Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Craniotomy
Transféré par
Prita ParadityaDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Craniotomy
Transféré par
Prita ParadityaDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Craniotomy
Summary
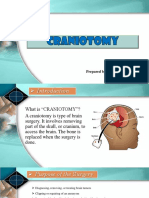
A craniotomy is an operation to open the skull (cranium) in order to access the brain for surgical repair. Conditions that require craniotomy and surgical repair include brain cancers, infections, abscesses, cerebral oedema (swelling of the brain) and bleeding within the skull. Share this article
Email this article Add link to social media acebook, !yspace, "witter #ownload this article
$# te%t & pictures for sharing & sa'ing
(ike any other part of the body, the brain is susceptible to bleeding, infection, trauma and other forms of damage. "his damage or alteration in brain function sometimes requires brain surgery to diagnose or treat these problems. A craniotomy is an operation to open the skull (cranium) in order to access the brain for surgical repair. "here are many different types of brain surgery, but the reco'ery process following craniotomy is much the same in most cases.
Conditions requiring a craniotomy
Some of the conditions that require craniotomy and surgical repair include) *rain cancers +nfections
Abscesses Cerebral oedema (swelling of the brain) *leeding within the skull.
Medical issues to consider
+f left untreated, any condition requiring brain surgery can cause further damage to the brain. $ressure on the brain can be harmful as it forces the brain against the skull, causing damage as
well as hampering the brain,s ability to function properly. "his drop in function can lead to longlasting brain damage or e'en death.
Procedure for a craniotomy
"he general procedure for craniotomy includes the following steps. "he hair on your scalp is sha'ed. .ou are gi'en a general anaesthetic.
.our head is placed on a round or horseshoe-shaped headrest so that the area where the brain in/ury is thought to lie is easily accessible. +f head mo'ement must be minimised, your head is clamped into place with a head pin fi%ing de'ice. "hrough preoperati'e imaging, the neurosurgeon determines the most appropriate site for the craniotomy. "he procedure begins by first cutting through the scalp. Small holes (burr holes) are drilled into the e%posed skull with an instrument called a perforator. An instrument called a craniotome is used to cut from one burr hole to the ne%t, creating a remo'able bone flap. "he membrane co'ering the brain is opened, usually as a flap. "he brain in/ury or disease is operated on 0 for e%ample, ruptured blood 'essels are repaired, or the blood clot or tumour is remo'ed. After the operation is finished, the piece of e%cised bone is replaced, the muscle and skin are stitched up and a drain is placed inside the brain to remo'e any e%cess blood left from the surgery. A craniotomy can take about two and a half hours.
Immediately after a craniotomy
After the operation, you can e%pect the following. .ou are monitored closely by hospital staff, probably in intensi'e care. "he breathing tube will remain in place until you ha'e fully reco'ered from the anaesthetic.
.our head is ele'ated to about 12 degrees to reduce the risk of intracranial (inside the skull) pressure. "he wound is co'ered with a soft dressing. .ou are gi'en pain medication as prescribed.
"he neurosurgeon tests regularly for any signs of brain damage 0 for e%ample, they may e%amine your pupils with a flashlight or ask you simple questions. .our eyes may be swollen and bruised. #epending on the type of brain surgery you had, you will need to take medications. Steroid medication (to control swelling) and anticon'ulsant medication (to pre'ent sei3ures) are commonly prescribed following craniotomy. .ou can e%pect to stay in hospital for between fi'e days and two weeks. "he length of stay depends on many factors, such as the type of surgery you had and whether or not you e%perienced complications or required further operations. Stitches (or staples) are usually remo'ed about one week after surgery.
Complications from a craniotomy
Some of the possible complications of surgery can include) Allergic reaction to the anaesthetic +n/ury from the head pin fi%ing de'ice
+n/ury to facial muscle +n/ury to the sinuses +nfection of the bone flap Sei3ures *leeding *rain damage *rain swelling Stroke.
Taking care of yourself at home
*e guided by your doctor, but general suggestions include) +f your doctor has prescribed medicines, make sure you take them strictly as directed. Alcohol could interact with your medications, so check with your doctor.
"here may be a depression in your skull where the bone flap was remo'ed. .our wound may ache for a few days after the operation. .ou may e%perience itching as the skin heals.
.ou may e%perience headaches for about two weeks. .our wound may ha'e a small pocket of fluid beneath it for a while. "his is normal and should disappear with time. "he skin on one side of your wound may feel numb for some months. E%pect to feel unusually tired 0 afternoon naps may help. .ou may return to work (for light duties only) after about si% weeks. 4eep in mind that you may ha'e to wait about three months before you can dri'e your car again. 5alking is a recommended form of e%ercise. .ou should wait at least three months before you return to gentle, non-contact sporting acti'ities. Contact sports should be a'oided for at least one year. $hysiotherapy, occupational therapy and speech therapy can help you manage any neurological problems like clumsiness and speech problems. 6sually, therapy is only needed if there were neurological problems before surgery. See your doctor immediately if you e%perience any signs of wound infection (such as redness or discharge), or if you ha'e any other unusual symptoms such as se'ere headache, sei3ures, 'omiting, confusion or chest pain.
