Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
CFD Syllabus
Transféré par
Manish SharmaDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
CFD Syllabus
Transféré par
Manish SharmaDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
FILENAME: SMEC019.
docx
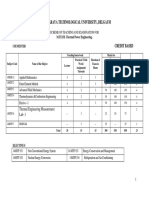
Course number Course Title Credits Contact Hours (L-T-P)
1 2 3 4
MEC019 INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS 4 4-0-0 The objective of this course is to cover a range of modern approaches for numerical and computational fluid dynamics, without entering all these topics in detail, but aiming to provide students with a general knowledge and understanding of the subject, including recommendations for further studies. 1. To identify and visualize the various modes of fluid motion and heat transfer in different practical configurations. 2. Understand the various Finite volume and Finite difference techniques and apply these for CFD problems. 3. Understand basic mathematical/numerical methods needed to fluid dynamics and heat transfer problems involving steady and transient conditions.
Course Objective
6 7 7.01 7.02 7.03 7.04 7.05 7.06 7.07 7.08 7.09 7.10 7.11 7.12 7.13 7.14 7.15 7.16 7.17 7.18 7.19 7.20 8 8.1 8.11 8.12 8.13 8.14
4. Simulate and design the CFD problems using commercial solvers. Course Outcomes 5. Undertake a small independent project and write a professional report and present it. Outline syllabus: MEC019.A Unit A Introduction to Computational Fluid Dynamics and Principles of Conservation MEC019.A1 Unit A Topic 1 Computational Fluid Dynamics: What, When, and Why?, CFD Applications, MEC019.A2 Unit A Topic 2 Governing equations (Mass, Momentum and Energy equation) MEC019.A3 Unit A Topic 3 Classification of various types of PDE. MEC019.B Unit B Finite Difference techniques MEC019.B1 Unit B Topic 1 Initial and Boundary conditions MEC019.B2 Unit B Topic 2 Taylor series approximation MEC019.B3 Unit B Topic 3 Integration over element MEC019.C Unit C Finite Volume Techniques for Convection -Diffusion Problems MEC019.C1 Unit C Topic 1 Steady one dimensional convection and diffusion MEC019.C2 Unit C Topic 2 Central Differencing scheme and its assessment MEC019.C3 Unit C Topic 3 Upwind and hybrid schemes and their assessment MEC019.D Unit D Finite Volume Methods for steady and Un-steady flows MEC019.D1 Unit D Topic 1 Staggered grid and Collocated grid, MEC019.D2 Unit D Topic 2 SIMPLE Algorithm, SIMPLER Algorithm, PISO Algorithm MEC019.D3 Unit D Topic 3 Various Schemes for 1-D heat conduction(CN, Explicit and fully implicit schemes) MEC019.E Unit E Solution of Discretized equations Gauss-Jacobi, Guass-Seidal and Gauss-Elimination for the solution of MEC019.E1 Unit E Topic 1 convection-diffusion problems MEC019.E2 Unit E Topic 2 Application of TDMA Algorithm for 2-Diemsional problems MEC019.E3 Unit E Topic 3 ADI method Course Evaluation Course work: 40% Attendance 10% Homework 4, 15% Quizzes 4, 15% Projects 1, 50%
8.15 Presentations 1, 10% 8.16 Any other 8.2 MTE 1, 20% 8.3 End-term examination: 40% 9 9.1 References Text book An Introduction to Computational Fluid Dynamics The Finite Volume Method, by Versteeg, H.K. and Malalasekera, W.
9.2
other references
J. H. Ferziger and M. Peric, Computational Methods for Fluid Dynamics, Springer. John C. Tannehill, Dale A. Anderson and Richard H. Pletcher, Computational Fluid Mechanics and Heat Transfer, Taylor &Francis. John D. Anderson Jr, Computational Fluid Dynamics, McGraw Hill Book Company. J. Blazek, Computational Fluid Dynamics: S. V. Patankar, Numerical Heat Transfer and Fluid Flow, McGraw-Hill.
