming function. (ne pro'lem, however, in converting a traditional lighting system is that many dimmers provide a )! to )*!+ dc signal rather than a #$% signal. ,lso, to increase the HBLEDs operating lifetimes, a controller should provide temperature'ased current fold'ack. -onverting a dc voltage to a #$% signal is easy. .he #$% signal appears at the output of a comparator when you apply the dc voltage at one input and a triangle wave at the other. Headaches can arise, however, when trying to align the triangle wave with the control voltage. /ou need a linear relationship 'etween duty cycle and control voltage, with a *0 duty cycle at the minimum control voltage and a )**0 duty cycle at the maximum.
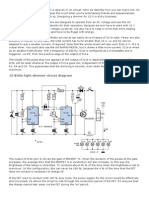
.he circuit in 1igure ) includes the hysteretic controller, 2) "%,3)456*&7 related power components7 and a control circuit 'ased on a quad op amp, 26 "L%3869&. 2) drives five HBLEDs from a 69!+ source, using only inductor L),
%(:1E. ;), and catch diode D). , sense resistor "<)& sets the current to *.= ,. 2) turns ;) on whenever the current! sense voltage drops 'elow )>* m+ and turns ;) off when that voltage exceeds 6)* m+. Hysteretic controllers have no clock and require no external compensation. 2) also provides a regulated = + to power the #$% conversion circuitry. 1igure 6 illustrates the currentsense waveform corresponding to a small ?(@A time in the #$% signal. .he difficulty in converting a control voltage to a #$% signal involves setting the triangle wave s peak and valley voltages to closely match the corresponding maximum and minimum values of the control voltage "+ -@.L&. .wo of 26 s op amps generate the triangle wave, which oscillates 'etween an upper voltage level set 'y the <B!<5 divider and a lower voltage level set 'y the divider formed 'y <B and <5 in parallel with <>. 26 s output is a =*0 duty cycle, rail!to! rail square wave. :etting 26'C equal to +--D6 causes 26' s output to integrate the square wave, producing a symmetrical and linear triangle wave. <)* and -9 set the operating frequency. ,chieving * + at the valley of the triangle wave is difficult, 'ecause 26' s output has a worst!case minimum of 4* m+. $e therefore chose a valley of 6=* m+ and a peak of 6 +. Because +-@.L ranges from * to )* +, <)6!<)8 divides +-@.L 'y =. .his limits the reduced control voltage, +<ED, to 6.* + and there'y matches the triangle wave s peak voltage. 26d creates the #$% pulse train 'y comparing the triangle wave to + <ED. .he triangle!wave valley is 6=* m+, so the #$% signal remains at *0 until +-@.L reaches ).6= +. .his action causes a small offset error that s most pronounced at low values of +-@.L, 'ut it also confers an advantage 'y guaranteeing an (11 position. 1igure 8 shows how the triangle wave converts the divided control voltage into a pulse!width!modulated waveform. (p!amp 26c provides the temperature!'ased current fold'ack. .he <9!<=!<4 divider delivers ).= + to 26c s noninverting input, which is almost a diode drop 'elow the triangle wave s peak "6 +&. .hermistor <6 "a resistor with negative temperature coefficient& is nominally )** kE at 6=F-, 'ut its value declines to 88 kE at =*F-. ,t that temperature the <6!<8 divider produces ).= +Ga 'alance point at which 26c s positive, negative, and output terminals are all at ).= +, and Hust a'out to pull +<ED lower, via D6. ,t B*F-, <6 drops to )=.= kE and the op!amp output drops to ).* +, pulling +<ED to a'out ).4 +. .his action achieves the desired current fold'ack 'y limiting the maximum duty cycle at B*F- to 5*0. , simple change of resistor values allows the circuit to accept different +-@.L ranges and to have different temperature! fold'ack characteristics.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1D'EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Évaluation : 2.5 sur 5 étoiles2.5/5 (3)
- Simulation and Experimental Results of 7-Level Inverter SystemDocument8 pagesSimulation and Experimental Results of 7-Level Inverter Systembacuoc.nguyen356Pas encore d'évaluation
