Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Prob Dinamica Noviembre 2013
Transféré par
Guillermo Aguilar HernandesCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Prob Dinamica Noviembre 2013
Transféré par
Guillermo Aguilar HernandesDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Evaluacin del Problemario
ESTUDIANTE:______________________________________
GRUPO:_____MATRICULA:________________29 de Noviembre 2013
1. Cules son las tres partes elementales de un sistema vibratorio?
2. Defina el concepto de grado de libertad de un sistema.
3. Cul es la diferencia entre un sistema libre y un sistema forzado?
4. Mencione los tipos comunes de amortiguamiento.
5. Defina los siguientes trminos: Ciclo, Amplitud, Angulo de fase, Frecuencia, Perodo y
Frecuencia natural.
6. Cmo se pueden relacionar: el perodo, la frecuencia angular y la frecuencia natural?
7. Investiga, al menos, dos nombre de Revistas Internacionales que realicen investigacin
sobre vibraciones mecnicas.
8. Cmo, y por cules frmulas se pueden obtener la amplitud y el ngulo de fase de un
movimiento armnico de un vector rotando?
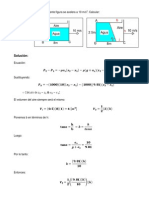
9. De la siguiente figura, encuentre la masa equivalente del sistema balancn con respecto
a la coordenada "X".
10. Encuentre la constante de rigidez equivalente y la masa equivalente mostrada en la
siguiente figura, con respecto al ngulo u, la barra vertical se considera como una
rigidez y no se toma encuentra la densidad del lquido.
11. Una masa de 0.453 Kg. unida a un resorte introduce un alargamiento (deformacin
esttica) de 7.87 mm. Determine la frecuencia natural, el perodo y la frecuencia
circular del sistema.
12. Un sistema con un resorte (k
1
) y una masa (m), tiene una frecuencia natural (f
n1
). Si
se aade un segundo resorte en serie (k
2
), y la frecuencia natural se reduce a 1/2 de
f
n1
. Halle la constante del resorte k
2
en trminos de k
1
.
13. Un volante que pesa 70 libras es soportado como se muestra en la Figura y dejado
oscilar como un pndulo. Si se midi un perodo de oscilacin de 1.22 seg.
Determine el momento de inercia del volante con respecto a su eje geomtrico.
14. Una biela que pesa 21.35 N oscila 53 veces en un minuto cuando se le suspende
como se muestra en la Figura. Halle su momento de inercia con respecto a su centro
de gravedad, localizado a 0.254 m del punto del soporte.
15. Determine la constante de rigidez torsional equivalente del eje que se presenta en la
Figura y calcule su perodo.
16. Obtenga la ecuacin de movimiento para cada una de las siguientes Figuras. Tenga
en cuenta las fuerzas de los resortes, la masa y la fuerza de gravedad.
17. Un motor elctrico es soportado por cuatro resortes, cada resorte tiene una constante
de rigidez k, como se muestra en la Figura. Si el momento de inercia del motor con
respecto al eje central de rotacin es J
0
. Determine la frecuencia natural de
oscilacin y la frecuencia circular de oscilacin del sistema.
18. Un disco homogneo semicircular de radio (r) y de masa (m) oscila libremente con
respecto a su centro como se muestra en la Figura. Determine su frecuencia natural
de oscilacin y su frecuencia circular de oscilacin para pequeos desplazamientos
angulares.
19. Una varilla uniforme rgida tiene restringido su movimiento en la direccin vertical
por dos resortes lineales y un resorte torsional, como se muestra en la Figura.
Calcule la frecuencia circular y la frecuencia natural de oscilacin en la direccin
vertical de la varilla.
20. Derive the equation of motion and find the stady-state angular oscilation response of
the system shown in figure for rotational motion about the hinge O for the following
data: k = 8000 [N/m], L = 1.5 [m], m = 20 [kg], c = 700 [N seg/m], F
o
= 30 [N] and
=
e
= 500 [rpm]. (40 puntos).