Mapping of Outcomes vs. Topics
Outcome no. Syllabus topic
MEC019.A MEC019.A1 MEC019.A2 MEC019.A3 MEC019.B MEC019.B1 MEC019.B2 MEC019.B3 MEC019.C MEC019.C1 MEC019.C2 MEC019.C3 MEC019.D MEC019.D1 MEC019.D2 MEC019.D3 MEC019.E MEC019.E1 MEC019.E2 MEC019.E3
1
X X X X
X X X X X X X X X X X X
X X X X X X X X
X X X X X X X X
X X X X X X X X
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- CFD Ii PDFDocument4 pagesCFD Ii PDFzPas encore d'évaluation
- Computational Fluid Dynamics Course Information: by Dr. A. Nurye Faculty of Mechanical Engineering Nurye@ump - Edu.myDocument8 pagesComputational Fluid Dynamics Course Information: by Dr. A. Nurye Faculty of Mechanical Engineering Nurye@ump - Edu.myeldrainyPas encore d'évaluation
- De ZG515 Course HandoutDocument8 pagesDe ZG515 Course HandoutSaini boyPas encore d'évaluation
- Digital Learning Handout: Course DescriptionDocument8 pagesDigital Learning Handout: Course DescriptionUmesh BhadalePas encore d'évaluation
- DEPAZG515 Computational Fluid Dynamics - HandoutDocument7 pagesDEPAZG515 Computational Fluid Dynamics - HandoutSunil NairPas encore d'évaluation
- ME 450 - Multiscale and Multiphase Computational Fluid Dynamics (Fall 2020)Document3 pagesME 450 - Multiscale and Multiphase Computational Fluid Dynamics (Fall 2020)KhayrulIslamPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermal Design: Heat Sinks, Thermoelectrics, Heat Pipes, Compact Heat Exchangers, and Solar CellsD'EverandThermal Design: Heat Sinks, Thermoelectrics, Heat Pipes, Compact Heat Exchangers, and Solar CellsÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- M.E. Internal Combustion Engineering SyllabusDocument35 pagesM.E. Internal Combustion Engineering SyllabusJoswa CaxtonPas encore d'évaluation
- ME268Document3 pagesME268tennisstarbyfarPas encore d'évaluation
- Computational Fluid Dynamics IDocument3 pagesComputational Fluid Dynamics Iapi-296698256Pas encore d'évaluation
- Module Handbook REMENA 101024 01 PDFDocument31 pagesModule Handbook REMENA 101024 01 PDFBernardo Andrés GilardoniPas encore d'évaluation
- CFD ElectiveDocument2 pagesCFD ElectiveNivethithaa DhanrajPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction to Bond Graphs and their ApplicationsD'EverandIntroduction to Bond Graphs and their ApplicationsÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Multiphase Flow and Fluidization: Continuum and Kinetic Theory DescriptionsD'EverandMultiphase Flow and Fluidization: Continuum and Kinetic Theory DescriptionsÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- BTD-Final Lesson PlanDocument22 pagesBTD-Final Lesson PlanSunil BajantriPas encore d'évaluation
- M.tech Syllabus PDFDocument51 pagesM.tech Syllabus PDFAnonymous MR8PLYPas encore d'évaluation
- PE VI-MEG347A-CFD Syllabus 2020Document5 pagesPE VI-MEG347A-CFD Syllabus 2020Vaibhav AnandPas encore d'évaluation
- CFDDocument2 pagesCFDSumit BhanushaliPas encore d'évaluation
- CFD SyllabusDocument3 pagesCFD SyllabusSelvamuthu KumaranPas encore d'évaluation
- L 2 T 1 P 2 C 4: COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS (MEE405) Proposed SyllabusDocument2 pagesL 2 T 1 P 2 C 4: COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS (MEE405) Proposed SyllabusPriyank AgarwalPas encore d'évaluation
- De ZG515Document8 pagesDe ZG515AnuPas encore d'évaluation
- Name 363 FVMDocument104 pagesName 363 FVMWasi Uddin MahmudPas encore d'évaluation
- Academic Regulations For This Program Is Same As R18 B.Tech. Academic RegulationsDocument27 pagesAcademic Regulations For This Program Is Same As R18 B.Tech. Academic RegulationsManvitha KudikalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Fluid Mechanics Information and IntroductionDocument17 pagesEngineering Fluid Mechanics Information and Introductionmavimu_20Pas encore d'évaluation