- HV Circuits Nut N BoltsDocument14 pagesHV Circuits Nut N Boltsamit281276Pas encore d'évaluation
- Spice Model Laser Diode 15diDocument8 pagesSpice Model Laser Diode 15diParker333100% (1)
- Ee 328 Lecture 11Document55 pagesEe 328 Lecture 11somethingfornowPas encore d'évaluation
- A Very High Frequency DC-DC Converter Based On A Class Pfi Resonant InverterDocument10 pagesA Very High Frequency DC-DC Converter Based On A Class Pfi Resonant InvertererdemsecenPas encore d'évaluation
- Güç Elektroniği Dersi Güç Yarıiletkenleri Ile Prtik Devre ÖrnekleriDocument21 pagesGüç Elektroniği Dersi Güç Yarıiletkenleri Ile Prtik Devre ÖrnekleriKutay ÇetinPas encore d'évaluation
- IC Questions With Ans AnilsirDocument22 pagesIC Questions With Ans AnilsirAniil J Kumaar50% (2)
- The International Conference On Renewable Energies: "ICRE-2010"Document30 pagesThe International Conference On Renewable Energies: "ICRE-2010"M VetriselviPas encore d'évaluation
- Resonant DC Link InvertersDocument6 pagesResonant DC Link InvertersSanchit AgarwalPas encore d'évaluation
- Learn How A Variety Voltage Integrated Circuits and Them: To BuildDocument6 pagesLearn How A Variety Voltage Integrated Circuits and Them: To BuildSudheesh Puthanpurayil100% (1)
- Power Supply Linear RegulatorDocument11 pagesPower Supply Linear RegulatorSurbhi100% (1)
- DiDocument6 pagesDipani256Pas encore d'évaluation
- Study and Design, Simulation of PWM Based Buck Converter For Low Power ApplicationDocument17 pagesStudy and Design, Simulation of PWM Based Buck Converter For Low Power ApplicationIOSRjournalPas encore d'évaluation
- STEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10D'EverandSTEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10Pas encore d'évaluation
- DC Voltage Converter Circuits: Ray MarstonDocument6 pagesDC Voltage Converter Circuits: Ray MarstonManuel BarriosPas encore d'évaluation
- Filters and Regulation For Power SupplyDocument3 pagesFilters and Regulation For Power SupplySunghoonie KangPas encore d'évaluation
- BS 7671 Voltage DropDocument4 pagesBS 7671 Voltage DropMohammed AbdulmuqeetPas encore d'évaluation
- AC Circuits: What's The Difference Between A.C. and D.C.? Transformers Rectifiers Capacitors ResonanceDocument12 pagesAC Circuits: What's The Difference Between A.C. and D.C.? Transformers Rectifiers Capacitors ResonanceamirhazwanPas encore d'évaluation
- Automotive LED Buck ConverterDocument3 pagesAutomotive LED Buck Converternacional007100% (1)
- Buck Converter AnalysisDocument4 pagesBuck Converter AnalysisJan Rafael EusebioPas encore d'évaluation
- Pdemarco 4Document4 pagesPdemarco 4Paul DeMarcoPas encore d'évaluation
- Power Supply NotesDocument48 pagesPower Supply NotespugazhendiraPas encore d'évaluation
- ELEC3300 Lesson 1 Analogue Circuit Design: Revision Date: 31/07/13Document6 pagesELEC3300 Lesson 1 Analogue Circuit Design: Revision Date: 31/07/13HrishiPrasoonPas encore d'évaluation
- Public A CaoDocument23 pagesPublic A CaoShaheer DurraniPas encore d'évaluation
- ADC BasicsDocument12 pagesADC Basicsapi-26100966Pas encore d'évaluation
- CUK ConverterDocument4 pagesCUK Converterranjitheee1292Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lab Week 3 EE462L Diode Bridge Rectifier PDFDocument18 pagesLab Week 3 EE462L Diode Bridge Rectifier PDFFrew FrewPas encore d'évaluation
- AC Equivalent Circuit ModelingDocument65 pagesAC Equivalent Circuit Modelinghey_gluppyPas encore d'évaluation
- DC-DC ConverterDocument24 pagesDC-DC ConverterkandularanjithPas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding Output Voltage Limitations of DC/DC Buck ConvertersDocument4 pagesUnderstanding Output Voltage Limitations of DC/DC Buck ConvertersLatif KurniaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ust8Lab: &" .RR, R T,.t,. S,/. !, L/, D-GR . T F F,"',4i18' - #+..Document5 pagesUst8Lab: &" .RR, R T,.t,. S,/. !, L/, D-GR . T F F,"',4i18' - #+..GiancarloRichardRivadeneyraMirandaPas encore d'évaluation