21. If the ground is subjected to a harmonic displacement with frequency 2800 [rpm]
and amplitude is 20 [mm]. Find the amplitude of vibration and the fase angule of
the floor (mass m). Assume the mass of the floor 2500 [kg], the damping constant is
500 [Nseg/m], the flexual stiffness (EI) of 4.5 [MN-m
2
], L = 3 [m]. (30 puntos).
22. An electric motor weighing 750 [lb] and running at 1800 [rpm] is supported on four
steel helical springs, each of which has eight active coils with a wire diameter of
0.25 [in]. and a coil diameter of 3 [in]. The rotor has a weigth of 100 [lb] with its
center of mass located at a distance of 0.01 [in]. from the axis of rotation. Find the
amplitude of vibration of the motor. Assume G = 11800 [lb/pulg
2
] (30 puntos).
23. Determine la ecuacin de movimiento, el perodo y las frecuencias del siguiente
sistema (viga): (20 puntos).
24. Halle la ecuacin de movimiento por el Mtodo de Energa del siguiente sistema,
con respecto al movimiento rotacional u, el momento de inercia de masa (J) pngalo
en funcin de la masa (m). Halle su perodo y sus frecuencias naturales. (25
puntos).
25. The differential equation governing the motion of the system of Fig. is:
t
r
M
kx x c x
r
I
m e sin 5
0
2
= + + |
.
|
\
|
+ Using the given values, determine the steady-state
amplitude of the block.
J ; m
26. An 82-kg machine tool is mounted on an elastic foundation. An experiment is run to
determine the stiffness and damping properties of the foundation. When the tool is
excited with a harmonic force of magnitude 8000N at a variety of frequencies, the
maximum steady-state amplitude obtained is 4.1m at the frequency of 40 Hz. Use
this information to estimate the stiffness and damping ratio of the foundation.
27. A 35-kg electric motor that operates at 60Hz is mounted on an elastic foundation of
stiffness 3 x 10
6
N/m. The phase difference between the excitation and the steady-
state response is 21
o
. What is the damping ratio of the system?
28. A 40-kg fan has a rotating unbalanced of magnitude 0.1 kg-m. The fan is mounted
on the beam of Fig. The beam has been specially treated to add viscous damping.
As the speed of the fan is varied, it is noted that its maximum steady-state amplitude
is 20.3 mm. What is the fan`s steady-state amplitude when it operates at 1000
r/min? (3.19)
29. The tail rotor of the helicopter of Fig. consists of four blades, each of mass 2.3 kg,
and an engine box of mass 28.5 kg. The center of each blade is 170 mm from the
rotational axis. The tail section is connected to the main body of the helicopter by an
elastic structure. The natural frequency of the tail section is observed as 135 rad/s.
During flight, the rotor operates at 900 r/min. What is the vibration amplitude of the
tail section if one of the blades falls off during flight? Assume a damping ratio of
0.05.