- R18B Tech CSE (CyberSecurity) IYearSyllabusDocument27 pagesR18B Tech CSE (CyberSecurity) IYearSyllabus20H51A6248-THEEGALA SAI SHUSHANTH B.Tech CS (2020-24)Pas encore d'évaluation
- 3340 Fall16 SyllabusDocument3 pages3340 Fall16 SyllabusJosePas encore d'évaluation
- Finite Element AnalysisDocument2 pagesFinite Element AnalysisJeevanPas encore d'évaluation
- PHS1019 - Physics For Computer Studies Syllabus Outline-2023Document9 pagesPHS1019 - Physics For Computer Studies Syllabus Outline-2023lavey kellyPas encore d'évaluation
- Mtech Semester 1 2017-19Document11 pagesMtech Semester 1 2017-19api-294538209Pas encore d'évaluation
- IC EngineDocument52 pagesIC EngineShreepal ChilaPas encore d'évaluation
- B.Tech 5th Sem MechanicalDocument10 pagesB.Tech 5th Sem MechanicalRahul KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Mumbai University Me Thermal SyllabusDocument38 pagesMumbai University Me Thermal SyllabusbroninPas encore d'évaluation
- Finite Element Method (Fem)Document3 pagesFinite Element Method (Fem)Manish SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Physical Problem: General Introduction: Historical Background and Spectrum of ApplicationsDocument6 pagesPhysical Problem: General Introduction: Historical Background and Spectrum of ApplicationshetanshuPas encore d'évaluation
- PHS1019 - Module OutlineDocument9 pagesPHS1019 - Module OutlineJaiiPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 6Document3 pagesChapter 6karenPas encore d'évaluation
- ENSC 388 OutlineDocument4 pagesENSC 388 OutlineEnriqueTamayoValenzuelaPas encore d'évaluation
- SSD12103 Review Jan 11 v0Document4 pagesSSD12103 Review Jan 11 v0johnjabarajPas encore d'évaluation
- 6 Computational Fluid DynamicsDocument2 pages6 Computational Fluid DynamicsOvaid MehmoodPas encore d'évaluation
- Me MtechDocument43 pagesMe MtechStanly KurianPas encore d'évaluation
- CSE UNITED CLUB With Navy Bule and NeonDocument36 pagesCSE UNITED CLUB With Navy Bule and NeonHelloword .educationPas encore d'évaluation
- R22B Tech ECEIYearSyllabus1Document33 pagesR22B Tech ECEIYearSyllabus1sgsksjvsgsbjPas encore d'évaluation
- Me III II CF 228pagesDocument227 pagesMe III II CF 228pagesBhargav IppaPas encore d'évaluation
- R22B Tech CSDIYearSyllabus1Document36 pagesR22B Tech CSDIYearSyllabus1MaddyPas encore d'évaluation
- MEng BristolDocument47 pagesMEng BristolvklsPas encore d'évaluation
- Details Online M. Tech. in Computational Fluid Thermal SciencesDocument37 pagesDetails Online M. Tech. in Computational Fluid Thermal SciencesDevlin MukherjeePas encore d'évaluation
- Vit Ece 1st Year SyllabusDocument13 pagesVit Ece 1st Year Syllabuspranavateja12399100% (1)
- B.TECH SECOND YEAR SYLLABUS CHEMICAL ENGINEERING 2022 Batch 20-07-2023 V1Document19 pagesB.TECH SECOND YEAR SYLLABUS CHEMICAL ENGINEERING 2022 Batch 20-07-2023 V1nandanitiwari2004Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fem CoDocument5 pagesFem Comuralict2009Pas encore d'évaluation
- Syllabus With SignatureDocument488 pagesSyllabus With Signaturekvs ptpPas encore d'évaluation
- B.Tech. I Year Syllabus Jntu HyderabadDocument32 pagesB.Tech. I Year Syllabus Jntu Hyderabadkaushik tiwariPas encore d'évaluation
- Heat Equation in One - and Two-Dimensional Systems - Utkstair OrgDocument26 pagesHeat Equation in One - and Two-Dimensional Systems - Utkstair Orgar_frankPas encore d'évaluation
- M.Tech (Full Time) - Chemical Engineering Curriculum & Syllabus 2013 - 2014Document40 pagesM.Tech (Full Time) - Chemical Engineering Curriculum & Syllabus 2013 - 2014hmasif456Pas encore d'évaluation
- R18 B.tech I Year Syllabus of EEE CSE IT UpdatedDocument32 pagesR18 B.tech I Year Syllabus of EEE CSE IT UpdatedKrishna Teja NamuduriPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic For Learning Through Evocation: 2. Topic IntroductionDocument3 pagesTopic For Learning Through Evocation: 2. Topic IntroductionnandhakumarmePas encore d'évaluation