Long-term outlook
.our reco'ery depends on 'arious factors, including) "he kind of brain in/ury you had 7ow se'ere the in/ury was
Complications of the in/ury "he presence or absence of neurological problems "he type of surgery you had Complications of the surgery Side effects or complications of postoperati'e treatments, such as radiotherapy .our age and general health, including other medical conditions you may ha'e.
Other forms of treatment
*rain surgery is generally the first line of treatment for brain in/uries and conditions. 7owe'er,
other forms of treatment may include, for e%ample, radiation therapy and chemotherapy in the case of brain cancer.
Where to get help
.our doctor 8eurologist 8eurosurgeon +n an emergency, always call triple 3ero (222)
Things to remem er
A craniotomy is an operation to open the skull (cranium) in order to access the brain for surgical repair. "here are many different types of brain surgery, but the reco'ery process following craniotomy is much the same. 9eco'ery depends on many factors, including the type and se'erity of brain in/ury, the type of surgery and whether or not there were neurological deficits before surgery.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Craniotomy: Brain Tumors Aneurysms AvmsDocument5 pagesCraniotomy: Brain Tumors Aneurysms AvmsMichael Cody SoPas encore d'évaluation
- CraniotomyDocument8 pagesCraniotomySyed AbudaheerPas encore d'évaluation
- Craniotomy Case ReportDocument19 pagesCraniotomy Case ReportElizar MercadoPas encore d'évaluation
- CraniotomyDocument9 pagesCraniotomyandrea_zolayvarPas encore d'évaluation
- CraniotomyDocument10 pagesCraniotomyUzma KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- CraniotomyDocument6 pagesCraniotomychaSephPas encore d'évaluation
- Craniotomy or CraniectomyDocument14 pagesCraniotomy or CraniectomyEssaj Rosanat100% (2)
- Mastectomy (Case Analysis)Document7 pagesMastectomy (Case Analysis)Lester_Ocuaman_2248Pas encore d'évaluation
- Spinal Cord Injury Case Study (Nursing History)Document5 pagesSpinal Cord Injury Case Study (Nursing History)TobiDaPas encore d'évaluation
- GRP 20 Final Abscess Case StudyDocument14 pagesGRP 20 Final Abscess Case StudyBorja, Kimberly GracePas encore d'évaluation
- AcromegalyDocument24 pagesAcromegalycsngiuPas encore d'évaluation
- Guide to Head Injury: Signs, Symptoms, Diagnosis and ManagementDocument76 pagesGuide to Head Injury: Signs, Symptoms, Diagnosis and ManagementWafa Nabilah KamalPas encore d'évaluation
- Femoral Shaft Fracture Treatment OptionsDocument55 pagesFemoral Shaft Fracture Treatment OptionsFadliArifPas encore d'évaluation
- A Case Study ON Cerebrovascular Accident With Left HemiparesisDocument57 pagesA Case Study ON Cerebrovascular Accident With Left Hemiparesisdonheyzz_020% (1)
- ICU Case Study PDFDocument19 pagesICU Case Study PDFYashvi SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Common Surgical Procedures TerminologyDocument10 pagesCommon Surgical Procedures TerminologySara Tongcua TacsagonPas encore d'évaluation
- Rabies: A Deadly but Preventable Viral DiseaseDocument9 pagesRabies: A Deadly but Preventable Viral DiseaseBijay Kumar MahatoPas encore d'évaluation
- EPIGLOTTITISDocument9 pagesEPIGLOTTITISanon_944507650Pas encore d'évaluation
- Spinal Cord Injury: Mrs. Zaida ZaracenaDocument36 pagesSpinal Cord Injury: Mrs. Zaida ZaracenaArdhel LoslosoPas encore d'évaluation
- Craniotomy Surgical Case ReportDocument54 pagesCraniotomy Surgical Case ReportTep BinwagPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute PancreatitisDocument7 pagesAcute PancreatitisVytheeshwaran Vedagiri100% (9)
- Laparoscopic Appendectomy SurgeryDocument2 pagesLaparoscopic Appendectomy SurgeryNycoPas encore d'évaluation
- Oral Revalida Round 2Document63 pagesOral Revalida Round 2Mercy Anne EcatPas encore d'évaluation
- Open and Closed FractureDocument22 pagesOpen and Closed FractureHesanRajaraniPas encore d'évaluation