30. Una masa de 0,907 [kg] es conectada al extremo de un resorte con una rigidez de
7,0 [N/cm]. Determine el coeficiente de amortiguamiento crtico.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Ejerccicios Unidad 2Document16 pagesEjerccicios Unidad 2Stephany Lopez Rojas0% (2)
- Problema 2.1 VibracionesDocument15 pagesProblema 2.1 VibracionesOmar Alvarez55% (11)
- Problemas Vibraciones ResueltosDocument11 pagesProblemas Vibraciones ResueltosOmar Puga0% (1)
- Deber 2Document8 pagesDeber 2Robin Chiluisa0% (3)
- GuiaDocument12 pagesGuiaMELENDEZ HERNANDEZ MONICA GUADALUPEPas encore d'évaluation
- La gran transformación de PolanyiDocument14 pagesLa gran transformación de PolanyiChiara100% (1)
- Problemas de dinámica de máquinasDocument9 pagesProblemas de dinámica de máquinasSnow Olveryus Bädx Yee0% (1)
- Vibraciones mecánicas ejerciciosDocument3 pagesVibraciones mecánicas ejerciciosUlises OrnelasPas encore d'évaluation
- Ejercicios U3 PDFDocument12 pagesEjercicios U3 PDFPaula DiazPas encore d'évaluation
- Vibraciones mecánicas: ejercicios de un sistema de resorte-masaDocument10 pagesVibraciones mecánicas: ejercicios de un sistema de resorte-masaPatricia Santana0% (1)
- Problemas U1Document6 pagesProblemas U1Patricia WongPas encore d'évaluation
- Problemas TraducidosDocument15 pagesProblemas TraducidosKarolaine De GraciaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ejecicios Dinamica 16-2 PDFDocument11 pagesEjecicios Dinamica 16-2 PDFJerson MartinezPas encore d'évaluation
- Problemario VIBRACIONES MECÁNICASDocument9 pagesProblemario VIBRACIONES MECÁNICASLuis Gerardo Chavez CovarrubiasPas encore d'évaluation
- Sanpacor - Taller 2 PDFDocument2 pagesSanpacor - Taller 2 PDFSAMUEL STEVEN ARICAPA PULGARINPas encore d'évaluation
- Parcial en MatlabDocument6 pagesParcial en MatlabZorielys RamírezPas encore d'évaluation
- Taller1 OscilacionesDocument3 pagesTaller1 OscilacionesJhony PosadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Problemario Vibraciones U3Document15 pagesProblemario Vibraciones U3Jorge Hernandez Anaya100% (1)
- Problemario Ingenieria en Mantenimiento Petrolero.Document11 pagesProblemario Ingenieria en Mantenimiento Petrolero.Josue Orozco LanderoPas encore d'évaluation
- Balotario de Preguntas 3Document5 pagesBalotario de Preguntas 3Cristian Ookami CcenchoPas encore d'évaluation
- Actividad U3Document18 pagesActividad U3JUAN MIGUEL FLORES SANTIAGOPas encore d'évaluation
- Práctico 2 - Sistemas de 1 y 2 GDLDocument9 pagesPráctico 2 - Sistemas de 1 y 2 GDLOliver KrausPas encore d'évaluation
- Taller 2 Calor y OndaDocument6 pagesTaller 2 Calor y OndaDavid Monsalve VarelaPas encore d'évaluation
- 05 Pendulo PohlDocument9 pages05 Pendulo PohlHellspawn.GeoPas encore d'évaluation
- Guia 1Document4 pagesGuia 1andresPas encore d'évaluation
- 499 Deber%2B%25233Document3 pages499 Deber%2B%25233Jorge SandovalPas encore d'évaluation
- Problemas de osciladores armónicos simples y péndulosDocument12 pagesProblemas de osciladores armónicos simples y péndulosAlejandro ValdezPas encore d'évaluation
- DinamiDocument10 pagesDinamiJhonatan Barzola IngaPas encore d'évaluation
- Taller #3 Sistemas Con Un Grado de Libertad Sin Amortiguacion PDFDocument9 pagesTaller #3 Sistemas Con Un Grado de Libertad Sin Amortiguacion PDFAndres RAMIREZPas encore d'évaluation