- Total Harmonics Distortion Investigation in Multilevel InvertersDocument8 pagesTotal Harmonics Distortion Investigation in Multilevel InvertersAJER JOURNALPas encore d'évaluation
- Ec1355 Esd EceDocument31 pagesEc1355 Esd EceSenthil KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- DC DC Design GuideDocument23 pagesDC DC Design Guidehammouche_soufianePas encore d'évaluation
- Analog To Digital Converter and Vise VersDocument7 pagesAnalog To Digital Converter and Vise VersSpyx MeniPas encore d'évaluation
- Power Supply Unit DesignDocument37 pagesPower Supply Unit DesignfamtaluPas encore d'évaluation
- Three-Phase Rectifier Using A Sepic DC-DC Converter in Continuous Conduction Mode For Power Factor CorrectionDocument7 pagesThree-Phase Rectifier Using A Sepic DC-DC Converter in Continuous Conduction Mode For Power Factor CorrectionuakragunathanPas encore d'évaluation
- Full Wave RectifierDocument6 pagesFull Wave RectifierSrinath ArsPas encore d'évaluation
- Resonant DC Link in PWM AC ChopperDocument5 pagesResonant DC Link in PWM AC ChopperMukesh SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Analysis of 12 Pulse Phase Control AC DC ConverterDocument10 pagesAnalysis of 12 Pulse Phase Control AC DC ConverterRizky Patra JayaPas encore d'évaluation
- Switched-Capaci T 6 - D C Converter Inrush Current and LowDocument7 pagesSwitched-Capaci T 6 - D C Converter Inrush Current and LowHamid BoualiPas encore d'évaluation
- Varistor Calculations (ID 16263)Document8 pagesVaristor Calculations (ID 16263)bspassov6Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ieee Current ModeDocument7 pagesIeee Current ModepqqpPas encore d'évaluation
- An Analysis and Survey of Multilevel Inverters Topologies, Controls, and ApplicationsDocument10 pagesAn Analysis and Survey of Multilevel Inverters Topologies, Controls, and ApplicationsDr-Ismayil CPas encore d'évaluation
- High Voltage DCDocument11 pagesHigh Voltage DCshanbel ayayuPas encore d'évaluation
- EDN Design Ideas 2000Document215 pagesEDN Design Ideas 2000chag1956100% (3)
- Assignment 01Document6 pagesAssignment 01Z S PlaysPas encore d'évaluation
- An725 MaximDocument9 pagesAn725 MaximJavierPas encore d'évaluation
- ReportDocument83 pagesReportNikita SaxenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Digital Simulation of ZVS DC To DC Converter Using Simulink: AbstractDocument13 pagesDigital Simulation of ZVS DC To DC Converter Using Simulink: AbstractAshok KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Of Loop AC: Design Feedback in Unity Power Factor To DC ConverterDocument9 pagesOf Loop AC: Design Feedback in Unity Power Factor To DC ConverterEjaz AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Compensation Method Peak Current Mode Control Buck AN028 enDocument13 pagesCompensation Method Peak Current Mode Control Buck AN028 ensadqazwsxPas encore d'évaluation
- A Comparison of Voltage-Mode Soft-Switching Methods For PWM ConvertersDocument10 pagesA Comparison of Voltage-Mode Soft-Switching Methods For PWM ConvertersAshish BhardwajPas encore d'évaluation
- High Speed, Low Power Current Comparators With Hysteresis: Neeraj K. ChastaDocument12 pagesHigh Speed, Low Power Current Comparators With Hysteresis: Neeraj K. ChastanengsintanovitaPas encore d'évaluation
- AND8241/D A 5.0 V/2.0 A Standby Power Supply For INTEL Compliant ATX ApplicationsDocument16 pagesAND8241/D A 5.0 V/2.0 A Standby Power Supply For INTEL Compliant ATX ApplicationsJonatan LunaPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment 4Document10 pagesExperiment 4djelbouPas encore d'évaluation
- High Efficiency DC-to-AC Power Inverter With Special DC InterfaceDocument6 pagesHigh Efficiency DC-to-AC Power Inverter With Special DC InterfacestrahinjaPas encore d'évaluation
- 2stage VSIDocument6 pages2stage VSIhismarchePas encore d'évaluation
- 060105-UK Water DescalerDocument1 page060105-UK Water DescalerOvidiu FratuPas encore d'évaluation