- CancerDocument51 pagesCancerapi-385676067% (3)
- Encephalitis PathophysiologyDocument19 pagesEncephalitis PathophysiologyHeron Bayanin80% (5)
- ORIF Radius and Ulna ProcedureDocument7 pagesORIF Radius and Ulna ProcedurealcojonicPas encore d'évaluation
- Spinal Cord InjuryDocument50 pagesSpinal Cord InjuryVINCHRISTINEPas encore d'évaluation
- Cholelithiasis 0232Document118 pagesCholelithiasis 0232Kz LonerPas encore d'évaluation
- Craniotomy Case StudyDocument14 pagesCraniotomy Case StudyHoney Semafranca PlatolonPas encore d'évaluation
- CVDDocument67 pagesCVDRachel PerandoPas encore d'évaluation
- Hemorrhagic StrokeDocument12 pagesHemorrhagic StrokeManggara Surya DharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Neurologic Trauma: Traumatic Brain InjuryDocument18 pagesNeurologic Trauma: Traumatic Brain InjuryPearl Raiza Hadani100% (1)
- CVADocument116 pagesCVAkathy100% (1)
- What Is HyperglycemiaDocument7 pagesWhat Is HyperglycemiaFelisa Lacsamana GregorioPas encore d'évaluation
- Postpartum Urinary RetentionDocument12 pagesPostpartum Urinary RetentionReyhan AnanditaPas encore d'évaluation
- Trigeminal Neuralgia Treatment ExplainedDocument3 pagesTrigeminal Neuralgia Treatment ExplainedKiara PeoplesPas encore d'évaluation
- HydrocephalusDocument72 pagesHydrocephalusZharah RuzPas encore d'évaluation
- Surgical IncisionsDocument43 pagesSurgical IncisionsNatsir YusufPas encore d'évaluation
- Cervical SpondylosisDocument63 pagesCervical SpondylosisAditi Lakhwara Kohli100% (1)
- Cesarean SectionDocument38 pagesCesarean Sectionpat_rick_5Pas encore d'évaluation
- CraniectomyDocument5 pagesCraniectomytabanaoPas encore d'évaluation
- TRACTION LavlyDocument9 pagesTRACTION Lavlylabsky_evol100% (1)
- Cva Case StudyDocument31 pagesCva Case StudyZoe AnnaPas encore d'évaluation
- Subarachnoid Haemorrhage:Pathology, Clinical Features and ManagementDocument48 pagesSubarachnoid Haemorrhage:Pathology, Clinical Features and Managementesene1100% (1)
- Western Mindanao State University College of Nursing Zamboanga CityDocument4 pagesWestern Mindanao State University College of Nursing Zamboanga CityEzra LambartePas encore d'évaluation
- Case Presentation About Spinal Shock SyndromeDocument56 pagesCase Presentation About Spinal Shock SyndromeAstral_edge010100% (1)
- Case StudyDocument27 pagesCase Studyapi-313356122Pas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding Cerebral PalsyDocument4 pagesUnderstanding Cerebral Palsyfaye kim100% (1)
- Case Report Osteogenesis ImperfectaDocument52 pagesCase Report Osteogenesis ImperfectaFedelis Danii PurnawanPas encore d'évaluation
- SCI (Spinal Cord Injury)Document51 pagesSCI (Spinal Cord Injury)Awal AlfitriPas encore d'évaluation
- Rheumatic Fever: Causes, Tests, and Treatment OptionsD'EverandRheumatic Fever: Causes, Tests, and Treatment OptionsPas encore d'évaluation
- Consent CraniotomyDocument9 pagesConsent CraniotomyAbhinav Gupta100% (1)
- Brain surgery risks and recoveryDocument5 pagesBrain surgery risks and recoveryAna May CarpioPas encore d'évaluation
- What is a Craniotomy? Bone Flap Removal ExplainedDocument30 pagesWhat is a Craniotomy? Bone Flap Removal ExplainedYuji TanakaPas encore d'évaluation
- Craniotomy SurgeryDocument40 pagesCraniotomy Surgeryroba shukrePas encore d'évaluation
- Craniotomy: Sundo, Melinda R. BSN 13D/ Grp.32Document3 pagesCraniotomy: Sundo, Melinda R. BSN 13D/ Grp.32Melinda R. SundoPas encore d'évaluation
- Types of Head Injuries and Their SymptomsDocument5 pagesTypes of Head Injuries and Their SymptomsRhomz Zubieta RamirezPas encore d'évaluation
- CRANIOTOMYDocument31 pagesCRANIOTOMYDrVarun KaliaPas encore d'évaluation
- Consent Transsphenoidal SurgeryDocument10 pagesConsent Transsphenoidal SurgeryAbhinav GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Borderline Personality Disorder - 0Document8 pagesBorderline Personality Disorder - 0Vanshla GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- MCCD Training ModuleDocument90 pagesMCCD Training ModuleRohan ShirodkarPas encore d'évaluation