- Singiresu, Rao, Vibraciones MecánicasDocument3 pagesSingiresu, Rao, Vibraciones MecánicasVázquezRaphaelPas encore d'évaluation
- Movimiento armónico simple y oscilaciones en Física IIIDocument3 pagesMovimiento armónico simple y oscilaciones en Física IIIDavid Rodríguez GranadosPas encore d'évaluation
- Taller 1 VyO Sem1 2014 PDFDocument4 pagesTaller 1 VyO Sem1 2014 PDFKmiSzPas encore d'évaluation
- Tarea 1 - Vibraciones Mecánicas IDMA09Document7 pagesTarea 1 - Vibraciones Mecánicas IDMA09Gabriel VazquezPas encore d'évaluation
- Taller OndasDocument6 pagesTaller OndasOscar ArizaPas encore d'évaluation
- Fisica I - Hoja 7Document12 pagesFisica I - Hoja 7zerachiel1728Pas encore d'évaluation
- Taller Mecánica EstructuralDocument5 pagesTaller Mecánica EstructuralCamila GarcíaPas encore d'évaluation
- Deber Dinã Mica RotacionalDocument4 pagesDeber Dinã Mica RotacionalSantiago PabonPas encore d'évaluation
- Ejercicios Taller 1 Física III UISDocument6 pagesEjercicios Taller 1 Física III UISJonathan Arley Torres CastañedaPas encore d'évaluation
- Problemas de Mecánica IIDocument3 pagesProblemas de Mecánica IIAmeliaPas encore d'évaluation
- Taller 9 Rotación de Un Cuerpo RígidoDocument4 pagesTaller 9 Rotación de Un Cuerpo RígidosamuelcanoazPas encore d'évaluation
- Taller-Repaso Primer Parcial-Física Oscilaciones, Ondas y ÓpticaDocument3 pagesTaller-Repaso Primer Parcial-Física Oscilaciones, Ondas y ÓpticaLaura Marcela Montoya GomezPas encore d'évaluation
- Problemas resueltos de dinámica de sistemas mecánicosDocument14 pagesProblemas resueltos de dinámica de sistemas mecánicosSANTIAGO DAVID PARDO ENCALADAPas encore d'évaluation
- Física III: Oscilaciones y Movimiento ArmónicoDocument2 pagesFísica III: Oscilaciones y Movimiento ArmónicoBrayanmarinPas encore d'évaluation
- Practica Vi Brac I On Ar MonicaDocument8 pagesPractica Vi Brac I On Ar MonicaJosuePas encore d'évaluation
- Práctica 2Document6 pagesPráctica 2Jorge EspinosaPas encore d'évaluation
- Vibraciones Mecanicas UNHDocument11 pagesVibraciones Mecanicas UNHJosephZevallosAyuquePas encore d'évaluation
- Tarea Unidad 04 Vibración ForzadaDocument3 pagesTarea Unidad 04 Vibración ForzadaJosé Jaén Castillo LopezPas encore d'évaluation
- Parcial 1 Diagnostico 2020Document2 pagesParcial 1 Diagnostico 2020Ana RodríguezPas encore d'évaluation
- Tarea1 Sem 2016-1Document3 pagesTarea1 Sem 2016-1Alejandro GarcíaPas encore d'évaluation
- HT Semana 2 SDocument3 pagesHT Semana 2 SGustavo CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- Semana 11Document25 pagesSemana 11YESSENIA ANACELI FERNANDEZ REYESPas encore d'évaluation
- Oscilaciones físicas: periodos de péndulos, bloques resorte y oscilaciones armónicasDocument3 pagesOscilaciones físicas: periodos de péndulos, bloques resorte y oscilaciones armónicasVictor RinconPas encore d'évaluation
- Ejercicios de Integrales de Línea, Superficie y VolumenD'EverandEjercicios de Integrales de Línea, Superficie y VolumenÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (2)
- Diseño Práctico De Cimentaciones Sujetas a Vibración Producida Por MaquinariaD'EverandDiseño Práctico De Cimentaciones Sujetas a Vibración Producida Por MaquinariaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cámaras HiperbáricasDocument7 pagesCámaras HiperbáricasGuillermo Aguilar Hernandes100% (1)