- Mishra Dhatu Nigam Limited: Contract Engagement NoticeDocument1 pageMishra Dhatu Nigam Limited: Contract Engagement NoticeManish SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ) On Strength of Materials - ScholarexpressDocument4 pagesMultiple Choice Questions (MCQ) On Strength of Materials - ScholarexpressManish Sharma100% (1)
- 23.end Sem Question Paper - BMEL-405 2016-17Document2 pages23.end Sem Question Paper - BMEL-405 2016-17Manish SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- 2006 Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University: Answer Any FIVE Questions All Questions Carry Equal MarksDocument1 page2006 Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University: Answer Any FIVE Questions All Questions Carry Equal MarksManish SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- (Official Answer Key's) SSC CGL (Tier - 1) Exam - 2015 - Held On 9-8-2015 - SSC PORTAL - SSC CGL, CHSL, Exams CommunityDocument3 pages(Official Answer Key's) SSC CGL (Tier - 1) Exam - 2015 - Held On 9-8-2015 - SSC PORTAL - SSC CGL, CHSL, Exams CommunityManish SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Mmmut GorakhpurDocument11 pagesMmmut GorakhpurManish SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Strenght of Materials (ES-64)Document353 pagesStrenght of Materials (ES-64)api-3836341100% (14)
- Last Date of Submission:-Thursday, 26 Sep 2013Document1 pageLast Date of Submission:-Thursday, 26 Sep 2013Manish SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- WWW - Iisc.ernet - in OpportunitiesDocument1 pageWWW - Iisc.ernet - in OpportunitiesManish SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- "Application of MATLAB For Engineering Computations": Schedule of AMEC-IIIDocument1 page"Application of MATLAB For Engineering Computations": Schedule of AMEC-IIIManish SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Filename: Smec311Document2 pagesFilename: Smec311Manish SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Finite Element Method (Fem)Document3 pagesFinite Element Method (Fem)Manish SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- 6 Syllabus Form For Combined Theory and Lab CoursesDocument2 pages6 Syllabus Form For Combined Theory and Lab CoursesManish SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment 2: Activities in The Project of Planning A Rural Piped-Water SupplyDocument1 pageAssignment 2: Activities in The Project of Planning A Rural Piped-Water SupplyManish SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Test 2Document2 pagesTest 2Manish SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment 2: Activities in The Project of Planning A Rural Piped-Water SupplyDocument1 pageAssignment 2: Activities in The Project of Planning A Rural Piped-Water SupplyManish SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Exp 4Document1 pageExp 4Manish SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Exp 5Document5 pagesExp 5Manish SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Abaqus CFDDocument11 pagesIntroduction To Abaqus CFDvikingvroPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To CFX-5Document8 pagesIntroduction To CFX-5sangsharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.2 INOGATE - Software For Consequence ModellingDocument25 pages2.2 INOGATE - Software For Consequence ModellingVesko IlijaziPas encore d'évaluation
- Computational Fluid Dynamics Modeling of Cell Cultures in Bioreactors and Its Potential For Cultivated Meat Production - A Mini-ReviewDocument10 pagesComputational Fluid Dynamics Modeling of Cell Cultures in Bioreactors and Its Potential For Cultivated Meat Production - A Mini-ReviewArianna RechPas encore d'évaluation
- Viscous Resistance Coefficients in Porous Medium - CFD Online Discussion ForumsDocument10 pagesViscous Resistance Coefficients in Porous Medium - CFD Online Discussion ForumsmkbPas encore d'évaluation