- A Light Dimmer Is Quite UnusualDocument2 pagesA Light Dimmer Is Quite UnusualOvidiu FratuPas encore d'évaluation
- Moray SecretDocument13 pagesMoray SecretOvidiu FratuPas encore d'évaluation
- Classic Das Ugly Stik Jason Niemier Ws-65 Glow 45-60Document1 pageClassic Das Ugly Stik Jason Niemier Ws-65 Glow 45-60Ovidiu FratuPas encore d'évaluation
- BITT Bitoroid Transformer CA2594905A1Document13 pagesBITT Bitoroid Transformer CA2594905A1Ovidiu FratuPas encore d'évaluation
- Patus6015476 TPUDocument30 pagesPatus6015476 TPUOvidiu FratuPas encore d'évaluation
- Overview of Myanmar-English Machine Translation System - NICTDocument29 pagesOverview of Myanmar-English Machine Translation System - NICTLion CouplePas encore d'évaluation
- YaRrr BookDocument247 pagesYaRrr BookBaalaji RavichandranPas encore d'évaluation
- Current Sensor - LTSR 15-NPDocument3 pagesCurrent Sensor - LTSR 15-NPFadhil Tresna NugrahaPas encore d'évaluation
- 2011 Goupil, P. AIRBUS State of The Art and Practices On FDI and FTC in FCSDocument16 pages2011 Goupil, P. AIRBUS State of The Art and Practices On FDI and FTC in FCScmpmarinhoPas encore d'évaluation
- MclustDocument57 pagesMclustfilip_nenadicPas encore d'évaluation
- Comandos de AutocadDocument23 pagesComandos de AutocadMartim Tavara AguileraPas encore d'évaluation
- Epicor ERP Inventory Transactions Technical Reference GuideDocument88 pagesEpicor ERP Inventory Transactions Technical Reference GuideVMRO100% (1)
- Latitude 9p0 Datasheet USDocument2 pagesLatitude 9p0 Datasheet USGuillermo IbarraPas encore d'évaluation
- Native InstallDocument64 pagesNative InstallSanthosh KrishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- Solutions To Selected Problems-Duda, HartDocument12 pagesSolutions To Selected Problems-Duda, HartTiep VuHuu67% (3)
- Information Sciences: Decui Liang, Bochun YiDocument18 pagesInformation Sciences: Decui Liang, Bochun YiRico Bayu WiranataPas encore d'évaluation
- Concept 2 Rowing D1 Users ManualDocument32 pagesConcept 2 Rowing D1 Users Manualmaestrokui100% (2)
- Smith 1997Document5 pagesSmith 1997Lucas SantosPas encore d'évaluation
- PVCMC 0296 Us - tcm106 35825Document233 pagesPVCMC 0296 Us - tcm106 35825enrique.riera7693Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cloud Native AttitudeDocument28 pagesCloud Native AttitudeRaghu VeerPas encore d'évaluation
- VTAM 4R2 Early User ExperiencesDocument248 pagesVTAM 4R2 Early User Experiencesgborja8881331Pas encore d'évaluation
- MECHANICAL - Muhammad Shafiq Bin Roslan - 0139724098Document3 pagesMECHANICAL - Muhammad Shafiq Bin Roslan - 0139724098philljohnPas encore d'évaluation
- Ad Guard DNSDocument867 pagesAd Guard DNSDaniel RafaelPas encore d'évaluation
- The Importance of Marc in Information Retrieval and StorageDocument16 pagesThe Importance of Marc in Information Retrieval and StorageSiti Nabila Zawawi100% (5)
- Laptop Fault BookDocument38 pagesLaptop Fault Bookredsky991100% (1)
- Week4 SoundDocument34 pagesWeek4 SoundCNTT - 7C-18 Nguyễn Minh ThảoPas encore d'évaluation
- Dd306 ManualDocument20 pagesDd306 Manualtiendat202Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 02 SlidesDocument57 pagesChapter 02 SlidesZahraa AlQallafPas encore d'évaluation
- MELSEC Q Series: Multiple CPU SystemDocument268 pagesMELSEC Q Series: Multiple CPU Systemajma86Pas encore d'évaluation
- DBC 1550nm EdfaDocument3 pagesDBC 1550nm EdfasonyPas encore d'évaluation
- Queue Unit3Document29 pagesQueue Unit3sinsinwarnavneet21391Pas encore d'évaluation
- GIGABYTE GA-H81M-DS2 Mainboard ManualDocument32 pagesGIGABYTE GA-H81M-DS2 Mainboard Manualcr33pz1llaPas encore d'évaluation
- ShockLog Essentials v10 4Document79 pagesShockLog Essentials v10 4William Rubio AvilaPas encore d'évaluation
- HB-2048-001 1099590 QIAgility Unpacking and Installation GuideDocument4 pagesHB-2048-001 1099590 QIAgility Unpacking and Installation GuideSHOBHAPas encore d'évaluation
- 15 SO2 Curs-06 Kernel DebuggingDocument39 pages15 SO2 Curs-06 Kernel DebuggingAlla MstislavPas encore d'évaluation