- La Rapidez de Una ReacciónDocument10 pagesLa Rapidez de Una ReacciónGuillermo Aguilar HernandesPas encore d'évaluation
- Agricultura de PrecisiónDocument3 pagesAgricultura de PrecisiónGuillermo Aguilar HernandesPas encore d'évaluation
- Banda TransportadoresDocument46 pagesBanda TransportadoresGuillermo Aguilar HernandesPas encore d'évaluation
- Depresión y TristezaDocument12 pagesDepresión y TristezaGuillermo Aguilar HernandesPas encore d'évaluation
- PodadorDocument23 pagesPodadorGuillermo Aguilar HernandesPas encore d'évaluation
- Inyección Electronica de CombustibleDocument29 pagesInyección Electronica de CombustibleGuillermo Aguilar Hernandes50% (2)
- Toma de Decisiones y Resolución de ConflictosDocument8 pagesToma de Decisiones y Resolución de ConflictosGuillermo Aguilar HernandesPas encore d'évaluation
- Sondas LambdaDocument38 pagesSondas LambdaGuillermo Aguilar HernandesPas encore d'évaluation
- Cómo funciona la caja de cambios de un tractorDocument9 pagesCómo funciona la caja de cambios de un tractorCarlos CorderoPas encore d'évaluation
- Reportaje Ensayo NarrativaDocument2 pagesReportaje Ensayo NarrativaGuillermo Aguilar HernandesPas encore d'évaluation
- Unidad 2Document35 pagesUnidad 2Guillermo Aguilar HernandesPas encore d'évaluation
- Calculo de EmbraguesDocument21 pagesCalculo de EmbraguesGuillermo Aguilar Hernandes80% (5)
- Calculo Traccional GAHDocument37 pagesCalculo Traccional GAHGuillermo Aguilar Hernandes100% (1)
- Manual Sistema Transmision Fuerza Automoviles Embrague Caja Velocidades Diferencial PDFDocument86 pagesManual Sistema Transmision Fuerza Automoviles Embrague Caja Velocidades Diferencial PDFJuan Fonseca100% (2)
- Ud2sistemasdetransmisionyfrenado 131009110404 Phpapp02Document72 pagesUd2sistemasdetransmisionyfrenado 131009110404 Phpapp02Guillermo Aguilar HernandesPas encore d'évaluation
- Trabajo de Curso MCIDocument71 pagesTrabajo de Curso MCIGuillermo Aguilar HernandesPas encore d'évaluation
- Qui MikaDocument1 pageQui MikaGuillermo Aguilar HernandesPas encore d'évaluation
- Dos Problemas 2nd UnidadDocument5 pagesDos Problemas 2nd UnidadGuillermo Aguilar HernandesPas encore d'évaluation
- Sistem AsDocument16 pagesSistem AsGuillermo Aguilar HernandesPas encore d'évaluation
- INTRODUCCIÓNDocument3 pagesINTRODUCCIÓNGuillermo Aguilar HernandesPas encore d'évaluation
- Formulas Segundo ExamenDocument4 pagesFormulas Segundo ExamenGuillermo Aguilar HernandesPas encore d'évaluation
- ABC de La Educación FinancieraDocument64 pagesABC de La Educación FinancieraferakkkkPas encore d'évaluation
- Potencia Indicada y Potencia Efectiva en Motores DieselDocument13 pagesPotencia Indicada y Potencia Efectiva en Motores DieselGuillermo Aguilar Hernandes0% (3)
- Potencia indicada y efectiva en motor diesel PerkinsDocument10 pagesPotencia indicada y efectiva en motor diesel PerkinsGuillermo Aguilar HernandesPas encore d'évaluation
- Dinamica de MaquinasDocument7 pagesDinamica de MaquinasGuillermo Aguilar HernandesPas encore d'évaluation
- 5 3 Hortic Zanahor y TomateDocument7 pages5 3 Hortic Zanahor y TomateGuillermo Aguilar HernandesPas encore d'évaluation
- Conceptos Basicos de Banca y FinanzasDocument98 pagesConceptos Basicos de Banca y FinanzasGuillermo Aguilar HernandesPas encore d'évaluation
- Resumen Del Libro HMBDocument17 pagesResumen Del Libro HMBGuillermo Aguilar HernandesPas encore d'évaluation