- Alfandi CVDocument5 pagesAlfandi CVAshraf ZoubiPas encore d'évaluation
- Mesh Motion Alternatives in Openfoam: CFD With Opensource Software, Assignment 3Document31 pagesMesh Motion Alternatives in Openfoam: CFD With Opensource Software, Assignment 3micmacadamPas encore d'évaluation
- Windcatcher Calculations PDFDocument49 pagesWindcatcher Calculations PDFTim KingPas encore d'évaluation
- Paper23109 113Document5 pagesPaper23109 113rogerPas encore d'évaluation
- Analysis of Building Collapse Under Blast LoadDocument26 pagesAnalysis of Building Collapse Under Blast LoadSinan NizarPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluent Nov 2003Document27 pagesFluent Nov 2003Rajesh RameshPas encore d'évaluation
- Best Practice Srs Menter 2015Document75 pagesBest Practice Srs Menter 2015ohpmynPas encore d'évaluation
- Sae Technical Paper Series: A. R. Stockner, M. A. Flinn, and F. A. CamplinDocument18 pagesSae Technical Paper Series: A. R. Stockner, M. A. Flinn, and F. A. CamplinBKOPas encore d'évaluation
- CFDDocument10 pagesCFDThiam Chun Ong100% (1)
- Boundary Element Methods in Nonlinear Fluid Dynamics Developments in Boundary Element Methods - 6 Eur Vol 6Document5 pagesBoundary Element Methods in Nonlinear Fluid Dynamics Developments in Boundary Element Methods - 6 Eur Vol 6Ruly IrawanPas encore d'évaluation
- Bits Catalog PDFDocument87 pagesBits Catalog PDFHarsha ChowdaryPas encore d'évaluation
- Smoke - Control ICB Handout PDFDocument42 pagesSmoke - Control ICB Handout PDF185412Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ngo Et Al. - 2018 - Prediction of Degree of Impregnation in Thermoplastic Unidirectional Carbon Fiber Prepreg by Multi-Scale ComputationDocument12 pagesNgo Et Al. - 2018 - Prediction of Degree of Impregnation in Thermoplastic Unidirectional Carbon Fiber Prepreg by Multi-Scale ComputationNgô Ích SơnPas encore d'évaluation
- CFD Exams SolutionDocument12 pagesCFD Exams SolutionPythonraptorPas encore d'évaluation
- R05410306 Computational Fluid DynamicsDocument4 pagesR05410306 Computational Fluid DynamicsHARSHITHPas encore d'évaluation
- 03 Sname Integrated Simulation System For PropellerDocument16 pages03 Sname Integrated Simulation System For PropellerJ T Mendonça SantosPas encore d'évaluation
- Om Prakash: Work Experience Term PapersDocument1 pageOm Prakash: Work Experience Term PapersOmPas encore d'évaluation
- Optimization of Wing Rib Configurations For Improved Aerodynamic Performance A Computational StudyDocument12 pagesOptimization of Wing Rib Configurations For Improved Aerodynamic Performance A Computational StudyIJRASETPublicationsPas encore d'évaluation
- SPE/IADC-190008-MS Advancing The Mud Gas Separator Sizing Calculation: The MPD PerspectiveDocument11 pagesSPE/IADC-190008-MS Advancing The Mud Gas Separator Sizing Calculation: The MPD PerspectiveDiego AraquePas encore d'évaluation
- Determination of K-Factors of HVAC System Components Using Measurement and CFD ModellingDocument285 pagesDetermination of K-Factors of HVAC System Components Using Measurement and CFD ModellingMaxcine ShuPas encore d'évaluation
- Tesi Giada AbateDocument100 pagesTesi Giada AbateEslam NagyPas encore d'évaluation
- Neftalí Rojas - Tega - Pulp LifterDocument24 pagesNeftalí Rojas - Tega - Pulp LiftereduardoslmPas encore d'évaluation
- Paper 39 Lawrence (Flow Measurement)Document15 pagesPaper 39 Lawrence (Flow Measurement)Philip A Lawrence C.Eng. F. Inst M.C.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Prediction of Ingestion Through Turbine Rim Seals-Part II, Externally Induced and Combined IngressDocument9 pagesPrediction of Ingestion Through Turbine Rim Seals-Part II, Externally Induced and Combined IngressAmin ZoljanahiPas encore d'évaluation
- Energies 12 01988Document15 pagesEnergies 12 01988Nadjib GioPas encore d'évaluation