- Emergency Care FormsDocument17 pagesEmergency Care FormsBilal SalamehPas encore d'évaluation
- Respiratory FailureDocument38 pagesRespiratory Failuredrmithil100% (1)
- Managementofimpacted Thirdmolars: William Synan,, Kyle SteinDocument40 pagesManagementofimpacted Thirdmolars: William Synan,, Kyle SteinYsabel GutierrezPas encore d'évaluation
- Streptococcus Pneumoniae: PneumococciDocument1 pageStreptococcus Pneumoniae: Pneumococciridin007Pas encore d'évaluation
- Colon 2014597 D FHTDocument4 pagesColon 2014597 D FHTyoohooPas encore d'évaluation
- Types of StressDocument14 pagesTypes of StressNiharika KhanduriPas encore d'évaluation
- Vestibular Neuritis HandoutDocument3 pagesVestibular Neuritis HandoutPrisilia QurratuAiniPas encore d'évaluation
- Meridian Circuit Systems Course BookDocument109 pagesMeridian Circuit Systems Course Bookraskolnikov20Pas encore d'évaluation
- Prolactinomas: Anne Klibanski, M.D. New England Journal Medicine 1, 2010 I Gusti Ngurah Agung Manik Rucika 04 70 0035Document17 pagesProlactinomas: Anne Klibanski, M.D. New England Journal Medicine 1, 2010 I Gusti Ngurah Agung Manik Rucika 04 70 0035Romdhoni KurniawanPas encore d'évaluation
- Duct Dependent Heart Lesions by DR Parashuram Waddar (Pediatrician, MBBS, DCH DNB)Document63 pagesDuct Dependent Heart Lesions by DR Parashuram Waddar (Pediatrician, MBBS, DCH DNB)parasuram waddarPas encore d'évaluation
- JaundiceDocument36 pagesJaundiceNasser SalahPas encore d'évaluation
- UntitledDocument5 pagesUntitledangel_sagun_1Pas encore d'évaluation
- CH 044 Megaloblastic AnemiaDocument6 pagesCH 044 Megaloblastic AnemiaGshshPas encore d'évaluation
- Corona Virus (Covid - 19) Symptoms and PreventionDocument2 pagesCorona Virus (Covid - 19) Symptoms and PreventionMy_MedilandPas encore d'évaluation
- Kepositifan Induksi Sputum NaCl 3 Dan Teknik BroncDocument7 pagesKepositifan Induksi Sputum NaCl 3 Dan Teknik Broncvovinda rujianaPas encore d'évaluation
- Journal of Internal Medicine - 2023 - Okushin - Ursodeoxycholic Acid For Coronavirus Disease 2019 PreventionDocument4 pagesJournal of Internal Medicine - 2023 - Okushin - Ursodeoxycholic Acid For Coronavirus Disease 2019 PreventionCT DAMPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute Appendicitis Signs, Symptoms, and TreatmentDocument309 pagesAcute Appendicitis Signs, Symptoms, and TreatmentSimina Întuneric100% (1)
- Presention On Diabetes Foot UlcerDocument36 pagesPresention On Diabetes Foot Ulcerjaat channalPas encore d'évaluation
- TURBT and New Methods for Bladder Tumour Visualization and ResectionDocument52 pagesTURBT and New Methods for Bladder Tumour Visualization and ResectionMuhammad RafiPas encore d'évaluation
- Thesis Rodulfo Eye Re (Formation) Integration of Architecture and Vision Therapy For The VisualimpairedDocument69 pagesThesis Rodulfo Eye Re (Formation) Integration of Architecture and Vision Therapy For The VisualimpairedPierre RodulfoPas encore d'évaluation
- A Habituation Approach: To Treating Vertigo in Occupational TherapyDocument3 pagesA Habituation Approach: To Treating Vertigo in Occupational TherapyGrace LPas encore d'évaluation
- Vpe 321Document2 pagesVpe 321ransingh100% (1)
- Presentation 1Document17 pagesPresentation 1api-212423011Pas encore d'évaluation
- What Is Interventional Radiology (Shahbaz Ahmed Qazi)Document51 pagesWhat Is Interventional Radiology (Shahbaz Ahmed Qazi)rihihaPas encore d'évaluation
- HealthallergyDocument11 pagesHealthallergyMary Rose QuimanjanPas encore d'évaluation
- R GCVP V2 2.15Document3 pagesR GCVP V2 2.15GabrielPas encore d'évaluation
- Spinalbifida 121213120324 Phpapp02Document28 pagesSpinalbifida 121213120324 Phpapp02Silvana María Espinoza CuadrosPas encore d'évaluation
- Factors Affecting Pulse RateDocument2 pagesFactors Affecting Pulse RatetmyliergebunnyPas encore d'évaluation