- Cuadro-De-Distribución-Horas-2020-Para La UgelDocument8 pagesCuadro-De-Distribución-Horas-2020-Para La UgelEfrain Carrera CutipaPas encore d'évaluation
- Caso SturbucksDocument15 pagesCaso SturbucksEliecer Roberto Escobar GonzalezPas encore d'évaluation
- Proyecto en El Aula de Ciencias NaturalesDocument2 pagesProyecto en El Aula de Ciencias NaturalesNadia Rocha100% (6)
- Control de La Información Documentada v.0Document7 pagesControl de La Información Documentada v.0josePas encore d'évaluation
- Decálogo del perfecto cuentistaDocument7 pagesDecálogo del perfecto cuentistaAna Rita VillarPas encore d'évaluation
- Alicia en El Pais de Las MaravillasDocument56 pagesAlicia en El Pais de Las MaravillasCarlos AvilaPas encore d'évaluation
- La Evolución y La Sobrepoblación HumanaDocument1 pageLa Evolución y La Sobrepoblación HumanaInes LazoPas encore d'évaluation
- Oposición Archiveros Cortes GeneralesDocument3 pagesOposición Archiveros Cortes GeneralesluisonPas encore d'évaluation
- PRUEBA UNIDAD 2 7°básico AgostoDocument8 pagesPRUEBA UNIDAD 2 7°básico AgostodanicastrorPas encore d'évaluation
- Mdu PiscoDocument35 pagesMdu PiscoAriana ChamachePas encore d'évaluation
- Diarrea Aguda: Causas, Síntomas y TratamientoDocument3 pagesDiarrea Aguda: Causas, Síntomas y TratamientoCaro Guevara0% (1)
- Crear pieza mecánica AutoCADDocument9 pagesCrear pieza mecánica AutoCADSamuel Esteban Valdivia LeivaPas encore d'évaluation
- Semana 05 Estres Oxidativo y CarcinogenesisDocument23 pagesSemana 05 Estres Oxidativo y CarcinogenesisKatia Pamela Torres AvellanedaPas encore d'évaluation
- HorarioBiocienciasUSLDocument2 pagesHorarioBiocienciasUSLBasti SkatePas encore d'évaluation
- SEM.3 - 3 Sec - FÍSICADocument5 pagesSEM.3 - 3 Sec - FÍSICAjoelPas encore d'évaluation
- Devocional 5 JobDocument6 pagesDevocional 5 JobElizzabethPas encore d'évaluation
- Regiones NaturalesDocument12 pagesRegiones NaturalesValeria Leon Rodriguez100% (1)
- Ecp Uce 18003 Gcu Id02 0 Gen CD 001 - 0Document55 pagesEcp Uce 18003 Gcu Id02 0 Gen CD 001 - 0David Fernando Bedoya Romero100% (1)
- AHUMADODocument42 pagesAHUMADOXimena Villanueva CastilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Electronica de ComunicacionesDocument3 pagesElectronica de ComunicacionesadriisequeraPas encore d'évaluation
- Capacitacion Hughes-2019Document116 pagesCapacitacion Hughes-2019ovc_etnPas encore d'évaluation
- Kant, Immanuel - Introducción A La Crítica Del Juicio.Document60 pagesKant, Immanuel - Introducción A La Crítica Del Juicio.Sonia RangelPas encore d'évaluation
- Jack Flower-TareaS2 LTEDocument4 pagesJack Flower-TareaS2 LTEJack FlowerPas encore d'évaluation
- Caso Practico Unidad 1 Teoria de La AdministracionDocument4 pagesCaso Practico Unidad 1 Teoria de La AdministracionTiffanny PatiñoPas encore d'évaluation
- Rubrica BanderaDocument1 pageRubrica BanderaIvan Nuñez Cornejo100% (1)
- Diagrama P&IDDocument10 pagesDiagrama P&IDFiLiPh TORWOLFPas encore d'évaluation
- MantenimientoDocument20 pagesMantenimientoCarlitos Mairena SozaPas encore d'évaluation
- Manual Tecnología para La ApiculturaDocument324 pagesManual Tecnología para La ApiculturamiltonPas encore d'évaluation
- Aceria Paz Del Rio Proyecto de MejoraDocument102 pagesAceria Paz Del Rio Proyecto de MejoraSpencer Ismael Mendoza RegaladoPas encore d'évaluation